(AnaPhy) Digestive System — Laboratory
1/84
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Hard Palate
The bony anterior (front) part of the roof of the mouth that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
Lip (Labia)
The fleshy folds surrounding the opening of the mouth.
Teeth
Hard, enamel-covered structures in the jaws used for biting and chewing food.
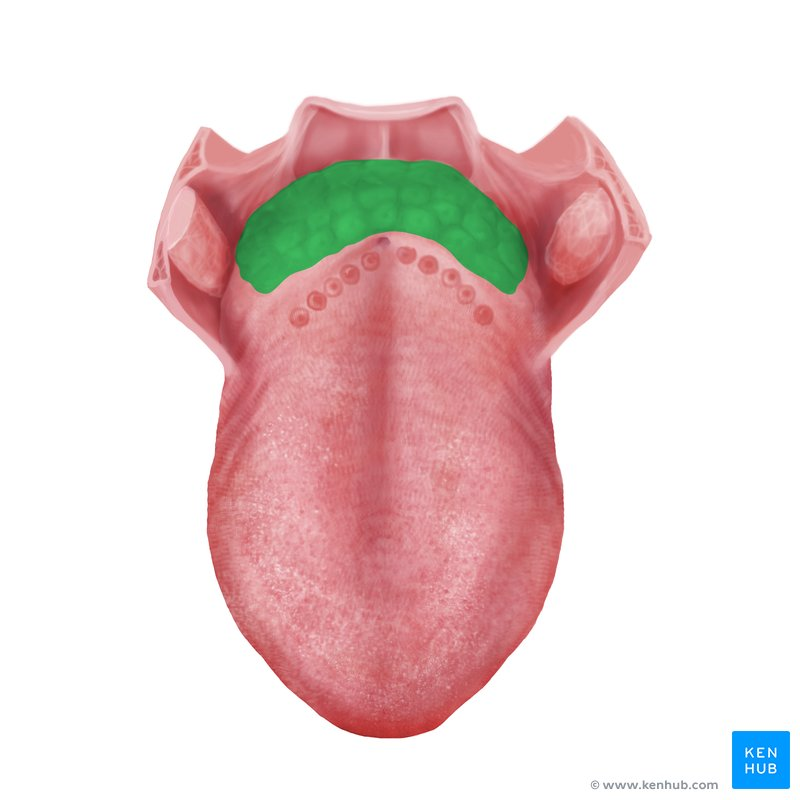
Lingual tonsil
A collection of lymphoid tissue located at the base (posterior part) of the tongue.
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach, transporting swallowed food.
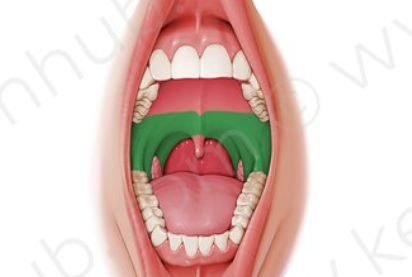
Oral cavity
The mouth; the space within the mouth bounded by the lips, cheeks, palate, and tongue.
Soft palate
The fleshy posterior (back) part of the roof of the mouth, which is muscular and movable.
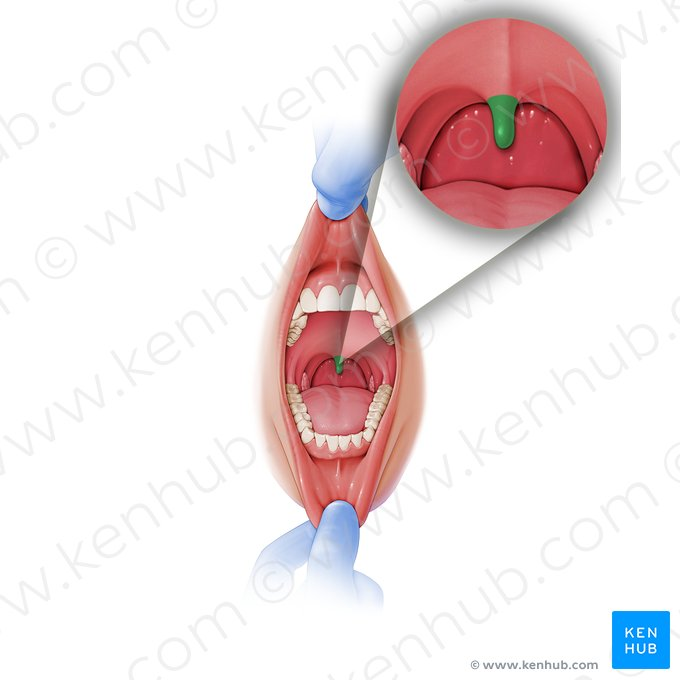
Uvula
A fleshy extension that hangs from the posterior border of the soft palate.
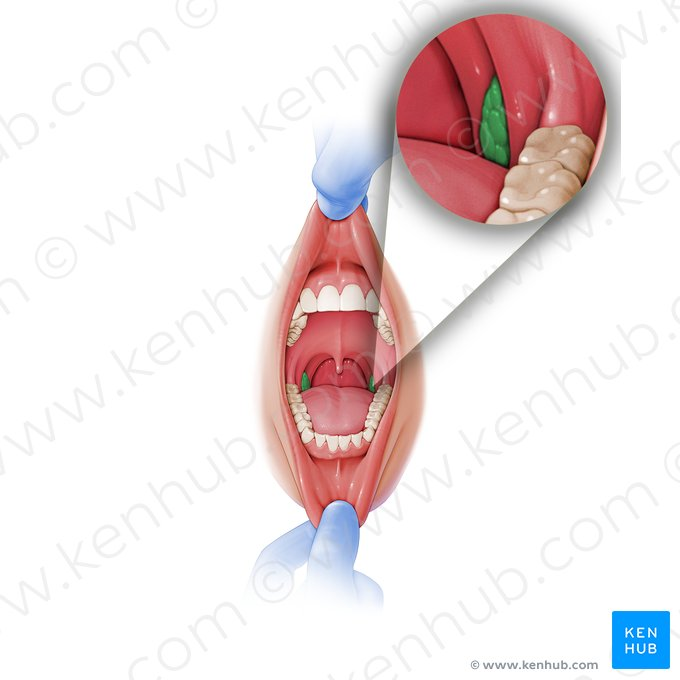
Palatine tonsil
A pair of lymphoid tissues located on either side of the oropharynx, between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches.
Nasopharynx
The uppermost part of the pharynx, located behind the nasal cavity and above the soft palate. It functions as an airway.
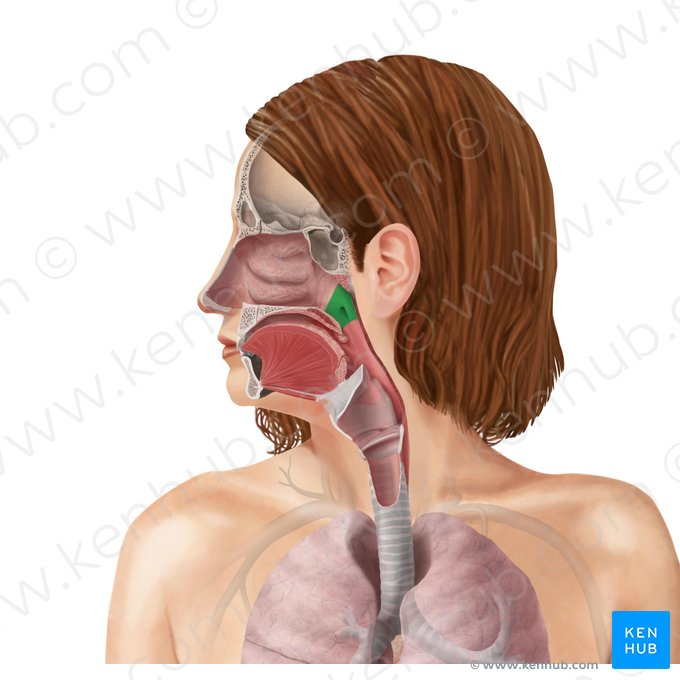
Oropharynx
The middle part of the pharynx, located behind the oral cavity and extending from the soft palate to the base of the tongue. It serves as a passageway for both air and food.
Laryngopharynx
The lowermost part of the pharynx, situated below the oropharynx and extending to the esophagus posteriorly and the larynx anteriorly. It is a passageway for both air and food and connects to both the respiratory and digestive tracts.
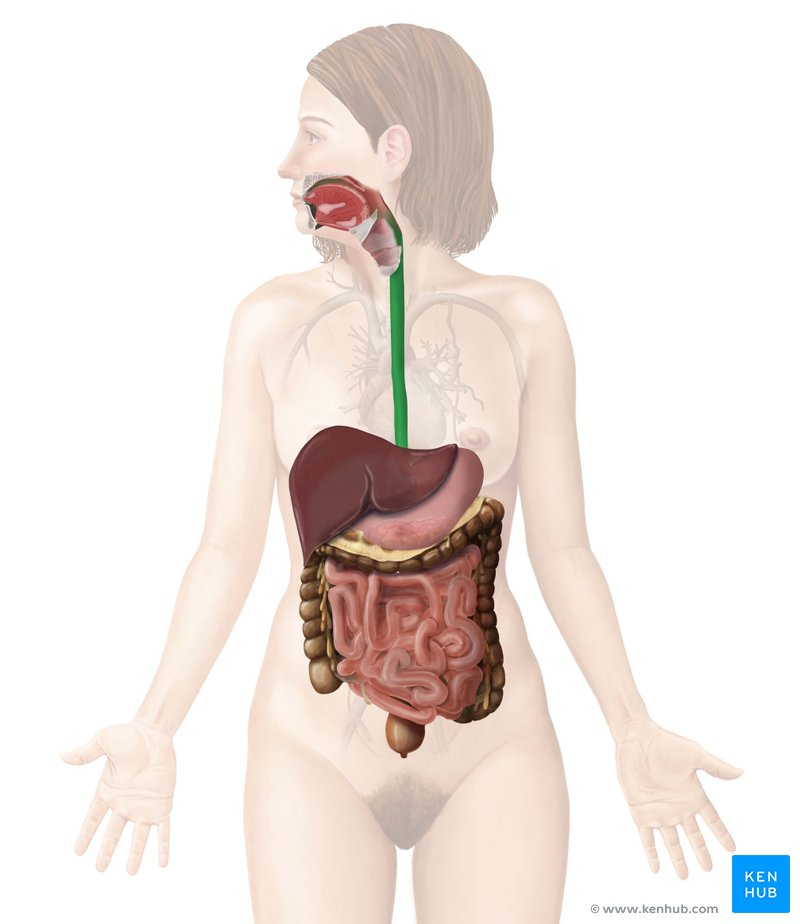
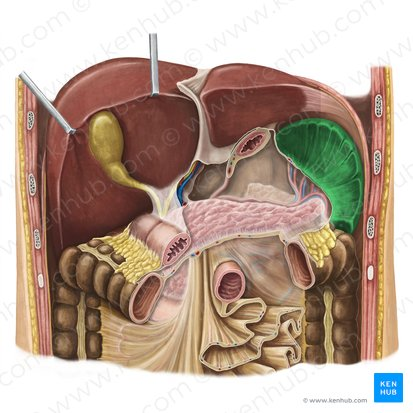
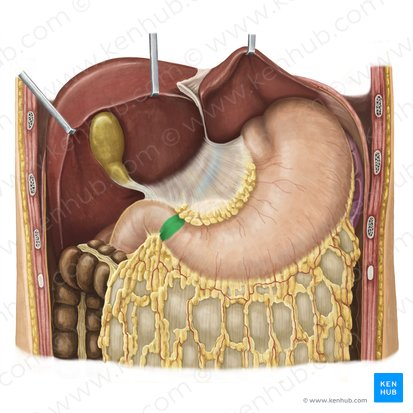
Liver
a large organ located in the upper right abdomen that produces bile, detoxifies blood, and performs many other metabolic functions.
Considered as the largest gland in the body
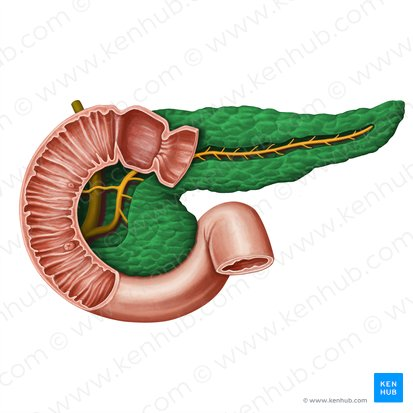
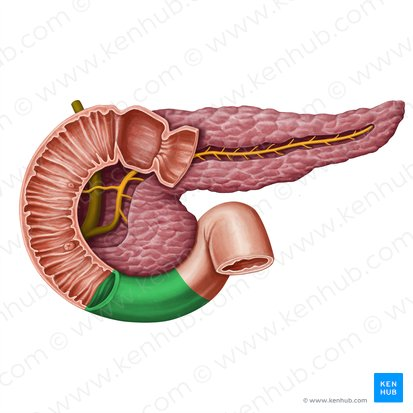
Pancreas
a gland located behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin and glucagon.
Small intestine / colon
the part of the digestive tract located between the stomach and the large intestine, where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs.
Duodenum
This is the first and shortest segment of the small intestine. It receives partially digested food (known as chyme).
Receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreatic and bile ducts.
Jejunum
This is the middle section of the small intestine, and is characterized by numerous folds and villi, which increase the surface area for nutrient absorption.
Most of the absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins occurs
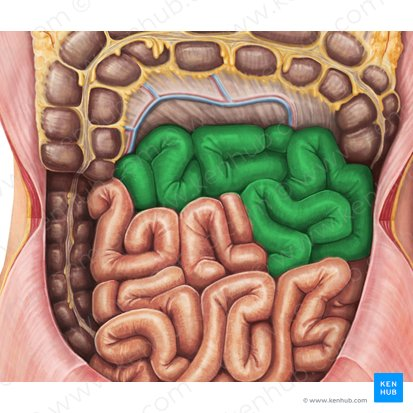
Ileum
The final and longest section of the small intestine, which controls the passage of material into the large intestine.
primarily absorbs vitamin B12, bile salts, and any remaining nutrients, and also plays a role in the transport of water and electrolytes.
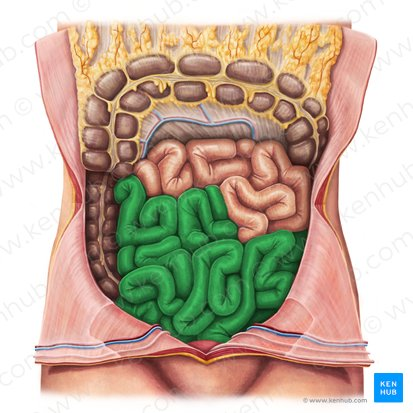
Appendix
a small, finger-like pouch attached to the large intestine.
Stomach
a J-shaped organ located in the upper abdomen that stores, mixes, and digests food.
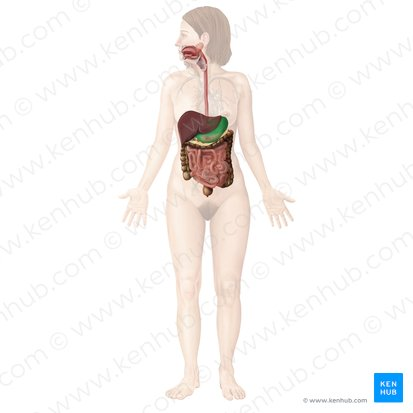
Spleen
An organ located in the upper left abdomen that is part of the lymphatic system, filtering blood and storing white blood cells
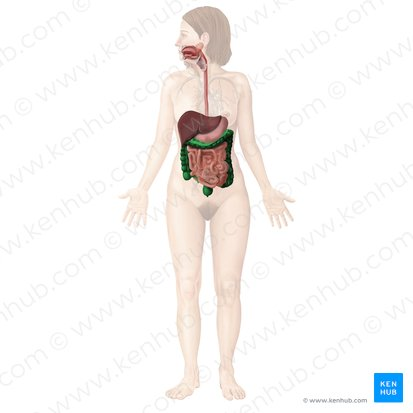
Large intestine / colon
the final section of the digestive tract, responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes and forming feces.
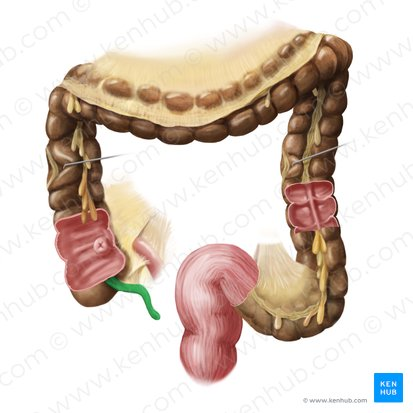
Ascending Colon
Travels upward from the cecum along the right side of the abdomen
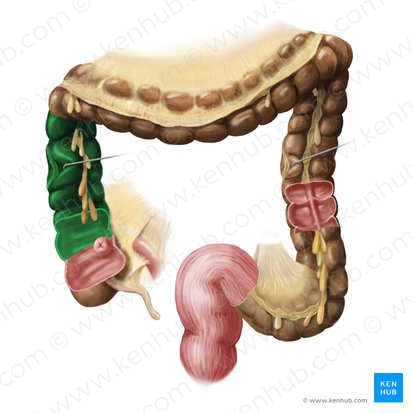
Transverse Colon
Travels across the abdomen from right to left.
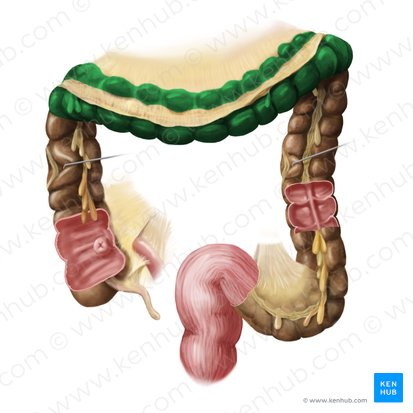
Descending Colon
Travels downward along the left side of the abdomen.
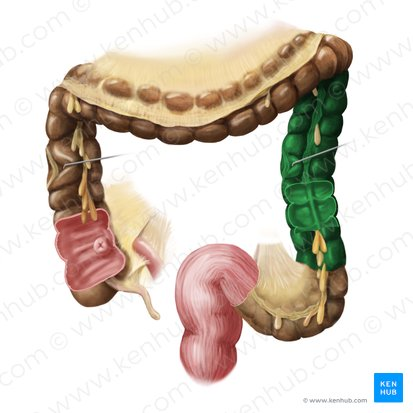
Sigmoid Colon
An S-shaped curve that connects the descending colon to the rectum.
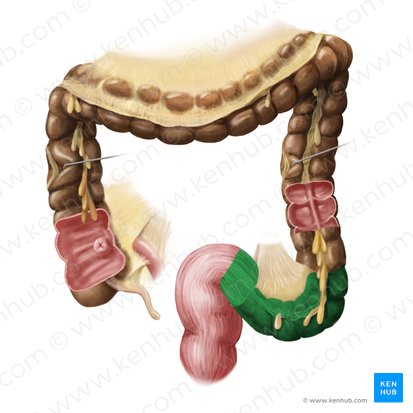
Rectum
the final section of the large intestine, terminating at the anus, that stores feces before elimination.
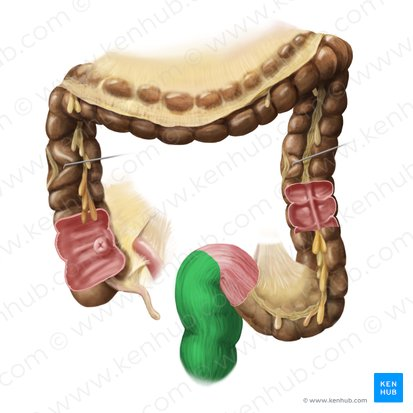
Anus
the opening at the end of the digestive tract through which feces are eliminated from the body.
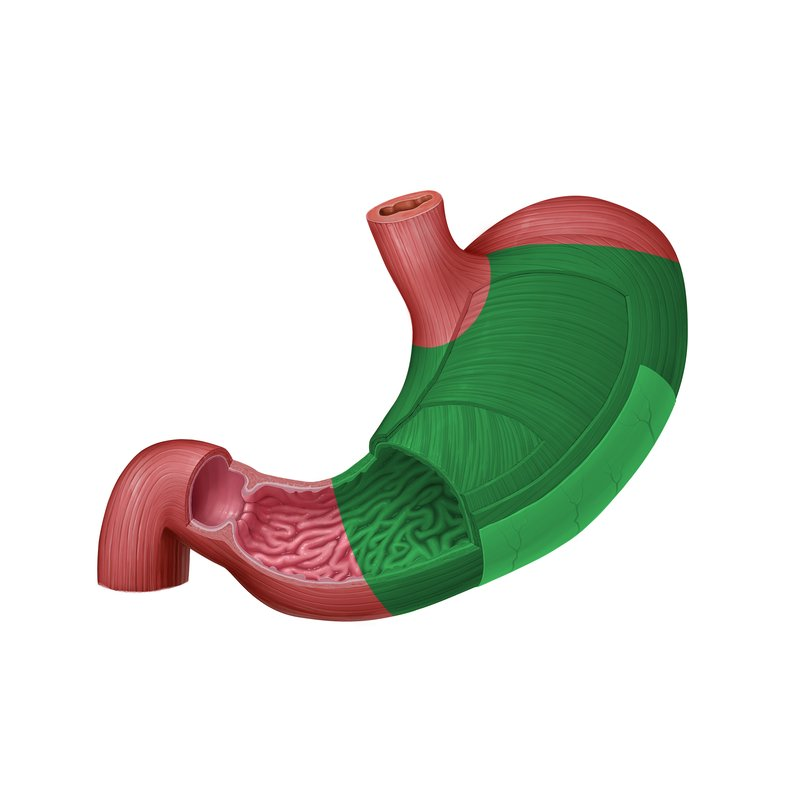
Lower esophageal sphincter
A muscular ring located at the junction of the esophagus and the stomach that controls the passage of food into the stomach and prevents reflux of stomach contents back into the esophagus
Body of stomach
the main, central part of the stomach.
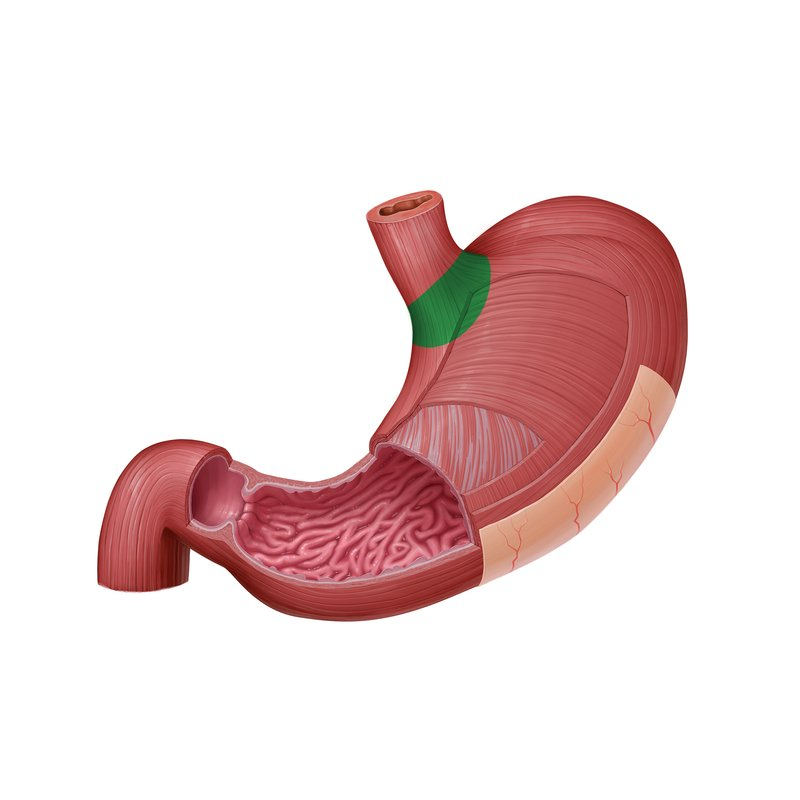
Cardia
The region of the stomach where the esophagus joins.
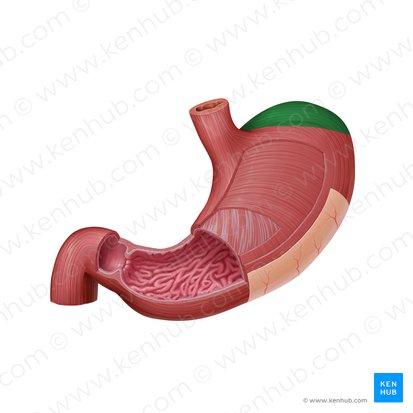
Fundus
The dome-shaped, upper portion of the stomach that lies superior to the esophageal opening.
Rugae
folds in the lining of the stomach that allow for expansion when the stomach is filled with food.
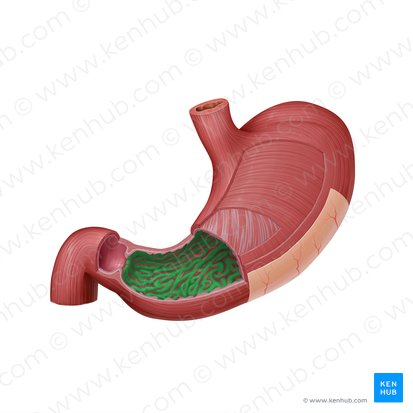
lesser curvature
the concave medial border of the stomach.

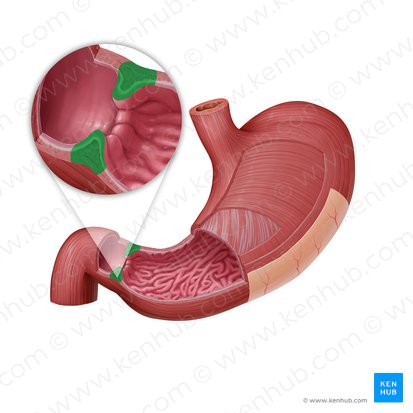
Pyloric sphincter
A muscular ring located at the junction of the stomach and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine) that controls the emptying of stomach contents into the duodenum.
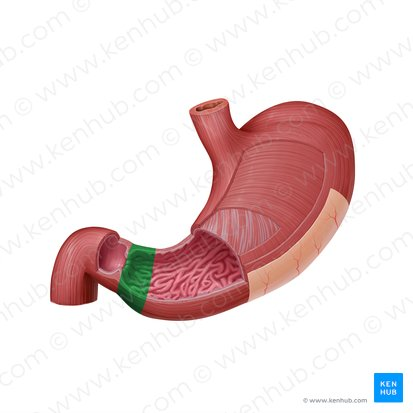
Pyloric canal
the narrow passageway that leads from the pyloric antrum to the pyloric sphincter.
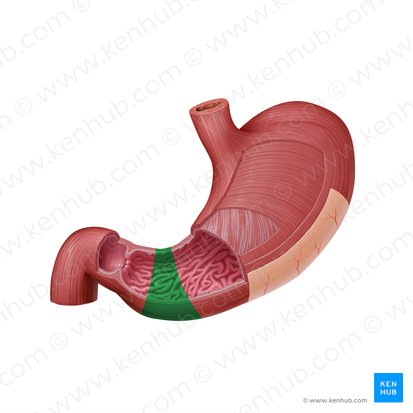
Pyloric antrum
The funnel-shaped region of the stomach that precedes the pyloric canal.
Pylorus
The distal, narrow region of the stomach that connects to the duodenum, including the pyloric antrum, pyloric canal, and pyloric sphincter.
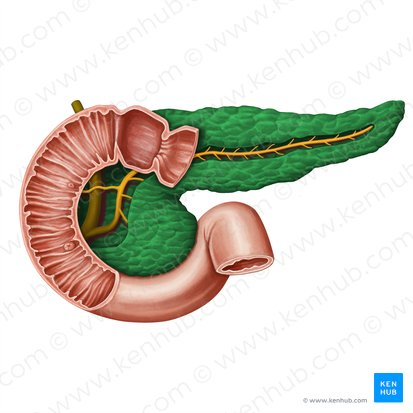
Pancreas
A gland located behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin and glucagon.
Pancreatic Duct
A duct that carries digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas to the duodenum. It typically joins with the bile duct before entering the duodenum.
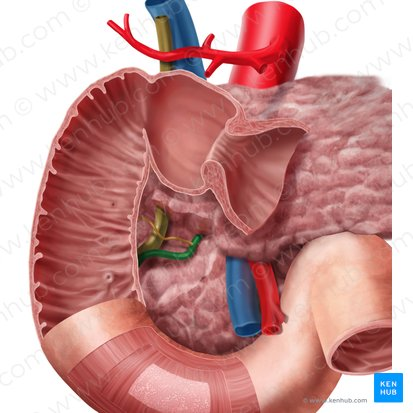
Bile duct
A duct that carries bile produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder to the duodenum, where it aids in the digestion of fats.
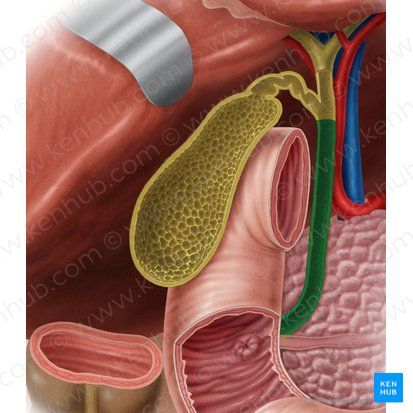
Major Duodenal Papilla
An opening in the wall of the duodenum where the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct typically enter to deliver bile and pancreatic enzymes.
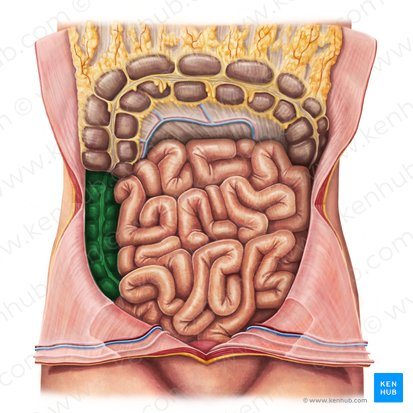
Mesocolon
A fold of peritoneum that attaches the colon to the posterior abdominal wall.
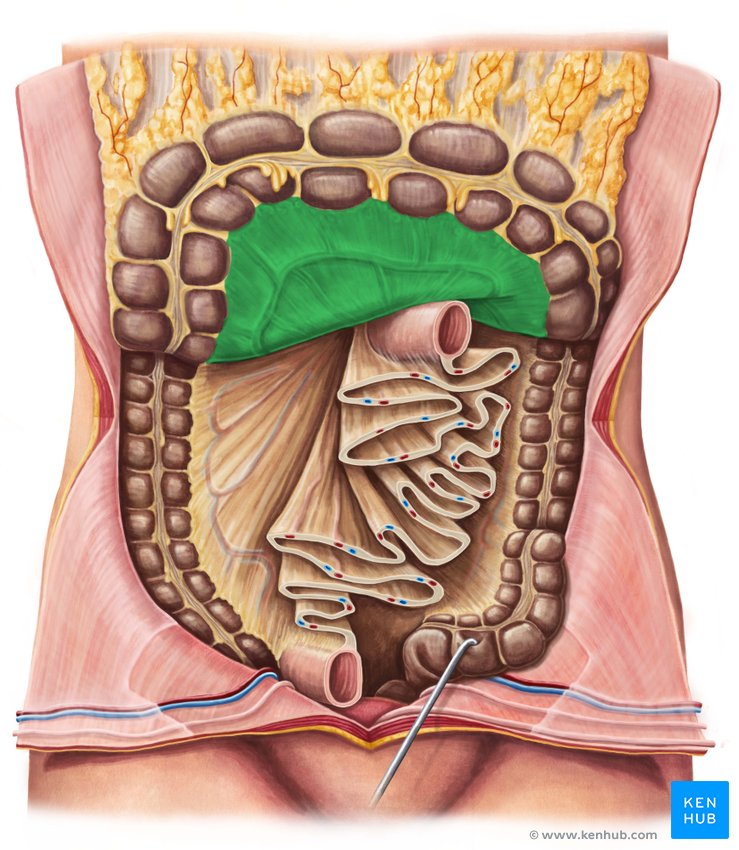
Right Colonic Flexure (Hepatic Flexure)
The bend in the large intestine where the ascending colon becomes the transverse colon, located on the right side of the abdomen.
Ascending Colon
The part of the large intestine that travels upward from the cecum along the right side of the abdomen.
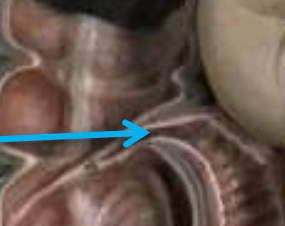
Ileocecal Valve
A sphincter muscle situated at the junction of the ileum and the cecum, which controls the flow of chyme from the small intestine into the large intestine and prevents backflow.
Cecum
A pouch-like structure connected to the junction of the small and large intestines.
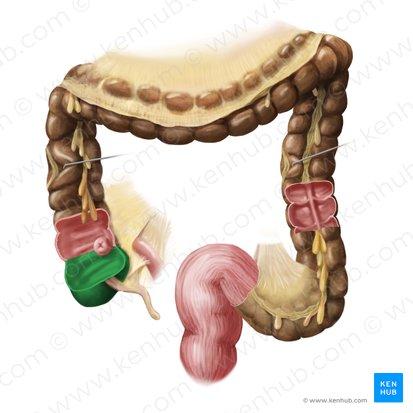
Appendix
A small, finger-like pouch attached to the cecum.
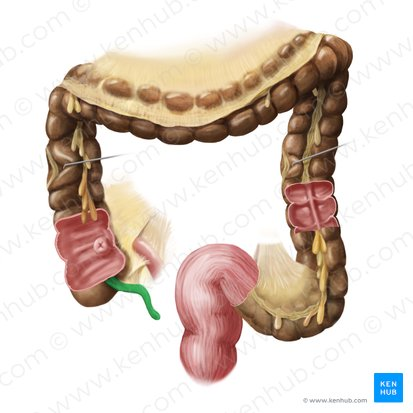
Ileum
The final and longest section of the small intestine, which absorbs vitamin B12, bile salts, and any remaining nutrients.
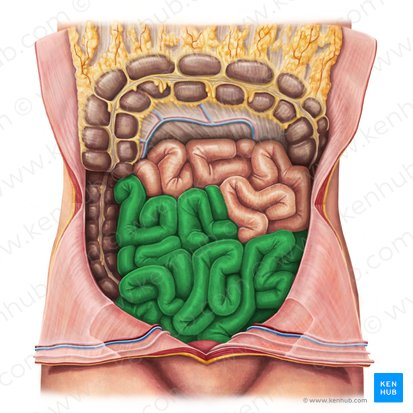
Jejunum
The middle section of the small intestine, where most of the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins occurs.
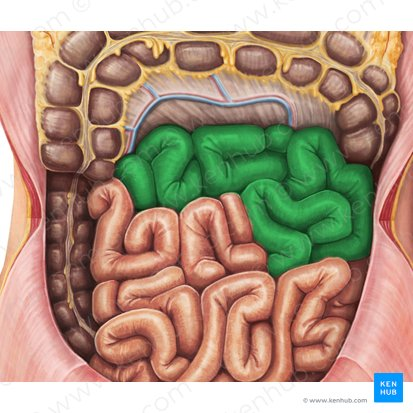
Transverse Colon
The part of the large intestine that travels across the abdomen from right to left.
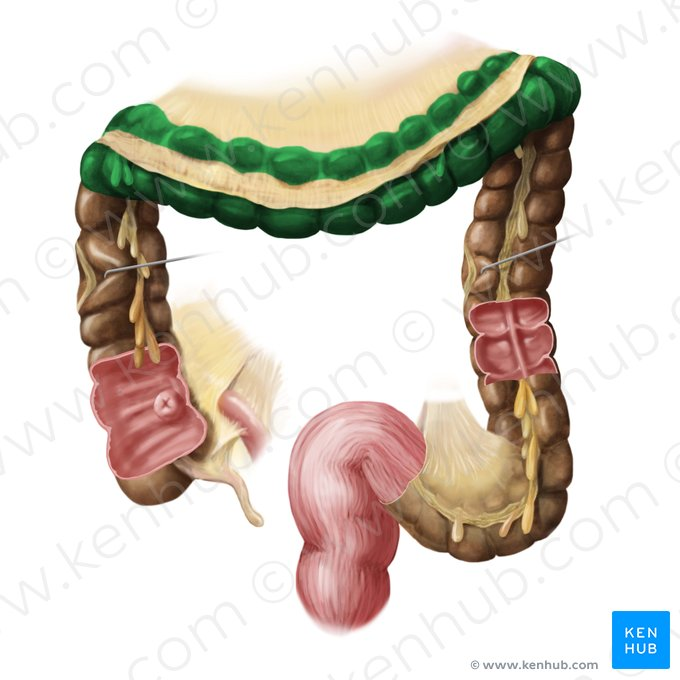
Left Colonic Flexure
The bend in the large intestine where the transverse colon becomes the descending colon, located on the left side of the abdomen.
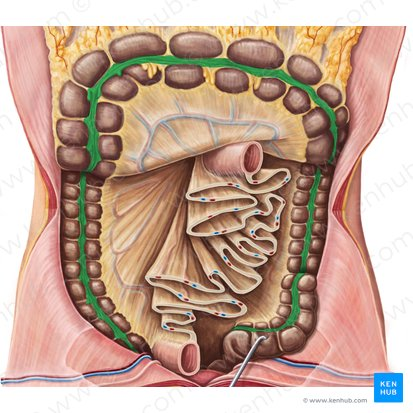
Taenia Coli
Three longitudinal bands of smooth muscle on the outer surface of the large intestine that create haustra.
Descending Colon
The part of the large intestine that travels downward along the left side of the abdomen.
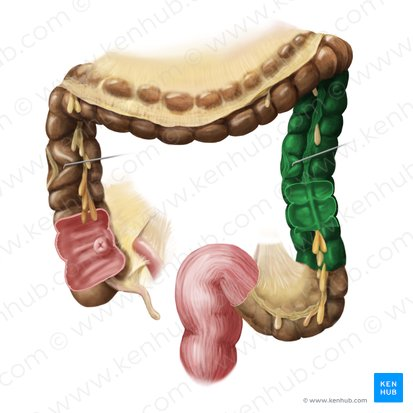
Haustrum
A pouch-like sacculation in the wall of the large intestine, formed by the contraction of the taenia coli.
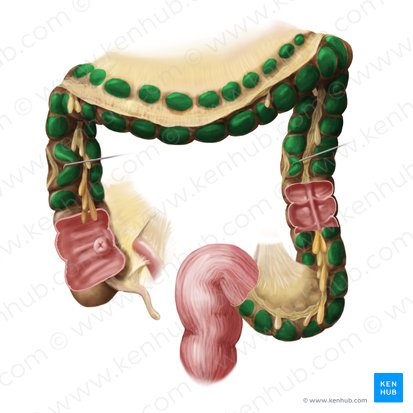
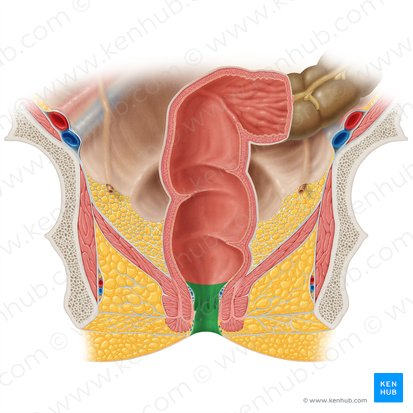
Internal Anal Sphincter
A thickened ring of smooth muscle that surrounds the anal canal. It is under involuntary control, meaning you don't consciously control its contraction or relaxation. It is normally contracted to maintain fecal continence.
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine, terminating at the anal canal. Its primary function is to store feces before they are eliminated from the body.
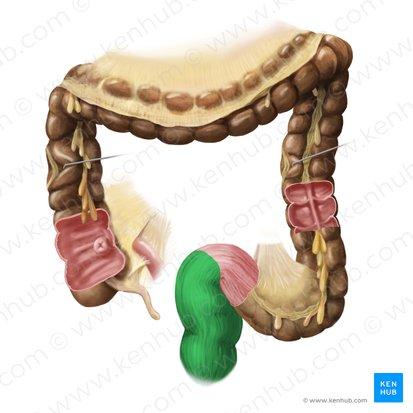
External Anal Sphincter
A ring of skeletal muscle that surrounds the anal canal, superficial to the internal anal sphincter. It is under voluntary control, meaning you can consciously choose to contract or relax it to control the passage of feces. This allows for the postponement of defecation.
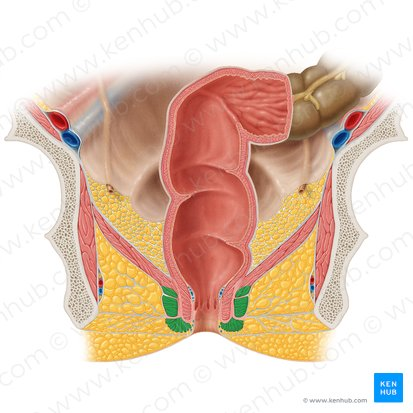
Anus
The opening at the end of the digestive tract through which feces are eliminated from the body. It is surrounded by the internal and external anal sphincters, which regulate the passage of waste.
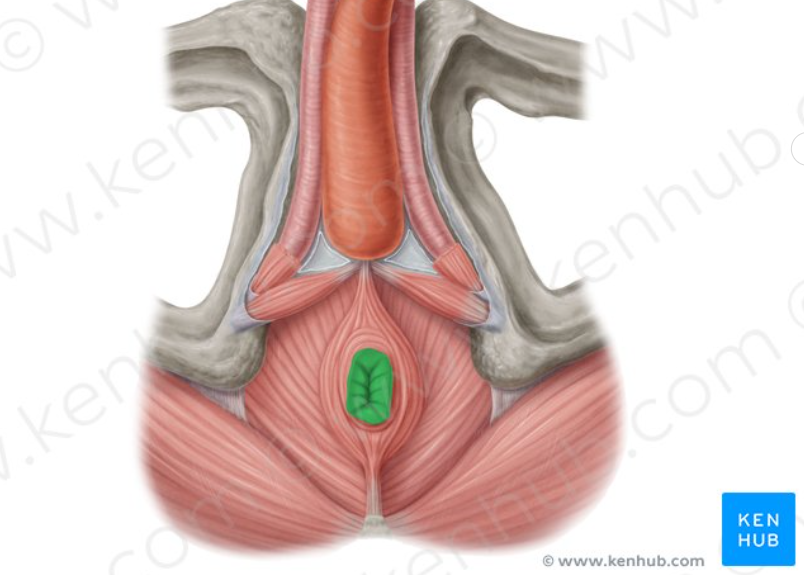
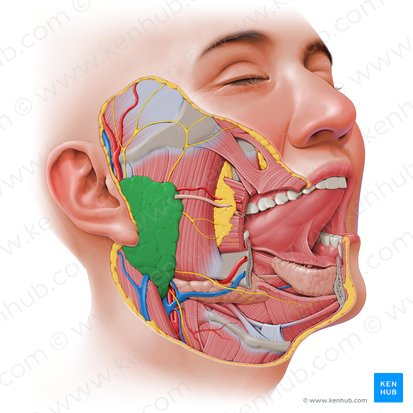
Parotid Gland
The largest of the major salivary glands, located superficially and somewhat posteriorly to the mandible (jawbone).
It produces saliva rich in enzymes (like amylase) which is secreted into the oral cavity to begin the digestion of carbohydrates.
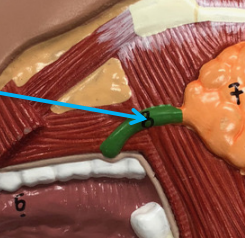
Parotid Duct
The duct that carries saliva from the parotid gland into the oral cavity. It typically opens into the vestibule of the mouth (the space between the cheek and gums) near the upper second molar tooth.
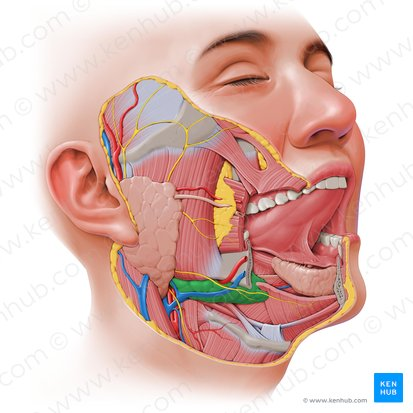
Submandibular Gland
One of the major salivary glands, located beneath the mandible. It produces a mixed serous and mucous saliva, contributing significantly to total salivary volume.
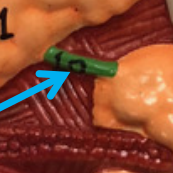
Submandibular Duct
The duct that carries saliva from the submandibular gland to the floor of the mouth, opening at the sublingual papilla under the tongue.
Sublingual Gland
The smallest of the major salivary glands, located beneath the tongue on the floor of the mouth. It primarily secretes a mucous-rich saliva, which contributes to lubrication.
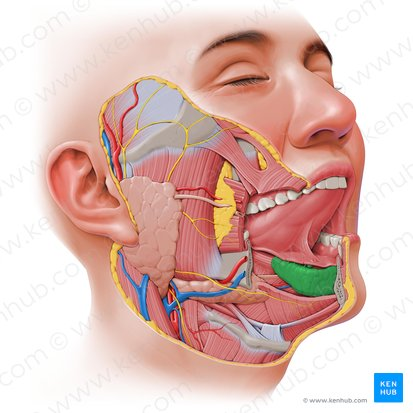
Sublingual Duct
Several small ducts that carry saliva from the sublingual gland directly into the floor of the mouth.
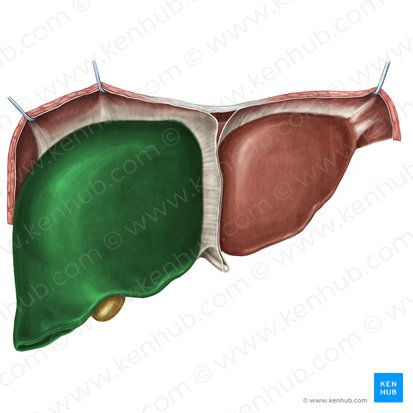
Right lobe of Liver
The larger of the two main lobes of the liver, located on the right side of the abdomen.
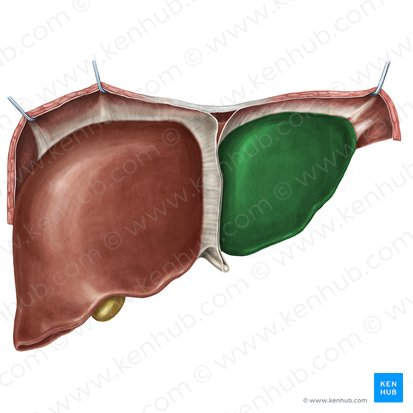
Left lobe of the Liver
The smaller of the two main lobes of the liver, located on the left side of the abdomen.
Quadrate Lobe
A small, quadrilateral lobe of the liver located inferiorly and medially on the visceral surface, bordered by the gallbladder and the fissure for the round ligament.
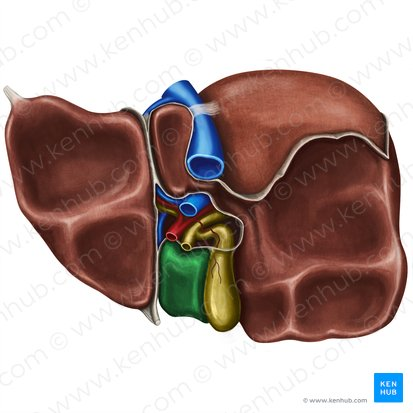
Caudate Lobe
A small lobe of the liver located posteriorly on the visceral surface, near the inferior vena cava and the fissure for the ligamentum venosum.
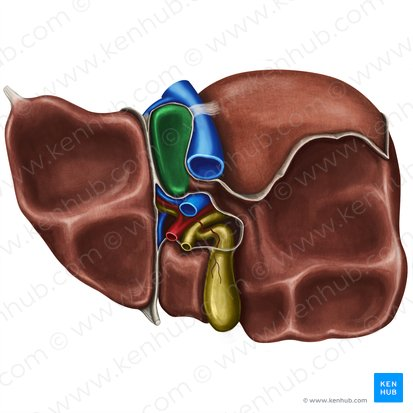
Falciform Ligament of the Liver
A broad, thin fold of peritoneum that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm. It also marks the division between the right and left lobes on the anterior surface.
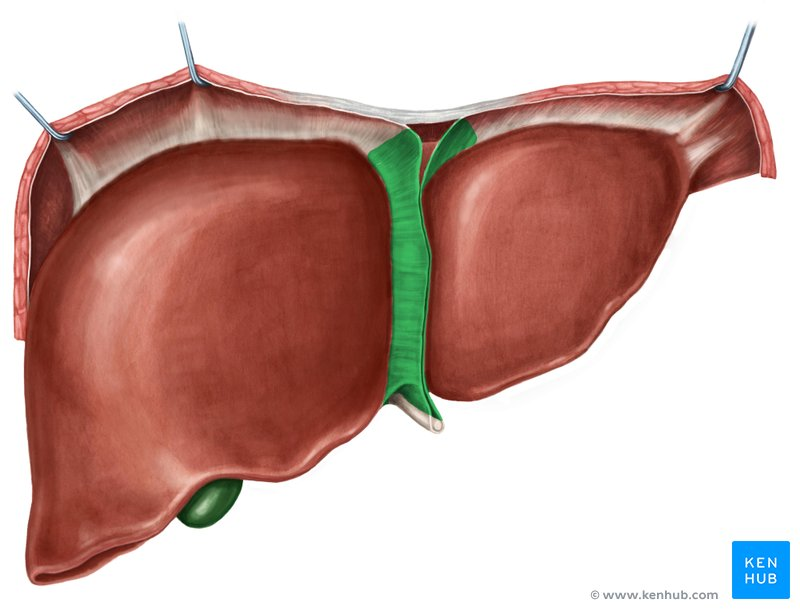
Round Ligament of the Liver
A fibrous cord that represents the remnant of the umbilical vein of the fetus. It is located in the free edge of the falciform ligament.
Gallbladder
A small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver that stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver.
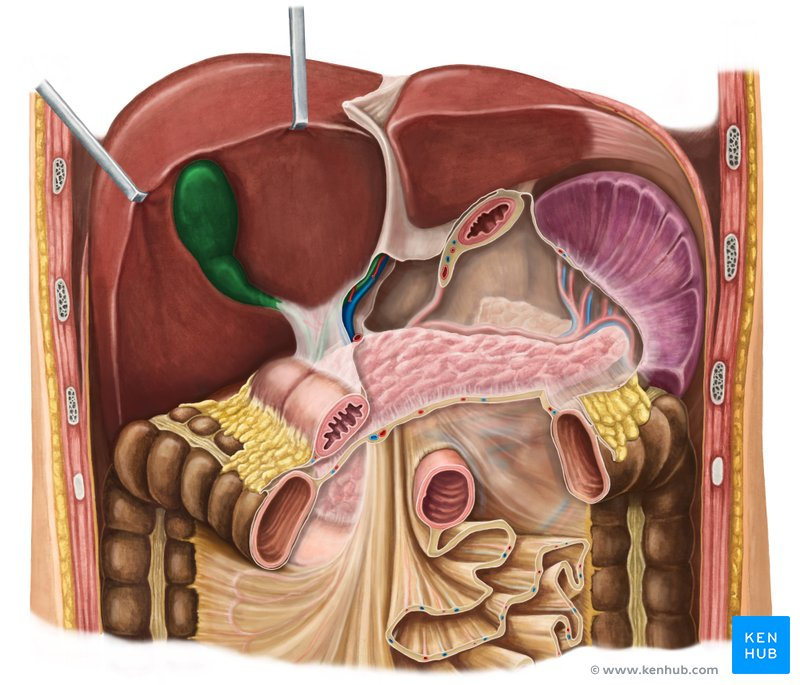
Right Hepatic Duct
A duct that carries bile produced by the right lobe of the liver.
Left Hepatic Duct
A duct that carries bile produced by the left lobe of the liver.
Common Hepatic Duct
The duct formed by the union of the right and left hepatic ducts, which carries bile away from the liver.
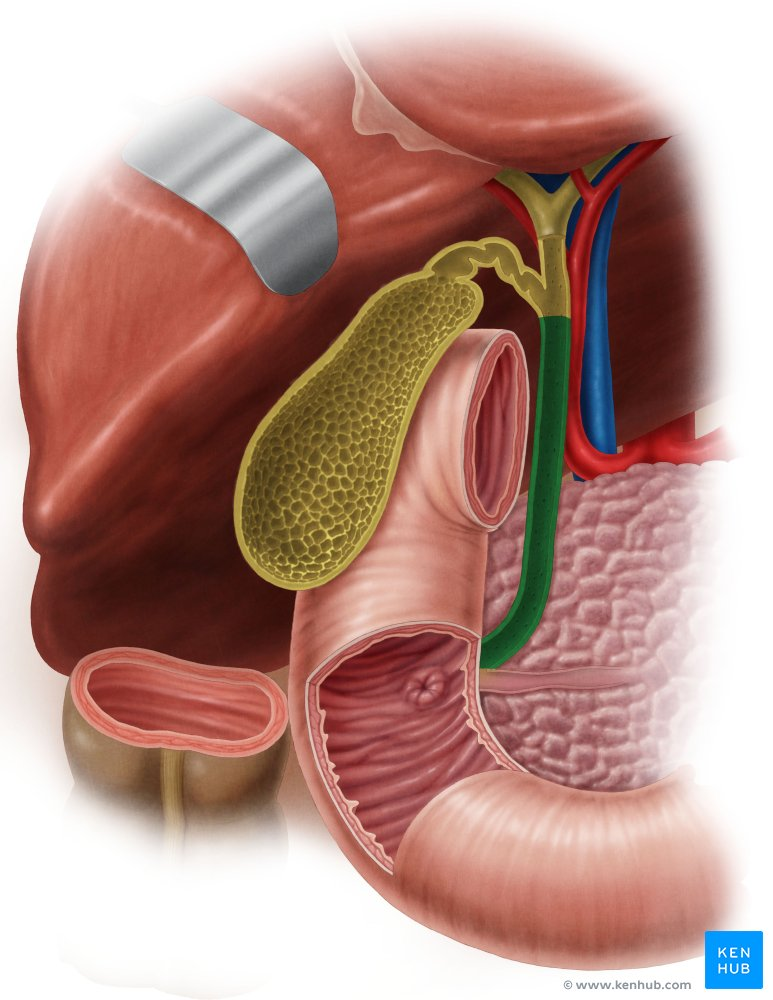
Cystic Duct
The duct that connects the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct, allowing bile to enter and exit the gallbladder.
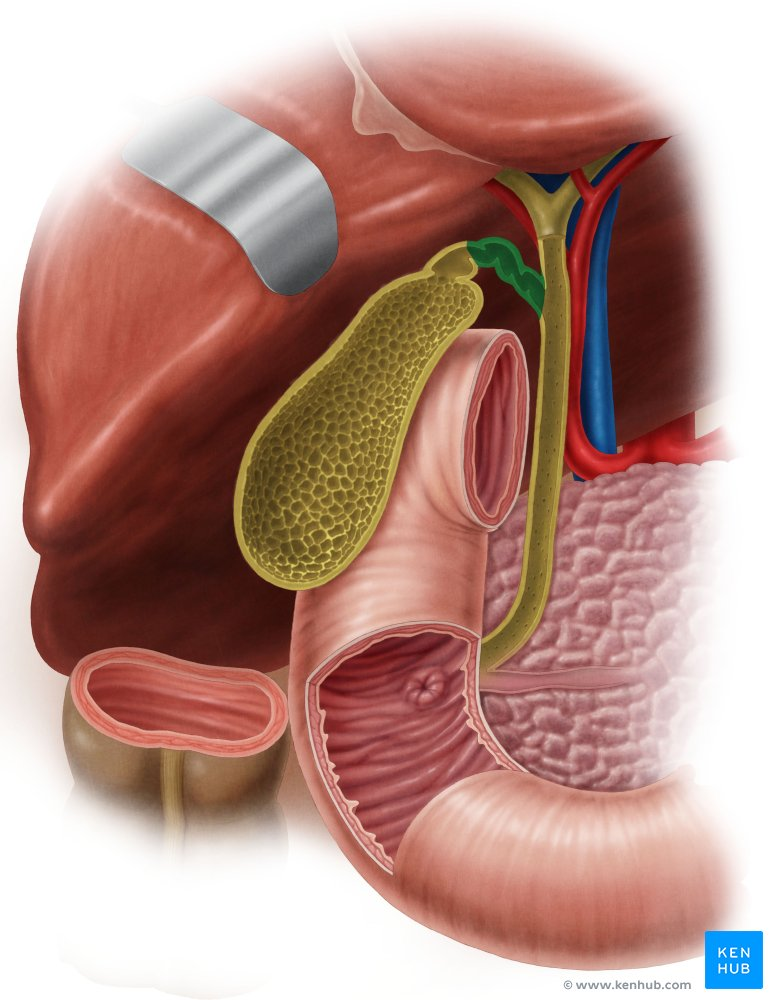
Hepatic Artery
A branch of the celiac artery that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.

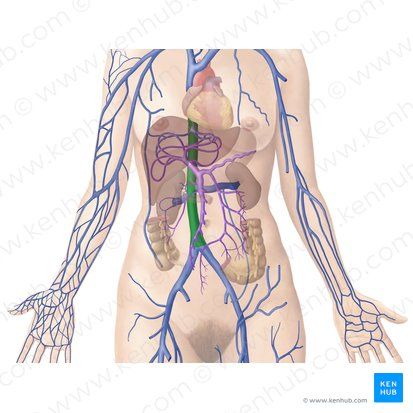
Hepatic Portal Vein
A large vein that carries deoxygenated but nutrient-rich blood from the digestive organs (stomach, intestines, spleen, pancreas) to the liver for processing.
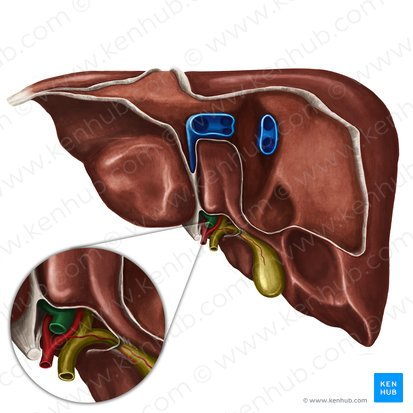
Inferior Vena Cava
A large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body back to the heart.
Pancreatic Duct / Duct of Wirsung
The main duct that runs through the length of the pancreas, collecting digestive enzymes from the pancreatic cells and transporting them to the duodenum.

Accessory Pancreatic Duct / Duct of Santorini
A smaller pancreatic duct that branches off the main pancreatic duct and may also empty into the duodenum, usually superior to the major duodenal papilla.

Hepatopancreatic Ampulla / Ampulla of Vater
A dilated chamber formed by the joining of the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct before they enter the duodenum.
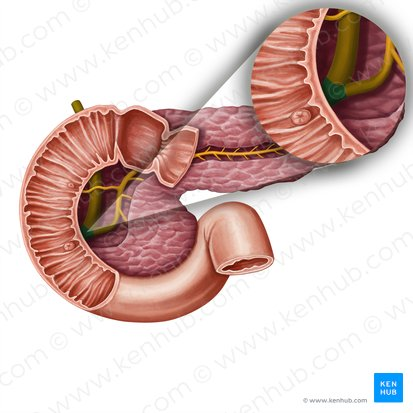
Sphincter of Hepatopancreatic Ampulla / Sphincter of Oddi
A muscular valve that surrounds the hepatopancreatic ampulla and controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Major Duodenal Papilla
The raised opening in the wall of the duodenum where the hepatopancreatic ampulla typically empties its contents.
Mucosa of Duodenum
The inner lining of the duodenum, which contains specialized cells for absorption and secretion.