Lab 2: Histology
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For the different tissues, write down the different CHARACTERISTICS, LOCATION, AND FUNCTIONS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Cell
The BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
Contains ORGANELLES AND CYTOPLASM
Organ
GROUPS OF SIMILAR TISSUES that functions together
Histology
STUDY OF TISSUES
Tissue
GROUP OF SIMILAR CELLS that WORK TOGETHER to CREATE A FUNCTIONAL UNIT
Organ System
GROUP OF ORGANS that work together to create a functional unit (like the integumentary system has many organs that creates that system)
Biopsy
EXAMINE TISSUES by EXTRACTING SOME TISSUE CELLS
Interstitial Fluid
This is a TYPE OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUID that SURROUNDS THE CELLS OF TISSUES
Organism
LIVING THING
Histopathology
This DIAGNOSIS + STUDY OF DISEASE OF TISSUES
Epithelial Tissue
A types of tissue that COVERS BODY SURFACES, LINES CAVITIES AND FORMS GLANDS
CELLS ARE PACKED TOGETHER
Function:
PROTECTION
PREVENT WATER LOSS
PREVENT PATHOGEN INVASIONS
Goblet Cell
Type of epithelial tissue that SECRETES MUCUS which are FOUND IN THE DIGESTIVE, RESPIRATORY, URINARY, and REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Mucus can:
Trap pathogens in the respiratory system
protect lining of digestive system from acids and abrasions
lubricate movement of food
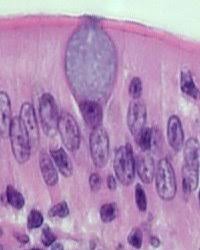
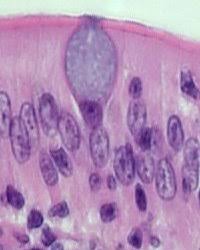
Cilia
These are STRUCTURES that WORK TO MOVE MUCUS (in respiratory system) and MOVE EGGS TOWARDS UTERUS (in the reproductive system)
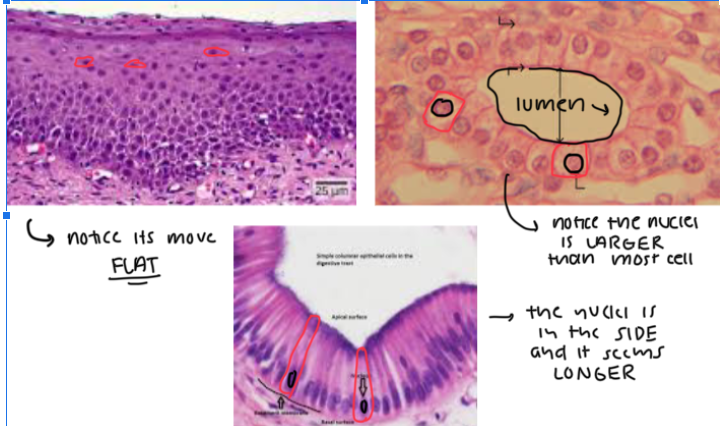
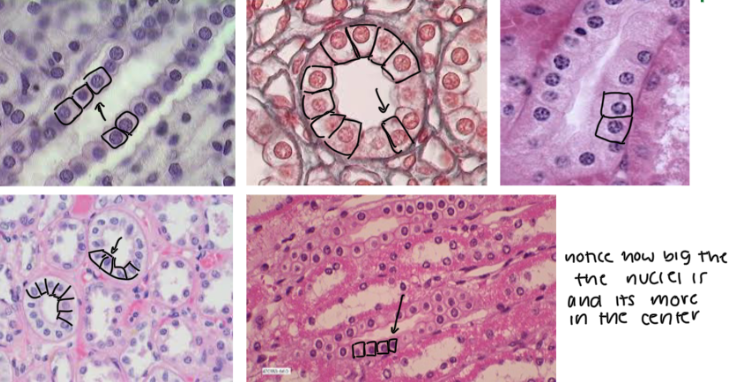
Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar Cells
(1) These are FLATTENED, SCALE-LIKE CELLS in the OUTERMOST LAYER OF THE SKIN where DIFFUSION IS EASY TO DO. The NUCLEI is ALSO FLATTENED
(2) These are CUBE-LIKE CELLS where the NUCLEI IS LARGER THAN MOST and it’s MORE IN THE CENTER
(3) These are COLUMN-LIKE CELLS where the NUCLEI IS TOWARDS THE SIDES of the cell
Key tip: LOOK FOR LUMENS BECAUSE EPITHELIAL CELLS SURROUND THEM
Simple VS Stratified Tissues
Simple tissues are SINGLE-LAYERED while stratified tissues HAVE MORE LAYERS
Simple squamous epithelium
Characteristic: SINGLE LAYER of FLAT, PLATE-LIKE CELLS (looks like fishscales)
Location: ALVEOLI (AIR SACS) within LUNGS and WALLS OF CAPILLARIES and CAVITIES
Function: EASY DIFFUSION; EFFICIENT EXCHANGES of materials and waste
Key thing: these (epithelial cells in general) LINE the LUMEN (CAVITIES/SPACES)
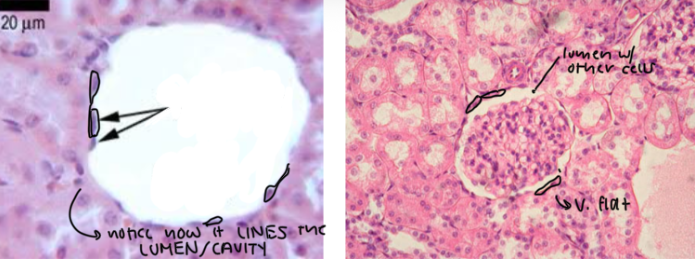
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Characteristic: CUBE-SHAPED CELLS, NUCLEI is in the CENTER, and it’s SINGLE LAYER
Location: KIDNEYS
Function: FILTERS BLOOD AND MAKE URINE
Key thing: these (epithelial cells in general) LINE the LUMEN (CAVITIES/SPACES)
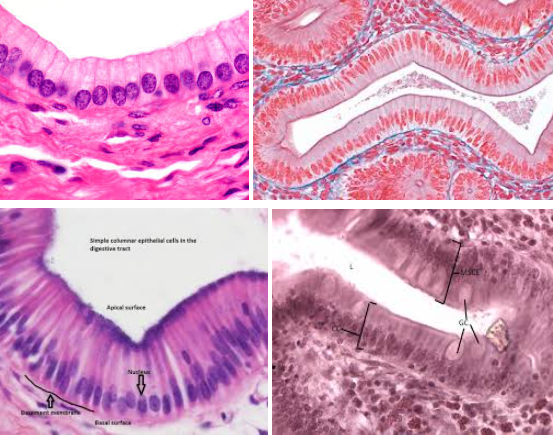
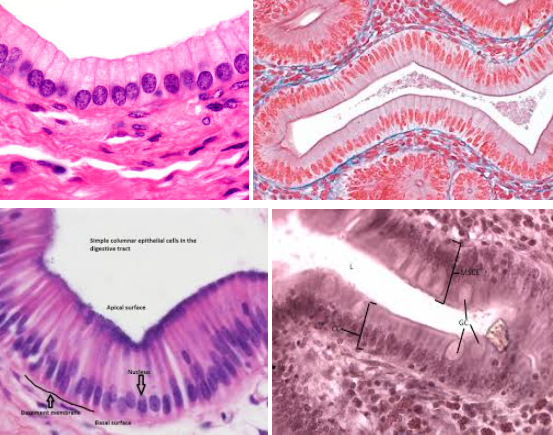
simple columnar epithelium
Characteristic: COLUMN-SHAPED CELLS and the NUCLEI IS ON ONE END OF THE CELL (it’s not in the middle)
Location: DIGESTIVE TRACT and FALLOPIAN TUBES
Function:
In the digestive tract it, MAKES LUBRICATING MUCUS (via goblet cells) and PROTECTS LINING FROM ACID AND ABRASION
In In the respiratory tract, MUCUS TRAPS MICROBES
In the fallopian tubes, CILIA MOVES EGGS
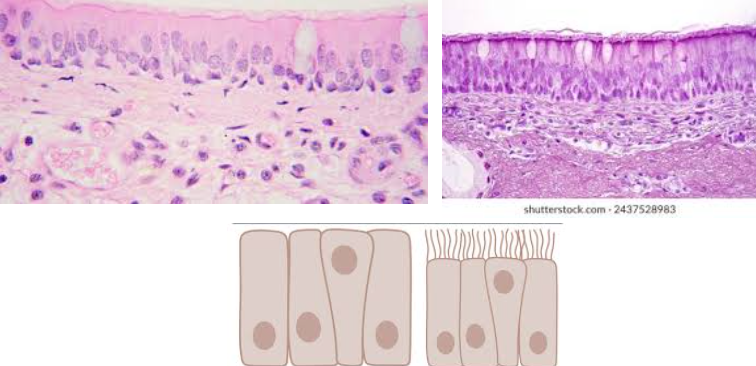
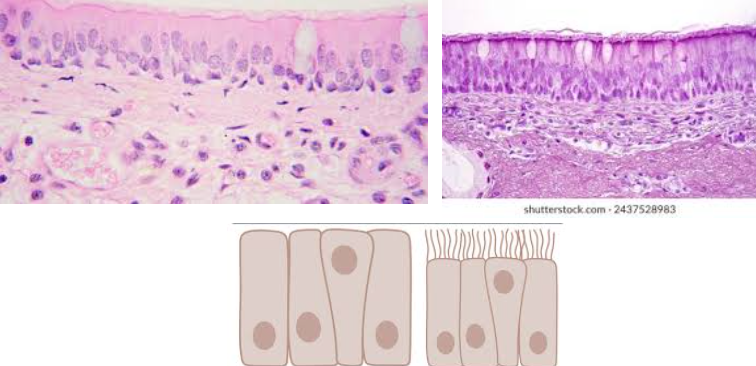
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Characteristic:
SINGLE LAYER OF COLUMNAR CELLS, but their nuclei appear at different levels
MAY CONTAIN SOME CILIA
Location: TRACHEA
Function: PROTECTION AND TRANSPORT MICROBES AWAY FROM LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT
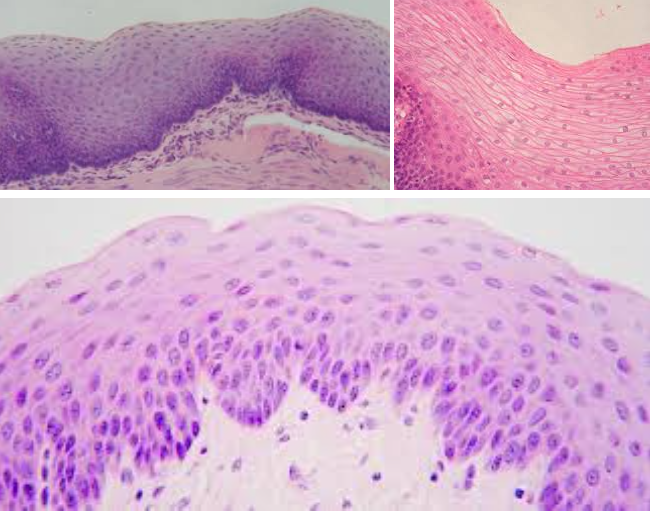
Stratified squamous epithelium
Characteristic: MULTIPLE LAYERS OF SQUAMOUS CELLS
It’s FLAT WITH A LOT OF LAYERS
Location: EPIDERMIS OF SKIN and LINING OF MOUTH
Function: PROTECTION
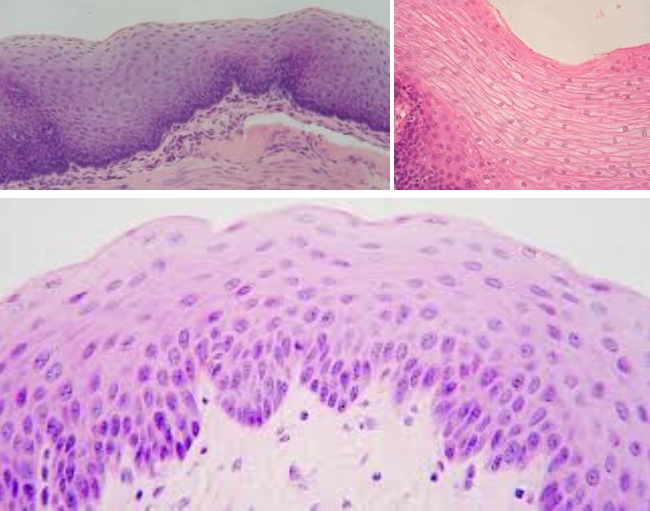
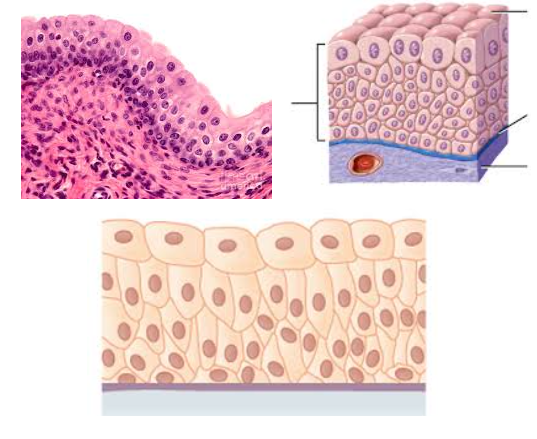
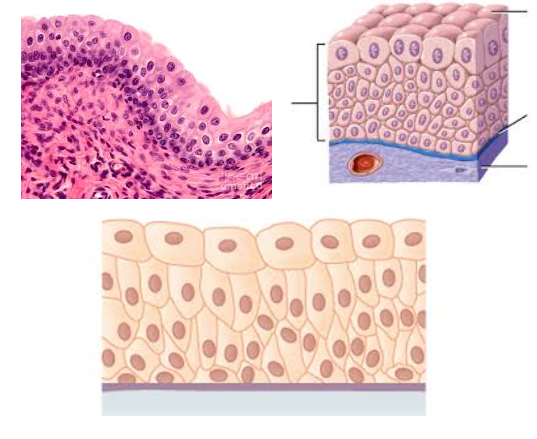
Transitional epithelium
Characteristic: STRATIFIED TISSUES that LOOK CUBOIDAL (when not stretched) and SQUAMOUS (when stretched)
Location: URINARY BLADDER
Function: WITHSTAND STRESS OF BEING STRETCHED as the organ fill up (with pee or some form of liquid)
Key tip: The DEEPEST LAYER (basal layer) looks more CUBOIDAL/COLUMNAR but as it starts reaching towards the surface, the size would vary
Extracellular Matrix
This is the SPACE OUTSIDE ANY CELL/TISSUE which HOLDS TISSUES TOGETHER and HELP CELL COMMUNICATION WITH OTHERS
Remember, the interstitial fluid is a type of extracellular matrix
Components are different proteins like collagen, elastin, fibronectin, ETC
Connective Tissue
These are TISSUES that CONNECT, SUPPORT, PROTECT, AND BIND OTHER TISSUES/ORGANS TOGETHER
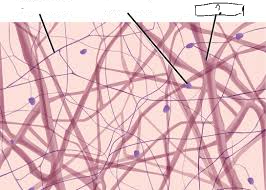
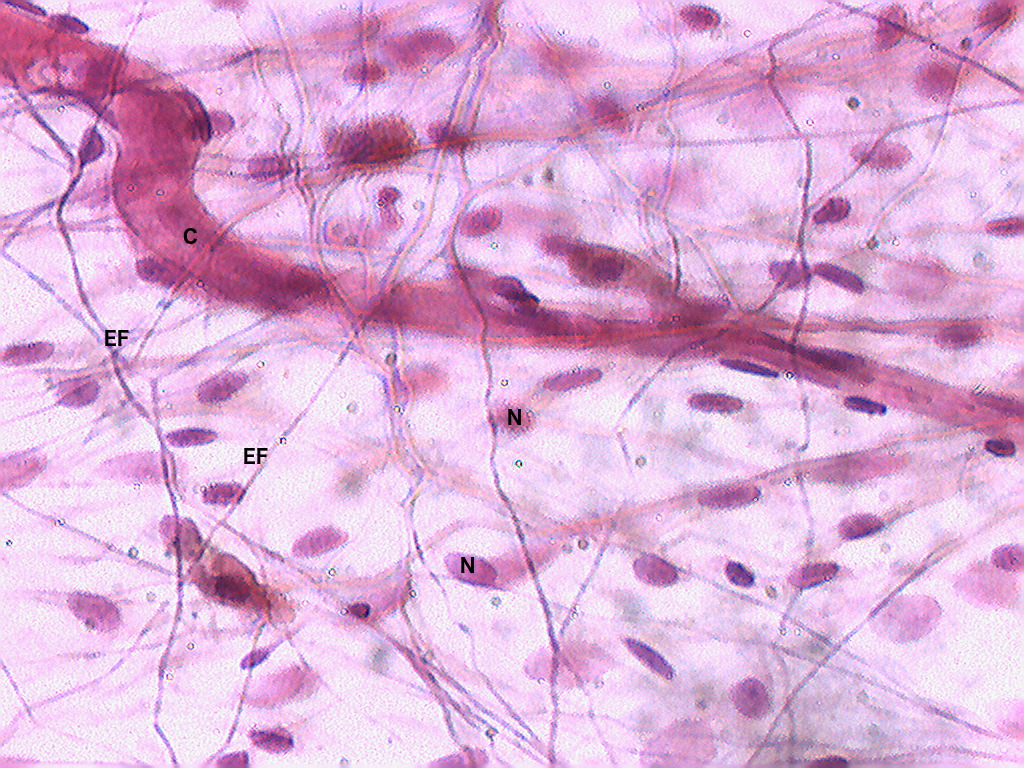
Fibroblasts
MOST COMMON CELLS in the tissue that MAKE/SECRETE COLLAGEN, ELASTIC, AND RETICULAR
These are the “FIBER-BUILDERS”
Looks CIRCULARISH under the microscope
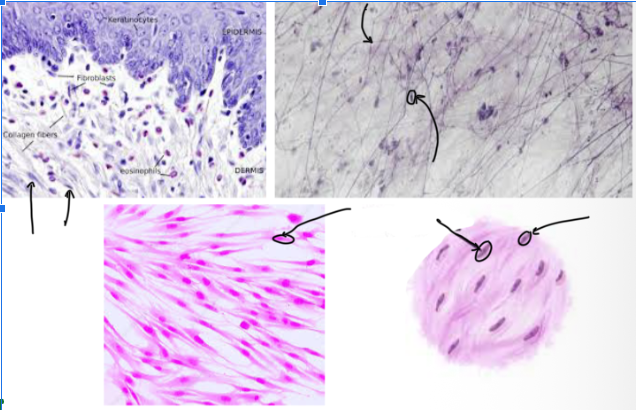
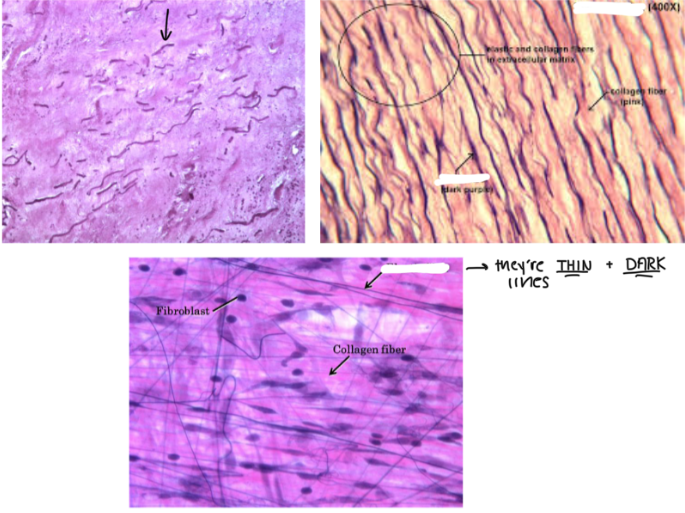
Elastic Fibers
These are STRETCHY FIBERS made of protein elastin which ALLOWS STRETCH AND RECOIL (like a rubber band)
THIN, DARK LINES in the microscope
Kinda looks like stretch marks under the microscope
Made from elastin (a type of fiber)
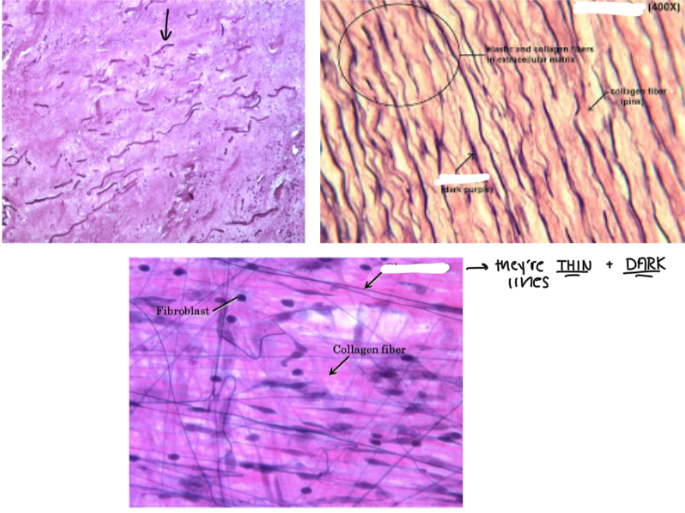
Collagen Fibers
These are FIBERS that RESIST STRETCH and MAKES THE SKIN MORE TIGHT
PREVENTS SAGGING AND WRINKLES
Losing collagen → more wrinkles around the face and body
These look THICK
Areolar Connective Tissue
Characteristics:
LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
CONTAINS FIBROBLASTS
PRODUCE ELASTIC AND COLLAGEN FIBERS
Arranged in a MESSY, IRREGULAR PATTERN
Location: DERMAL LAYER of the SKIN
Function: CUSHIONING, HYDRATION, ELASTICITY, STRENGTH
Think CHES
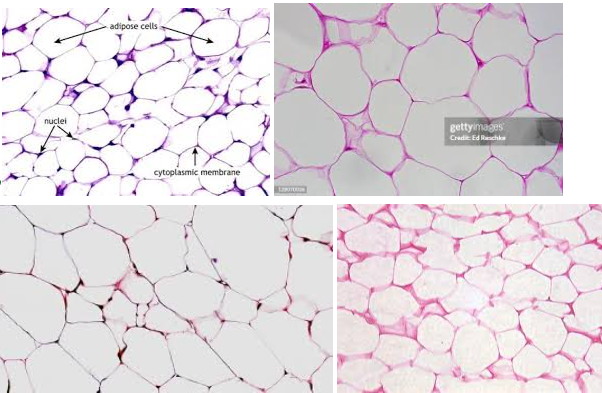
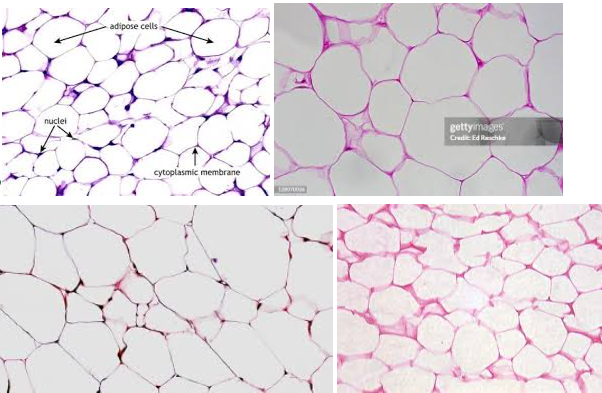
Adipose connective tissue
Characteristics: LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE with cells called adipocytes (these LOOK LIKE EMPTY SACS)
Contains MOSTLY of EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX
Location: HYPODERMAL LAYER OF SKIN
Function: INSULATION, ENERGY STORAGE
Tip: these LOOK SKINNYYYYYYY with a lot of empty space (adipocytes) in the middle
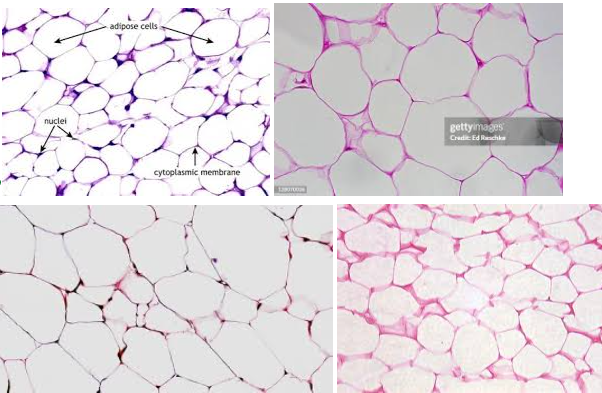
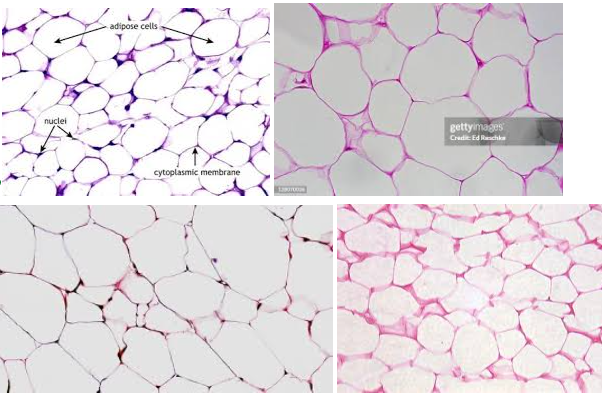
Adipocytes
These APPEAR LIKE EMPTY SACS, but it’s ACTUALLY COLORLESS LIPIDS with things that are stored inside
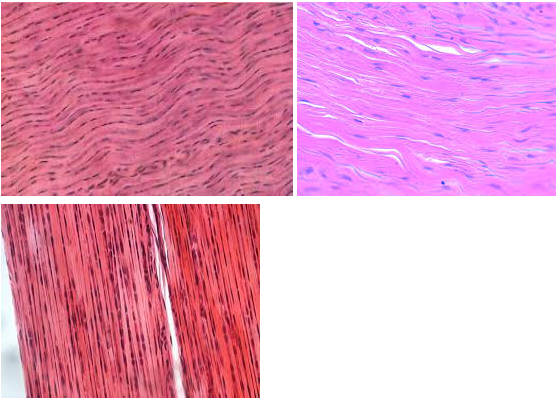
Dense regular connective tissue
Characteristic: Has TIGHTLY PACKED COLLAGEN FIBERS that MAKE A WAVE-LIKE PATTERN
Location: TENDONS/LIGAMENTS
Function: STRENGTH
Cartilage connective tissue
These are AVASCULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUES with DENSE MATRIX
These are tissues that DON’T HAVE BLOOD CELLS
Tip: ANYTHING WITH __________ CONNECTIVE TISSUES ARE AVASCULAR
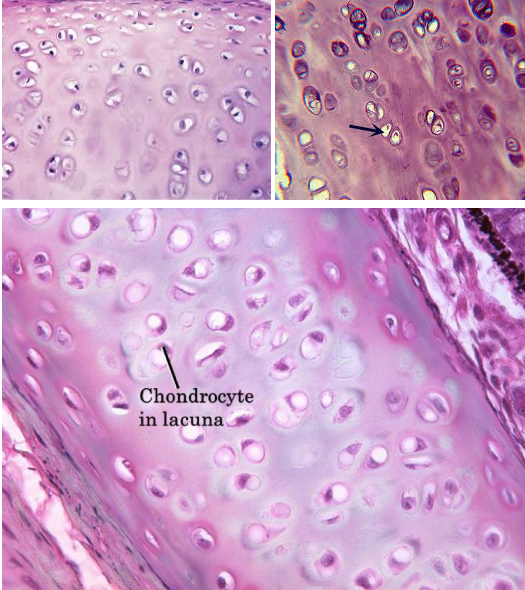
Chondrocytes
These are CARTILAGE CELLS that MAINTAIN AND FORM CARTILAGE MATRIX
Lacunae (s. lacuna)
These are EMPTY, SMALL SPACES IN THE CARTILAGE AND BONE where the chondrocytes would live in
THINK OF A UNFINISHED, NEW YORK APARTMENT (these are typically SMALL)
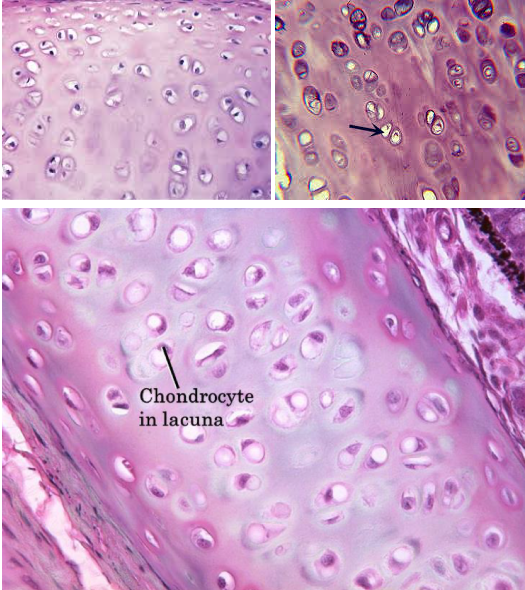
Hyaline cartilage connective tissue
Characteristic: These are AVASCULAR TISSUES that have A LOT OF COLLAGEN FIBERS
Location: ENDS OF LONG BONES
Function: REDUCE FRICTION BETWEEN MOVING BONES
The difference between the hyaline and the elastic cartilage connective tissue is that the _____ IS MORE PINK TONED, while the ELASTIC IS MORE PURPLE TONES
Both have lacunae and chondrocytes though
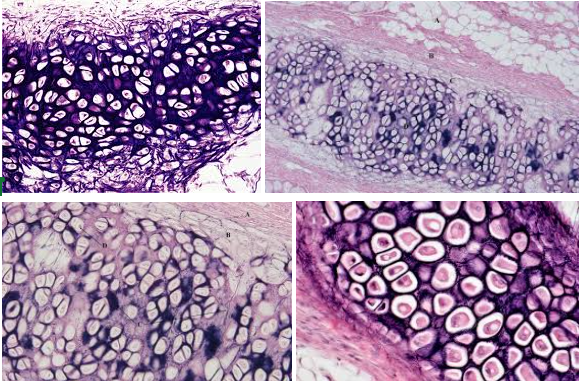
Elastic cartilage connective tissue
Characteristic:
DARK-STAINED ELASTIC FIBERS
LOOKS LIKE EYEBALLS
Location: EXTERNAL EAR STRUCTURE; EPIGLOTTIS
Function: GIVE MORE FLEXIBILITY
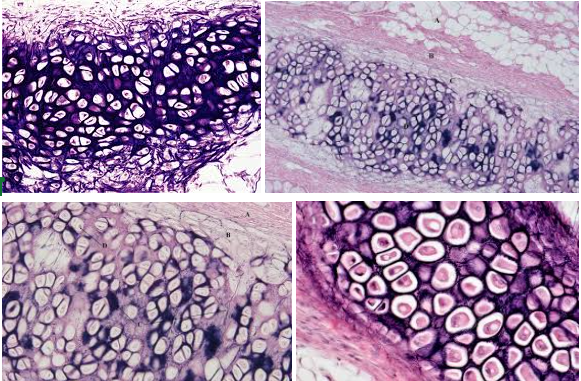
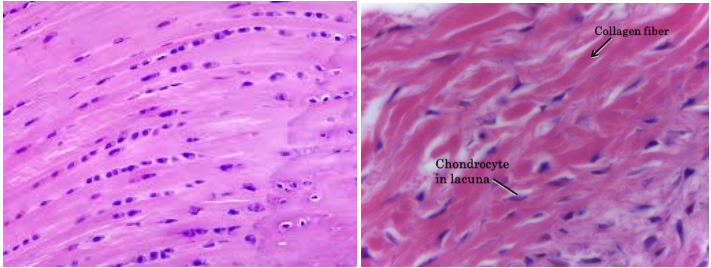
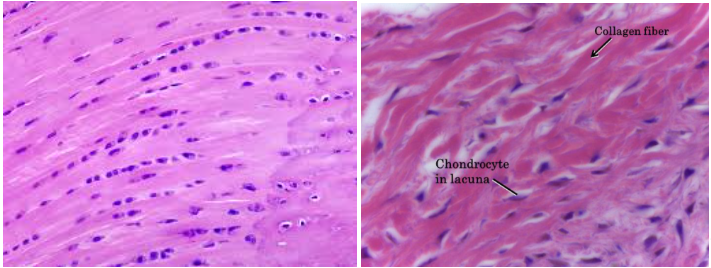
Fibrocartilage connective tissue
Characteristic: SLIGHTLY LESS FIRM MATRIX which means we could SEE THE COLLAGEN FIBERS; still has the chondrocytes and lacunae
Location: VERTEBRAL DISKS
Function: GIVE MORE SUPPORT AND PADDING
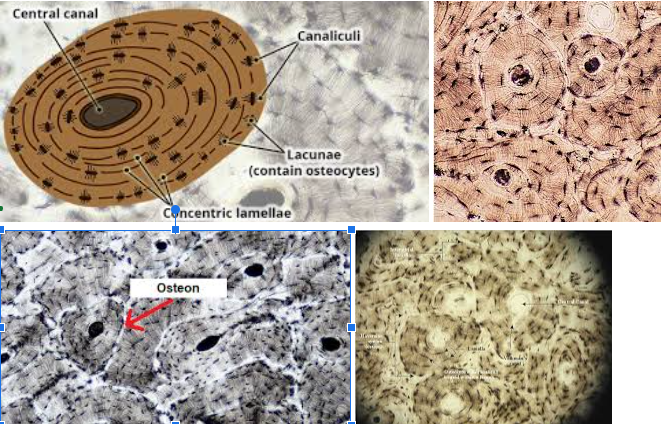
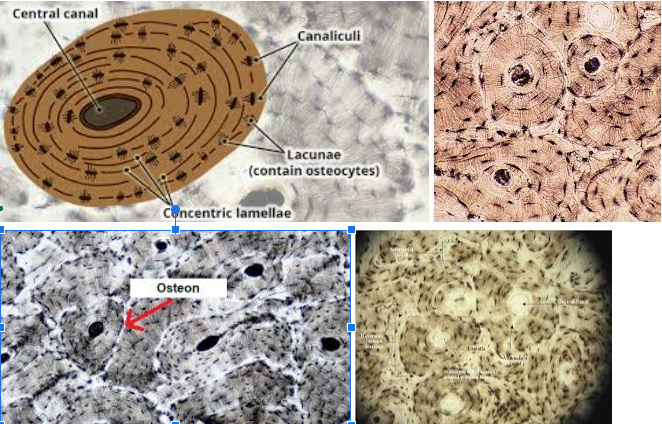
Bone connective tissue
Characteristic: HAS OSTEOCYTES that LIVE IN LACUNAE; The FUNCTIONAL UNIT of a bone is the OSTEON which HAS THE LAMELLAE and CANALICULI (little canals) that connect osteocytes
Location: ALL BONES OF SKELETON
Function: GIVE STRUCTURAL FRAMEWORK, PROTECT UNDERLYING TISSUES, STORE IMPORTANT NUTRIENTS
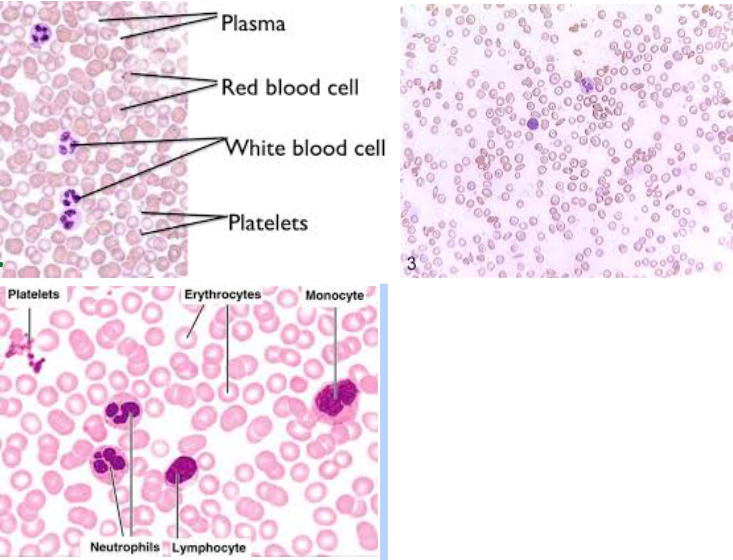
Blood connective tissue
Characteristic: HAS PLASMA and THREE CELL TYPES (erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes).
Location: WITHIN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Function: Erythrocytes carry gases; leukocytes function within the immune system; thrombocytes play a role in blood clotting
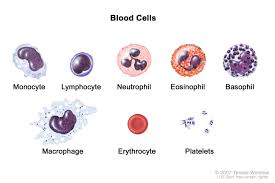
Erythrocytes
These are RED BLOOD CELLS that CARRY OXYGEN
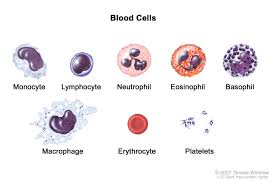
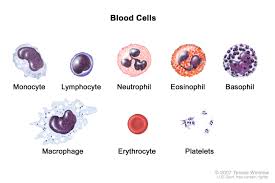
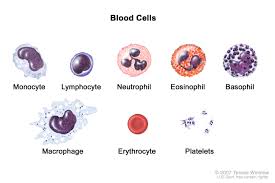
Leukocytes
WHITE BLOOD CELLS that FIGHT INFECTIONS/DISEASES
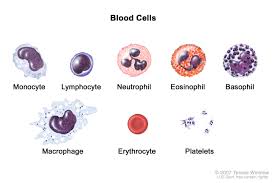
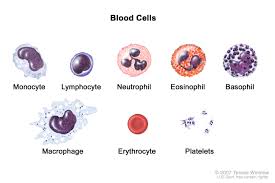
Thrombocytes
PLATELETS which HELPS IN BLOOD CLOTTING
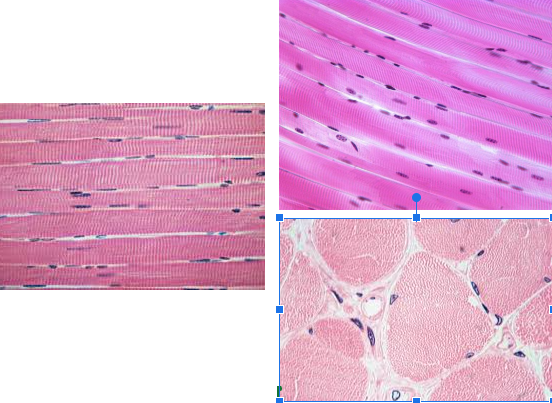
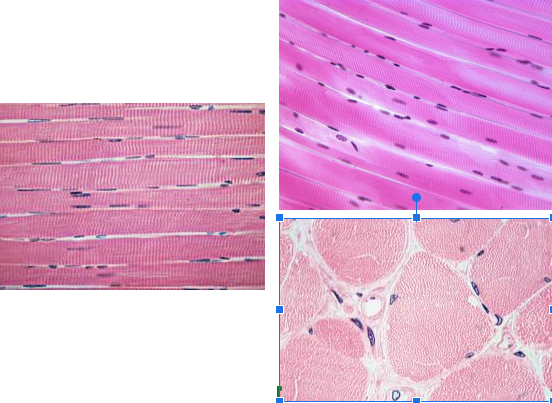
Skeletal muscle tissue
Characteristic:
VOLUNTARY
MULTINUCLEATE
STRIATIONS
Location: Attaches to bones to move the body
Function: Contract to produce body movements
Looks more CLEAN and NOT BRANCHY LOOKING
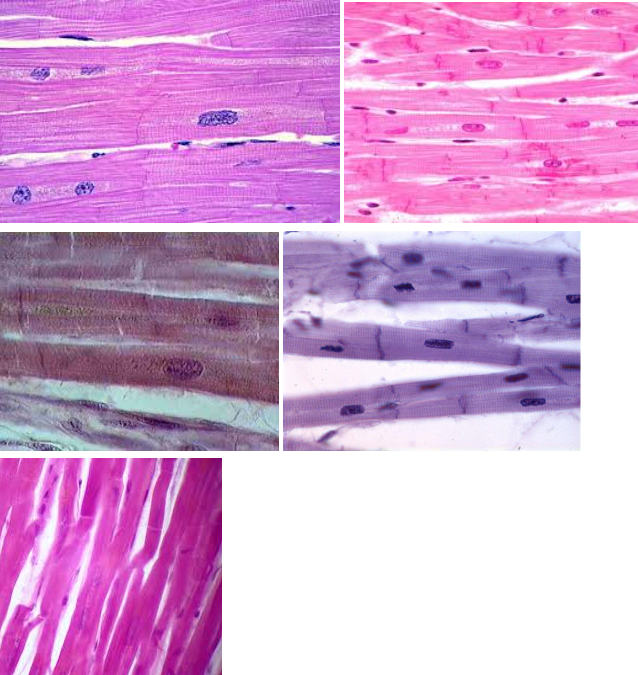
Cardiac muscle tissue
Characteristic:
INTERCALATED DISCS
THIN STRIATION
BRANCHY
UNINUCLEATE
Location: HEART
Function: Allows the heart to pump blood throughout the body
This looks VERY BRANCHY
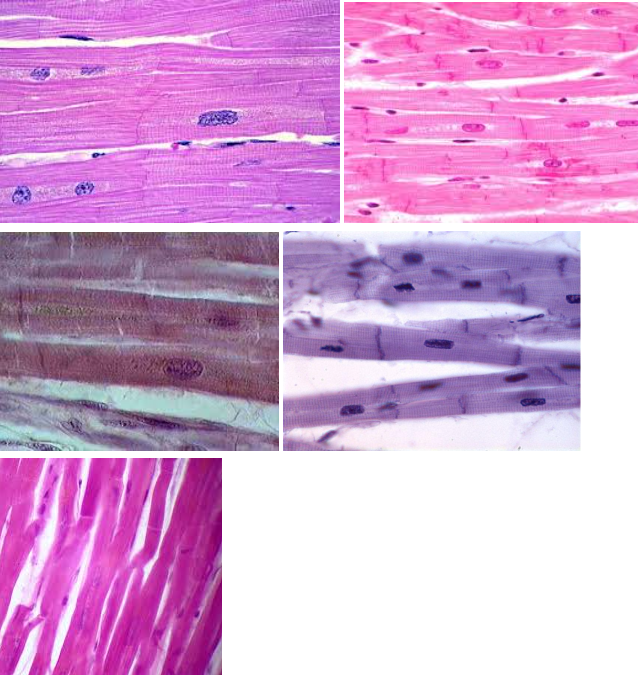
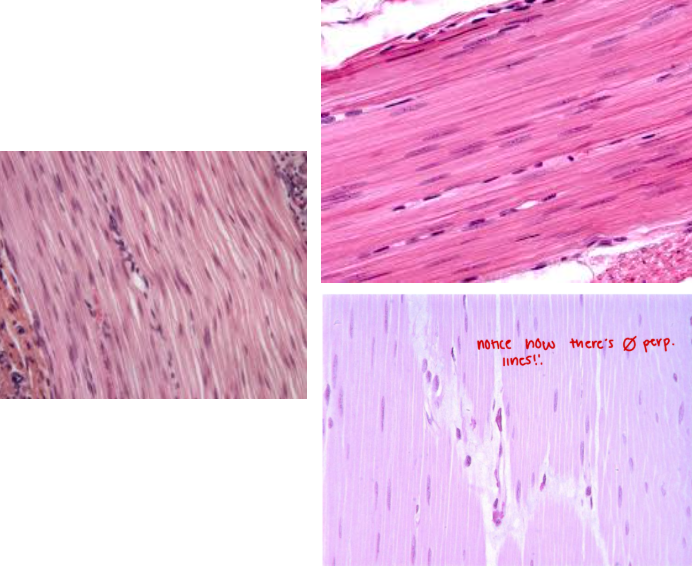
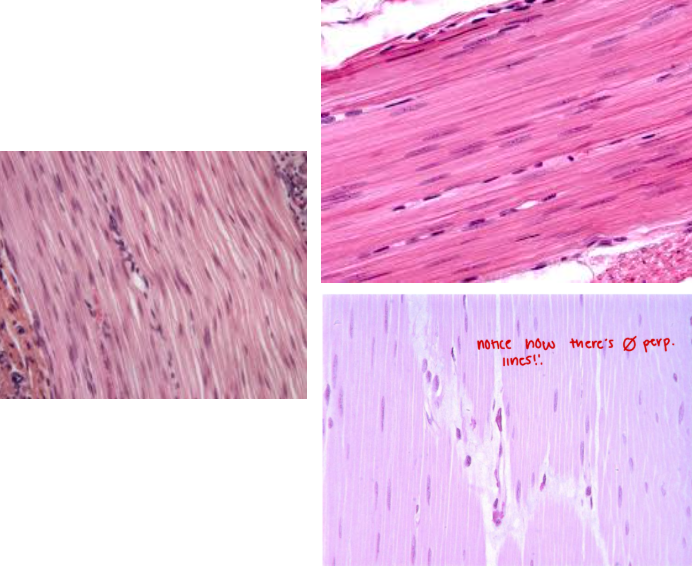
Smooth muscle tissue
Characteristic:
INVOLUNTARY
NO STRIATION
SMOOTH
Location: INTERNAL ORGANS (IRIS in the eye OR DIGESTIVE TRACT)
Function: CONSTRICT BLOOD VESSELS/CONTRACT MUSCLES
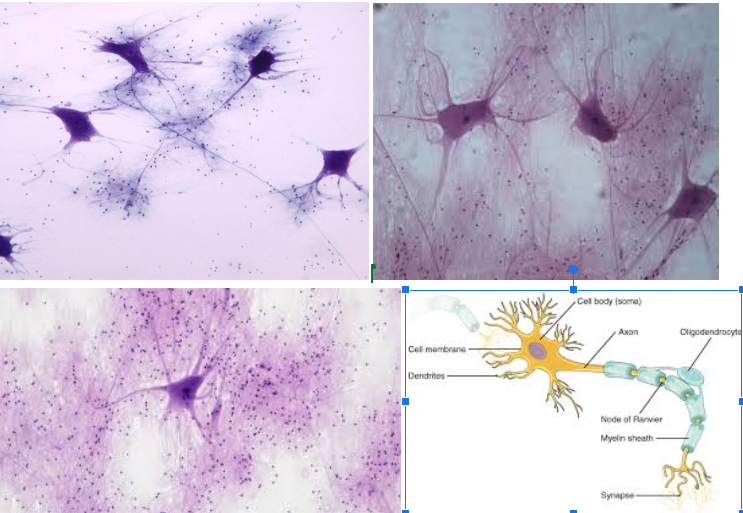
Nervous tissue
Characteristic: Made of NEURONS and NEUROGLIAL CELLS. There’s a CELL BODY, DENDRITE, and AXON.
Location: BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD
Function: TRANSMIT ELECTRICAL SIGNALS for the brain and body to process certain things