Basic Properties of Amines
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
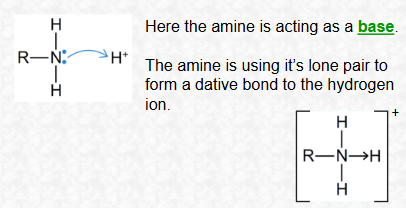
Why do amines act as bases?
Because the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons that can accept a proton (H⁺).
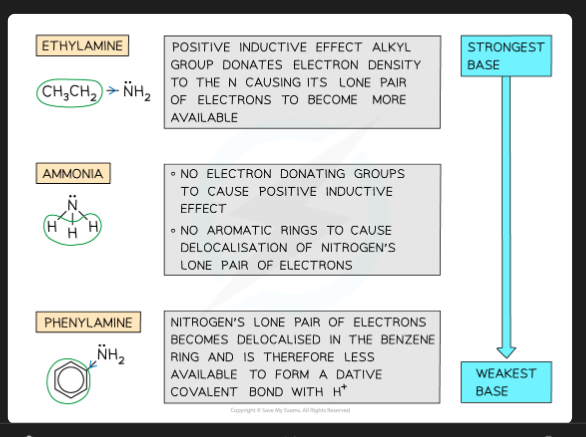
Why are aliphatic amines (e.g., methylamine) stronger bases than ammonia?
Alkyl groups are electron-releasing. They increase the electron density on the nitrogen's lone pair, making it more available to accept a proton.
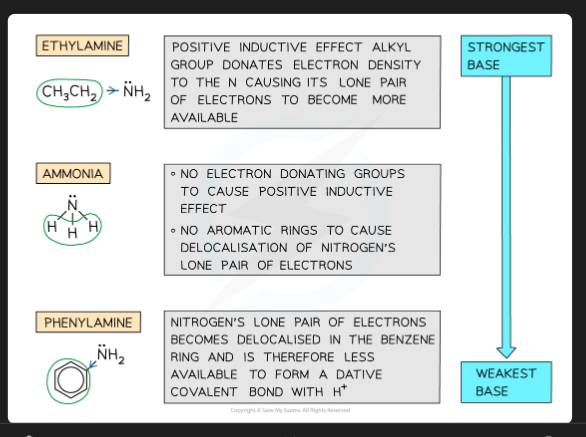
Why are aromatic amines (e.g., phenylamine) weaker bases than ammonia?
The lone pair on the nitrogen delocalises into the benzene ring's π-system. This makes the lone pair less available to accept a proton.
Write the equation for ethylamine acting as a base in water.
CH₃CH₂NH₂ + H₂O ⇌ CH₃CH₂NH₃⁺ + OH⁻
What is the general product when an amine reacts with an acid?
An alkylammonium salt.
Example: CH₃NH₂ + HCl → CH₃NH₃⁺Cl⁻
What is the name of the salt formed when propylamine reacts with nitric acid?
Propylammonium nitrate (CH₃CH₂CH₂NH₃⁺NO₃⁻)
Explain the base strength difference between ethylamine and phenylamine.
Ethylamine is a stronger base than phenylamine.
In ethylamine, the alkyl group is electron-releasing, which increases the electron density on the nitrogen's lone pair, making it more available to accept a proton.
In phenylamine, the lone pair on the nitrogen delocalises into the stable benzene π-ring.
This delocalisation makes the lone pair less available to accept a proton, resulting in a weaker base.
Equation for methylamine + HCl and name the product.
CH₃NH₂ + HCl → CH₃NH₃⁺Cl⁻
Name of Product: Methylammonium chloride
Explain how the positive inductive effect increases base strength.
The alkyl group pushes electron density towards the nitrogen atom.
This increases the electron density on the nitrogen's lone pair.
A lone pair with higher electron density is more readily available to form a bond with a proton (H⁺), making the amine a stronger base.