Vcert Health and Fitness -Muscular System
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
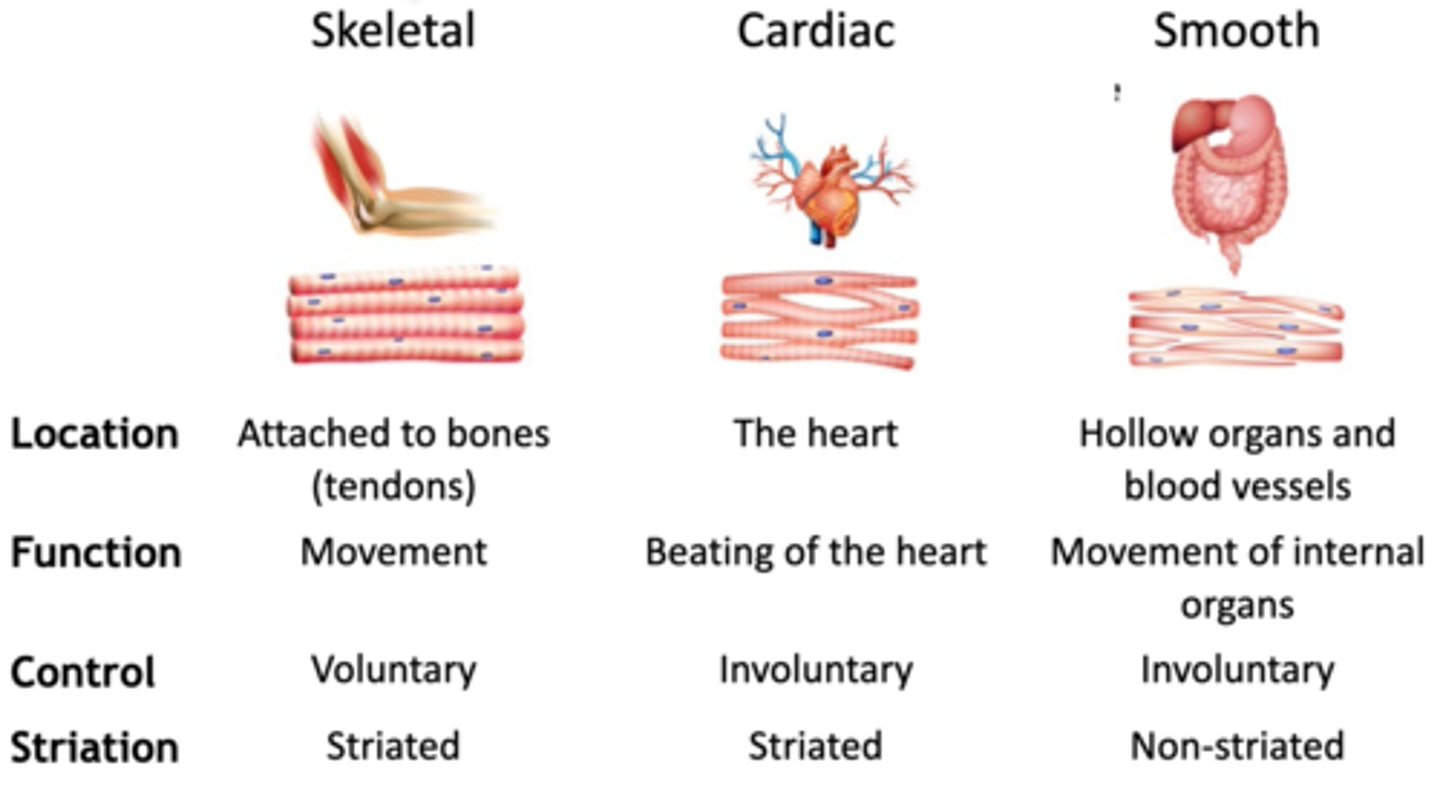
What are the types of muscles ?
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
What is the function of the skeletal muscles ?
voluntary movement(lengthen),attach to bones via tendons
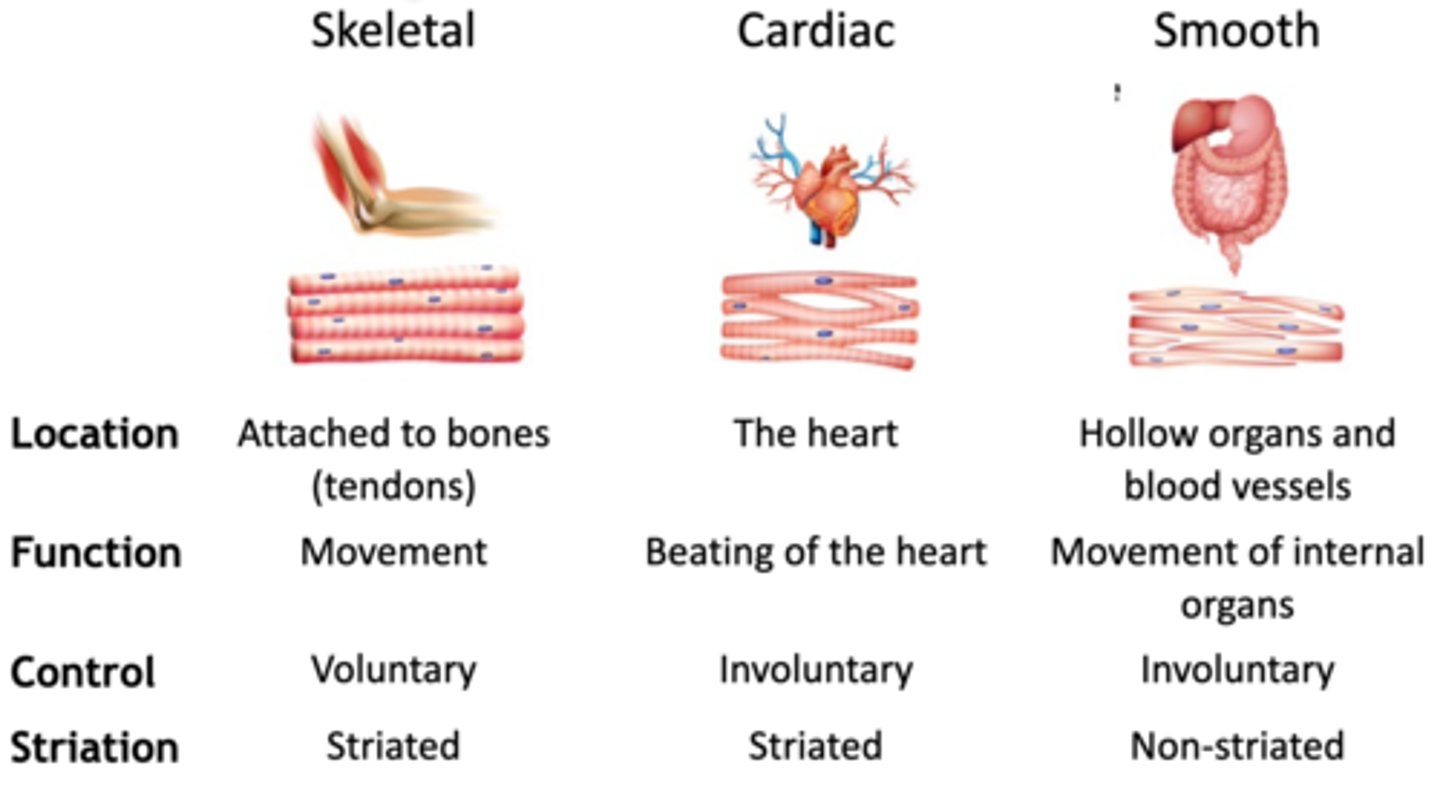
What is the function of the cardiac muscles ?
involuntary,contract the heart chambers to move blood around the body
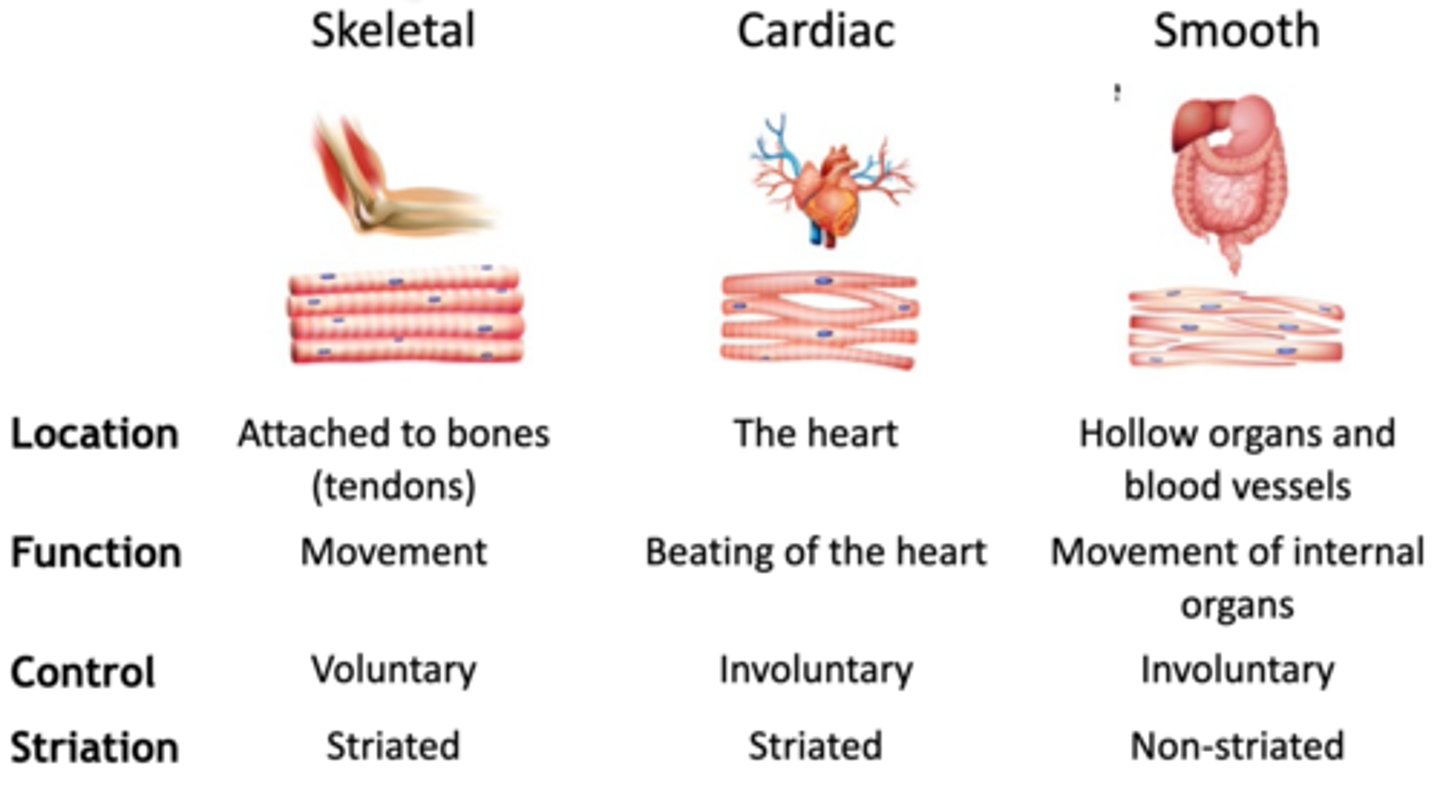
What is the function of the smooth muscles ?
involuntary,aids digestion + distributes blood around the body + work with O2
What are all the muscles at the back of your body ?
Trapezius,Triceps,Latissmus dorsi,Gluteals Maximus,Hamstrings,Gastrocnemius,Soleus
What are all the muscles at the front of the body ?
Pectorals,Biceps,Abdominals,Obliques,Quadriceps,Tibialis Anterior
What is an agonist in antagonistic muscle action ?
the working muscle(the one contracting)
What is the antagonist in antagonistic muscle action ?
the relaxing muscle(the one which is relaxing)
Give some examples of antagonistic pairs:
Biceps - triceps
Trapezius - Pectorals
Abdominals- back muscles
Deltoids - latissimus dorsi.
Quadriceps - hamstrings.
Tibialis anterior - gastrocnemius.
What are isotonic contractions?
muscle changes in length so movement occurs:
- when the muscle lengthens - eccentric contraction
- when the muscle shortens - concentric contraction
What are isometric contractions?
when force is applied to a msucle but there is no change in movement(just muscle tension)
What are the types of muscle fibres ?
- Slow twitch (Type 1)
- Fast twitch (Type 2A) (Type 2B)
What are slow twitch muscles ?
Type 1, endurance runners, dense capillary network & lots of mitochondria to support aerobic respiration, allowing them to work for long durations without fatigue(red in colour)
What are fast twitch muscles ?
Type 2a - uses anaerobic respiration, repetition of explosive movements, good for activities requiring speed and endurance, like swimming or 400m.
Type 2b - uses anaerobic respiration, ideal for short bursts of power and speed, like sprinting or weightlifting.(both white and fatigue easily)
What are the effects on slow twitch ?
when training(low intensity and high reps),they become bigger,increased capillarisation and O2
What are the effects on fast twitch ?
when training(high intensity and low reps),they become stronger,contract more force and delays lactic acid