Cellular Accumulations
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
what is excessive production
accumulates faster than can get rid of
what are the reasons production cannot be removed
problems metabolizing, packaging, and excreting
what organ is extremely important in lipid metabolism
liver
what are causes of hepatic lipidosis
increased mobilization of free fatty acids
abnormal hepatocellular metabolism of lipids
impaired release of lipoproteins
how can lipid accumulation be confirmed
histochemical stains Sudan Black or Oil-Red-O
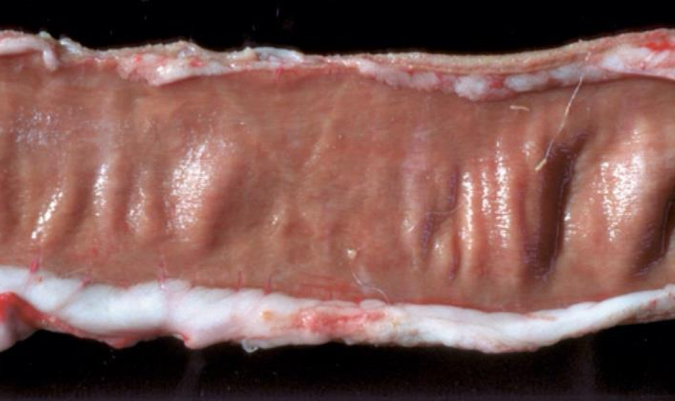
what does liver with lipid accumulation look like
swollen with rounded edges
yellow/ yellow-brown
greasy to touch
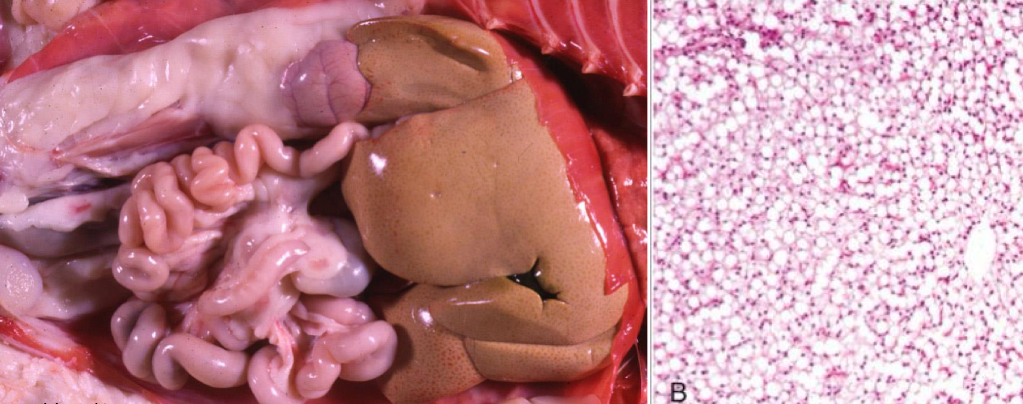
what is being shown in this liver **
lipid accumulation
where does glycogen accumulation occur
liver and skeletal muscle cells
what does liver with glycogen accumulation look like
enlarged with rounded edges
pale, light brown
mottled in appearance
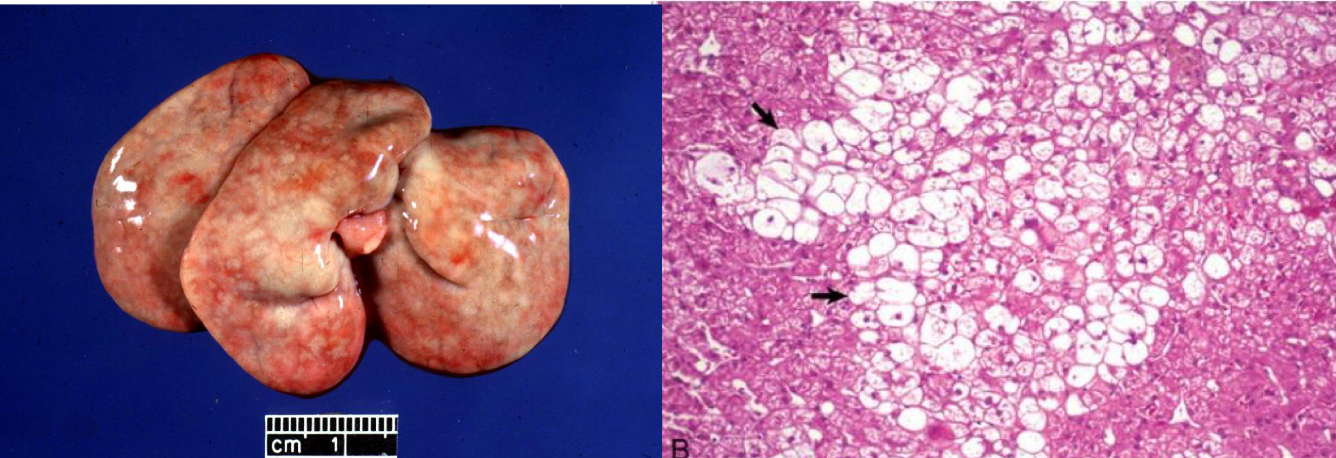
what is being shown in this liver **
glycogen accumulation
what will you see histologically with glycogen accumulation
swollen/ enlarged hepatocytes
what special stain can be used to identify glycogen accumulation
PAS with diastase
what will you see histologically with lipid accumulation
colorless punctate cytoplasmic vacuoles
what can cause protein accumulation
increased resorption, storage, or production
what color do proteins normally stain
pink to orange
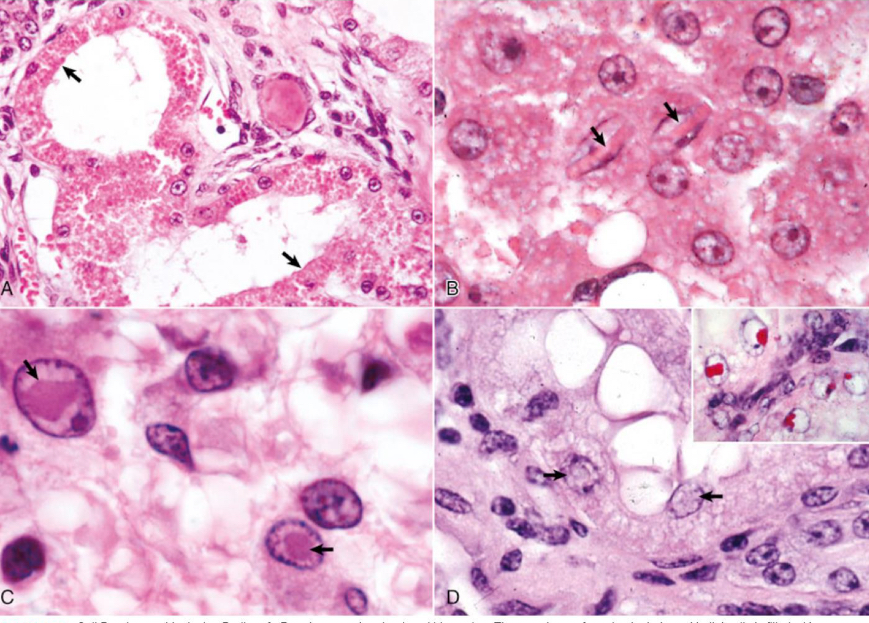
what is being shown in image A**
protein accumulation
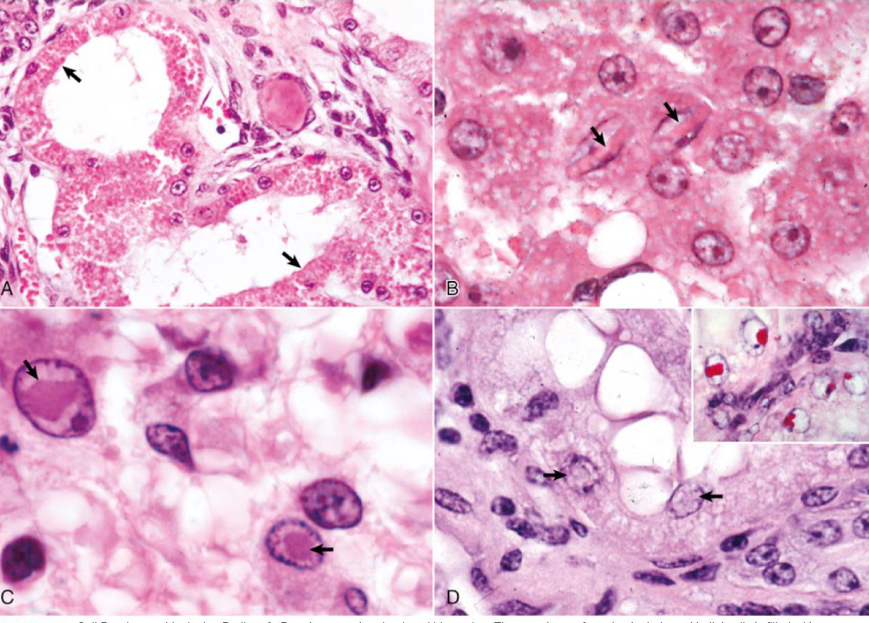
what is being shown in image B**
crystalline protein
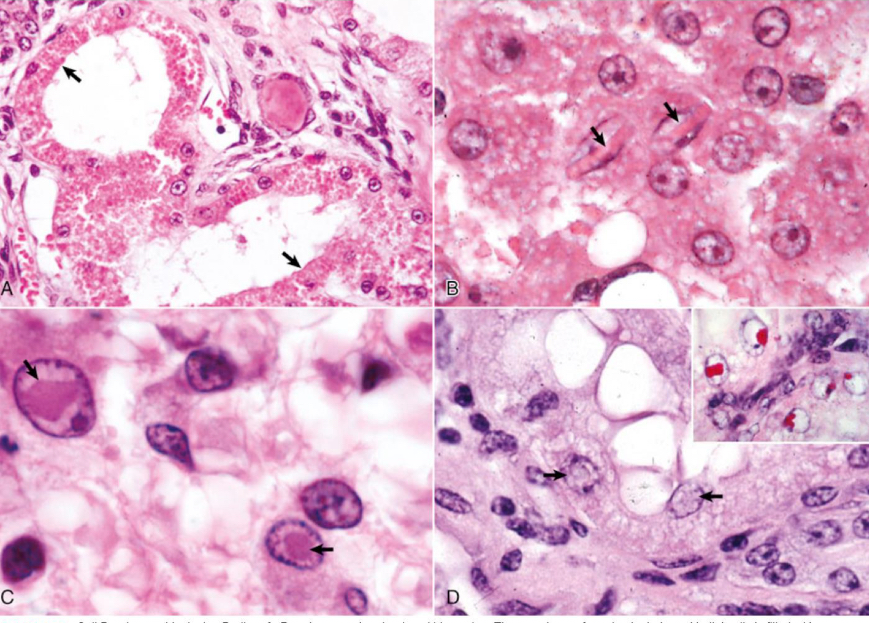
what is being shown in image C**
viral inclusions
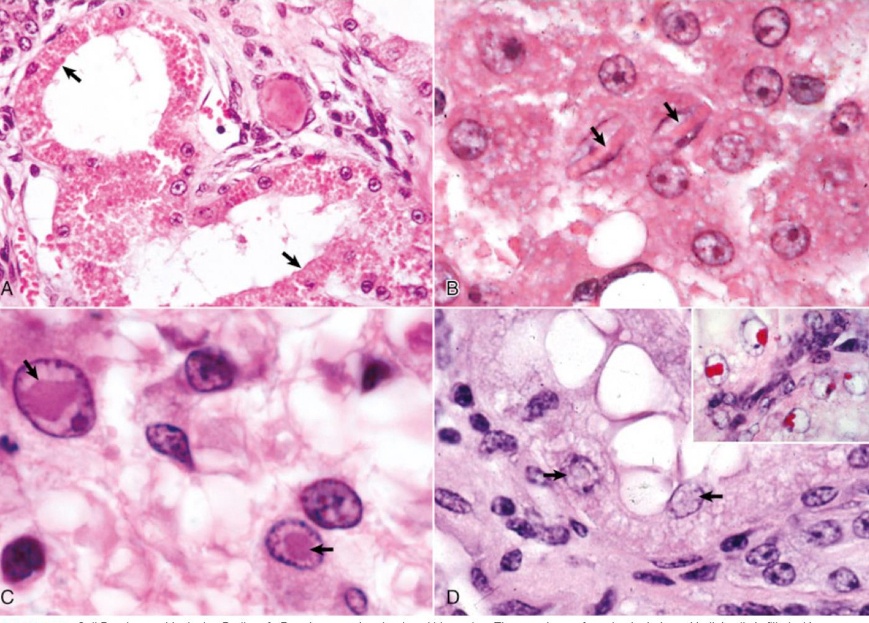
what is being shown in image D**
lead inclusion bodies
what is amyloidosis
protein misfolding disorder converting them into insoluble non-functional aggregrates
where are amyloid deposits frequently found
blood vessels, basement membranes, spleen
what is the mechanisms of amyloidosis
1. propagation of misfolded proteins that self replicate
2. accumulation of misfolded precursor peptides with failure to degrade them
3. genetic mutations which promote protein misfolding
4. protein overproduction because of abnormality of proliferation in synthesizing cells
5. loss of chaperone molecules or other essential components of protein assembly process
what are the types of amyloidosis
AL amyloid
AA amyoid
beta-amyloid
when are AL amyloid secreted
B cell proliferative disorders
when will you see beta-amyloid amyloidosis
dogs with cognitive dysfunction and Alzheimer's
what occurs in AA amyloid
liver secretes serum amyloid A during inflammation
what is serum amyloid A
inflammatory protein
if chronic, can cause a misfolding cascade
what animals have hereditary amyloidosis
Shar Pei
Abyssinian cats
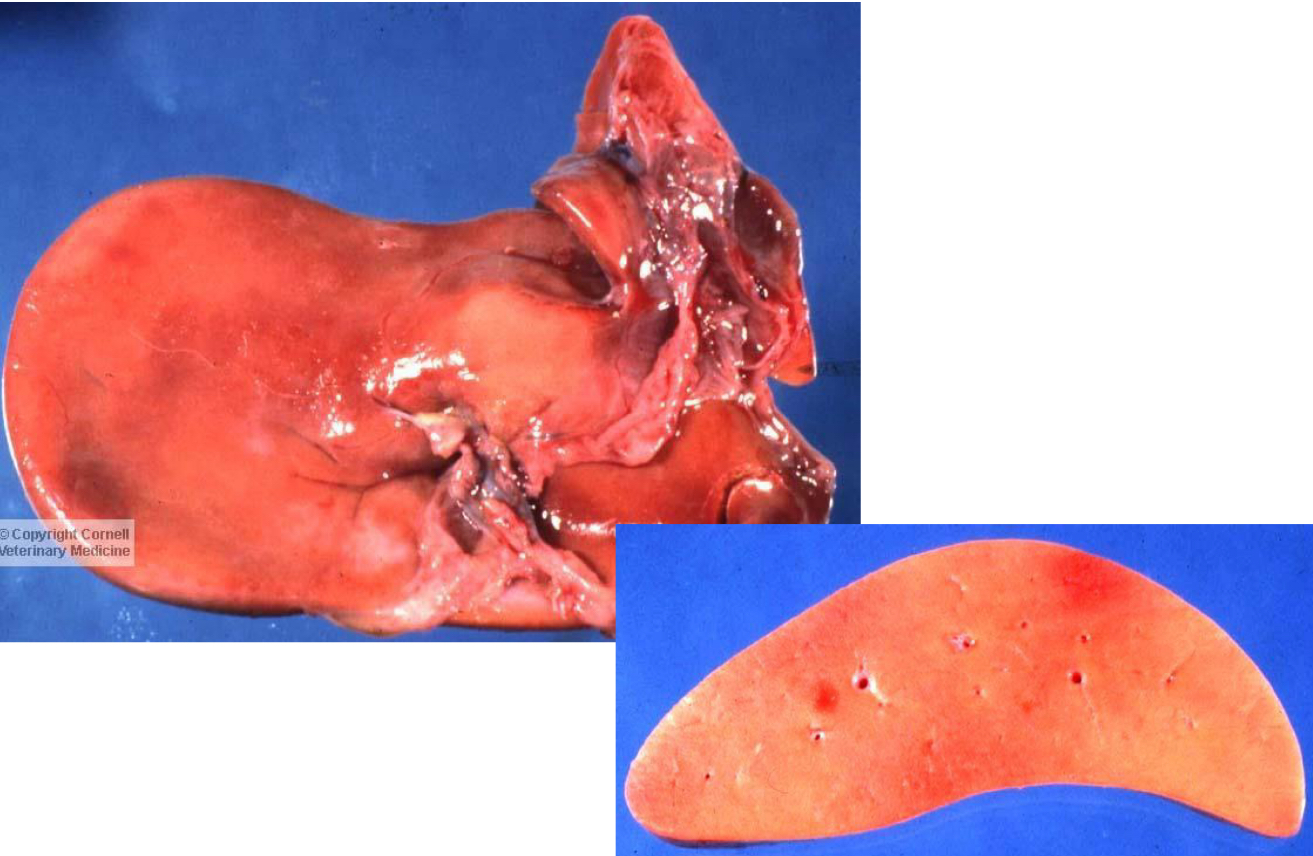
what is being shown in this liver**
amyloidosis
how to diagnose amyloidosis
iodine stain (appears black)
congo red stain --> shows apple-green perfringence
what is being shown**
amyloidosis
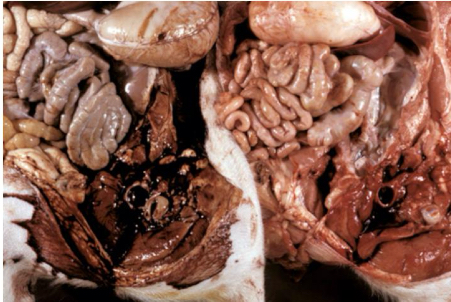
what is gout
deposition of sodium urate crystals extracellularly in tissue
what causes gout
dehydration
renal failure
excess protein intake
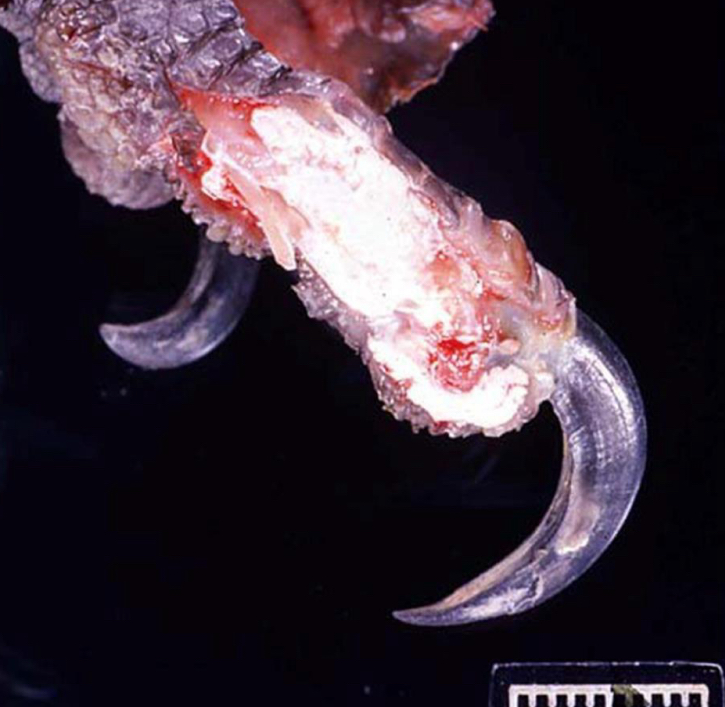
what is being shown in this foot**
gout
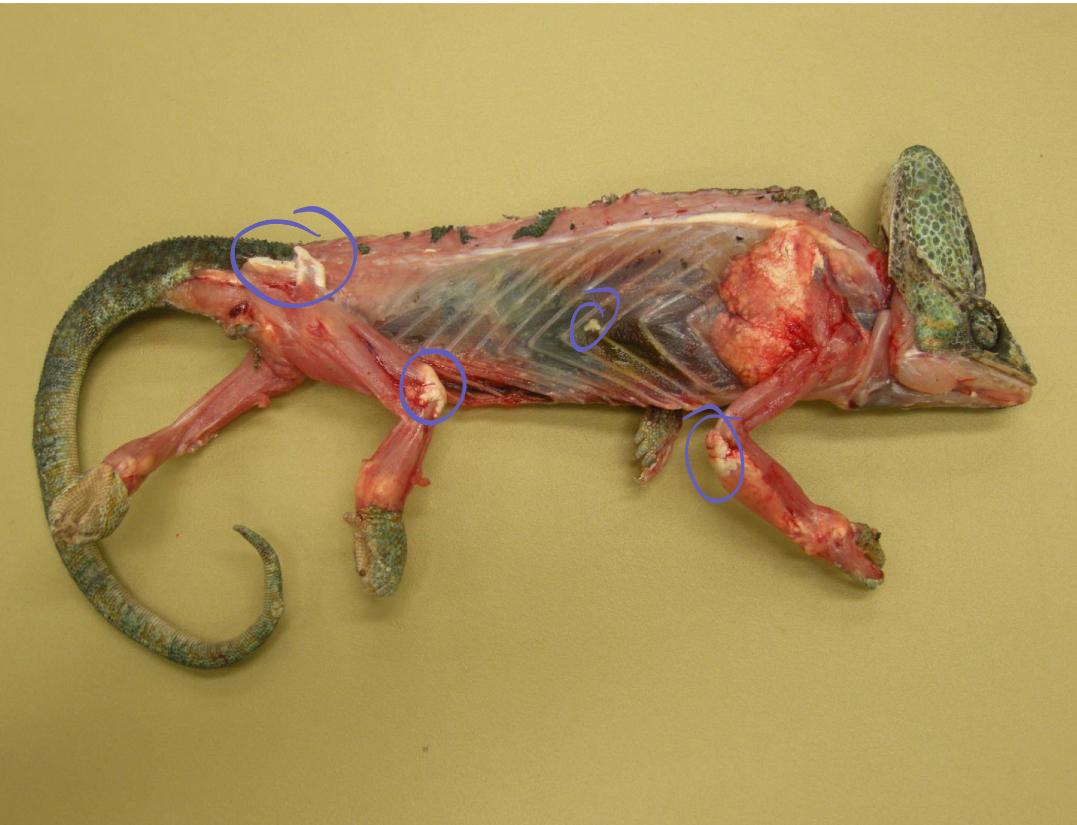
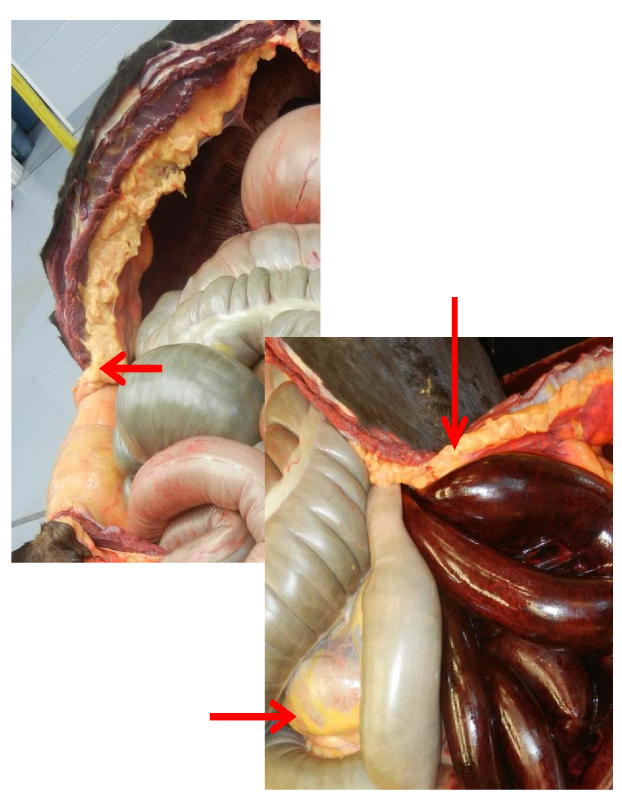
what is being shown in this reptile**
gout
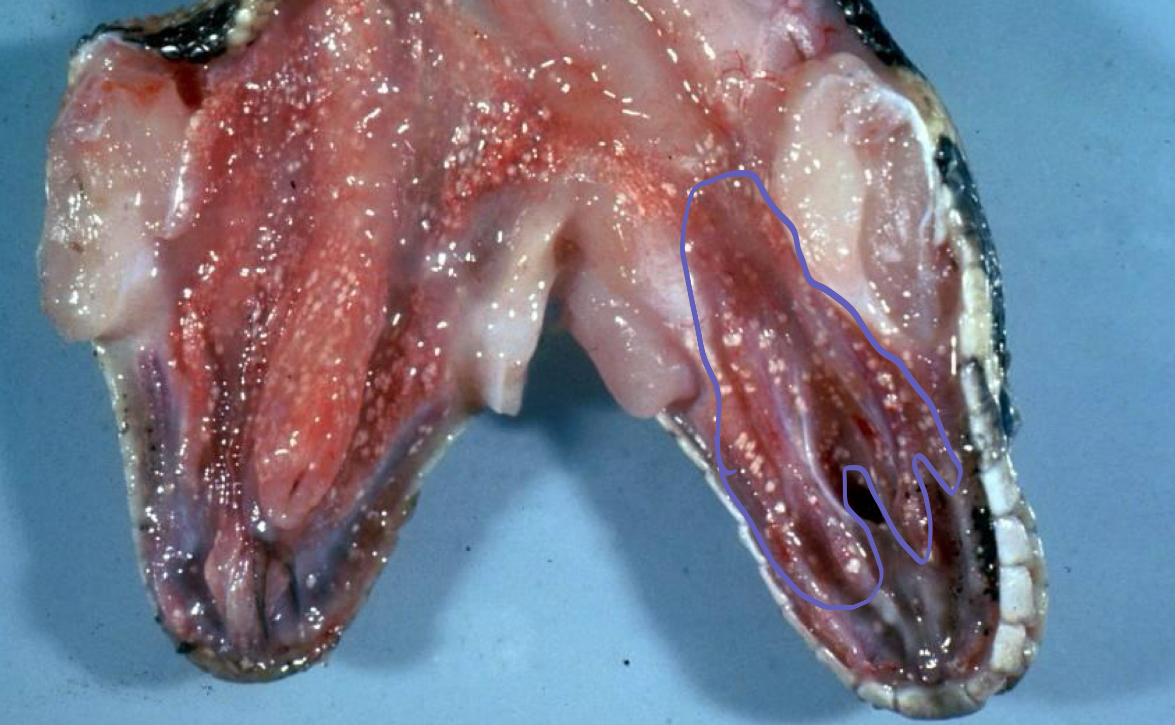
what is being shown in this snake
visceral gout
cholesterol crystals form at
sites of necrosis and elicit granulomatous inflammation
what does cholesterol accumulation look like on histology
needle shaped clefts
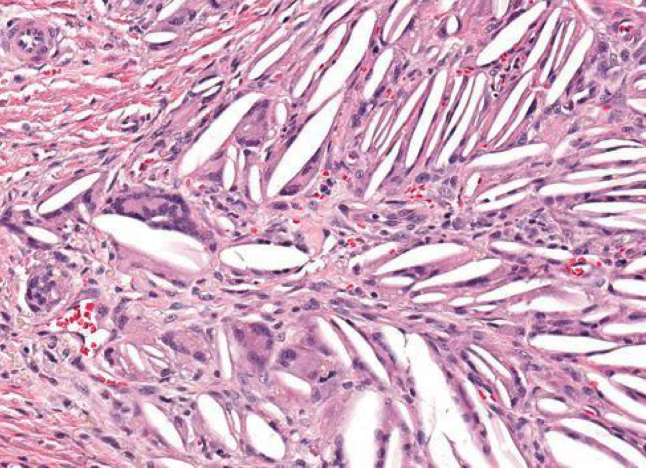
what is being shown **
cholesterol accumulation
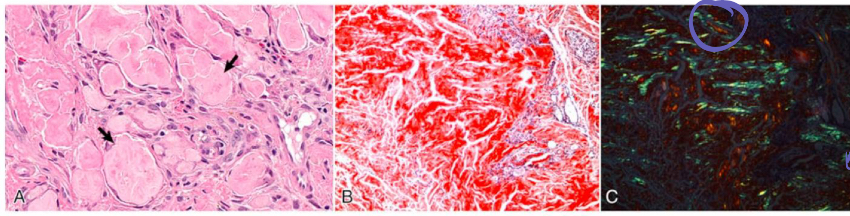
what is fibrosis
collagen deposition (type I) in interstitium of organs or tissues
what is fibrosis a result of
necrosis or inflammation
part of healing!
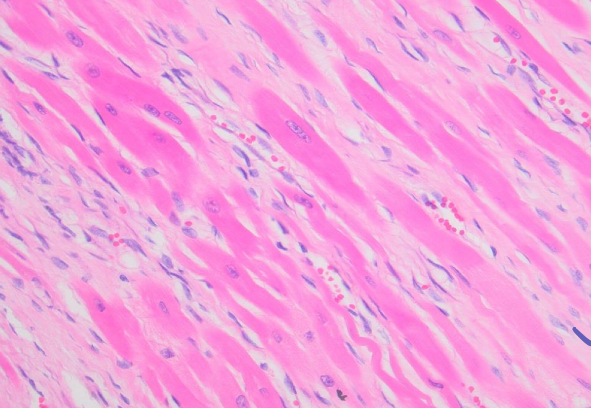
what is being shown in the pale pink matrix**
fibrosis
what is fatty infiltration
increase in number of adipocytes in organ or tissue
what causes fatty infiltration
obesity
certain cardiomyopathies
what is pathologic calcification
deposition of calcium salts in soft tissues
What is dystrophic calcification?
result of necrosis where intracellular calcium is released from sequestered places within cell or into extracellular space
What is metastatic calcification?
targets specific sites first
what causes metastatic calcification
calcium/phosphate imbalances!!
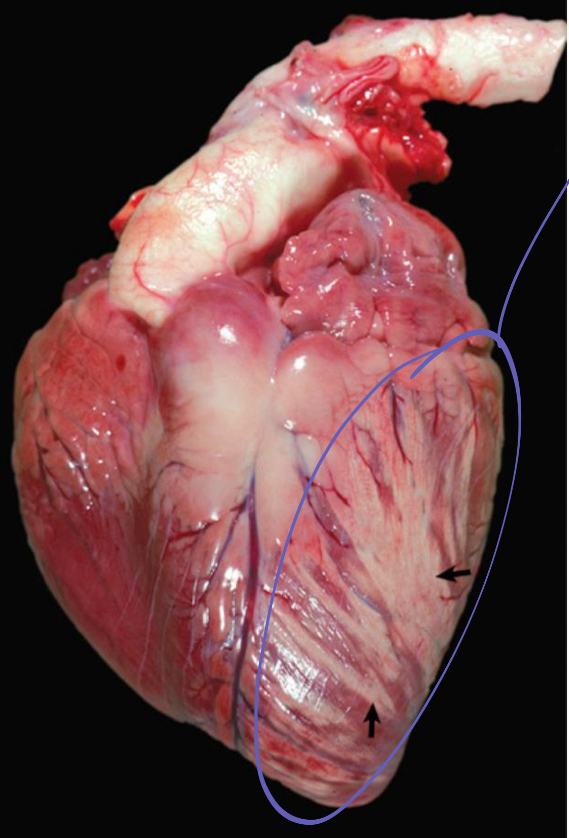
what is being shown in this heart
myocyte degeneration, necrosis, and mineralization
what is melanin
brown black intracellular pigment produced by melanocytes
what is albinism due to
lack of tyrosinase
what causes depigmentation
copper deficiency
chediak-higashi syndrome
what is congenital melanosis
non pathologic, just pigment
can happen to any organ
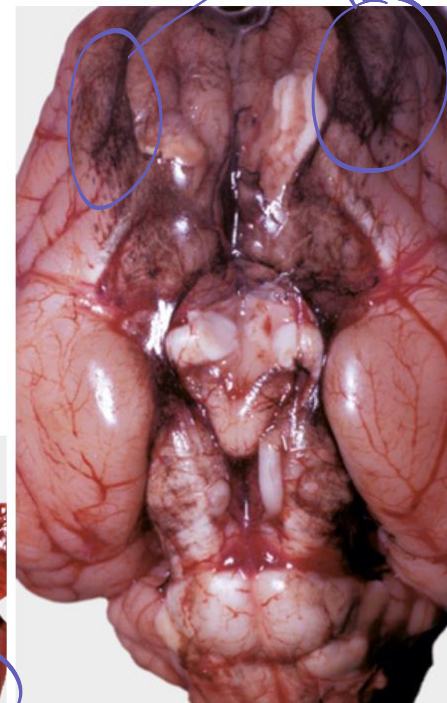
what is being shown on this brain**
congenital melanosis
what is lipofuscin
lipoprotein which accumulates in lysosomes
wear and tear pigment
what does lipofuscin stain
PAS positive
reacts with Sudan black and Oil Red O
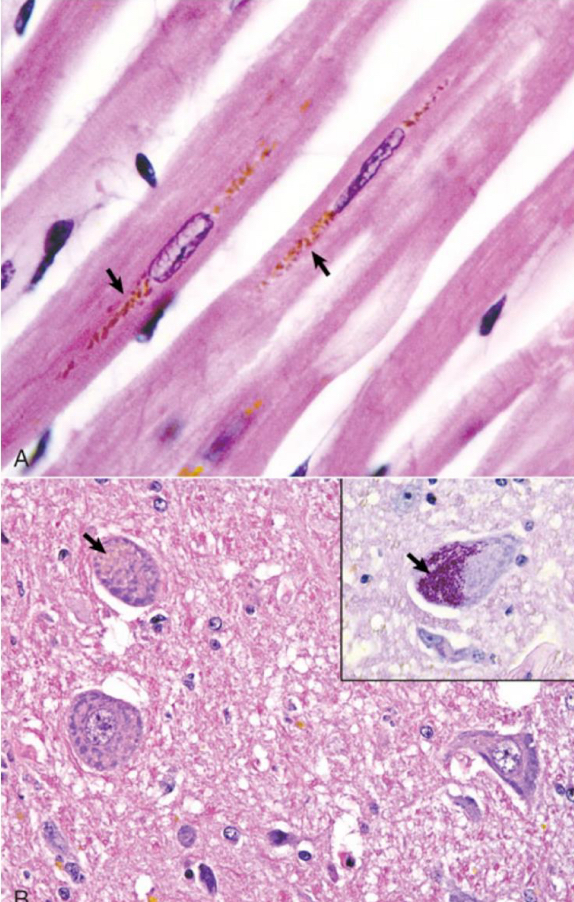
what is being shown**
lipofuscin
what are ceroids
looks similar to lipofuscin but different biochemical composition
PATHOLOGIC
what causes ceroid
Vitamin E deficiency !
cachexia
lysosomal storage disease
what is being shown **
ceroid
what are carotenoids
fat soluble pigments from plants
precursor to vitamin A
how to differ carotenoids from icterus
check other parts of the body for pigmentation
what is being shown **
cartenoids
what is anthracosis
accumulation of carbon in tissues
what are common causes/ sites of carbon accumulation
skin after tattooing
inhalation of smoke or dust
tracheobronchial lymph nodes
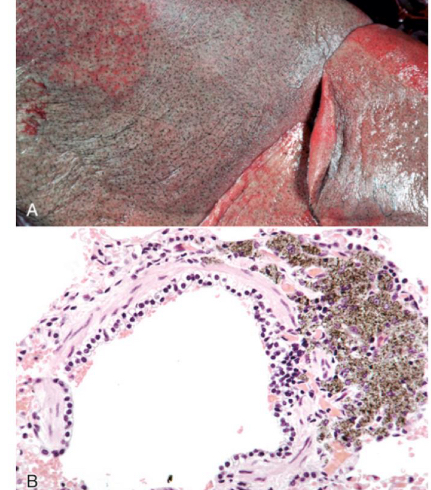
what is being shown**
carbon accumulation
what is tetracycline
antibiotic that binds to calcium phosphate in teeth and bones
what discoloration with tetracycline cause
stain yellow initially, after exposure to light and oxidation turns brown
what is hemoglobin
normal red pigment of RBCs
what is methemoglobin
ferrous ion in hemoglobin that is converted to ferric ion
what does methemoglobin result in
brown colored blood
what is being shown on the left
methemoglobin
what is hemosiderin
formed from aggregates of ferritin
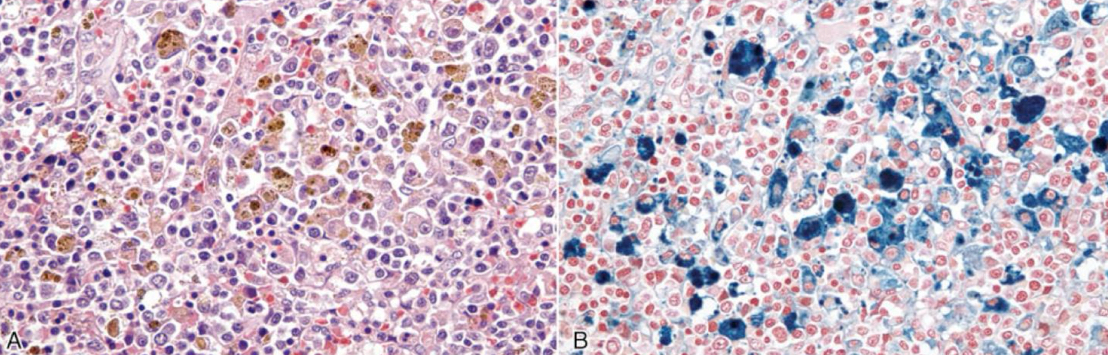
what is being shown on the left
hemosiderin
what is hematoiden
bright yellow brown to orange-red crystalline pigment derived from hemosiderin
does hematoidin contain iron
NO!!
what is bilirubin
results from RBC degradation in macrophages
what is icterus an accumulation of
bilirubin
what is porphyria
inherited metabolic defect in heme synthesis
deficiency of uroporphyrinogen III cosynthetase
what does porphyria result in
pink to red brown discoloration of dentin and bone
icterus can be
prehapatic
hepatic
posthepatic
can you have hyperbilirubinemia without icterus
YES!