Materials Test 1
5.0(8)
5.0(8)
Card Sorting
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Assignment and Quiz Questions and slideshow info
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
1
New cards
What percentage of US GDP is accounted for by the manufacturing industries?
12%
2
New cards
Manufacturing technologically
the application of physical and chemical processes to alter the geometry, properties, and appearance of a given starting material to make parts or products
3
New cards
Manufacturing economically
The transformation of materials into items of greater value by means of one or more processing and or assembly operations. Manufacturing adds value to material by changing or combining it.
4
New cards
Primary industries
one that cultivates and exploits natural resources, such asSecon agriculture or mining
5
New cards
Secondary industries
takes the outputs of primary industries and converts them to consumer and capital goods like textiles and electronicsT
6
New cards
Tertiary industries
the service sector of economy, like banking and education
7
New cards
Consumer good
product purchased directly by consumer like car, TV, phone
8
New cards
Capital goods
purchased by companies in order to product goods or provide services like computers, trucks, construction equipment
9
New cards
Product variety v production quantity
Production quantity is inversely related to product variety. A factory that produces a large variety of products will produce a smaller quantity of each. A company that products a single product will product a large quantity.
10
New cards
Technological processing capability
available set of manufacturing processes. What distinguishes plants is the processes they can perform. Technological processing capability is not only physical processes but also expertise possessed by plant personnel in these processing technologies.
11
New cards
Four categories of engineering materials in manufacturing
metals, ceramics, polymers, composite materials
12
New cards
Steel
iron-carbon alloy. compositions includes other alloying elements as well to enhance property of metal Typ
13
New cards
Typical applications of steel
construction, transportation, and consumer products
14
New cards
Thermoplastic polymer
can by subjected to multiple heating and cooling cycles without substantially altering the molecular structure of the polymer
15
New cards
thermosetting polymer
chemically transform (cure) into a rigid structure on cooling from a heated plastic condition
16
New cards
Process layout
A process layout is one where the machinery in a plant is arranged based on the type of process it performs. To product a product it must visit the departments in the order of the operations being performed.
17
New cards
Product layout
machinery is arranged based on the general flow of the products that will be produced. Works well when all products tend to follow the same sequence of production
18
New cards
Overhead costs
all the expenses of operating the company other than material, labor, and equipment
19
New cards
Factory overhead
costs of running the factory excluding materials, direct labor, and equipment. Includes plant supervision, maintenance, insurance, heat, lightco
20
New cards
corporate overhead
company expenses not related to the factory, such as sales, marketing, accounting, legal, engineering, health benefits
21
New cards
availability
the proportion uptime of the equipment
22
New cards
Polymer bonding
covalent
23
New cards
If stress values were measured during a tensile test what would have higher value
true stress>engineering stress
24
New cards
Behavior of brittle materials such as ceramics and thermosetting plastics
perfectly elastic
25
New cards
Types of elements
metals, nonmetals, semimetals
26
New cards
Noble metals
copper, silver, gold
27
New cards
Primary bonding
strong bonding between atoms in a material, for example to form a molecule
28
New cards
Secondary bonding
not as strong and is associated with attraction between molecules in the material
29
New cards
Ionic bonding
atoms of one element give up their outermost electrons to the atoms of another element to form complete outer shells
30
New cards
Crystalline structures
located at regular and repeating lattice positions in three dimensions, thus the crystal structure possesses a long range order which allows a high packing density
31
New cards
Noncrystalline structure
atoms are positioned randomly in the material not possessing any repeating, regular pattern
32
New cards
Common point defects in a crystal lattice structure
Vacancy-a missing atom in the lattice structure, Ion-pair vacancy-a missing pair of ions of opposite charge in a compound, interstitially-a distortion in the lattice caused by an extra atom present, Frenkel defect-an ion is removed from a regular position in the lattice and inserted into an interstitial position not normally occupied by such an ion
33
New cards
How do grain boundaries contribute to the strain hardening phenomenon in metals?
Grain boundaries block the continued movement of dislocations in the metal during straining. As more dislocations become blocked, the metal becomes more difficult to deform; in effect it becomes stronger
34
New cards
Materials with crystalline structure
metals, ceramics other than glass, some plastics have a partially crystalline structure
35
New cards
Materials with noncrystalline structure
glass, rubber, certain plastics (thermosetting)
36
New cards
Basic difference in the solidification process between crystalline and noncrystalline structures
crystalline structures undergo an abrupt volumetric change as they transform from liquid to solid state and vice versa. This is accompanied by an amount of energy called the heat of fusion that must be added to the material during melting or released during solidification. Noncrystalline materials melt and solidify without the abrupt volumetric change and heat of fusion.
37
New cards
The thermal expansion properties of polymers
greater than those of metals
38
New cards
Solidus
marks the beginning of melting in the heating of most metal alloys
39
New cards
the mass diffusion rate dm/dt across a boundary between two different metals is a function of
concentration gradient dc/dx
40
New cards
Superconductor
zero resistivity
41
New cards
Tolerance
total permissible variation from a specified dimension
42
New cards
Outside micrometer could measure
shaft diameter
43
New cards
In Go/NO-GO gage, a GO gage
checks maximum material condition
44
New cards
What is the dilemma between design and manufacturing in terms of mechanical properties?
To achieve design function and quality, the material must be strong; for ease of manufacturing, the material should not be strong, in general.
45
New cards
What are the three types of static stresses to which materials are subjected?
Tensile, compressive, and shear. Tensile stresses tend to stretch the material, compressive stresses tend to squeeze it, and shear involves stresses that tend to cause adjacent portions of the material to slide against each other.
46
New cards
Hooke’s Law
Hooke's Law defines the stress strain relationship for an elastic material where E = a constant of proportionality called the modulus of elasticity.
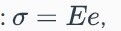
47
New cards
What is the difference between engineering stress and true stress in a tensile test?
Engineering stress divides the load (force) on the test specimen by the original area; whereas true stress divides the load by the instantaneous area which decreases as the specimen stretches.
48
New cards
Define tensile strength of a material.
The tensile strength is the maximum load experienced during the tensile test divided by the original area.
49
New cards
Define yield strength of a material.
The yield strength is the stress at which the material begins to plastically deform. It is usually measured as the 0.2% offset value, which is the point where the stress strain curve for the material intersects a line that is parallel to the straight-line portion of the curve but offset from it by 0.2%.
50
New cards
What is work hardening?
Work hardening, also called strain hardening, is the increase in strength that occurs in metals when they are strained.
51
New cards
How does the change in cross sectional area of a test specimen in a compression test differ from its counterpart in a tensile test specimen?
In a compression test, the specimen cross sectional area increases as the test progresses; while in a tensile test, the cross sectional area decreases.
52
New cards
Tensile testing is not appropriate for hard brittle materials such as ceramics. What is the test commonly used to determine the strength properties of such materials?
A three point bending test is commonly used to test the strength of brittle materials. The test provides a measure called the transverse rupture strength for these materials.
53
New cards
How is shear strength S related to tensile strength TS, on average?
S = 0.7 TS, on average.
54
New cards
What is hardness, and how is it generally tested?
Hardness is defined as the resistance to indentation of a material. It is tested by pressing a hard object (sphere, diamond point) into the test material and measuring the size (depth, area) of the indentation.
55
New cards
Why are different hardness tests and scales required?
Different hardness tests and scales are required because different materials possess widely differing hardnesses. A test whose measuring range is suited to very hard materials is not sensitive for testing very soft materials.
56
New cards
Define the recrystallization temperature for a metal
The recrystallization temperature is the temperature at which a metal recrystallizes (forms new grains) rather than work hardens when deformed.
57
New cards
Define viscosity of a fluid.
Viscosity is the resistance to flow of a fluid material; the thicker the fluid, the greater the viscosity.
58
New cards
What is the defining characteristic of a Newtonian fluid?
A Newtonian fluid is one for which viscosity is a constant property at a given temperature. Most liquids (water, oils) are Newtonian fluids.
59
New cards
What is viscoelasticity, as a material property?
Viscoelasticity refers to the property most commonly exhibited by polymers that defines the strain of the material as a function of stress and temperature over time. It is a combination of viscosity and elasticity
60
New cards
The manufacturing engineering department in an organization is best described as which one of the following:
technical staff function
61
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a usual responsibility of the manufacturing engineering department?
marketing the product
62
New cards
Which of the following is considered a basic process, as opposed to a secondary process?
impression die forging
63
New cards
Which of the following would be considered a secondary process, as opposed to a basic process?
machining a metal casting
64
New cards
In a make or buy situation, the decision should always be to purchase the component if the vendor ’s quoted price is less than the in-house estimated cost of the component:
False
65
New cards
Which of the following is an operation to enhance physical properties?
annealing
66
New cards
A route sheet is a document whose principal function is which one of the following
specifies the process plan
67
New cards
Which one of the following types of computer-aided process planning relies on parts classification and coding in group technology?
retrieval CAPP
68
New cards
The thermal expansion properties of polymers are generally _____ those of metals.
greater than
69
New cards
In the heating of most metal alloys, melting begins at a certain temperature and concludes at a higher temperature. In these cases, which of the following temperatures marks the beginning of melting:
solidus
70
New cards
Copper is generally considered easy to weld because of its high thermal conductivity:
false
71
New cards
Which of the following pure metals is the best conductor of electricity:
silver
72
New cards
A superconductor is characterized by which of the following :
zero resistivity
73
New cards
A tolerance is which one of the following:
total permissible variation from a specified dimension
74
New cards
An outside micrometer would be appropriate for measuring which of the following?
shaft diameter
75
New cards
Mining is classified in which one of the following industry categories:
primary
76
New cards
Inventions of the Industrial Revolution include which one of the following:
steam engine
77
New cards
High volume production of assembled products is most closely associated with which one of the following layout types?
product
78
New cards
A production planning and control department accomplishes which of the following functions in its role of providing manufacturing support?
schedules the order of products on a machine
79
New cards
Polymers are characterized by which of the following bonding types ?
covalent
80
New cards
If stress values were measured during a tensile test, which of the following would have the higher value:
true stress
81
New cards
Which one of the following types of stress strain relationship best describes the behavior of brittle materials such as ceramics and thermosetting plastics:
perfectly elastic
82
New cards
Which one of the following materials has the highest hardness:
alumina ceramic
83
New cards
Precision
Precision in measurement is the degree to which random errors are minimized.
84
New cards
Accuracy
Accuracy is the degree to which the measured value agrees with the true value of the quantity of interest. It is a measurement procedure that is absent of systematic errors.
85
New cards
What is the difference between a bilateral tolerance and a unilateral tolerance?
A bilateral tolerance allows variation in both positive and negative directions from the nominal dimension, whereas a unilateral tolerance allows the variation from the nominal dimension to be either positive or negative, but not both.
86
New cards
tolerance
A tolerance is defined as the total amount by which a specified dimension is permitted to vary.
87
New cards
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is an ionized solution capable of conducting electric current by movement of the ions.
88
New cards
Why are metals better conductors of electricity than ceramics and polymers?
Metals are better conductors because of metallic bonding, which permits electrons to move easily within the metal. Ceramics and polymers have covalent and ionic bonding, in which the electrons are tightly bound to particular molecules.
89
New cards
What is thermal conductivity as a material property?
Thermal conductivity is the capacity of a material to transfer heat energy through itself by thermal movement only (no mass transfer).
90
New cards
Define specific heat as a material property.
specific heat is defined as the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the material by one degree.
91
New cards
Describe the melting characteristics of a noncrystalline material such as glass.
In the heating of a noncrystalline material such as glass, the material begins to soften as temperature increases, finally converting to a liquid at a temperature defined for these materials as the melting point.
92
New cards
What is the difference in melting characteristics between a pure metal element and an alloy metal?
A pure metal element melts at one temperature (the melting point), while an alloy begins melting at a certain temperature called the solidus and finally completes the transformation to the molten state at a higher temperature called the liquidus. Between the solidus and liquidus, the metal is a mixture of solid and liquid.
93
New cards
Density
Density is the weight per unit volume of a material.