Biology Unit 2 Ecology IHS Skavaril
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Why is ecology important
it helps us understand how life on Earth is connected and how we depend on the environment for things like clean air, water, and food; humans + Earth = healthy and clean
Pyramid of Biomass
Shows how matter cycles in a ecosystem; measures mass of biotic factors.

Explain the carbon cycle
Atmosphere to biotic factors: photosynthesis
Atmosphere to water: dissolve
Water to rock: sedimentation
Water to atmosphere: diffusion
Biotic factors to atmosphere: decomposition/respiration
Biotic factors to fossil fuels: fossilize
Fossil fuels to atmosphere: combustion
Explain the nitrogen cycle
Atmosphere to soil: nitrogen fixation
Ammonia to nitrate in soil: nitrification
Soil to water: leeching
Soil to atmosphere: denitrification
Organism that does the work of transforming nitrogen: bacteria
Explain the hydrological cycle
Atmosphere to surface: precipitation
Surface to atmosphere: evaporation
In the atmosphere: condensation
Surface to body of water: runoff
Surface to ground water: seepage
Biotic factors to atmosphere: transpiration
How is carrying capacity determined
By limiting factors (food, water, shelter, space
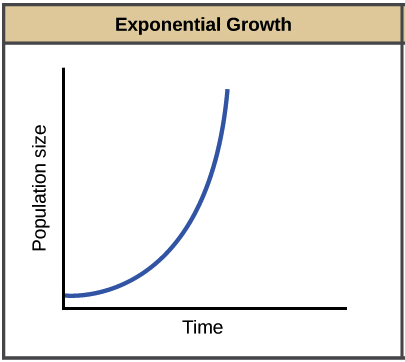
What is exponential growth (aka J curve)
Fast growth; population is rapidly increasing
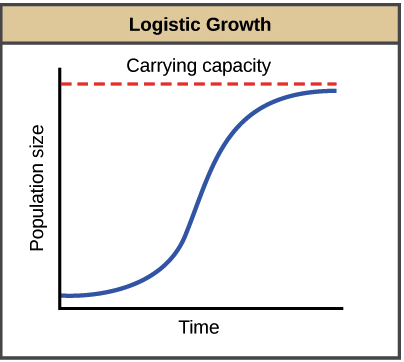
What is logistic growth (aka S curve)
After exponential growth, rate can slow and stop
What is population crash
Exceed in carrying capacity; population plummets down

What are density-dependent factors
Factors more likely to change carrying capacity as the population increases (e.g. predation, competition, disease)
What are density-independent factors
Factors likely to change carrying capacity no matter what the population is (e.g. weather, humans, natural disasters)
What causes population to increase
Birth and immigration
What causes population to decrease
Death and emmigration
What is a food chain
Shows energy flowing in one direction
What is a food web
Shows energy flowing in all directions
Which way does energy flow
In one direction through an ecosystem, away from the sun
Where does energy usually start
Energy usually starts with the sun, which is captured by autotrophs, and then consumed by heterotrophs
What is a system
Interconnected parts that functions as a whole
What is systems thinking
Everything is connected in systems; if one thing works differently, so will the system. One part changes, everything does
What is the atmosphere
A mixture of gases that surround Earth
What is the geosphere
Rocky, solid part of the earth. minerals, mountains, interior of Earth
What is the hydrosphere
All the water on earth
What is the biosphere
The part of Earth where life exists; all living things
What is random population dispersion
Put in random places
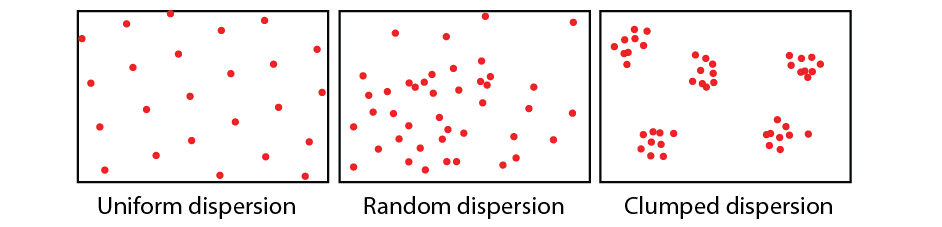
What is uniform population dispersion
Spread out evenly

What is clumped population dispersion
One big group
What is the importance of keystone species in a ecosystem?
Keystone species protects producers → increase in producer population → increase in consumers → more interactions → more biodiversity → more resilient → more stable
Autotroph/Producer
An organism that gets energy via photosynthesis and chemosynthesis (abiotic factors)
Herbivore
An organism that gets energy by eating producers
Decomposer
An organism that gets energy by breaking down dead organic matter
Biodiversity
The variety of life on Earth; provides essential services like clean air and water, supports food security and medicine, and makes ecosystems more resilient to change. Increase interactions and stabilize an ecosystem
Carnivore
An organism that gets energy by only eating animals
Commensalism
One organism benefits and the other organism is not impacted/affected
Biome
All the ecosystems controlled by one climate
Community
All the biotic factors in one ecosystem
Ecosystem
All abiotic and biotic factors in one area
Mutualism
Both organisms benefit
Resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to recover and adapt after being disturbed, such as from a natural disaster or human activity
Niche
The role an organism plays within its ecosystem
Habitat
The place where a particular animal or plant (or species of animal or plant) lives
Interspecific competition
Organisms from different species competing for the same resources
Intraspecific competition
Organisms from same species competing for the same resources
Primary consumer
An organism that gets energy by consuming producers
Secondary consumer
An organism that gains energy by eating primary consumers
Tertiary consumer
An organism that gains energy by eating secondary consumers
Immigration
The movement of individuals into a population's area from another population or region
Emigration
The act of a population of organisms leaving their habitat to move to another place
Nitrogen fixation
Process where atmospheric nitrogen, which most organisms cannot use, is converted to a useable nitrogen compound (e.g. ammonia)
Omnivore
An organism that gets energy by eating both plants and animals
Chemosynthesis
Capturing energy from chemicals
Detritivore
An organism that gets energy by eating dead organic matter (smaller matter like feces, dead leaves)
Scavenger
An organism that gets energy by eating dead organic matter (large pieces like dead animals)
Trophic level
A level of energy (producers, primary consumers, etc.) 90% of energy is lost in each level
Nitrification
Two-step process where bacteria in soil and water convert ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates
Denitrification
Microbial process where bacteria convert nitrates and nitrites into nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere
Population
All members of one species in one community
Population density
Number of individuals / area (unit²)
Parasitism
One organism benefits and one organism is negatively impacted
Predation
One organism hunts and kills another organism
Weather
Day to day conditions of Earth's atmosphere
Climate
Long term patterns of temperature and precipitation over many years
Energy pyramid
Shows how energy flows in a ecosystem

Pyramids of Numbers
Shows # of organisms available in a ecosystem/in each trophic level
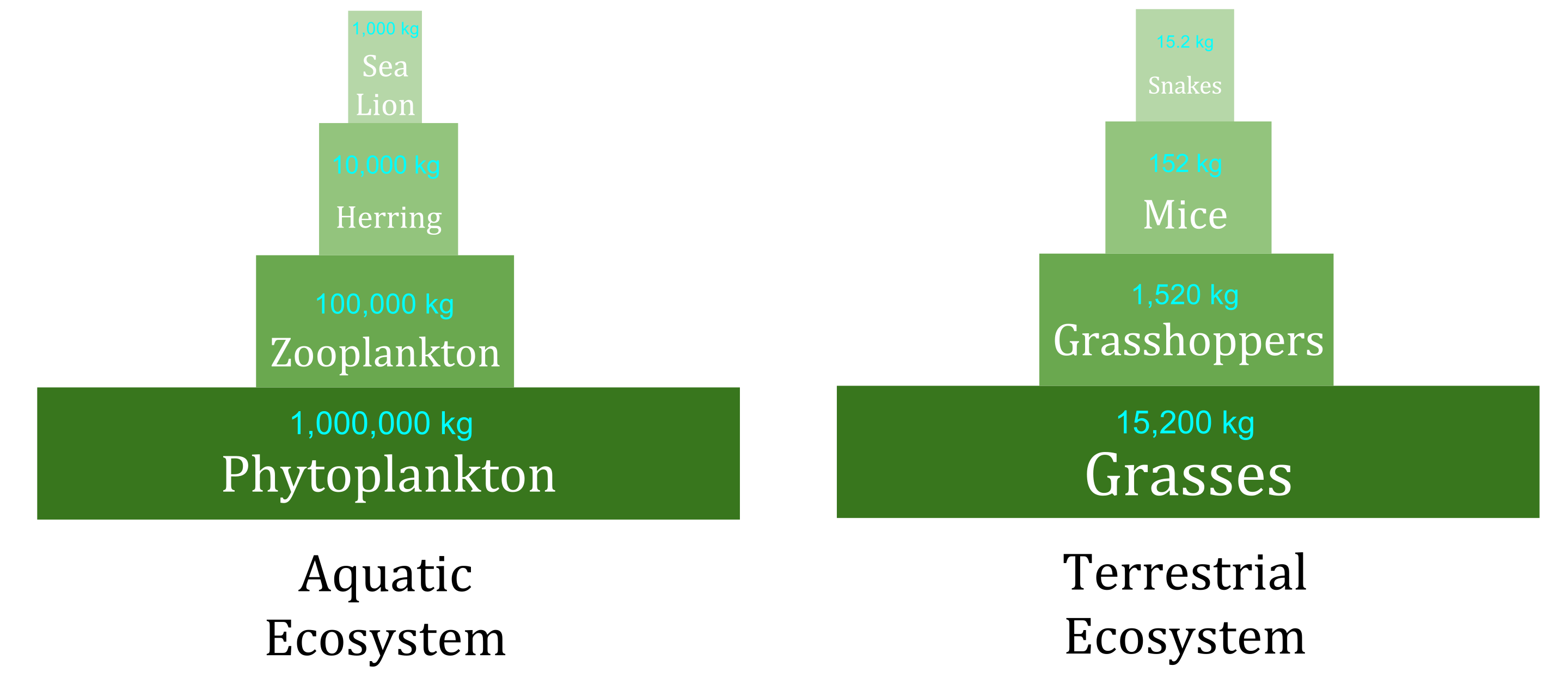
Individual
One of a population
Photosynthesis
Capturing energy from sunlight
What makes biomes different from each other
Climate
Which is one way that the movement of matter through an ecosystem is different from the transfer of energy
Only the movement of matter occurs in an unending cycle; matter cycles, energy flows