Bio Lab 6 - Measurement of Enzyme Activity
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
peroxidase
enzyme used a model to generalize all enzymes
one member of a group of enzymes found in all life
eliminates toxic H2O2, usually produced in metabolic rxns in cells
H2O2
byproduct of metabolic rxns in cells that is eliminated by enzymes immediately
suffix -ase
signifies an enzyme
heme
porphyrin molecule with an iron ion sitting at its center (like hemoglobin)
coenzyme tucked into peroxidase active site
found in hemoglobin
Peroxidase substrates
Has two:
1) filled with H2O2
2) second varies
guaiacol
phenolic compound used as second substrate in peroxidase
phenolic compound
6 carbon ring with at least one hydroxyl group
Reaction catalyzed by peroxidase
guaiacol gets oxidized to quinone
H2O2 gets reduced to water
methanol is by product

what do quinones do
spontaneously react with each other or other molecules to form colored complexes
How do we measure amount of colored product?
colorimeter set to 500nm wavelength
rate of reaction
Amount of colored product measured by Spectro Vis plus over time (product/time)
concentration of colored product and transmittance relationship
As concentration of colored product increases the percent transmittance decreases
Inversely related
More product stops light from passing through
Preparation of lab
put ice to 1/3 beaker full
add tap water until 2/3 beaker full
Leave test tube containing enzyme in bath (enzymes denature after being removed from cells but low temps delays this)
Cut up onion into ¼ inch pieces and add 10g and 200mL DI water to liquify in food processor
Strain extract through cheesecloth and keep in ice bath
Assay
Do the test one time:
combine volumes of different solutions than measure change in %T with colorimeter
Sources of error
water left over after washing test tube before moving onto next assay
inaccurate pipette measurements
Not mixing solutions well enough
What is assay #1 used for
It is the blank used to calibrate the colorimeter
Accounts for water, substrate, and cuvette but there is no enzyme
Calibration of colorimeter
plug in and allow colorimeter to heat up
have blank (assay #1) ready
Select %transmittance vs. time
place cuvette inside
click finish calibration
Set wavelength at top to 500nm and click done
Usage of colorimeter for other assays
pipette specified volumes of guaiacol, water, and H2O2 into test tube and swirl
Swirl enzyme extract and pipette into separate test tube
Pour first test tube into the one with enzyme extract and mix well
transfer to cuvette and place in colorimeter
Click collect and %T will start around 90%-80%
%T will start decreasing so stop at 48%
Measure time between 70%-50%
For assay #12 how long will the reading take to drop from 70% to 50% transmittance?
Won’t drop because no H2O2 (substrate) is present so the guaiacol has nothing to react with meaning no quinones will be present to produce colored products.
What do we know about the reaction rate if the reading is not changing and there are no products being made?
The reaction rate is not being catalyzed and is very slow
assay concentration differences
All assays are 5.0mL
Guaiacol is always 2.0mL (constant, so no difference in effect on rxn)
Enzyme is always 0.2mL (constant)
H2O2 varies (independent variable)
water volume adjusts to H2O2 volume to keep constant 5.0mL solution
Why change only volume of H2O2 in assays?
To see how the effect of the H2O2 substrate has on reaction rate
Effect of higher H2O2 conc
More substrate increases product formation per unit of time (faster drop from 70 to 50 percent transmittance)
rate of enzyme activity
amount of product formed per unit of time or amount of substrate consumed per unit of time
(As product is formed substrate is consumed)
What is the time needed to drop from 70% to 50% dependent of
substrate (H2O2) concentration. (higher concentration, faster it drops)
What is the amount of colored product that corresponds to drop from 70% to 50%
200 micromoles
How to calculate rate of rxn
200 micromoles / time to drop 70% to 50%
What is the independent and dependent variables on the graph
Independent (X-axis) - Substrate (H2O2) concentration
Dependent (Y-axis) - rate of reaction
Michaelis-Mentin curve correlation to this lab
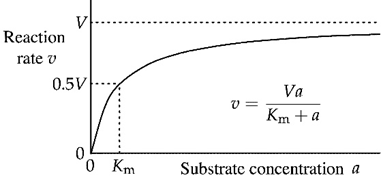
Origin will be assay #12 (0,0) then going backwards (11, 10, 9) curve will rise and level off at highest substrate conc
Saturation
Highest conc of substrate where reaction rate levels off (no more substrate can be added, enzyme is working at max rate)
Change in assay #13-15
Substrate concentration is held constant but enzyme concentration varies
What will the trend in rate be when enzyme conc differs (#13-15)?
More enzymes increases rate (More enzyme means more active sites to catalyze rxn)
assays #16-18 and possible error
Same concentrations as assay 5 which should yield same times. Variation among them is due to errors such as, pipetting, differences in temp, improper mixing, human reaction time, instrumental error from colorimeter.
True value (16-18)
The average of the repeated trials