Comprehensive Software Design and Python OOP Principles Guide
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is software design?
The process of defining the architecture, components, interfaces, and data for a software system to satisfy specified requirements.
What is the primary goal of software design?
To ensure that the software is functional, efficient, maintainable, scalable, and flexible for future changes.
What are the key aspects of software design?
High-Level Design, Low-Level Design, Interface Design, Data Design, Design Patterns, and Non-Functional Requirements.
What does High-Level Design refer to?
The overall structure of the system, including how different modules or components interact.

What is Low-Level Design?
It involves defining the internal workings of individual components or modules.
What is the focus of Interface Design?
Defining how users or other systems interact with the software, including UI and API design.
What does Data Design encompass?
Defining how data will be stored, accessed, and manipulated, including database schema design.
What are Design Patterns?
Reusable solutions to common design problems in software development.
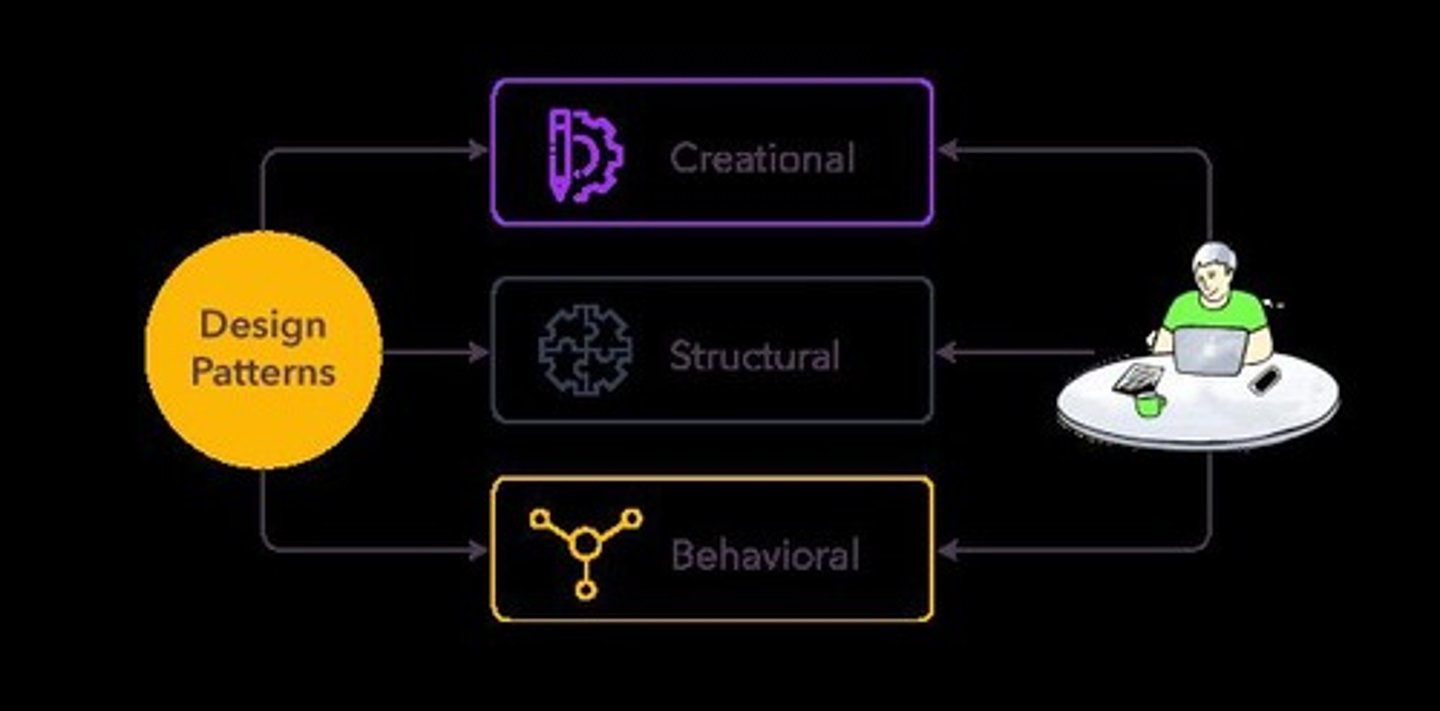
Why is software design important?
It improves maintainability, scalability, quality, performance, collaboration, security, reduces complexity, and enhances user experience.
What is Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)?
A programming paradigm that uses objects and classes to represent real-world entities and their behavior.
What is a class in OOP?
A user-defined prototype for an object that defines a set of attributes and methods.
What is an object in OOP?
An instance of a class.
What is encapsulation in OOP?
The practice of hiding implementation details and exposing only essential features of an object.
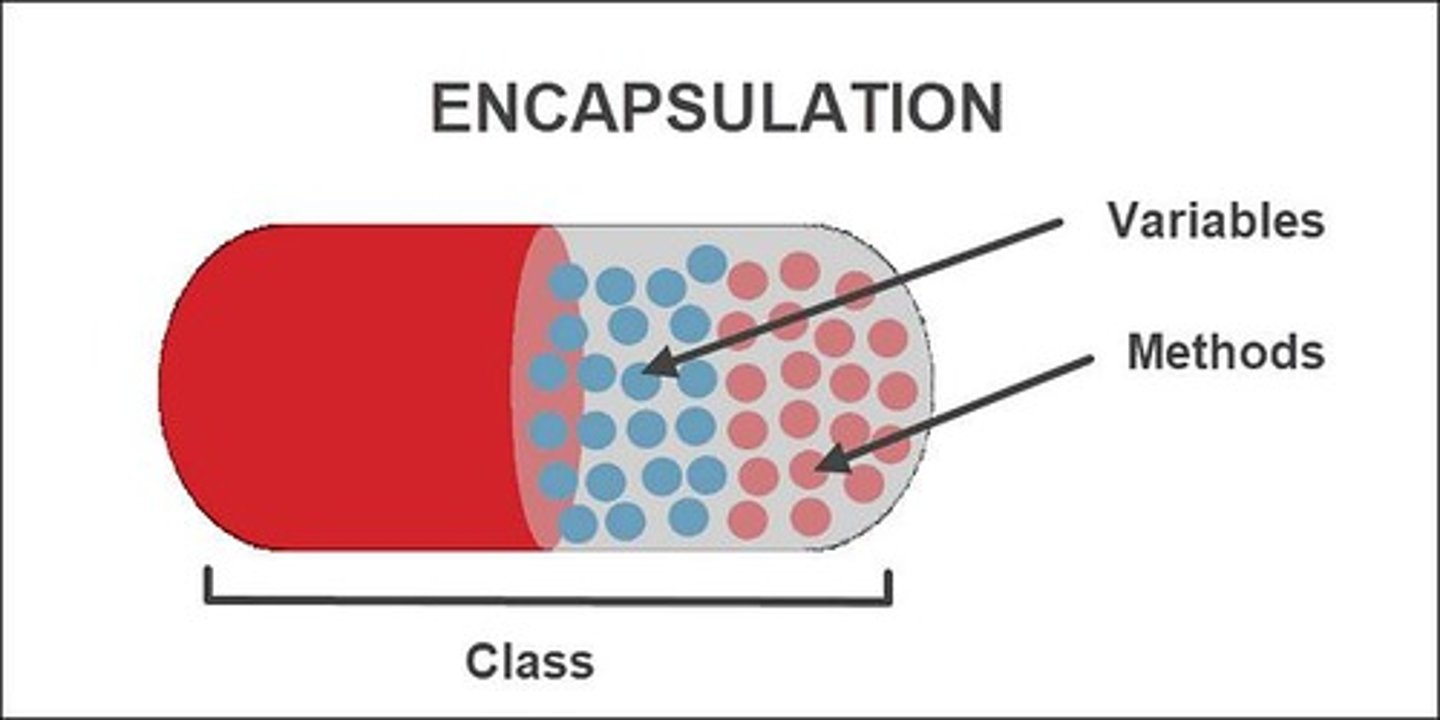
How is encapsulation achieved in Python?
Through the use of access modifiers: public, protected, and private.
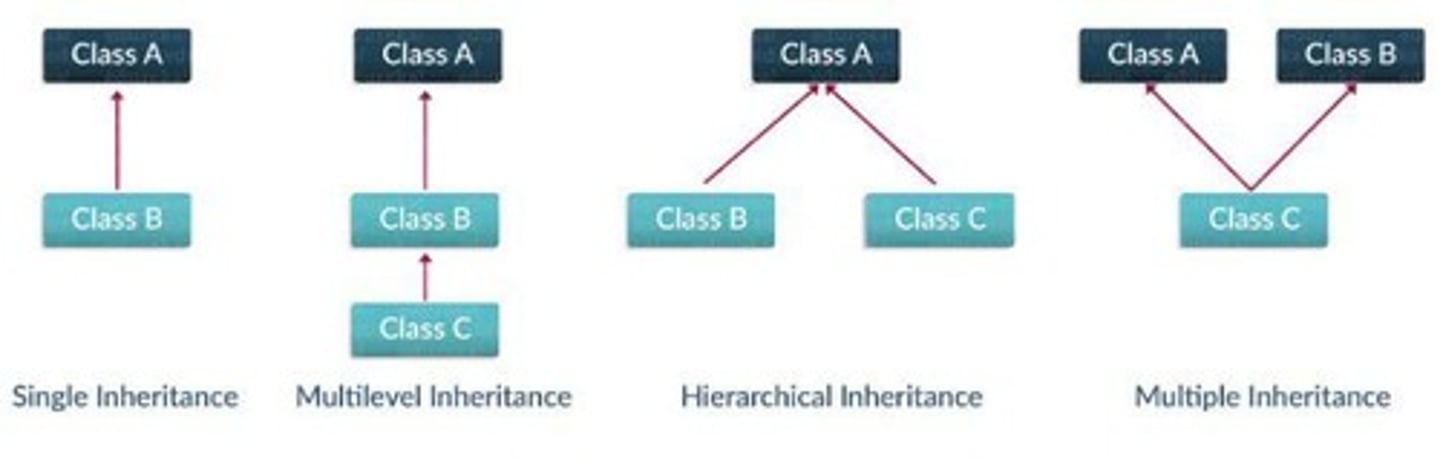
What is inheritance in OOP?
A mechanism where a child class acquires properties and methods from a parent class.
What is polymorphism in OOP?
The ability for methods to have the same name but behave differently based on the object's context.
What is compile-time polymorphism?
Polymorphism determined during compilation, allowing methods or operators to behave differently based on input parameters.
What is run-time polymorphism?
Polymorphism determined during execution, where a subclass provides a specific implementation for a method defined in its parent class.
What is abstraction in OOP?
The practice of hiding internal implementation details while exposing necessary functionality.
What are the types of abstraction?
Partial Abstraction (contains both abstract and concrete methods) and Full Abstraction (contains only abstract methods).
Give an example of how OOP can be applied in a cafe scenario.
In the FAU Cafe, beverages are represented as objects with attributes like name, size, and price, and customers can order multiple beverages.
