DSA22 - Potassium Disorders
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Potassium
() is the principal cation of intracellular fluid with concentration inside cells of between 120-150 mEq/L
Its absorption there is not specifically controlled
Why is Potassium absorption in the small intestine proportional to the amount consumed?
kidney
The main regulator of body potassium balance is the ()
CCD
Where does the major regulation of K+ excretion occur in the nephron?
-Amount of Na+ delivered to CCD
-Impact of aldosterone
What are two factors K+ excretion in the nephron depends on?
-Increased Aldosterone
-Increased Distal Na+ Delivery
What are the underlying causes of renal K+ wasting?
Serum K+ concentration below 3.5 mEq/L
Define Hypokalemia
-Inadequate K+ intake
-GI losses of K+ (Diarrhea, laxatives)
-Renal losses of K+ (Loop/ Thiazide Diuretics, VOMITING/NG Tube Suction, Mg deficiency, RTAs, Osmotic diuresis, AMGs, Hyperaldo, Genetic conditions)
-Redistribution (cellular shift)
What are the 4 major underlying causes of Hypokalemia?
Since secretion of K+ in the collecting tubules is under negative control by intracellular Mg in luminal cells, low Mg releases this control --> enhanced K+ excretion
How can Hypomagnesemia lead to Hypokalemia (seen with AMGs)?
Can lose significant volume by vomiting --> RAAS activation to improve hemodynamic status ==> lose potassium through renal collecting tubule exchange for reabsorbed sodium
How does Vomiting or NG tube suction lead to RENAL losses of K+?
Caused by impaired Na/K/2Cl reabsorption in the TAL (mutation in a number of channels causes salt wasting and mild volume depletion) --> secondary hyperaldosteronism (Na+ reabsorption normal but also has hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis (similar to loop diuretic)
How does Bartter Syndrome (ar inherited disease) lead to Hypokalemia via Renal losses?
Amiloride (or other K+ sparing diuretic) and K+ replacement
How is Bartter Syndrome Txed?
Caused by loss of function mutation to the thiazide-sensitive NaCl co-transporter (NCCT) in the DCT --> Increased Na+ Loss (HYPONATREMIA) AND secondary hyperaldosteronism ==> hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis (Similar to effect of thiazide diuretics)
How does Gitelman Syndrome (ar inherited disease) lead to Hypokalemia via Renal losses?
Amiloride (or other K+ sparing diuretic) and K+ replacement
How is Gitelman Syndrome Txed?
Caused by gain of function mutations in ENaCs expressed on the apical surface of CD cells --> Increased Na+ retention (HYPERNATREMIA), with increased K+ excretion ==> HTN and a hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis with appropriately suppressed aldosterone
How does Liddle Syndrome (AD inherited disease) lead to Hypokalemia via Renal losses?
Low Na+ diet +/- amiloride (or other K+ sparing diuretic)
How is Liddle Syndrome Txed?
Drives K+ into cells
Why can insulin be used to treat Hyperkalemia (making it a risk for Hypokalemia)?
Beta 2-agonists
What medication used for obstructive lung disease or premature labor can cause Hypokalemia by intercellular shift of K+?
-Fatigue
-Constipation
-Muscle Weakness (paralysis)
-Cardiac arrhythmias
What are the Sx of Hypokalemia?
-Aldosterone antagonists (K+ sparing diuretics)
-ACE-Is or ARBs (reduce K+ losses)
Besides prevention, what medications can treat Hypokalemia?
Potassium Chloride
What should be given when total K+ stores are reduced in Hypokalemia + Hypochloridemia?
Potassium Bicarbonate
What should be given when total K+ stores are reduced in Hypokalemia + Metabolic Alkalosis?
Serum concentration of potassium above 5.0 mEq/L; MOSTLY caused by acute or chronic renal failure
Define Hyperkalemia
-Excess K+ intake
-Renal retention (reduced excretion)
-Redistribution (cellular shift)
-Pseudohyperkalemia
What are the 4 underlying causes of Hyperkalemia/
-AKI
-CKD
-Drugs
-Addison Disease
-RTA Type 4
-Pseudohypoaldosteronism
-Any inhibitor of RAAS
What can cause Renal Retention of K+?
-Beta-blockers (block Renin)
-Aliskiren (Renal Inhibitor)
-ACE-I
-ARB (block Ang II)
-Heparin/Ketoconazole (stops Aldosterone synthesis)
-Aldosterone blockers
-ENaC blockers
-Autoimmune disease destroying adrenal gland
What are clinically important inhibitors of RAAS that can cause Hyperkalemia?
Develops in patients with longstanding diabetes mellitus as a result of progressive interstitial renal disease with atrophy or destruction of renin–secreting cells in juxto-glomerular apparatus; can lead to RTA Type 4 due to hyperkalemia inhibiting ammonia synthesis
Define Hyporeninemic Hypoaldosteronism
-Damage of cell membrane
-Insulin deficiency
-Hyperosmolarity (Hyperglycemia)
-Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
-Drugs (Succinylcholine, Digoxin toxicity, Nonselective Beta-Blockers)
What can cause Cellular Redistribution leading to Hyperkalemia?
By reducing Na-K-ATPase activity in cells
How do Nonselective Beta-Blockers cause Redistribution-induced Hyperkalemia?
Consistently promotes cellular potassium efflux --> esp worse with underlying NM or renal disease
How does Succinylcholine cause Redistribution-induced Hyperkalemia?
Inhibits Na/K-ATPase in cardiac myocytes & even systemic muscle cells at toxic levels
How does Digoxin (used in HF or AFib) cause Redistribution-induced Hyperkalemia?
Condition where potassium release from blood cells occurs after phlebotomy procedures (from release of blood after prolonged tourniquet ischemia); may also happen from severe leukocytosis OR thrombocytosis
Define Pseudohyperkalemia
-Fatigue
-Myalgia
-Muscle Weakness/Cramps (can progress to ascending paralysis, hypoventilation, Resp Fail)
-EKG Changes/Cardiac arrhythmias
What are Sx of Hyperkalemia?
Elevated T waves due to Hyperkalemia; caused by repolarization in cardiac myocytes
What is being shown in this EKG? What causes this?
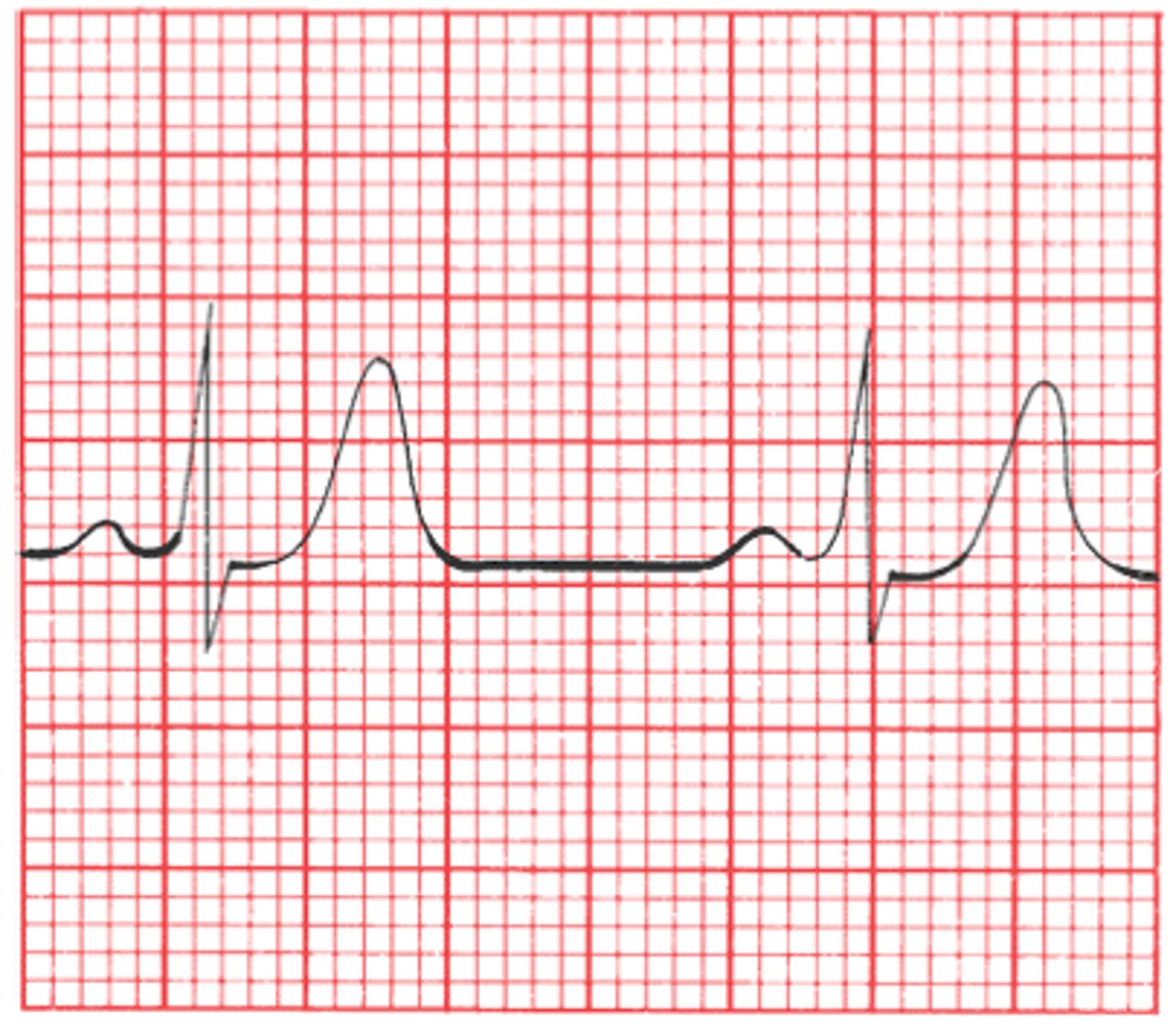
-Calcium Gluconate (reverses K+ cardiotoxicity)
-Insulin (+/- glucose if pt is not hyperglycemic)/NaHCO3 Infusion + Beta 2 blockers
-IV fluid/diuretics + Induce Diarrhea + K-binding resins
-Hemodialysis ONLY IF pts aren't responding to normal therpay
What is the Tx for Acute & Severe Hyperkalemia?
Calcium directly antagonizes the cardiac membrane depolarizing effect of hyperkalemia --> benefits seen immediately, but short lived (1-2 hours) so used ONLY as initial treatment
How does Calcium Gluconate reverse K+ cardiotoxicity?