alcohols
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
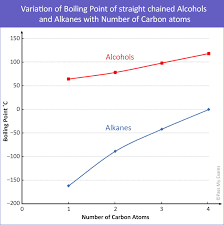
trend in boiling point
as chain length increases, number of e- per molecule increases, so induced dipole forces get stronger, boiling point increases
so volatility and flammability decrease
alcohols less volatile than alkanes due to H bonds
viscosity
trend in difference between boiling point of alkane and alcohol
-decreases
-only one hydrogen bond per alcohol molecule
-molecule becomes more dominated by non-polar hydrocarbon chain
-molecule becomes more bulky, harder to form hydrogen bonds
-number of e- increases so induced dipole forces get stronger so boiling point becomes more dependent on ID forces
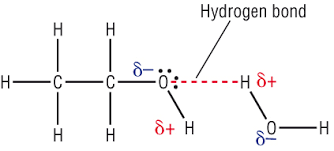
what happens when alcohol and water are mixed
-hydrogen bonds are made between water and alcohol molecules
-energy released when new H bonds from compensate for energy required to break original H bonds
trend in alcohol solubility in water
-decreases
-molecule more dominated by large hydrocarbon chain, which obstructs formation of H bonds with water
-chain interacts more with other chains by ID forces
-energy released when H2O and alcohol interact isn’t sufficient to compensate for energy required to overcome intermolecular forces
oxidation of ethanol (primary alcohol)
-use acidified potassium dichromate (H+/ K2Cl2O7)
-aldehyde and water (1st stage) (immediately distil to keep aldehyde as it has a low boiling point due to no hydrogen bonding)
-potassium dichromate turns orange to green
-carboyl (C=O)
-carboxylic acid (2nd stage), for complete oxidation, reflux
oxidation of propan-2-ol (secondary alcohol)
-ketone (propanone) + water
-use acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cl2O7) which turns orange to green, and reflux
-ketone has no hydrogens attached so 2nd stage of oxidation isn’t possible, and tertiary alcohols can’t be oxidised
-e.g. CH3CHOHCH3 + O => CH3COCH3
-carbonyl group (C=O)
production of ethanol
-ethene + water = (phosphoric acid catalyst) = ethanol
-100% atom economy
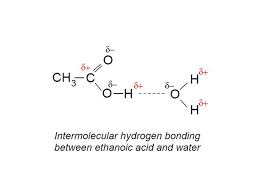
trend in solubility of carboxylic acids
-when molecule gets to a certain size, harder for water molecule to form hydrogen bonds with carboxylic acid molecules
-they’re weak acids as their molecules only partially dissociate into ions in aq solutions
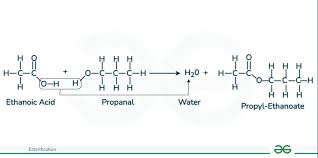
esterification: ethanoic acid + pentan-1-ol
-alcohol + carboxylic acid = (conc acid catalyst + heat) = ester + water
-OH from carboxylic acid and H from alcohol make water
-pentyl ethanoate
how does branching affect solubility of an alcohol
-more branching increases solubility
-weaker induced dipole forces to overcome, less energy required to overcome them
formation of induced dipole forces
-random movement of electrons in molecule results in instantaneous dipole, which induces a dipole on adjacent molecule
2 molecules attract each other
reaction of alcohol with halogenating agent to make haloalkanes
-nucleophilic substitution
-produces haloalkane
-OH replaced by halogen
-condensation
-conc. sulphuric acid catalyst
dehydration of alcohol to make alkene
-elimination reaction
-alcohol heated with conc. phosphoric acid
reaction/hydration of alkene to make alcohol
-steam
conc. phosphoric acid catalyst (H+ act as catalyst)
-e.g. ethene + steam = ethanol
reaction of haloaklane to make alcohol
-hydrolysis
-NaOH
-nucleophilic substitution
-:OH- is nucleophile