Unit 6 Quiz APHG
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ms Bradys APHG Unit 6 Quiz Study Set
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
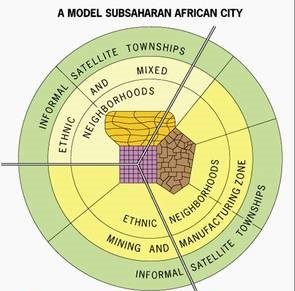
African City Model
Influences left from colonial period
Diversity between colonial past and African tradition make it difficult to create one model for an African city
Studies find that many African cities contain multiple CBDs instead of one = remnants of a colonial CBD, informal market zone and a transitional business center
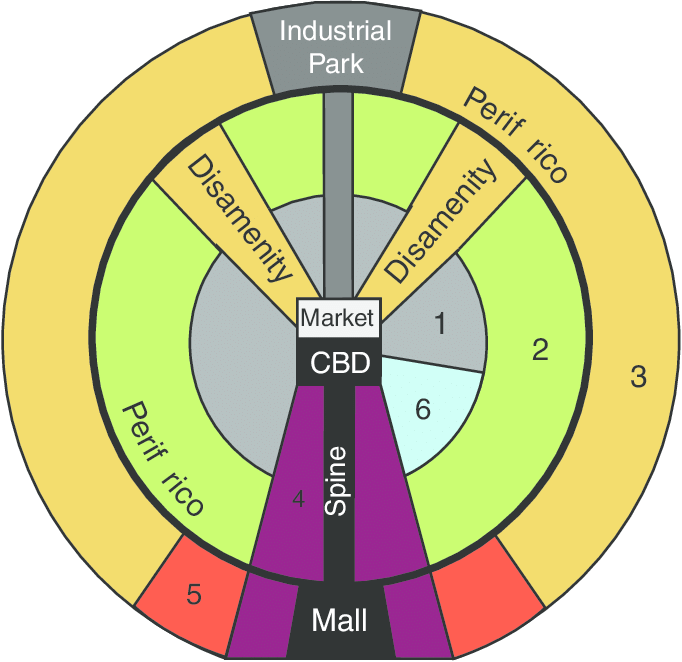
Latin American City Model
Griffin-Ford Model – created in the 1980s
Socioeconomic status decreases as one moves away from the city center (meaning the more wealthy live in the interior and the outskirts contain squatter settlements and zones of disamenity (poorest parts of the city)
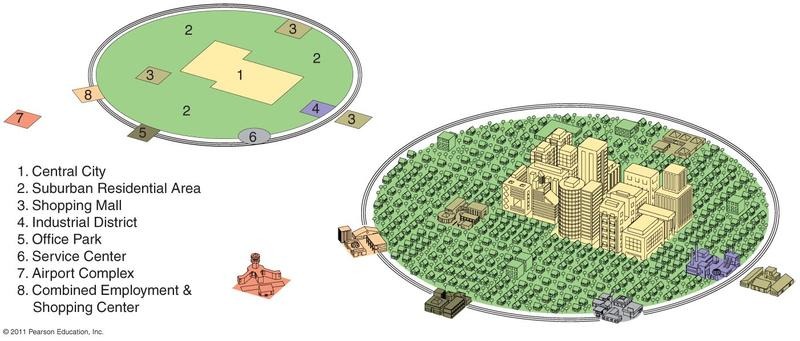
The Galactic City Model
or Peripheral Model
CBDs start to be specialized towards a particular industrial or service sector
“Post industrial city”
Manufacturing has declined & become specialized – moved to specified industrial parks in periphery (low cost land)
Transportation nodes
See other services like research & development, banking & finance, universities, high-tech & computing, etc.
Harris & Ullman Multiple-Nuclei Model
Created in 1945 by CD Harris & Edward Ullman and shows the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a collection of nodes or activities ex. University, airport, business center, park, etc.
More than one commercial center
Urban periphery for heavy industry, suburbs, etc.
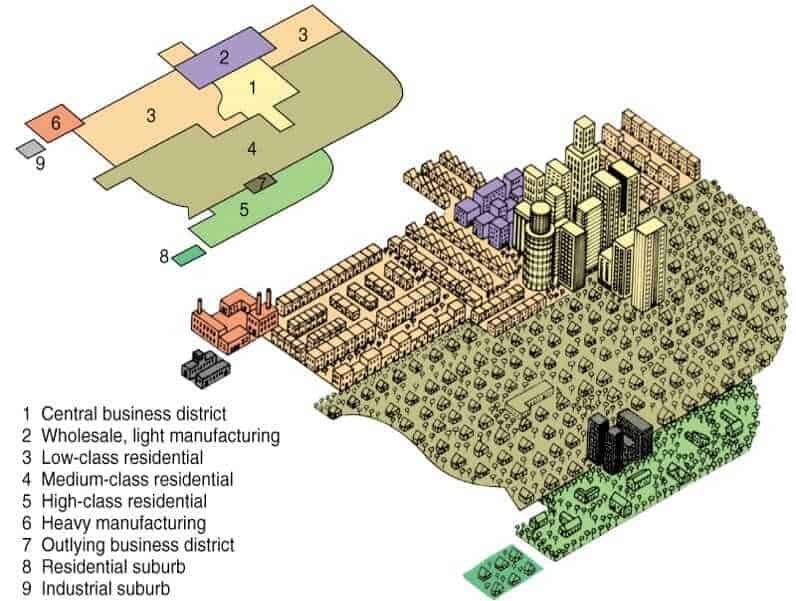
Hoyt Sector Model
Created in 1939 by Homer Hoyt and theorized that cities developed in sectors, not rings; can show ethnic variations in the city
CBD in the center
Industrial space organized around a linear corridor surrounding a main transportation line (railroad line or yard, riverfront, harbor, etc. = gives factories access to transport)
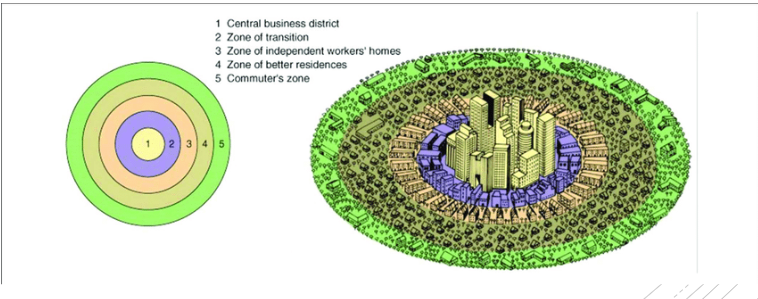
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
A structural model of a central city that suggests the existence of five concentric land-use rings arranged around a common center
Theoretical model (no city is laid out in perfect rings)
Entrepôt
Is a port, city or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored and/or traded, typically to be exported again
In the days of wind-powered sailing, such centers had a critical role
In modern times customs areas have largely made such entrepôts obsolete, but the term is still used to refer to duty-free ports with a high volume of re-export trade
Megalopolis
urbanized areas of two or more cities that merge together; usually through suburban growth and expansion
Hamlet
smaller settlement, very few residence (usually under 100) & services
Village
settlements that are larger than hamlets but less complex than towns
Town
clustered settlement with a CBD but is smaller and less functionally complex than a city
City
conglomeration of people and buildings clustered together to serve as a center of politics, culture and economics = legally incorporated into an independent self-governing unit
Megacity
a metropolitan area with more than 10 million people
Metacity
a metropolitan area with more than 20 million people
Megalopolis
urbanized areas of two or more cities that merge together; usually through suburban growth and expansion
World City
a metropolitan area as a global center for finance, trade and commerce
What does ranking of world cities include
Economic, Political, Cultural, and Infrastructure factors
Economic factors
# of multinational corporation headquarters, law firms & financial institutions that influence global economy
Political factors
hosting headquarters of international organization and capitals of countries that are key players in international affairs; meeting point for international representatives like diplomats
Cultural factors
location of renowned cultural institutions, influential media outlets, educational institutions, largest museums, theaters, etc.
Infrastructure factors
major international airports, well renowned medical facilities, & advanced communication systems
Rank Size Rule
Statistical relationship between the largest city and the next largest city based on population
Example of Rank Size Rule
Leading largest city would be twice the size of the next largest city, then three times the city after that, etc.
Primate city
Lead city in terms of size (larger in size compared to the next largest city) & influence within a country
Characteristics of a Primate City
Usually receives a large majority of the country’s economic development and investment
Most expressive of the national culture and usually but not always the capital city
Why is Bangkok a primate city
Developing through industry & more services provided leading to an improvement in the standard of living for residents, however the rest of the country is mostly rural with few services available
Gravity model
Predicts the degree of interaction and probability of mobility between two places
As distance increased interaction decreases
Ex. High interaction between New York City and New Jersey as many use public transportation to commute between the two for work/other services
Some geographers argue it is less relevant as new technology allows worldwide connectivity
Consumer behavior reflects what two patterns according to the Gravity Model
1. Greater number of people living in a particular place, the greater number of potential customers for a service
2. The farther people are from a particular service, the less likely they are to use it
Central Place Theory
Explains the distribution of goods and services across a region
Distribution of cities & services is based on size
Helps explain threshold & range = what services can that area hold? How far are you willing to drive?
Won’t drive miles for a loaf of bread when I have a local grocery store (low range), however might drive farther for a specialty item like a sporting event (high range)
Hexagon shape prevents gaps
John Borchert Four Epoch of Transportation
Recognized four epochs in the evolution of the American metropolis based on the impact of transportation & communication:
1) Sail-Wagon Epoch (1790-1830) – associated with low technology
2) Iron Horse Epoch (1830-70); steam-powered locomotive & spreading rails
3) Steel-Rail Epoch (1870-1920); full impact of Ind. Rev. (steel), hinterlands expand
4) Auto-Air-Amenity Epoch (1920-70); gas-powered internal combustion engine
5) High Technology Epoch or Telecommunications Epoch (1970-?)
-#5 was added to his original four
Urban Sprawl
Rapid expansion of development over the landscape; unrestricted growth of housing, development, roads, etc.
Why is urban sprawl happening
Developers look for cheaper land further out from the cit
Land for the construction of new housing is more restricted in European urban areas than the USA (Ex. more historic buildings that cannot be torn down)
Roads and utilities must be extended to connect isolated new development
Edge city
Located on outskirts of large cities, typically near major road systems
Term introduced by U.S. journalist Joel Garreau to describe the shifting focus of urbanization in U.S. from CBDs towards new locations of economic activity at urban edge
How are edge cities characterized
Extensive amounts of offices/retail spaces - remember land is cheaper the further you move from the city ceenter (Bid-Rent Theory)
Office Park: property designed and developed specifically to attract corporate offices and provide them with all facilities required to carry out business
Contain low density office parks, big-box retail, strip mall type developments, more open air paking and housing is usually in sub-divisions
Examples of edge cties
Irvine, CA (outskirts of Los Angeles), Tyson Corner, VA (outskirts of Washington D.C.)
Boomburb
Rapidly growing (double-digit growth) suburban cities that emerged in the last 25-30 years
Characteristics of a boomburb
A population greater than 100,000
Cannot be the largest city in their metropolitan area
Developed along interstate beltways around large U.S. metropolitan areas
Examples of a boomburb
Henderson (NV), Irvine (CA), Escondido (CA), Glendale (AZ), etc.
Even as the grow, they still maintain a suburban character – do not have the feel, density, or scale of traditional cities. They do contain housing, retail, office parks, entertainment, etc.
Some have become “bustburbs” due to economic challenges in the high tech industry (i.e. Sunnyvale and Daly City)
Urbanization
The process in which large numbers of people become permanently concentrated in areas, forming cities
Suburbs
An outlying, functionally uniform part of an urban area and is often (but not always) adjacent to the central city
Detached homes, office parks, shopping malls, less crimes, and more open space than in cities
Urban Banana
Early Eurasian urban areas extended in a crescent-shaped zone across Eurasia from England in the west to Japan in the east
Ex. Was extended along early major trade routes; if you add Eastern Coast of U.S. it is sometimes called the “urban snake”
Site
Physical characteristics of a place; its absolute location
Ex. Natural resources, climate, water sources, land forms, vegetation, etc.
Ex. Is the city located along a natural harbor? Is there a source of fresh water from a local river? Etc.
Ex. New York City: located at the mouth of the Hudson River, natural harbor, water source from rivers and creeks
Situation
A places relationship with other locations; its relative location
Ex. Connection between sites = trade, accessibility, etc.
Ex. An island portion of a country can be situated far from the economic mainland where manufacturing occurs, etc.
Ex. Singapore: Maritime Trade = developed along trade routes (one of the busiest ports in the world), member of ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
Forward Thrust Capitals
Modern, planned cities & administrative capitals)
Ex. Brasilia (Brazil), Islamabad (Pakistan), Canberra (Australia), etc.