Marketing Exam Ch12-16
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
promotion mix
(also called its marketing communications mix) consists of the specific blend of: advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, and public relations
advertising
any paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor (digital, broadcasts, print, online, mobile, outdoor)
sales promotion
short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of product or service (discount, coupons, displays, demonstrations); marketer-controlled communication to stimulate immediate audience response by enhancing the value of an offering for a limited time
personal selling
personal customer interactions by the firm’s salesforce to engage customers, make sales, and build customer relationships (sales presentations, trade shows, incentive programs); direct interaction between a company representative and a customer
public relations (PR)
activities designed to engage the company’s various publics and build good relations with them (stories, sponsorship, events, and webpages); communication activities that create or maintain a positive image of a firm and its products
content marketing
creating, inspiring, and sharing brand messages and conversations with and among consumers across a fluid mix of paid, owed, earned, and shared channels
integrated marketing communications (IMC)
carefully integrating and coordinating the company’s many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its products; the process that marketers use to plan, develop, execute, and evaluate coordinated, measurable, persuasive brand communication programs over time to targeted audiences
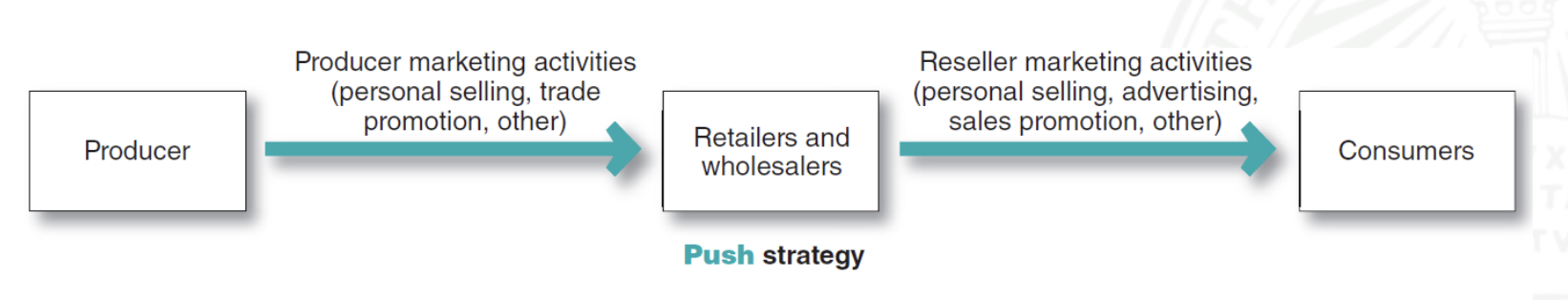
push strategy
the company “pushes” the product to resellers, which in turn “push” it to consumers
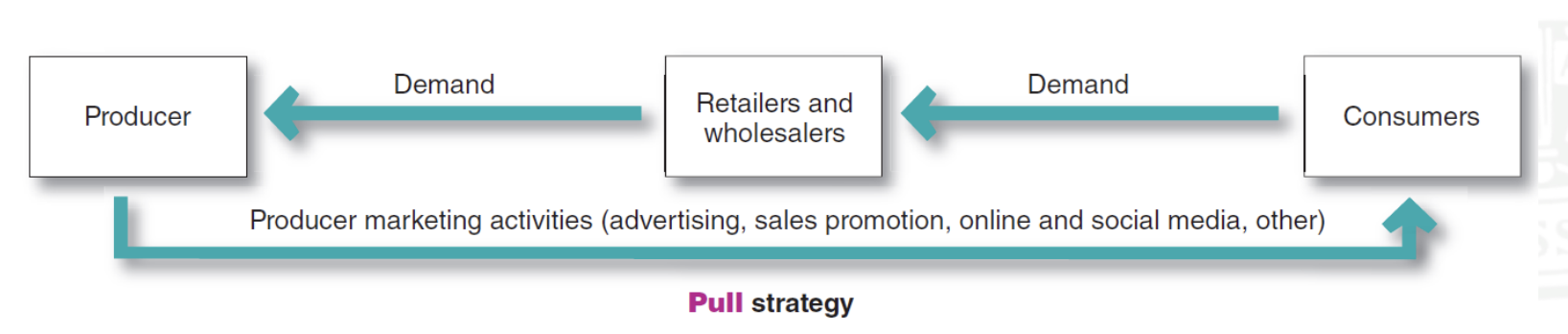
pull strategy
the company promoted directly to final consumers, creating a demand vacuum that “pulls” the product through the channel
major advertising decisions
setting advertising objectives
setting the advertising budget
developing advertising strategy
evaluating advertising effectiveness
advertising objective
a specific communication task to be accomplished with a specific target audience during a specific period of time, can be classified by their primary purpose
informative advertising
used heavily when introducing a new product category, objective is to build primary demand
persuasive advertising
becomes more important as competition increases, objective is to build selective demand
comparative advertising
advertising strategy in which the company directly or indirectly compares its brand with one or more other brands
reminder advertising
important for mature products, it helps to maintain customer relationships and keep consumers thinking about the product
advertising budget
the dollars and other resources allocated to a product or a company advertising program
affordable method
setting the promotion budget at the level management thinks the company can afford
percentage-of-sales method
setting the promotion budget at a certain percentage of current or forecasted sales or as a percentage of the unit sales price
competitive-parity method
setting the promotion budget to match competitors’ outlays
objective-and-task method
developing the promotion budget by (1) defining specific promotion objectives, (2) determining the tasks needed to achieve these objectives, and (3) estimating the costs of performing these tasks → the sum of these costs is the proposed promotion budget
advertising strategy
the strategy by which the company accomplishes its advertising objectives; it consists of two major elements: (1) creating advertising messages and (2) selecting advertising media
native advertising
(also called sponsored content) advertising or other brand-produced online content that appears to be “native to” the web or social media site in which it is placed
creative concept
the compelling “big idea” that will bring an advertising message strategy to life in a distinctive and memorable way → should be meaningful, believable, and distinctive
types of advertising appeals
the approach, style, tone, words, and format used for executing an advertising message
unique selling proposition
comparative advertising
demonstration
slice of life: shows one or more “typical” people using the product in a normal way
lifestyle: shows how product fits in with a particular lifestyle
fantasy: creates a fantasy around the product or its use
mood or image: builds a mood or image around the product or service, such as beauty, love, intrigue, serenity, or pride
musical: employs music or dance to engage viewers with the brand
personality symbol: creates a character that represents the product (the character might be animated or real)
technical expertise: shows the company’s expertise in making the product
scientific evidence: presents survey or scientific evidence that the brand is better or better liked than one or more other brands
testimonial evidence or endorsement: features a highly believable or likable source endorsing the product
fear appeals
sex appeals
humorous appeals
slogans, jingles, and music
advertising media
the vehicles through which advertising messages are delivered to their intended audience
determining reach, frequency, impact, and engagement
choosing among major media types
selecting specific media vehicles
choosing media timing
return on advertising investment
the net return on advertising investment divided by the costs of the advertising investment
advertising agency
a marketing services firm that assists companies in planning, preparing, implementing, and evaluating all or portions of their advertising programs
functions of PR
press relations or press agency: creating and placing newsworthy information in the news media to attract attention to a person, product, or service
product and brand publicity: publicizing specific products and brands
public affairs: building and maintaining relationships with legislators and government officials to influence legislation and regulation
investor relations: maintaining relationships with shareholders and others in the financial community
development: working with donors or members of nonprofit organizations to gain financial or volunteer support
consumer-influence strategies
strategies for engaging consumers and influencing how they think, feel, and act toward a brand or market offering through the use of marketing communications
major promotion tools
advertising and sales promotion
personal selling and public relations
direct and digital marketing
sponsorship
a way of publicly associating a brand with an event or activity that the company supports financially
buzz
word-of-mouth communication that consumers view as authentic
buzz marketing
using high-profile entertainment or news that gets people to talk about the brand
viral marketing
creating entertainment or informative messages to be passed along; the digital version of word-of-mouth marketing: videos, ads, and other marketing content that are so engaging and infectious that consumers will seek them out and pass them along to friends
word-of-mouth (WOM) marketing
activities that give people a reason to talk about the product
guerrilla marketing
activities that “ambush” consumers with promotional content in places they are not expecting to encounter this kind of activity
experiential marketing
marketing activities that attempt to give customers an opportunity to actually interact with a brand
consumer-generated media
the online consumer-generated comments, opinions, and product-related stories available to other consumers through digital media
advertising campaign
a coordinated, comprehensive plan that carries out promotion objectives and results in a series of ads placed in media over a period of time
institutional advertising
enhances a company’s image rather than promotes a particular product
product advertising
touts the benefits of a specific good or service
retail and local advertising
encourages customers to shop at a specific store or use a local service
do-it-yourself advertising
“generation C” phenomenon: consumer-generated ad content on the web
media selection considerations
cost per contact: the cost of reaching one member of the target market
reach: the number of target consumers exposed to a commercial at least once during a time period
frequency: the number of times an individual is exposed to a message during a time period
audience selectivity: the ability of an advertising medium to reach a precisely defined market
salesperson
an individual who represents a company to customers by performing one or more of the following activities: prospecting, communicating, selling, servicing, information gathering, and relationship building
salesforce management
analyzing, planning, implementing, and controlling salesforce activities
major steps in salesforce management
designing salesforce strategy and structure
recruiting and selecting salespeople
training salespeople
compensating salespeople
supervising salespeople
evaluating salespeople
territorial salesforce structure
a salesforce organization that assigns each salesperson to an exclusive geographic territory in which that salesperson sells the company’s full line
product salesforce structure
a salesforce organization in which salespeople specialize in selling only a portion of the company’s products or lines
customer salesforce structure
a salesforce organization in which salespeople specialize in selling only to certain customers or industries
outside salesforce
salespeople who travel to call on customers in a field
inside salesforce
salespeople who conduct business from their offices via telephone, online, and social media interactions, or visits from prospective buyers
team selling
teams of people from different departments used to service large, complex accounts
sales quotas
a standard that states the amount a salesperson should sell and how sales should be divided among the company’s products
social selling
the use of digital platforms and sales tools to engage customers, build stronger customer relationships, and augment sales performance
selling process
the steps that salespeople follow when selling
prospecting and qualifying
preapproach
approach
presentation and demonstration
handling objections
closing
follow-up
prospecting
the sales step in which a salesperson or company identifies qualified potential customers
preapproach
the sales step in which a salesperson learns as much as possible about a prospective customer before making a sales call
approach
the sales step in which a salesperson meets the customer for the first time
presentation
the sales step in which a salesperson tells the “value story” to the buyer, showing how the company’s offer solves the customer’s problems
handling objections
the sales step in which a salesperson seeks out, clarifies, and overcomes any customer objections to buying
closing
the sales step in which a salesperson asks the customer for an order
follow-up
the sales step in which a salesperson follows up after the sale to ensure customer satisfaction and repeat business
consumer promotions
sales promotion tools used to boost short-term customer buying and engagement or enhance long-term customer relationships
event marketing
creating a brand-marketing event or serving as a sole or participating sponsor of events created by others
trade promotions
sales promotion tools used to persuade resellers to carry a brand, give it shelf space, and promote it in advertising
business promotions
sales promotion tools used to generate business leads, stimulate purchases, reward customers, and motivate salespeople
transactional selling (the hard sell)
high-pressure process that focuses on making an immediate sale with no concern for developing long-term customer relationship
relationship selling
process of building long-term customers by developing mutually satisfying, win-win relationships with customers
straight commission
earn a percentage of sales margin or selling price
commission with a draw
advance salary to be paid with future commissions
straight salary
base salary with bonuses based on making quotas
salesforce promotions
sales promotion tools used to get more salesforce support for current or new products and motivate salespeople to sign up new accounts
consumer promotion tools
samples: offers of trial amount of a product, most effective and expensive
coupons: certificates that save buyers money when they purchase specified products
rebates (cash refunds): price reduction occurs after the purchase, customer sends proof of purchase to the manufacturer which then refunds part of the purchase price by mail
price packs (cents-off deals): offer consumers savings off the regular price of a product
premiums: goods offered either free or at low cost as an incentive to buy a product
advertising specialties: useful articles imprinted with an advertiser’s name, logo, or message that are given as gifts to consumers
point-of-purchase promotions: displays and demonstrations that take place at the point of sale
contests, sweepstakes, and games: give consumers the chance to win something
event marketing (or event sponsorships): creating a brand-marketing event or serving as a sole or participating sponsor of events created by others
digital marketing
the use of technology-intensive platforms such as the internet, mobile networks and devices, and social media to engage directly with carefully targeted individual consumers, consumer communities, and businesses
digital-consumer personas
detailed, nuanced, tangible representations of prototypical consumers to be targeted by the digital marketing campaign
consumer omni-channel navigation behavior
the consumer’s use of multiple marketing channels, both digital and nondigital, across stages of the consumer buying decision process
online marketing
marketing via the internet using company websites, online ads and promotions, email, online video, and blogs
marketing websites
a website that engages consumers to move them closer to a direct purchase or other marketing outcome
branded community websites
a website that presents brand-related content that engages consumers and creates a customer community around a brand
online advertising
advertising that appears while consumers are navigating on other digital platforms, including display ads and search-related ads
online display ads
digital ads that appear anywhere on an internet or mobile user’s screen and are often related to the information being viewed
search-related ads
text- and image-based ads and links appear atop or alongside search engine results on sites such as Google
email marketing
sending highly-targeted, highly personalized, relationship-building marketing messages via email
spam
unsolicited, unwanted commercial email messages
blogs
online forums where people and companies post their thoughts and other content, usually related to narrowly defined topics
social media
independent and commercial online social networks where people congregate to socialize and share messages, opinions, pictures, videos, and other content
mobile marketing
marketing messages, promotions, and other content delivered to on-the-go consumers through their mobile devices
omni-channel marketing
creating a seamless cross-channel buying experience that integrates in-store, online, and mobile shopping
public policy issues in direct and digital marketing
irritation: loud, long, and insistent TV commercials, junk mail and spam
unfairness: taking unfair advantage of impulsive buyers
deception and fraud: investment scams or phony collections for charity, internet fraud, phishing, online and digital security, access by vulnerable or unauthorized groups
consumer privacy: fear of invasion of privacy, ready availability of information leaves consumers open to abuse
need for action
direct mail marketing
sending an offer, announcement, reminder, or other item directly to a person at a particular address
catalog marketing
print, video, or digital catalogs that are mailed to select customers, made available in stores, or presented online
global marketing
the full process of marketing products and services within and across multiple countries
economic communities
groups of nations organized to work toward shared global trade and other goals (like the EU)
exporting
entering foreign markets by selling goods produced in the company’s home country, often with little or no modification
joint venturing
entering foreign markets by joining with foreign companies to produce or market a product or service
licensing
entering foreign markets by developing an agreement with an entity in the foreign market to use the company’s brand, trademark, patent, trade secret, manufacturing process, or some other item of value in return for some payment
contract manufacturing
a joint venture in which a company contracts with manufacturers in a foreign market to produce its product or provide its service
management contracting
a joint venture in which the domestic company supplies the management know-how to a foreign company that supplies the capital; the domestic company exports management services rather than products
joint ownership
a cooperative venture in which a company creates a local business with investors in a foreign market who share ownership and control