4- etiology 2
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the Socransky criteria? (5)
Associated with a disease- more pathogens at disease site
Eliminating pathogen should eliminate disease
Demonstrates a host response
Capable of causing disease in animal models
Demonstrates virulence factors
What are characteristics of periodontal disease?(identification, condition, etiology, importance of …)
Impossible to identify all bacterial species
Chronic condition combines continuous progression and outbreaks- asynchronous
Mixed bacterial etiology
Amount of pathogens more important than presence
How is periodontal disease a multifactorial disease?(reduced, complicated, strain, quality, ? or ?)
Has reduced specificity- just because a pathogen is present, doesn’t mean disease is
Complicated etiology- no standardised threshold of how much causes disease
Need genotype level to estimate strain
Quality of host response- hard to estimate
Endogenous or exogenous
How is the type and number of specific microorganisms that colonise something determined by?
The type and quantity of nutrients there are- so oral ecosystem is dynamic
What is the difference between allogeneic and autogenic succession?
When change in bacterial composition is determined by environmental change (abiotic) vs biotic factors, interactions between bacteria or virus
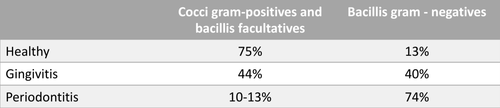
What is the difference in percentage of Gram + cocci and faculative bacilli vs gram - bacilli?
Healthy- 75, 13
Gingivitis- 44, 40
Periodontitis- 10-13, 74
When there is disease present, what can we see morphologically under a microscope?
Periodontal pathogens are immobile bacilli, fewer cocci
What are the 2 main factors that cause periodontal disease?
Host susceptibility
Presence of pathogenic bacteria
What are some factors of host susceptibility?
Partially genetic- link between genetic markers- increased interleukin 1
Influenced by environment- smoking, stress, diabetes- reciprocal relationship
Why do smokers suffer worse than healthier individuals with periodontal disease?
Have lower igg2 serum levels and antibodies against actinomyces comitans
Have lower implant success, heal worse after periodontal and muco gingival therapy and tissue regeneration
Which virus has been linked to higher incidence of chronic periodontitis and necrotising forms?
HIV
Changes host response to local subgingival microbiota
What are the key periodontal pathogens (Socranky red complex) and what are they related to?
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans
Tannerella forsythia
Porphyromonas gingivalis
Treponema denticola
Periodontitis, unsuccessful therapy
If their concentration passes the threshold, which bacteria can cause periodontal disease? (Putative periodontal pathogens)
Prevotella intermedia and nigrescens
Campylobacter rectus
Fusobacetrium nucleatum
What are characteristics of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans?
facultative anaerobic bacillus, non-mobile, gram negative
Role in progressive destructive periodontitis
Hard to eliminate, only with mechanical treatment
Genetic component
Large number of virulence factors- induce bone and ct destruction
What are characteristics of Porphyromonas gingivalis?
anaerobic bacillus, non-mobile, gram negative
Related to chronic periodontitis
Absent or small numbers in healthy sites, large in active
Virulence factors induce bone resorption, destruction of ct, inhibit host protection mechanisms
What are characteristics of tannerella forsythia?
Gram negative anaerobic bacillus
Pleomorphic
In subgingival plaque, deep pockets, aggressive periodontitis
What are characteristics of fusobacetrium nucleatum?
In adult periodontitis
Produces infections in other body parts
More when it progresses
What are characteristics of spirochaetes?
Anaerobic gram negative mobile helical
Common in pockets, can cause necrotising form
Indicator of treatment results- if present in healthy sites- high risk
How can some bacteria be beneficial?
Passively occupying a site that could be colonised by pathogens
Prevent pathogens ability to adhere and produce virulence factors
Affect pathogen growth
What is the evolution of periodontal diseases caused by?
Mixed infections
Composition of bacterial plaque differs among patients and locations within same patient
What is an example of a beneficial bacteria?
Streptococcus sangria- produces hydrogen peroxide
What viruses are related to periodontitis?
CMV, ebv, papilloma, herpes