MCAT PSYCHOLOGY AND SOCIOLOGY
1/853
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
854 Terms
Social stratification
Social stratification refers to a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy. In the United States, it is perfectly clear that some groups have greater status, power, and wealth than other groups. These differences are what led to social stratification
Class consciousness
awareness of one's place in a system of social classes, especially (in Marxist terms) as it relates to the class struggle.
Instrumental support
instrumental support refers to the various types of tangible help that others may provide (e.g., help with childcare/housekeeping, provision of transportation or money).
Symbolic interactionism
Symbolic meaning and interpretation allow for sustained interaction
Antecedent predisposition
An antecedent is a stimulus that cues an organism to perform a learned behavior. When an organism perceives an antecedent stimulus, it behaves in a way that maximizes reinforcing consequences and minimizes punishing consequences.
Antecedent stimuli that have been paired with reinforcing consequences activate centers of the brain involved in motivation,while antecedents that have been paired with punishing consequences activate brain centers involved in fear
Lazarus theory of emotion
Interpretation happens before arousal or emotion, and this interpretation can cause emotion. Since there is no evidence that any of the subjects experienced a physiological response to any of the stories, the Lazarus theory is the correct response.
Fixed ratio vs variable ratio
Fixed ratio is based on a set number of responses, intervals are based on timing
Extinction burst
When an animal no longer receives regular reinforcement, its original behavior will sometimes spike (meaning increase dramatically) - this is known as an extinction burst.
Central executive
Supervises cognitive process of memory
Articulatory rehearsal component
The Articulatory Rehearsal Component had minimal effect on the test since there was not enough time for rehearsal before the subject was required to repeat the digit string.
Phonological Store
The Phonological Store is being tested. It is believed that the phonological store capacity is around 7
Type I Error
Incorrect rejection of the null hypothesis (false positive)
Most knoweledgeable other
it refers to someone who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept (Vygotsky theory)
Door in the face phenomenon
a compliance method commonly studied in social psychology. The persuader attempts to convince the respondent to comply by making a large request that the respondent will most likely turn down, much like a metaphorical slamming of a door in the persuader's face.
Phonological loop, central executive, visuospatial sketchpad
Model of working memory (Baddeley)
The central executive is a flexible system responsible for the control and regulation of cognitive processes. It has the following functions:
binding information from a number of sources into coherent episodes
coordination of the slave systems
shifting between tasks or retrieval strategies
selective attention and inhibition
The phonological loop (or "articulatory loop") as a whole deals with sound or phonological information. It consists of two parts: a short-term phonological store with auditory memory traces that are subject to rapid decay and an articulatory rehearsal component (sometimes called the articulatory loop) that can revive the memory traces.
The visuo-spatial sketchpad is this store that holds visual information for manipulation
Procedural bias
When researchers put some pressure (such as money reward) on participants.
Overgeneralization
Overgeneralization occurs when the individual comes to a conclusion based on one episode or bit of evidence
Avoidant personality disorder
Patients with avoidant personality disorder, like patients with schizoid personality disorder are also socially withdrawn. However, patients with avoidant personality disorder are withdrawn due to hypersensitivity to rejection rather than from indifference
Schizoid personality disorder
indifferent, aloof, withdrawn, and often preoccupied with fantasy and/or excessive daydreaming
Antisocial personality disorder
Patients with antisocial personality disorder have a deceitful attitude and show no remorse when abusing others
Gender differentiation
"Gender differentiation" is a social construct, the meaning of which includes social differences, value/attitude differences, and cultural differences. Biological differences are a part of sex differentiation, not gender differentiation
crit·i·cal the·o·ry
a philosophical approach to culture, and especially to literature, that seeks to confront the social, historical, and ideological forces and structures that produce and constrain it.
Synesthesia
s a neurological phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to automatic, involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. In one common form of synesthesia, known as grapheme-color synesthesia or color-graphemic synesthesia, letters or numbers are perceived as inherently colored.
Gender schema
Gender schema refers to how people become "gendered", and how those stereotypes/whatever get perpetuated from generation to generation.
Gender script
Gender script refers usually to interactions between people, and how we "expect" people to act based on their "script" (a preset list of conventions that we ascribe to that gender).
Gender Schema Theory: Parents encouraging their son to play with action figures and wear blue t-shirts, and avoid wearing dresses or playing with barbie dolls.
Gender Script: Think "chivalry". Man helping a woman carry a heavy box, holding door open for her.
Place theory (hearing)
Place theory is a theory of hearing which states that our perception of sound depends on where each component frequency produces vibrations along the basilar membrane. By this theory, the pitch of a musical tone is determined by the places where the membrane vibrates, based on frequencies corresponding to the tonotopic organization of the primary auditory neurons. High frequency sounds selectively vibrate the basilar membrane of the inner ear near the entrance port (the oval window). Lower frequencies travel further along the membrane before causing appreciable excitation of the membrane.
Self handicapping
Self-handicapping is a cognitive strategy by which people avoid effort in the hopes of keeping potential failure from hurting self-esteem.
Operationalization
In research design, especially in psychology, social sciences, life sciences, and physics, operationalization is a process of defining the measurement of a phenomenon that is not directly measurable, though its existence is indicated by other phenomena
Perceived behaviour control
restraint/control over one's actions, related to how difficult or easy we believe a certain task to be
Stroop effect
the Stroop effect is a demonstration of interference in the reaction time of a task. When the name of a color (e.g., "blue", "green", or "red") is printed in a color that is not denoted by the name (e.g., the word "red" printed in blue ink instead of red ink), naming the color of the word takes longer and is more prone to errors than when the color of the ink matches the name of the color.
parallel play
Parallel play is a form of play in which children play adjacent to each other, but do not try to influence one another's behavior. Children usually play alone during parallel play but are interested in what other children are doing. This usually occurs after the first birthday.
Internal validity
In scientific research, internal validity is the extent to which a causal conclusion based on a study is warranted, which is determined by the degree to which a study minimizes systematic error (or 'bias'). It contrasts with external validity, the degree to which it is warranted to generalize results to other contexts.
External validity
External validity is the validity of generalized (causal) inferences in scientific research, usually based on experiments as experimental validity.In other words, it is the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other situations and to other people. Mathematical analysis of external validity concerns a determination of whether generalization across heterogeneous populations is feasible, and devising statistical and computational methods that produce valid generalizations.
Ecological validity
In research, the ecological validity of a study means that the methods, materials and setting of the study must approximate the real-world that is being examined.
Me - Herbert Mead
Me - what society thinks you should do
I
I - what you think is best for you
Deterministic theory of development
Those that focus on childhood influence (Freud and Skinner)
Emotions and hemispheres
Positive emotion - Left
Negative - Right
Projection
Projection is more of a defense mechanism to protect your ego in a situation like really hating some guy. You justify your unpleasant feelings by rationalizing that it's actually him that hates you, so it's natural to reciprocate. Or like the computer example, your ego fears you may actually be incompetent, so you project those feelings onto your computer and blame it for being stupid and not working.
Displacement
Kicking dog in anger due to something else
Halo efect
Jun 14, 2016 - The halo effect is a type of cognitive bias in which our overall impression of a person influences how we feel and think about his or her character. Essentially, your overall impression of a person ("He is nice!") impacts your evaluations of that person's specific traits ("He is also smart!").
The halo effect is a cognitive bias in which an observer's overall impression of a person, company, brand, or product influences the observer's feelings and thoughts about that entity's character or properties. It was named by psychologist Edward Thorndike in reference to a person being perceived as having a halo.
Cost signaling theory
Showing off of resources to appear as a better mate
Interposition
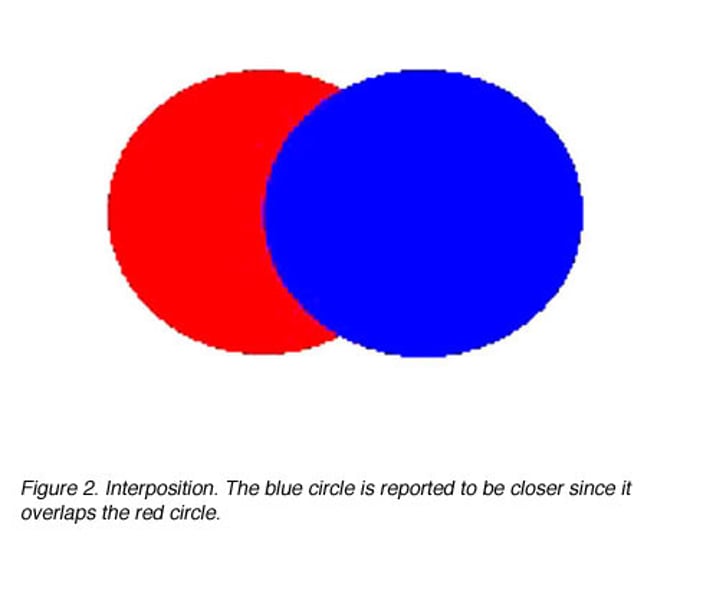
Constancy
Somatosensation
Vestibular sense
for sense of balance and spatial orientation, from inner ear
Semicircular canals
3 (posterior, lateral, anterior) at right angles to each other located in the inner ear, lines up to 3 axes. Endolymph movement sensed by canals to get strength of rotation
Otolithic organs
Utricle and siccule contain crystal movement to pull hair cells to convey spatial orientation to brain
Diziness / vertigo
Caused when endolymph does not stop moving even after one has stopped moving. Also, astronauts have no gravity causing utricle and siccule crystals to float, causing confusion about which way is up or down. Also affects scuba divers.
Signal detection theory
Decision making under situations of uncertainty, at what point are we able to detect a signal
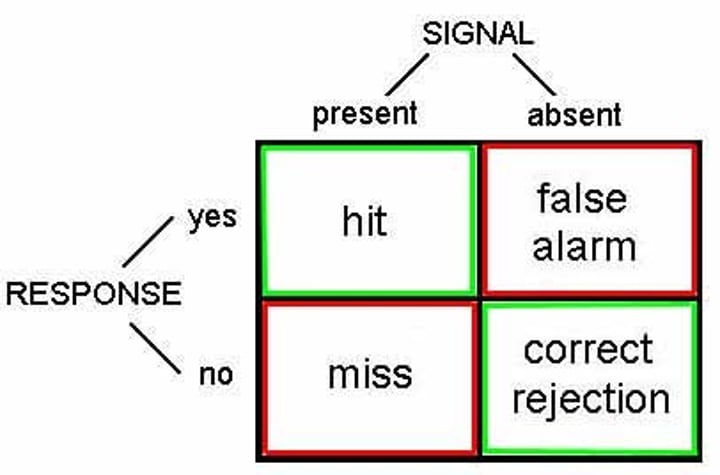
Signal detection theory
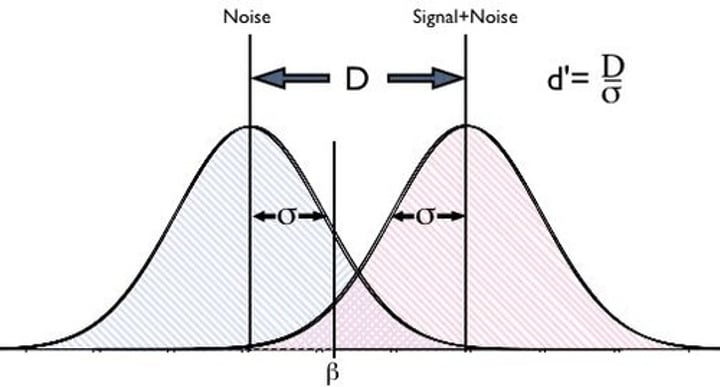
d' / c
strength of signal / strategy.
types of strategy
conservative (always say no), liberal (always say yes - can result in false alarms)
Noise distribution and signal distribution
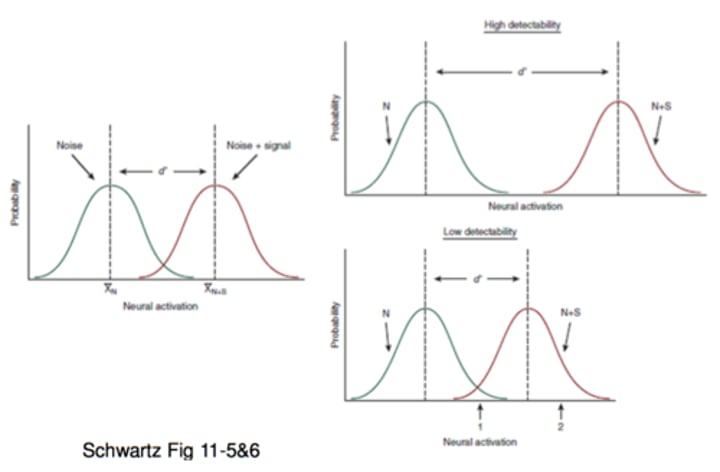
Gestalt principles
Gestalt principles explain why we perceive things the way we do. Similarity: items that are similar are grouped together. Pragnanz: reality is reduced to simplest form possible (Olympic ring example). Proxmity: objects that are close to one another are grouped together. Continuity: lines are seen as falling the smoothest path. Closure.
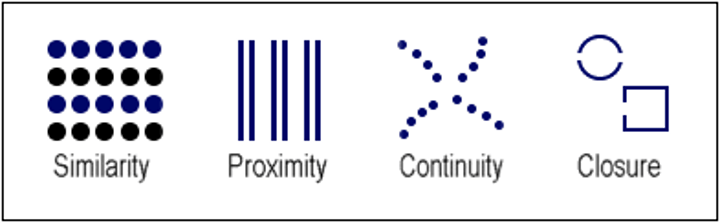
Structure of the eye
iris controls pupil, ciliary muscle controls lens shape
Fovea
filled with cones, lets us see with high levels of detail. the retina is red and causes red - eye effect in photos. red eye reduction fires two flashes, the first flash causes constriction of the pupil causing less reflection off of the retina
ROYGBIV
Violet = 400 nm, Red = 700 nm
Retinal cells (photoreceptors)
Rods and cones
Rods
located in the retina, take light and convert into neural impulse. 120 million rods, good for night vision, sensitive to light, found mostly in periphery of eyes // very sensitive to light, have a very slow recovery time, magnocellular pathway (motion)
Cones
6-7 million cones / retina, responsible for color vision. 3 types: Red, green, blue. they are concentrated in the fovea (allows us to see fine details), have a fast recovery time, parvocellular pathway (form and color)
Phototransduction cascade
What occurs when light hits the retina. Steps: light turns a rod off (rod is normally on), causing bipolar cell to turn on, which turns on a retinal ganglion cell, which is connected to the optic nerve.
Phototransduction cascade in rods
light turns a rod off (rod is normally on), causing bipolar cell to turn on, which turns on a retinal ganglion cell, which is connected to the optic nerve. In rods, there are stacks of disks with proteins, including rhodopsin (photopsin in cones). In rhodopsin, there is cis-retinal. When light strikes cis-retinal, it becomes trans-retinal. This causes the rod to turn off and carry out the above cascade via transducin. Transducin breaks away from rhodopsin when trans retinal forms, and bods to phosphodiesterase. This converts cyclic GMP to GMP. This prevents sodium channels from being open and causing hyperpolarization of the cell (sodium leaves cell and does not enter causing increased negative potential)
Visual field processing
temporal side does not cross optic chiasm. all information from right visual field goes to left side of brain, all visual information from left visual field goes to right side of brain.
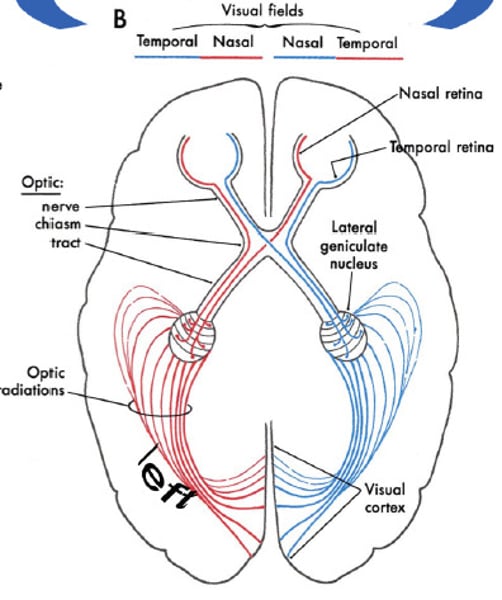
If you're split-brained, you won't recognize written words in your left visual field.
This is because language information is processed in the left brain (Wernicke and Broca's areas); in split brained patients the corpus callosum is severed causing information unable to cross over from right side to left side.
Trichromatic theory of color vision
3 types of cones (R, G, B) exist and allow us to see color by activating a specific type of cone)
Parvocellular pathway
used for spatial resolution (cones)
Magnocellular pathway
used for temporal resolution (rods)
Parallel processing
ability to see the color, form, and motion of an object at the same time using both the parvo and magno pathways
Audition
How a hair cell responds to a pressurized sound wave
Place Theory
Lower frequencies travel further in the ear (cochlea). In base of cochlea, higher frequencies cause activation while in apex of cochlea lower frequencies cause activation
Ear anatomy
auditory canal - eardrum - MIS (ear bones) - oval window - fluid in cochlea is pushed - circular window - auditory nerve.
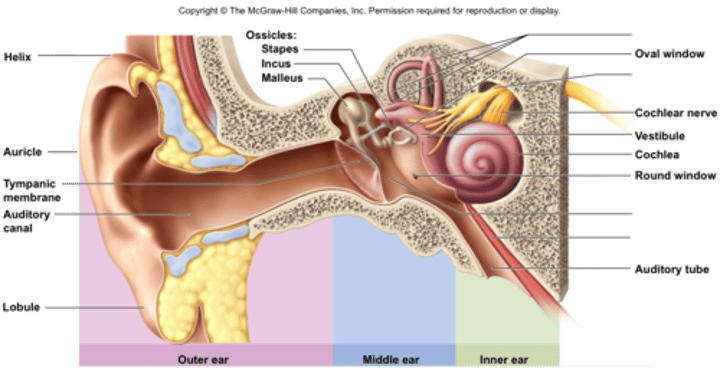
Organ of Corti
located in cochlea, contains the basilar membrane and tectorial brain, prevents fluid from reaching elliptical oval when flowing back from the cochlea. Also contains hair cells which vibrate. vibration results to opening of potassium gates causing nerve impulse to brain
Parts of ear
outer: auditory canal + eardrum, middle: bones, oval and circular window, inner: cochlea etc
somatosensory homonculus
map of body in the brain located in sensory strip (FMSPOT), each map of the homonculus corresponds to a part of the body
propioception
position and balance, based on contraction of muscles throughout the body, cognitive
kinesthesia
movement of body, behavioral awareness of body movement
nociception
sensation of pain
thermoception
sensation of temperature, TrpV1 receptor, also sensitive to pain, heat causes conformational change of the protein. pain (such as prick) causes cells to break up and binding of ligands to TrpV1 receptor, also causing nerve impulse. 3 types of fibers exist connected to TrpV1: fast, medium, slow.
3 types of fibers causing thermoception and nociception
Fast: myelinated, large diameter (a-Beta fibers), convey information quickly. Medium: a-Delta fibers, convey information less fast, Slow: slow diameter, c fibers unmyelinated.
Hot stove: fast fiber causes movement of hand, then a delta fiber causes pain, then c causes lingering pain. capcacin also binds to TrpV1 receptors.
pheromones
specialized olfactory cues, induce a response in other animals to trigger an innate response. important in mating, fighting of animals, particularly insects. They are not perceived consciously, information travels to the amygdala in the temporal lobe to exert a subconscious influence on behaviors, such as aggression and sexual behavior.
olfactory epithelium
region of head dealing with smell, separated from brain with cribiform plate. extension from brain is olfactory bulb (cranial nerve), sends projection of nerves into olfalctory epithelium.
glomerulus
designation point in the olfactory buble corresponding to a particular smell
mitral/tufted cell
connected to a glomerulus, which connects to the brain
GPCRs
located in the olfactory epithelium. when GPCR activated, G protein hydrolyzed leading to cascade and ion channel opening causing action potential. also found in taste buds
5 tastes
bitter, salty, sweet, sour, umami (glutamate)
taste buds
3 types, all taste buds can recognize any of the 5 tastes.
labeled lines model
each cell from taste bud has its own neuron and mapping to gustatory cortex
G protein coupled receptors
when ligand binds, G protein dissociates from receptor and causes opening of ion channels, leading to depolarization and ion channel. only for sweet, umami, bitter. sour/salty have conformational change of ion channels directly.
olfactory pathway
bypasses the thalamus, olfactory bulb projects directly to the olfactory cortex in the temporal lobe and amygdala / hippocampus.
temporal lobe structures
contains the hippocampus and amygdala, Wernicke's area (left side). Limbic system concerned with memory and emotion
gustatory cortex
located in frontal lobe
Consciousness
awareness of our selves and our environment, can be affected by drugs, etc. Ranges from alertness to sleep.
Types of consciousness
Alertness / Daydreaming / Meditation / Drowsiness / Deep Meditation / Sleep
EEG
measures brain waves
alpha waves
8-13hz, in daydreaming / drowsiness
beta waves
12-30hz, waking consciousness and concentration
delta waves
.5-2Hz (stage 3)
theta waves
4-7 waves light sleep
Stages of sleep
First 3 are NREM, last is REM