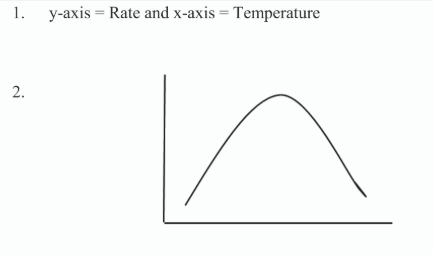
9 & 10 - Enzymes + Higher Level Energy carriers
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Enzyme
Biological (or organic or protein) catalyst
Metabolism
(All) chemical reactions in a cell (or organism)
Distinguish between the terms anabolic and catabolic
Anabolic: building up large molecules from small molecules or (a reaction) using energy
Catabolic: breaking down large molecules to small molecules or (a reaction) releasing energy
Describe the active site theory of enzyme action to explain enzyme function and specificity
Active site has a complimentary shape to only one substrate / active site changes shape (or induced fit) to accommodate substrate / enzyme substrate complex is formed / product formed / enzyme unchanged or active site changes back to original shape
What is the function of the active site of an enzyme?
To combine with the substrate or convert substrate to product
Give the products of each of the following enzymes:
i) Amylase
ii) Lipase
iii) Protease
i) Maltose
ii) Glycerol and fatty acids
iii) Amino acids or peptides
To which group of biomolecules do enzymes belong
Protein
Specificity (in terms of enzymes)
Enzymes can only act on one substrate
Give two factors that affect the function of an enzyme
pH / temperature
What is a denatured enzyme?
An enzyme that has lost it’s function
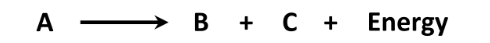
Is the reaction shown below an anabolic reaction or a catabolic reaction? Explain your answer.
Catabolic
Large molecule broken down into smaller molecules or energy released
Give one example of a catabolic enzyme and one example of an anabolic enzyme
Catabolic: Amylase
Anabolic: DNA ligase
Explain the term optimum activity in relation to enzymes
Working at its maximum rate
What is an immobilised enzyme?
An enzyme that has been trapped in an insoluble material / attached to an inert object (or each other)
Give one advantage of immobilised enzymes
Pure product formed or more stable than free enzyme or reusable
Describe how enzymes may be immobilised
Enzyme added to (sodium) alginate / calcium chloride added to solidify gel
Identify the cell organelle where enzymes are produced
Ribosome
In the context of cell metabolism, what does NAD stand for?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Name two types of particle that are transferred by NAD
Electrons (e-)
Protons (or hydrogen ions or H+)
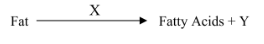
Identify X and Y
X = lipase
Y = glycerol
Suggest why enzymes are included in washing powder
To break down food-based (or other biological) stains
Write notes on the following topics. You are required to make a minimum of three points concerning each topics.
i) Metabolism
(The sum of) all reactions in cell (or organism) / controlled by enzymes / catabolism explained / anabolism explained
Write notes on the following topics. You are required to make a minimum of three points concerning each topics.
ii) ADP
Adenosine di-phosphate / a low energy (molecule) /
+ phosphate (P) / + energy / ATP formed
Comment upon enzymes molecular shape
Folded (Globular)
Is the conversion of ADP to ATP catabolic or anabolic?
Anabolic
Bioprocessing
The use of enzyme-controlled reactions to produce a product
Bioreactor
Vessel in which products are made by cells (or organisms)
Give one application of a named immobilised enzyme. In your answer, refer to substrate, enzyme and product
Lactase - converts lactose into glucose and galactose
or
Glucose Isomerase - converts glucose into fructose
Experiment: Enzyme immobilisation
Name the enzyme you immobilised
Sucrase (in yeast)
Experiment: Enzyme immobilisation
Describe the procedure you used to immobilise the enzyme
Dissolved alginate in water and added yeast / dropped into solution of calcium chloride / beads hardened or beads filtered or rinsed
Points may be obtained from an appropriately labelled diagram
Experiment: Enzyme immobilisation
Describe how you examined the application of the immobilised enzyme
Place beads of immobilised enzyme into a separating funnel / add a solution of yeast and water into a second separating funnel / pour sucrose solution into each separating funnel / test the products by letting them drip onto glucose strips / immobilised yeast is slower to start forming glucose / glucose is formed more quickly by the non-immobilised yeast
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of heat denaturation on enzyme activity
Name the enzyme you used, its substrate and its product
Enzyme: Catalase
Substrate: Hydrogen Peroxide
Product: Oxygen + water
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of heat denaturation on enzyme activity
Describe how you carried out the investigation. Use a labelled diagram if necessary.
Boil enzyme / unboiled enzyme /
place enzyme solution into a graduated cylinder /
pH 9 buffer added /
washing liquid added /
placed in water bath at 25oc /
left for a time /
noted production of foam or not
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of heat denaturation on enzyme activity
Describe the results of this investigation.
Boiled enzyme showed no activity (did not produce foam)
Fresh enzyme showed activity (produced foam)
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of pH on the rate of activity of an enzyme
Name the enzyme you used in this investigation
Catalase
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of pH on the rate of activity of an enzyme
Describe how you varied the pH in this activity
Added different pH buffers
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of pH on the rate of activity of an enzyme
Describe how temperature was kept constant during this investigation
Waterbath
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of pH on the rate of activity of an enzyme
Briefly describe how you measured the rate of enzyme activity
Determined the volume of foam / produced in a set period of time
Experiment: Investigation of the effect of pH on the rate of activity of an enzyme
Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus that you used in this investigation
Diagram: graduated cylinder with liquid
Labels: Graduated cylinder / Enzyme / waterbath / foam / washing up liquid / buffer
Experiment: Investigation into the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme action
Name the enzyme that you used
Catalase
Experiment: Investigation into the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme action
Name the substrate of this enzyme
Hydrogen Peroxide
Experiment: Investigation into the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme action
Why was it necessary to keep the pH constant in the course of this investigation?
To eliminate it as a possible influence on rate or only one variable
Experiment: Investigation into the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme action
How did you vary the temperature in the course of the investigation?
Waterbaths
Experiment: Investigation into the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme action
Use the axes below to summarise the results of your investigation. Do this by
labelling the axes,
drawing a graph to show how the rate of enzyme action varied with temperature.