History inventions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms

what invention is this?
Spinning Jenny
Spinning Jenny
James Hargreaves (c. 1764)
Spinning Jenny
A multi-spindle spinning frame. It significantly reduced the amount of work needed to produce yarn, allowing a worker to operate eight or more spools at once. This invention was a crucial catalyst for the Industrial Revolution.

what invention is this?
steam engine
steam engine
James Watt(Improvements, c. 1769).
Steam Engine
A heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. Watt's improvements—particularly the separate condenser—made the engine much more efficient, reliable, and practical, powering factories, locomotives, and ships worldwide.

what invention is this?
cotton gin
Cotton gin
Eli Whitney (1793)
Cotton gin
A machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds. It made cotton production profitable on a massive scale but, tragically, also dramatically increased the demand for enslaved labor in the American South.
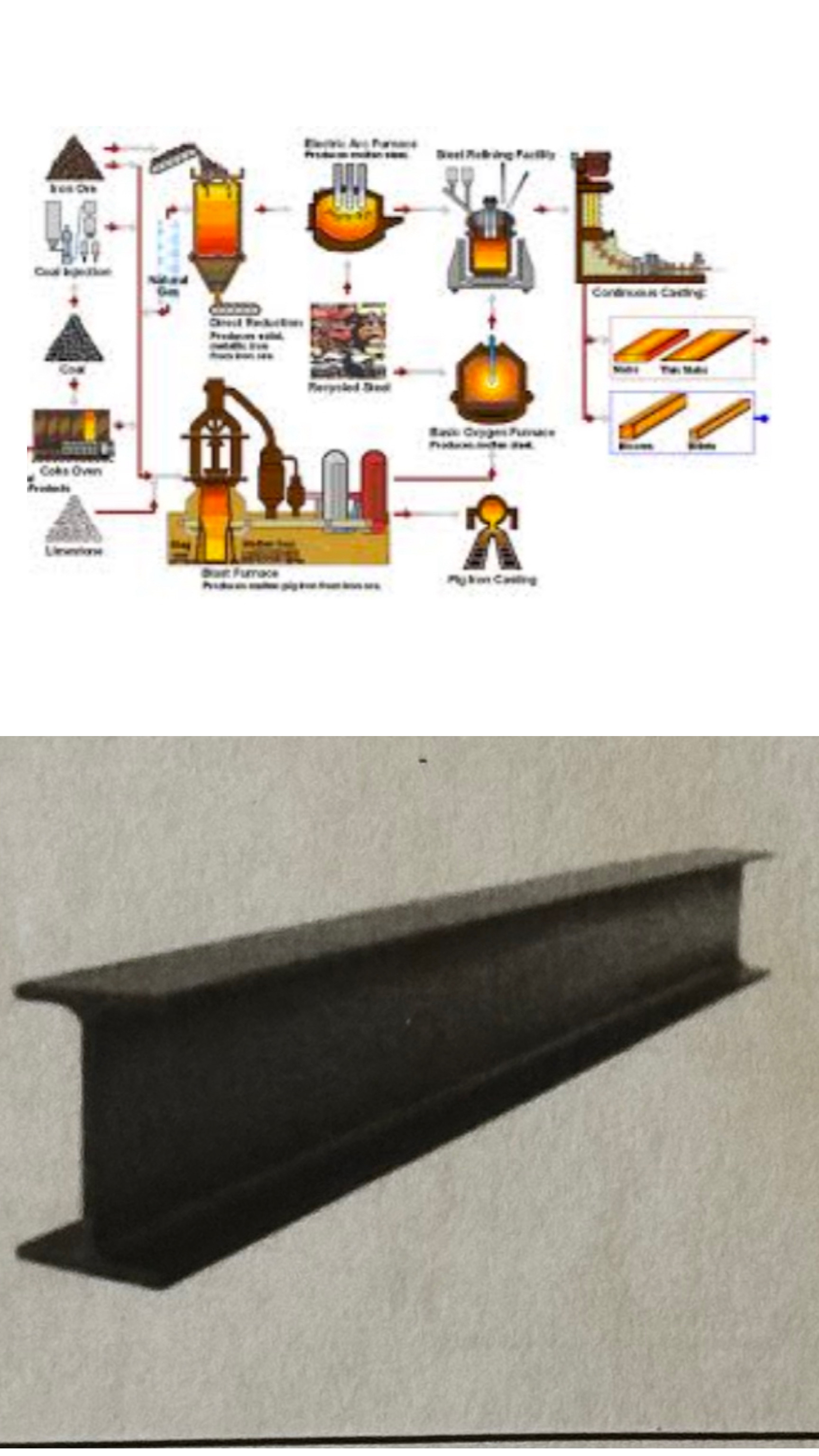
what invention is this?
Bessemer process (steel process)
Bessemer process (steel)
Henry Bessemer (1856)
Bessemer Process (Steel)
The first inexpensive industrial process for the mass-production of steel from molten pig iron. It involved blowing air through the molten iron to oxidize (remove) the impurities. This made large-scale production of strong, low-cost steel possible, essential for modern skyscrapers, bridges, and railways.
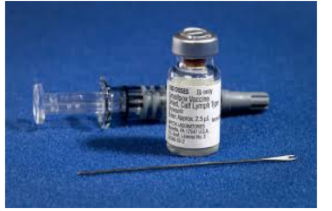
what invention is this?
Smallpox vaccine
Smallpox vaccine
Edward Jenner (1796)
Smallpox vaccine
The world's first successful vaccine. Jenner observed that milkmaids who had contracted cowpox (a mild disease) were immune to smallpox. He inoculated a boy with cowpox, who then proved immune to smallpox. This breakthrough established the science of immunology.
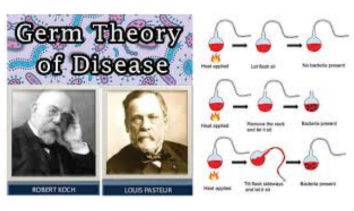
what invention is this?
Germ theory of disease
Germ Theory of Disease
Louis Pasteur (and Robert Koch) (1860s-1870s)
Germ Theory of Disease
The scientific concept that microorganisms, or "germs," are the cause of many diseases. Pasteur's experiments confirmed this theory, leading to advancements like pasteurization, sterile surgical techniques, and personal hygiene practices, fundamentally transforming medicine and public health.

what is this invention?
telephone
Telephone
Alexander Graham Bell (1876)
Telephone
A device that converts sound (voice) into electrical signals for transmission and then reconverts those signals into audible sound at a receiving location. It revolutionized communication by allowing two people to talk instantly over long distances.

what invention is this?
phonograph
phonograph
Thomas Edison (1877)
phonograph
The first device capable of both recording and reproducing sound. It worked by engraving sound vibrations onto a rotating cylinder or disc, which could then be played back. It marks the beginning of the music and recording industries.

what invention is this?
practical automobile
Practical automobile
Karl Benz (1886)
Practical automobile
Benz is credited with inventing the first practical automobile powered by an internal combustion engine, the Benz Patent-Motorwagen. It was a three-wheeled vehicle and is widely regarded as the first true car.

what is this invention?
Radio (Wireless Telegraphy)
Radio (Wireless Telegraphy)
Guglielmo Marconi (Key patents and demonstrations, late 1890s)
Radio (Wireless Telegraphy)
A technology that uses electromagnetic waves to transmit information (sound or data) through the air without wires. Marconi successfully achieved the first transatlantic wireless transmission, leading to global communication and broadcasting.

what is this invention?
Airplane (powered flight)
Airplane (powered flight)
Orville and Wilbur Wright (The Wright Brothers) (1903)
Airplane (powered flight)
The invention of the first successful heavier-than-air powered aircraft. On December 17, 1903, their Wright Flyer made the first sustained, controlled flight by a human-piloted machine, opening the door to modern aviation.