Viruses
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Viral Structure
•Virion – infectious viral particle
–Assembled with a protein coat around nucleic acid
•Nucleic acid
–RNA or DNA
–Single or double
–Linear or circular
–If RNA, it can be sense (+) or nonsense (-)
•Sense – has codons
•Nonsense – need to make sense strand to translate
–2,000-250,000 nucleotides
•E. coli – 4 million
•Humans – 3 billion
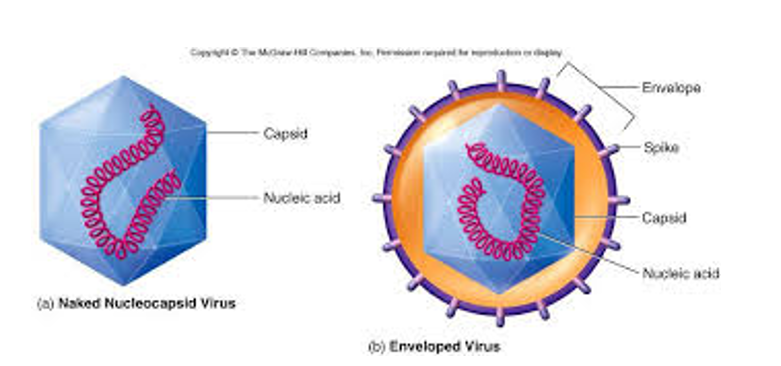
Capsid – the protein coat
Subunits are capsomeres
Some capsids have pentons – protein-carb pointed projections for attachment
Envelop – around the capsid on some viruses (called enveloped viruses)
some envelopes have carb-protein complexes called spikes (also used for attachment)
Coronavirus (cold) and influenza (flu) virus have high mutation rates in spike genes
Mechanism for evading immune system
Slightly different spikes appear new to immune system
Viral Morphology part 1
Capsid structure can be distinct and sometimes help identify a virus
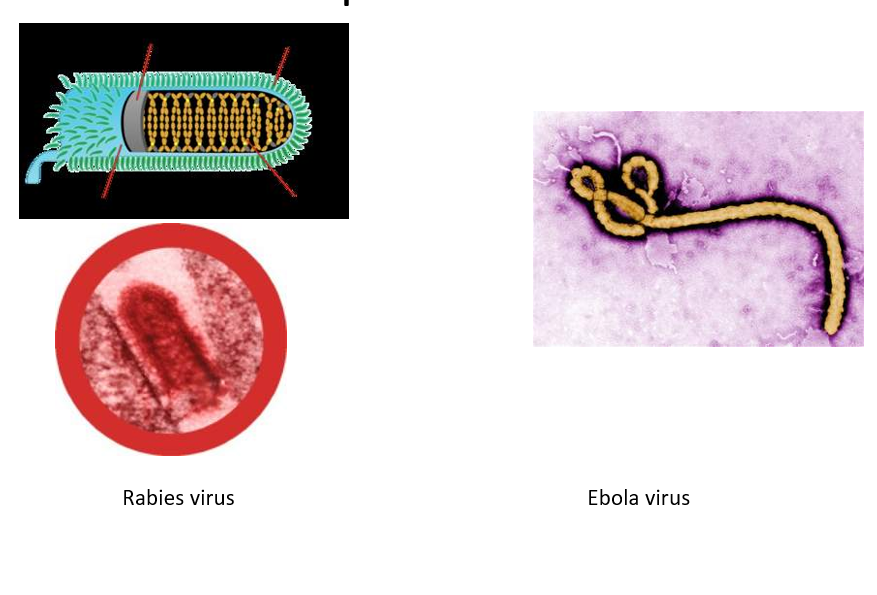
Helical
Cylindrical capsid
Nucleic acid wound up inside
Viral Morphology part 2
Capsid structure can be distinct and sometimes help identify a virus
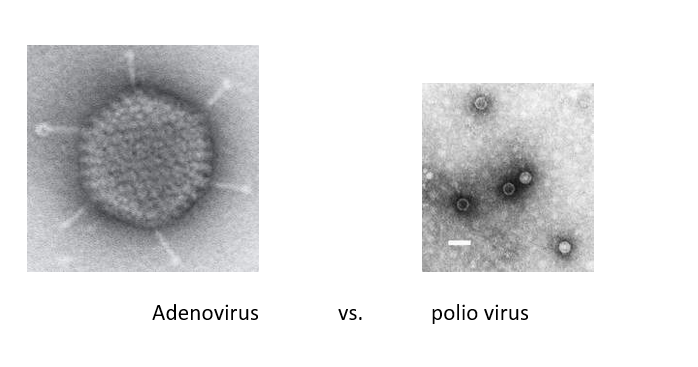
Helical
Polyhedral
Most are icosahedrons (20 equilateral triangle faces and 12 corners)
Enveloped virus
Appear spherical due to the envelope
Complex viruses – unique shape
Bacteriophage – capsid and accessory structures
Pox virus – no clear capsid, just several protein layers around the nucleic acid
Viral Taxonomy pt 1
Viral “species” is a group of viruses sharing
Same genetic information….viral genomics
Same ecological niche (host range – animal virus, plant virus or bacteriophage)
Species names not used
Usually just given a Genus name that ends in ‘virus’ and a common name
Grouped into families
Names end in ‘-viridae’
Families based on
1. nucleic acid type
2. strategy for replication
3. morphology – capsid, envelope presence, physical dimensions
Viral Taxonomy pt 2
Most commonly identified by their common name
Learning the family groups has little relevance to disease ID
For example
Family: Herpesviridae
Genus: Simplexvirus
Herpes Simplex Virus 2 (HSV2)
aka HHV-2, human herpesvirus 2
Viral Identification
Require electron microscopy for viewing
Some are distinct enough to be recognized on sight
Others are identified by
Disease symptoms
Cytopathic effects
Serological methods (ELISA, Western blot)
Nucleic acid sequencing (RFLP/DNA fingerprinting, PCR)
Cultivating viruses for study
Obligate intracellular parasites Must be grown in living cells (usually their host) Can not be grown in culture media alone Three ways to grow animal viruses in lab: 1. Animal models 2. Embryonated eggs 3. Cell culture
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect specific bacteria
Well studied example of a virus life cycle because they are easy to grow
Bacteria is easy to grow
Bacteriophages are easy to grow
Bacteriophages – 2 possible types of infections cycle
Lytic cycle: Ends with cell lysis
Host cell dies
Lysogenic cycle: Virus is carried in the host genome
Host cell remains alive
Multiplication of Animal Viruses pt 1
Attachment
Penetration/entry
Uncoating
Biosynthesis
Maturation and release
Viral capsid assembles spontaneously around the viral nucleic acid
Multiplication of Animal Viruses pt 2
Attachment
Penetration/entry
Uncoating is the separation of the viral nucleic acid from its protein coat
Non-enveloped – capsid digested by virl or host enzymes and viral enzymes allow the genetic material to escape the vessicle
Enveloped – performed by host enzymes (proteases) in the host cytoplasm
Biosynthesis of DNA viruses
Viral DNA replicated in host nucleus
Viral proteins made in the cytoplasm
Viral proteins migrate to the nucleus to join the DNA and assemble into virions
Virions transported through host endoplasmic reticulum for release
Both viral RNA AND proteins synthesized in the cytoplasm
Virions assembled in the cytoplasm
Biosynthesis of Retroviruses
Viruses have a ds RNA genome and make reverse transcriptase
Make a ds DNA copy of their RNA using the reverse transcriptase and incorporate the DNA into host cell genome as a provirus
Provirus can remain latent in the genome or be expressed to create virions
E.g. HIV can remain latent for years before it starts replicating
Viruses and cancer
Infectious cancer first observed in mice and chickens in early 1900s
A viral cause of cancer in humans was hard to recognize
Virus discovery part 1
1892: Ivanovsky - found the aagnt of tobacco mosaic diseases passes thru filter that retain bacteria
1898: Beijeernick made some finding but suggested that pathogen was distinct agnt
Virus discovery part 2
1898: Loeffler & Frosch: agent of hand foot mouth disease is filterable
agents small and only replicate in host. 0.2 micron filters
Virus discovery part 3
1901: first human virus, yellow fever
1903: rabies
1906: variola
1908: chicken leukemia virus, poliovirus
1911: rous sarcoma
1915: bacteriophages
1923: influenza
Darwinian machine
model for survival of fittest concept: too successful viruses may kill host and eliminate themselves. passive viruses may be eliminated