Liver, Pancreas, and Biliary Tract Dx
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Pancreas
The pancreas has an endocrine function because it releases juices directly into the bloodstream, and it has an exocrine function because it releases juices into ducts.
Exocrine - it helps with the digestion of food
Enzymes, or digestive juices, are secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine. There, it continues breaking down food that has left the stomach.
The pancreas also produces the hormone insulin and secretes it into the bloodstream, where it regulates the body’s glucose or sugar level. Problems with insulin control can lead to diabetes.
endocrine function of pancreas
helps with the regulation of sugar with insulin
exocrine function of the pancreas
it helps with the digestion of food - fats, CHO, protein
bile excretion & storage in GB
toxin metabolism—> alcohol
Blood coagulation→ metabolism of RBC into bilirubin
enzymatic function-→ trypsin, lipase, amylase
pancreatic disorders: pancreatitis
Inflammation of pancreas presenting in two forms (acute and chronic) that have different courses and must be considered as two different disorders. Disease can ranges from mild inflammation to hemorrhagic complications.
Major complications of pancreatitis is hemorrhage
If the patient has pancreatitis, the function is diminished
- Not able to regulate glucose
Issues with digestion/ excretion
Acute Pancreatitis + common causes
Inflammation of the pancreas
Present many times with life-threatening conditions
Causes—most common
Alcohol
Obstruction- Gallstones
Trauma/Biliary tract disease
Viral Infections
Drug hypersensitivity (BB)
gallstones causing pancreatitis
If bile contains too much cholesterol, too much bilirubin, or not enough bile salts, gallstone is formed.
Gallstones are a common cause of pancreatitis. Gallstones, produced in the gallbladder, can slip out of the gallbladder and block the bile duct, stopping pancreatic enzymes from traveling to the small intestine and forcing them back into the pancreas. The enzymes then begin to irritate the cells of the pancreas, causing the inflammation associated with pancreatitis.
Move through the common bile duct
- Enzymes in the pancreas is inactive but when the duct is blocked, the inactive enzymes become activated in the pancreas causing a lot of pain
- The enzymes are supposed to be activated in the small BI
- Stones moves through the common bile duct and blocks the duct, preventing the inactive enzymes in the pancreas from traveling through SI
- The enzymes become active in the pancreas eating it, causing pain and inflammation
→ Trypsin→ lipolysis, proteolysis
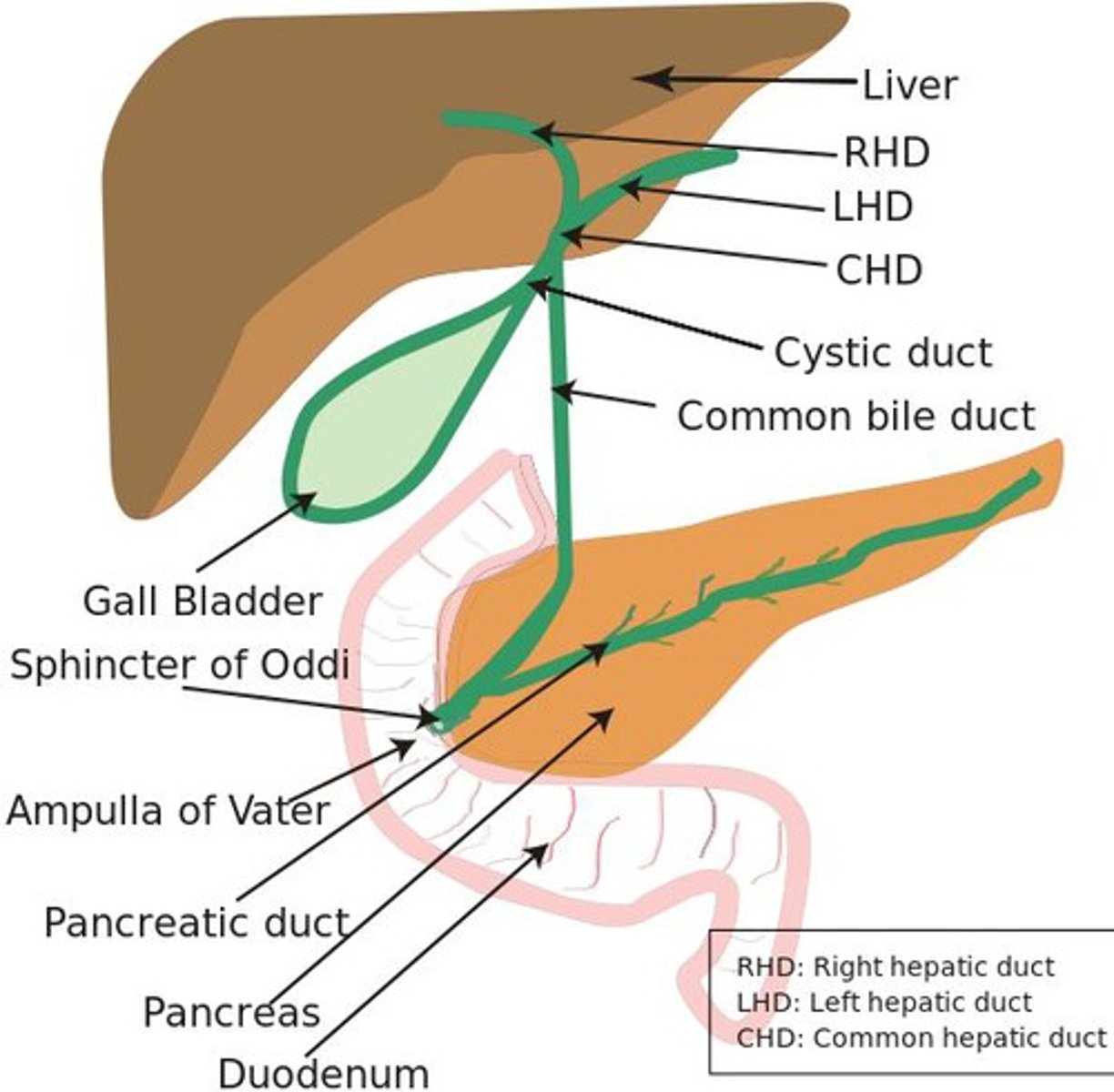
gallbladder + function
part of the digestive system.
Function= storage of bile
Bile helps the digestive system break down fats
Pathophysiology of Acute Pancreatitis & cx
loss of intracellular and extracellular compartmentation, by an obstruction of pancreatic secretory transport and by an activation of pancreatic enzymes.
Pancreatitis occurs when digestive enzymes become activated while still in the pancreas, irritating the cells of the pancreas and causing inflammation. With repeated bouts of acute pancreatitis, damage to the pancreas can occur and lead to chronic pancreatitis.
Autodigestion of organ
ETOH and biliary disease
Infections such as mumps, scarlet fever and endocrine disorders
Enzyme activation
Major concern is hemorrhage
trypsin
enzyme that helps us digest protein
Trypsin is produced by the pancreas in an inactive form called trypsinogen. The trypsinogen enters the small intestine through the common bile duct and is converted to active trypsin.
lipase
amylase
pancreatic enzyme necessary to digest fats, turns fat into glycerol
pancreatic enzyme necessary to digest carbs
Acute Pancreatitis: Assessment/clinical manifestations
Sudden onset of epigastric pain—upper left quadrant or mid-abdomen
- Severe pain
- Pain can radiate to left flank/ back
- Deep and very sharp pain
N/V/anorexia
- Nursing intervention is to watch for dehydration
- Raise HOB
- admin isotonic IV, fluid replacement NPO
Abdominal fullness
- Too many things going on in the body
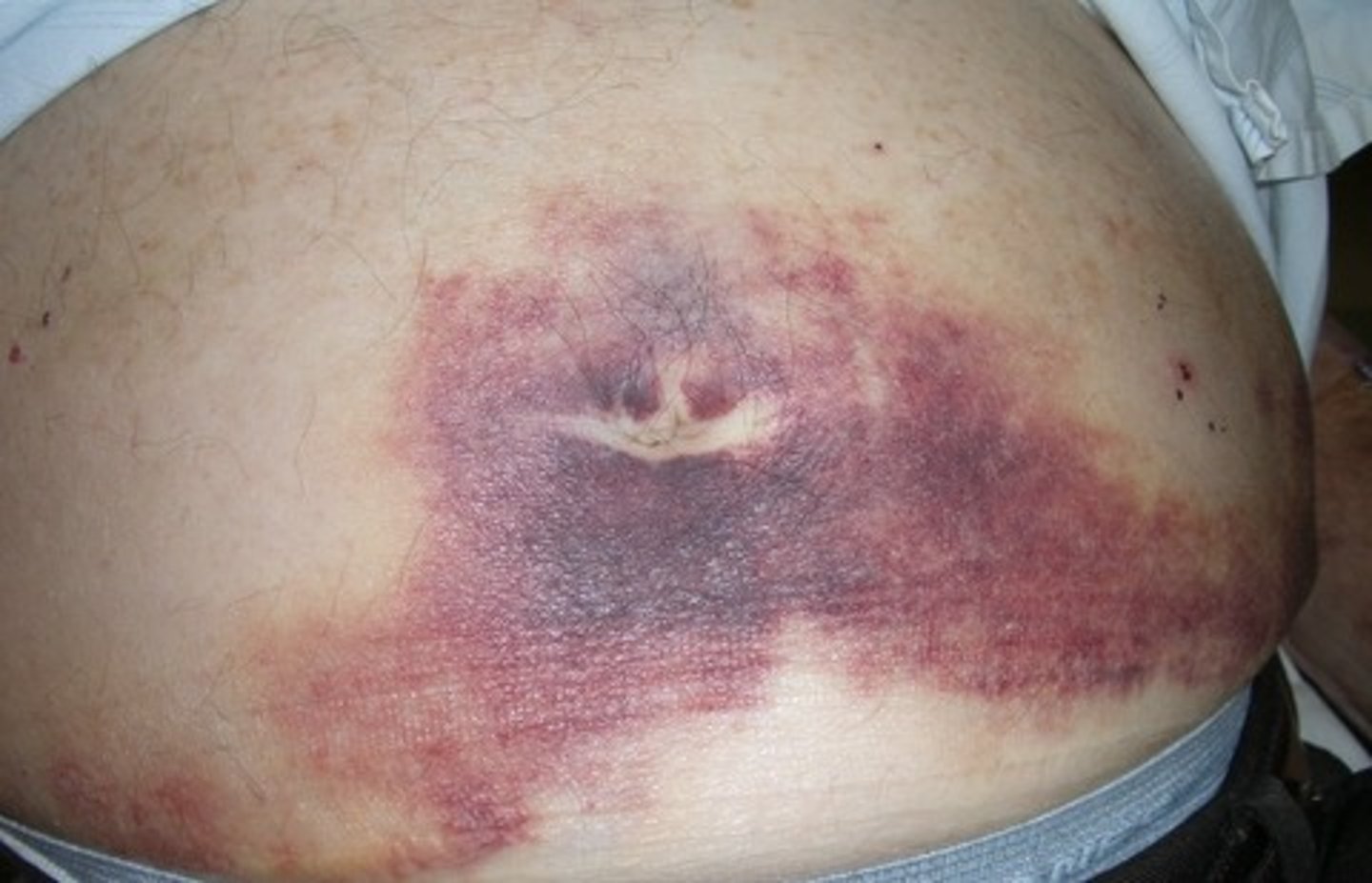
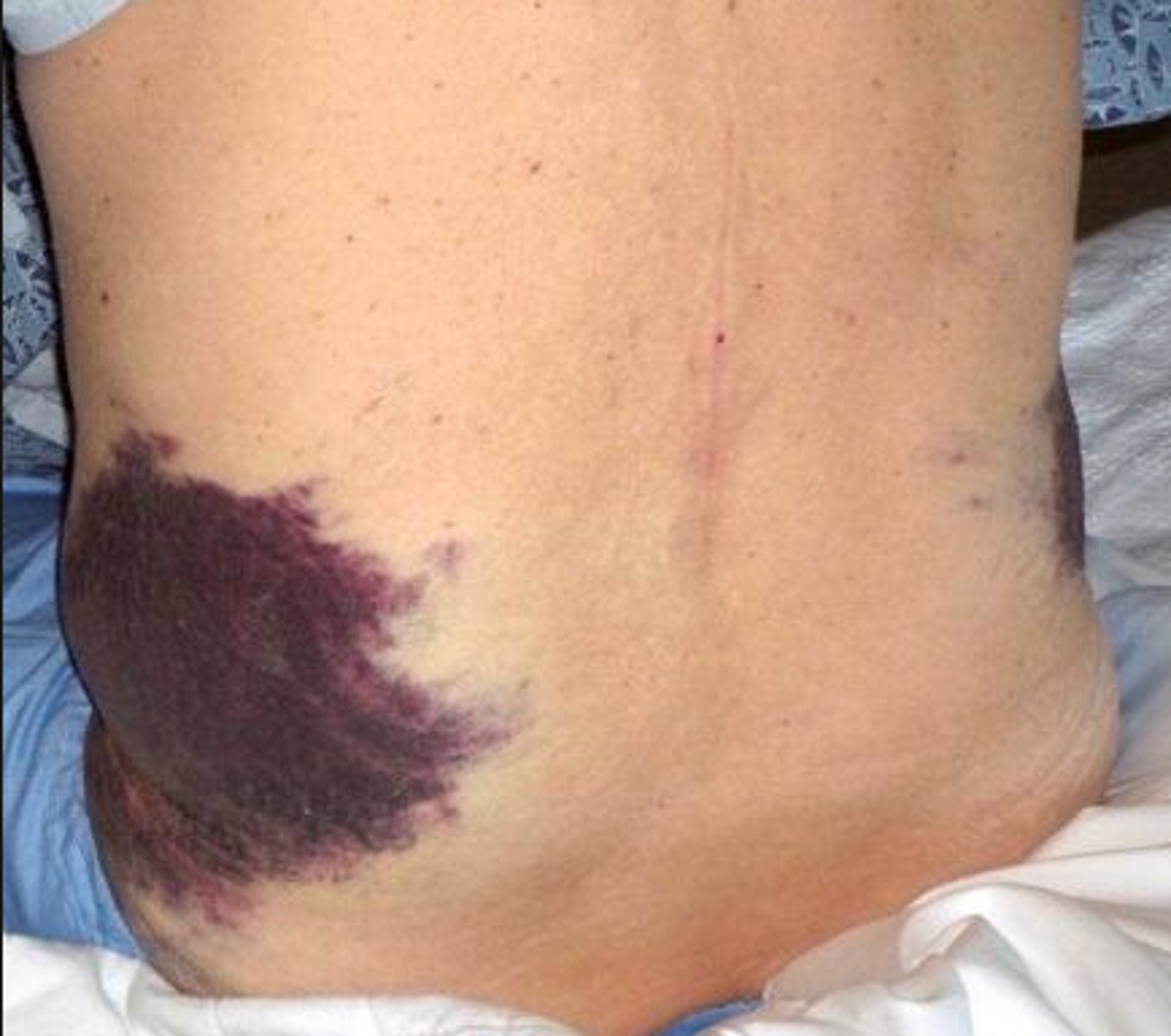
Cullen’s sign – indicates hemorrhage
- Redness within the umbilical region
- Sign of hemorrhage
Grey Turner’s sign- indicates hemorrhage
- Redness on the flank area
- Sign of hemorrhage
Steatorrhea, clay-colored stools
- Fatty stools
Islets of Langerhans are usually not impaired.
- Alpha (production of glucagon) and beta (production of insulin) cells
Respiratory distress due to accumulation of fluids in retroperitoneal.
- Fluid accumulation near the kidney→ Kidney disease
- Can have SOB and crackles, dyspnea
Labs: increased amylase, lipase, leukocytosis, WBC, glucose, C-reactive protein
If complications present
- Hypotensive, tachycardia
- Fever, abdominal rigidity, tenderness & guarding (peritonitis)
- Decreased bowel sounds
- Decreased lung sounds or adventitious breath sounds
Positive Trousseau’s or Chvostek’s sign
- Low calcium (fat necrosis)
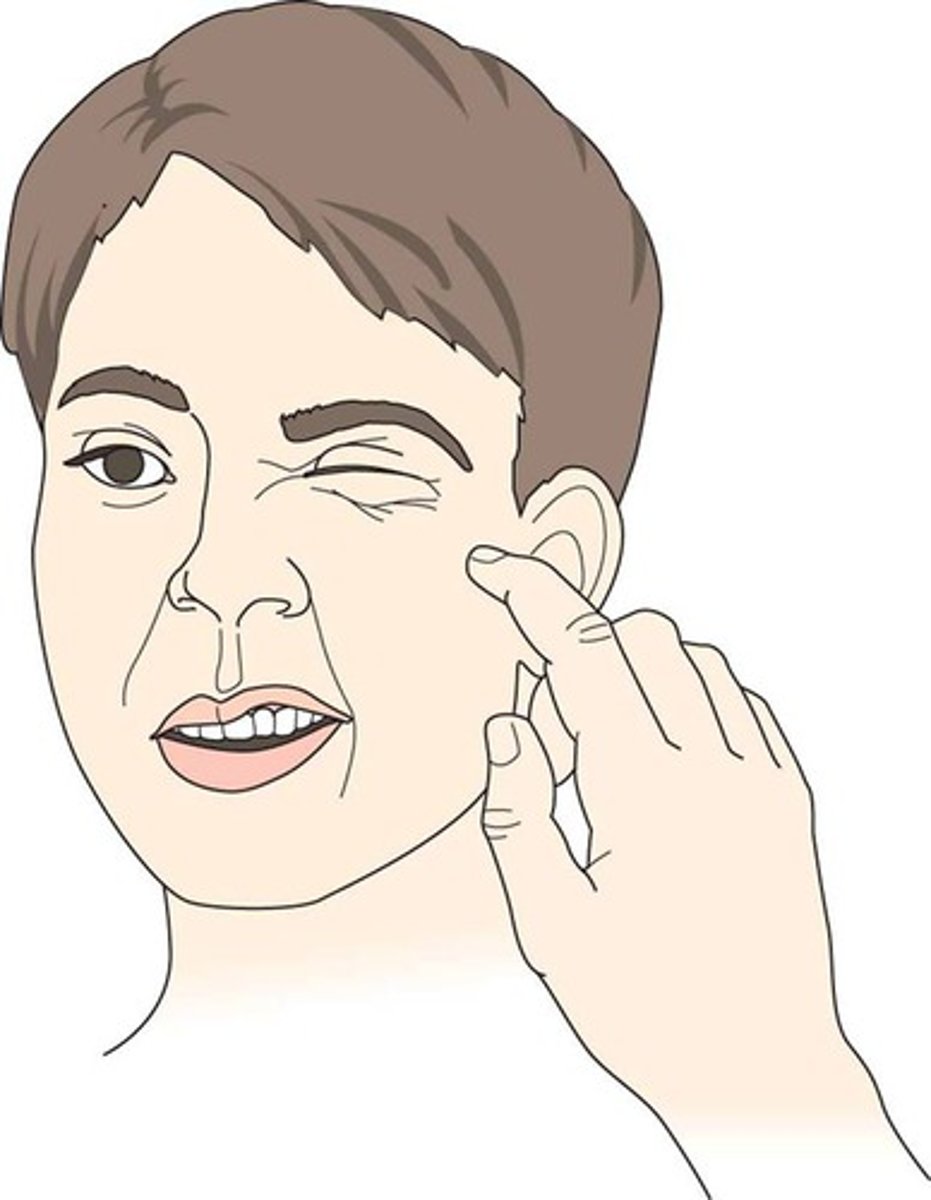
Chvostek's sign
twitching of facial muscles in response to tapping over the area of the facial nerve
Tap near the cheek and see if the face twitches
Low calcium can be a sign of hypoparathyroidism
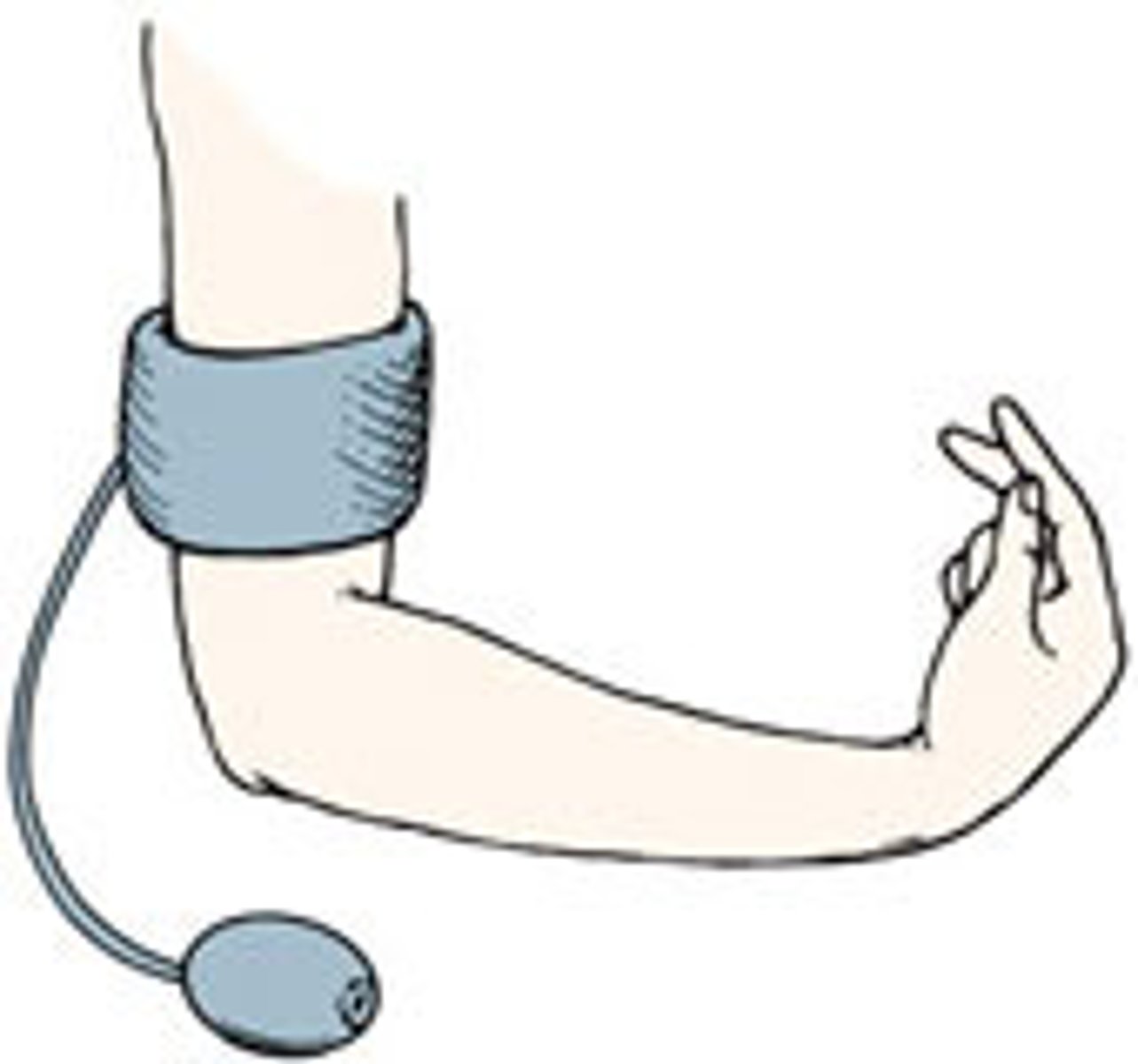
Trousseau's sign
carpopedal spasm (spasms that are extremely painful cramps or contractions that mostly occur in the hand and feet muscles) that results from ischemia, such as that induced by pressure applied to the upper arm from an inflated sphygmomanometer cuff
Inflate the BP cuff, start complaining of spasms in the arm
Low calcium can be a sign of hypoparathyroidism
Cullen sign
hemorrhagic discoloration of the umbilical area
Hemorrhage
Grey Turner sign
discoloration (Grey Color) of the left flank associated with acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis.
Hemorrhage
Acute Pancreatitis Diagnostic Assessment
Amylase
Lipase
Trypsin
Elastase
CBC
- WBC
BMP
- BUN/CR
-- Creatine may be high bc of kidney impairment
- Glucose—may be elevated
-- Pancreas infected, beta cells infected, insulin not produced, blood glucose is high
- Ca & Mg—may be decreased
LFT
- Associated with gallstones, liver involvement
- Gallbladder and liver work complementary to each other
CT scan- most accurate diagnostic test
MRI
Abdominal ultrasound
Acute Pancreatitis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - NPO
NPO
When you eat food, body releases enzymes, this causes more irritation to the pancreas→ PAIN
May require TPN if NPO for prolonged period or jejuna TEN
Daily weights & I&O- Document any changes
- If they are throwing up, want to see if they are becoming emaciated
If on TPN—monitor F&E status, blood glucose, monitor for infection
If on TEN—monitor for residuals
- Aspiration
- 150CC and above - put it back, notify doctor, and hold feeding for 2 hr
Once eating—small frequent meals
- Moderate to high carbs, high protein, low-fat meals
- Low fat cause high cholesterol leads to gallstones
- Do not want dumping syndrome
NPO patients, monitor their glucose q 6
- Want to make sure that sugar does not drop low
Acute Pancreatitis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - other interventions
IV Fluids
- Dehydration from throwing up
Replacement of Ca and Mg
- Usually low and need to be compensated
NGT—for severe pancreatitis
- Bc they are throwing up a lot, to decrease the stomach
- Intermittent suction to allow for rest
-- Continuous suction is drastic and can cause bleeding to the stomach
Acute Pancreatitis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions: pain management
Side-lying with legs draw up to chest (fetal position) most comfortable to decrease abdominal tension
- Also decreases the secretions of those enzymes
- Not supine or prone, or raise HOB
Opioids- hydro/morphine
PPI-zoles’ &/or H2RA- famotidine
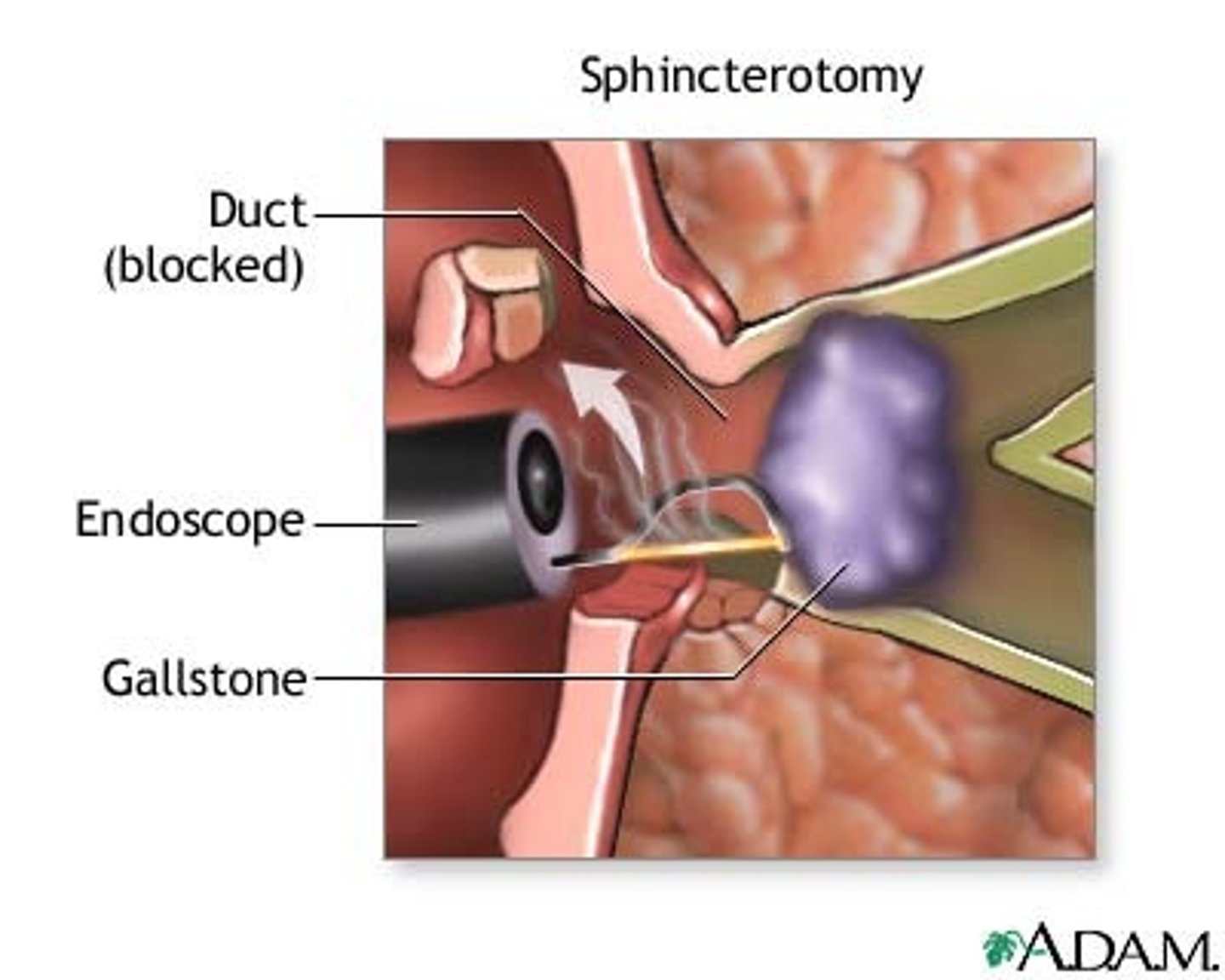
Acute Pancreatitis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions: Sphincterotomy
(remove common bile duct/Stone)
If caused by gallstones
Opens sphincter of Oddi
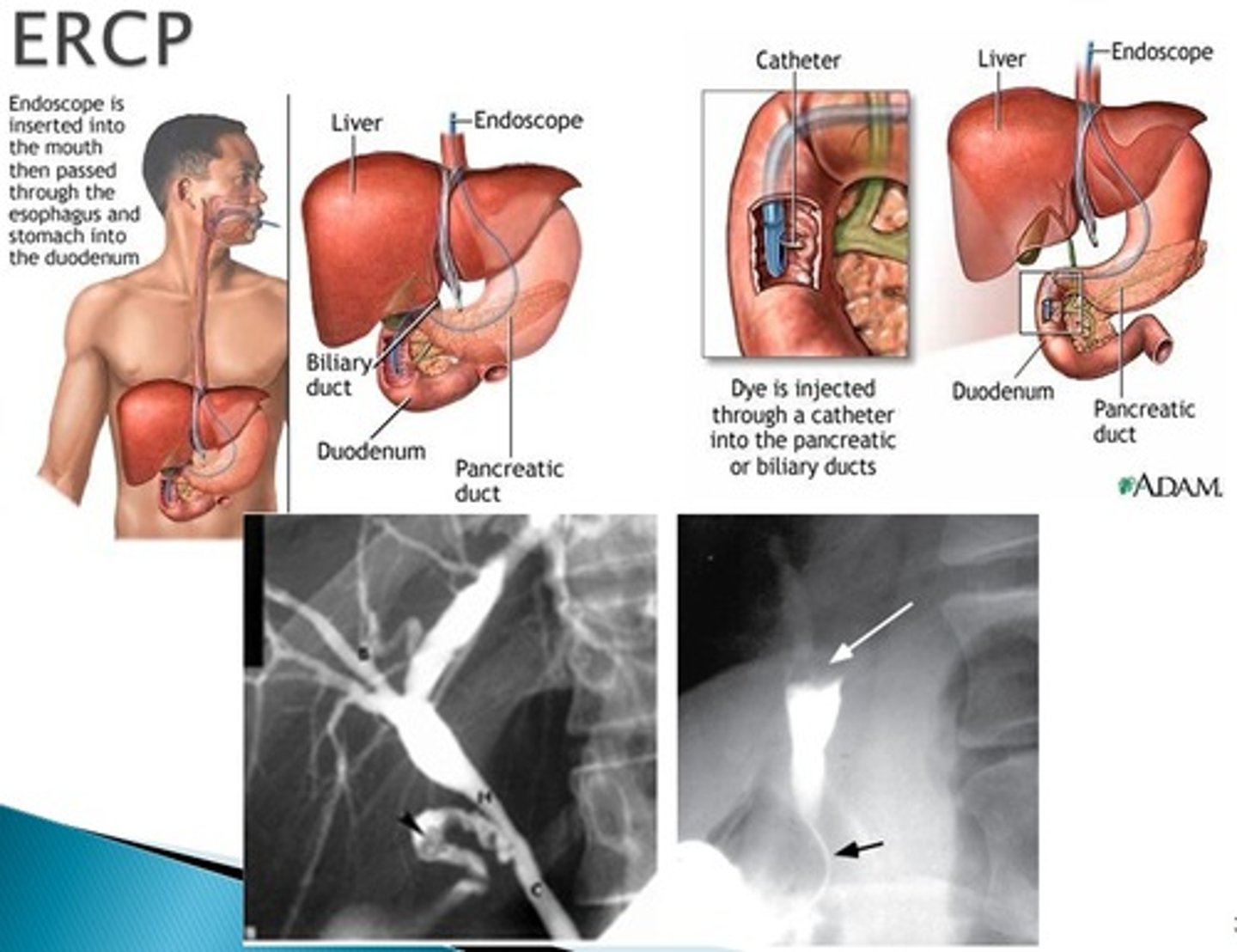
Acute Pancreatitis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
ERCP used diagnosis and treatment
MRCP is only used for diagnosis (perfered bc it has a small mortality rate)
NPO
Consent is required
MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography)
non-invasive, useful for imaging the gallbladder, bile ducts and surrounding tissues but does not offer a way to treat the disease found
US is less expensive and easier test to perform for the diagnosis of cholecystitis
Acute Pancreatitis Complications
Necrotizing Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis
- Infection in the pancreatitis
→ Low grade fever,
Hypovolemic shock
Pancreatic hemorrhage and pancreatic pseudocyst
AKI
ARD’s
Acute Pancreatitis Summary of treatment
NPO
Fluids and Electrolyte replacement
- Calcium and magnesium
Pain control
Nutrition Support/TPN
NG/Bowel Rest
- Decompress the stomach
Surgery to Remove source
cholysysectomy
Secondary Prevention
avoid fatty foods, alc, caffeine
Chronic Pancreatitis
Most common cause is prolonged, heavy, alcohol use
Similar signs/symptoms of acute Pancreatitis
- Same symptoms but the difference with chronic is that it comes and goes (remission and exacerbation)
Acute pancreatitis once you have it, does not happen again
Complications:
T2 DM. [c/b damage to panc cells]
DEC bicarb.
Pleural effusions [r/t
Pancreatic ascites [r/t FVO]
Chronic Pancreatitis treatment
TX: Lifelong abstinence from alcohol
Pain management
Lifelong pancreatic enzyme replacement
CP SRG Tx
indicated: ongoing pain, reoccurring episodes, cx- pseudocyst or abscess
Laparoscopy- drain abscess
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy- incision made in CBD
sphincterotomy- enlarge sphincter
Pathophysiology of Chronic Pancreatitis
Continuous, progressive, and irreversible destructions of cells, with replacement with fibrotic tissue.
Alternating periods of remission and exacerbation
Clinical Manifestations of chronic pancreatitis
Characterized by remissions and exacerbations
Intense, unrelenting pain is the hallmark
Hypocalcemia due to increased serum lipids, which bind with free calcium
Symptoms of malabsorption, especially of fats (steatorrhea, weight loss).
Diabetes mellitus develops later in disease due to malfunction of islets of Langerhans.
- Beta cells are damaged (BG regulatory issues)
Mean duration of the disease is 25 years after diagnosis; death is often not related to pancreatic failure.
- Usually bc they have necrotizing pancreatitis
Medical and Nursing interventions of chronic pancreatitis
Diet
Initiate and maintain a low-fat, high-carbohydrate, low-protein diet to provide rest to organs.
Teach
importance of taking enzyme supplements after every snack and meal. [PERFT]
→ Viokase, Cotazym (with meals)
- Will need this supplement for the rest of their life
Monitor stools for fat to help determine pancreatic enzymes
enzyme for fat digestion
Explain to the patient the importance of avoiding ETOH [avoid alc pls] & unnecessary drugs
Medical and Nursing interventions of chronic pancreatitis: surgical interventions
may be performed to remove the source of problems (gallstones. Psuedocysts), removal of necrotic pancreatitis tissue, or repair problems with the biliary system
pancreatisis Continued Care and rehabilitations
Patient with acute pancreatitis may never experience another episode but should be counseled to exercise moderation in food and alcohol intake.
Patients with chronic pancreatitis will experience remissions and exacerbations of the problem.
- Pain management will be constant problem; counsel regarding excesses in alcohol, adherence to diet and medication regimen.
- Diabetes mellitus may develop several years after diagnosis- patient education. [consult w/ CDE, may need insulin due to beta cell damage tx]
Pancreatitis Evaluation
Patient remains complication free
Patient verbalizes medical treatment plan
Pain free or at acceptable levels of pain [3-4/10]
Maintains weight (or gains if necessary)
Abstains from alcohol
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by the presence of gallstones (cholelithiasis)
Gallstones in the gallbladder causes inflammation (cholecystitis)
Key features of Cholecystitis
Upper ABD pain
N/V
dyspepsia
eructation [burping]
flatulence
fever (in some cases)
cholelithiasis [actual gallstone present]
Presence of the stone (cholelithiasis)
Patients with cholecystitis has cholelithiasis
Patients with cholelithiasis does not necessarily have cholecystitis
Cholecystitis Etiology and pathophysiology
Stone development usually occurs in individuals with consistently high blood cholesterol levels
Stasis of bile in gallbladder results in aggregation of particles leading to stones.
Lodging of stone in neck of gallbladder or common bile duct results in symptoms
Cholecystitis Clinical Manifestations
Pain: biliary colic or epigastric pain that may radiate to right shoulder; usually occurs after a heavy meal or lying-down position.
RUQ tenderness, rigidity.
Nausea, vomiting, indigestion especially after ingestion of fat.
Signs/symptoms of inflammation: fever, increased WBC.
Jaundice with bile duct obstruction.
May be asymptomatic.
Murphy’s Sign (Pain on palpation under the rib cage during inspiration) = cholecystitis
- Raise right arm up, take a deep breath and hold it, tap the abdomen, patient will complain of pain, sign of inflammation of the gallbladder
Cholecystitis: Diagnostic Assessment
- important test for gallbadder
Abdominal x-ray
- Trying to find stone and x ray in the gallbladder
Ultrasound
- Trying to find stone in the gallbladder
Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan (HIDA)
- Most important test for gallbladder
- Patient will be NPO for 4 hours
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Cholecystography - allergic to iodine
Cholangiogram - allergic to iodine
CBC
- Elevated WBC
LFTs
- Elevated
- Anything that involves the bile duct - liver enzymes will be elevated
ACUTE Cholecystitis: FE balance & Pain mx
NPO
IV hydration
- Bc of N/V
Correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances
Pain & nausea management [analgesics & antiemetics]
NGT
decompress from gastric secretions
Cholecystitis: Lithotripsy Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
nonsurgical alternative to manage gallstone to relieve stones
Lithotripsy
uses radiofrequency to break apart gallstone into pieces
Pre-Op
Informed consent
Post-Op
Monitor I&O for elimination of stone
send stone to lab
Cx associated w Procedure
Cholecystitis: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy [OPEN] **
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (too big of a stone, open cholecystectomy)
- Put CO2 in the stomach fill it up for more space
- Expected to find shoulder pain, CO2 that has migrated to shoulder
T-tube assessment
- Monitor T-tube output
- Protect the skin from bile drainage
- Anchor T-tube to prevent accidental dislodgement.
May include common bile duct exploration (CBDE or Cholechodotomy); this requires an open procedure
Big surgery
Transhepatic biliary catheter to relieve bile duct obstruction
- Catheter goes into the biliary to take out the stone
Cholecystitis: Diets and med Mx
Diet
-AVOID Fatty foods, red meats, heavy alcohol (will exacerbate the stones)
Medications
- Ursodiol, Actigal, chenodeoxycholic acid to dissolve stones
- Cholestyramine for pruritus
Itching because of an increase in Bile
- Fat soluble vitamins.
Cholecystitis: Patient Education
Conservative treatment includes low fat diet, weight loss program
- Most patients that have cholecystitis are overweight
Following cholecystectomy, fats are slowly introduced to diet
Once duodenum becomes accustomed to constant infusion of bile, dietary restrictions only based on individual intolerance.
Teach about pain medications: analgesics, NSAIDs, anticholinergics to reduce spasms.
- AVOID Aspirin/salicylates, patients with GERD/upper GI problem should not take aspirin because of risk for bleeding
Liver Disorders: Cirrhosis
Extensive, irreversible scarring of the liver
Post necrotic cirrhosis
Caused by viral hepatitis, certain drugs, or toxins
Laennec’s or alcoholic cirrhosis
caused by alcohol
Biliary cirrhosis or cholestatic
Caused by chronic biliary obstruction or autoimmune disease
S/S
Ascites
Jaundice
itching c/b INC bilirubin.
Cirrhosis: Liver Functions - storage
minerals and vitamins
Iron, Magnesium, Fat Soluble Vitamins (DEAK)
Cirrhosis: Liver Functions - protective
Kupffer cells
- Engulf harmful bacteria and anemic red blood cells
- Destroys and engulfs any bacteria in the body
Detoxifies
- Any toxins in the body i.e alcohol & drugs
Cirrhosis: Liver Functions - metabolsim
Amino acids—broken down into urea and excreted by kidneys
//Cx= increased urea→ increase ammonia→ TOXIC to brain=Hepatic encephalopathy.
Synthesis of plasma proteins
- Albumin, prothrombin, and fibrinogen
//Cx = risk of bleeding
Storing and releasing of glycogen
- Liver stores glycogen, so when body needs more glucose, converts the fat into glucose
Synthesizes, breaks down, and temporarily stores fatty acids and triglycerides
Production of antibodies
- Antibodies help to fight in the immune system
Cirrhosis Complications
Portal hypertension
- The pressure in the hepatic vein gets high bc of the build up of metabolism in the body
Ascites and esophageal varices
- Swelling of the stomach
- Metabolites in the body
Coagulation defects
- No thrombin
Jaundice
Portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) with hepatic coma
Hepatorenal syndrome
- Liver affected, the kidney's can also be affected
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Cirrhosis: early Compensated Cues
Slow onset
Fatigue
Change in weight
Anorexia and vomiting
Pain associated w [Abd., liver tenderness]
Abnormal LFT + thrombocytopenia (c/b hepatic cell destruction)
Advanced Cirrhosis Uncompensated Cues
End stage Liver failure
Skin:
Jaundice and icterus
Dry skin
Rashes
Petechia/ecchymosis
Palmar erythema
Spider angiomas
Ascites
Peripheral dependent edema
Both will cause Resp issues bc of fluid buildup.
Vitamin deficiency
Hepatomegaly
Splenomegaly
Caput medusa (a cluster of swollen veins in the abdomen).
Fetor hepaticus (Rotten egg smell)
- Bad smell from the mouth
Amenorrhea= blood in stools/vomit
- Hemorrhoids bc of impairment of the coagulation factors
Gynecomastia (overdevelopment or enlargement of breast in men or boys) C/b INC estrogen
Asterixis (Involuntary movement)
Change in mental status
Clay-colored stools
Dark urine
Hepatic encephalopathy
c/b increased levels of NH4
hepatorenal syndrome characterized by
oliguria- sudden decrease in urinary output <500 ml
elevated BUN/Cr with low Na excretion
increased urine osmolality (urine specific gravity/concentrated)
Cirrhosis: Diagnostic labs
Elevated LFTs
- Anytime there is an issue of kidney, gallbladder, and liver
Total protein
- Elevated—acute liver disease
- Decreased—chronic liver disease
Decreased albumin
advanced liver disease (hepatic destruction)
Elevated serum ammonia (10-20)
- Confusion, hepatic encephalopathy or ALD
Prolonged PT and INR
CBC
- Low platelet count
- Decreased H&H—with bleeding
- WBC—may be low
BMP
- Dilutional hyponatremia (ascites) or Hypernatremia
-- Low sodium because of lots of fluid in the patient stomach
- Elevated BUN/CR
→ kidney damage r/t hepatorenal syndrome
Cirrhosis: Diagnostic Tests
Plain abdominal x-rays
hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, ascites
CT scan
MRI
- MR elastography
Ultrasound
biliary stones, bile duct obstruction
EGD
visualize upper GI tract (esophageal varices, stomach ulceration, duodenal ulceration)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Liver biopsy
- To see if there is carcinoma of the liver
risk for bleeding
Jaundice
c/b biliruben build up
urine→ frothy, dark
feces→ light, grey colored
skin→ yellowing, itchy
Rx for itching
Choleycystraine [helps excrete biliruben]
benedryl
bathe reg, lotion q8h
Portal hypertension
obstruction of blood flow through liver
INC pressure in portal vein→ major vein that leads to liver
pressure backs up→ causing scarring of liver lobules
dilated veins→ esophageal varices [rectum too]
splenomegaly→ bc of turbulent blood flow out of liver
Periumbilical veins→ caput medusae
Rectal veins→ hemoroids
Most common cause of the portal hypertension is the cirrhosis of the liver
Cirrhosis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - nutrition and fluid
FLUID BALANCE:
Nutritional therapy
- Low sodium diet (1-2g/day)
- Trying to decrease the BP & fluid retention
- Vitamin supplementation (thiamine, folate, MVI)
Cirrhosis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - drug therapy
Diuretics (Furosemide, Spironolactone)
→ goal is to dec edema
- Monitor daily weights
- Monitor electrolytes and I&O
dehydration & f/e shift
Cirrhosis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - Ascites
→ Albumin and furosemide
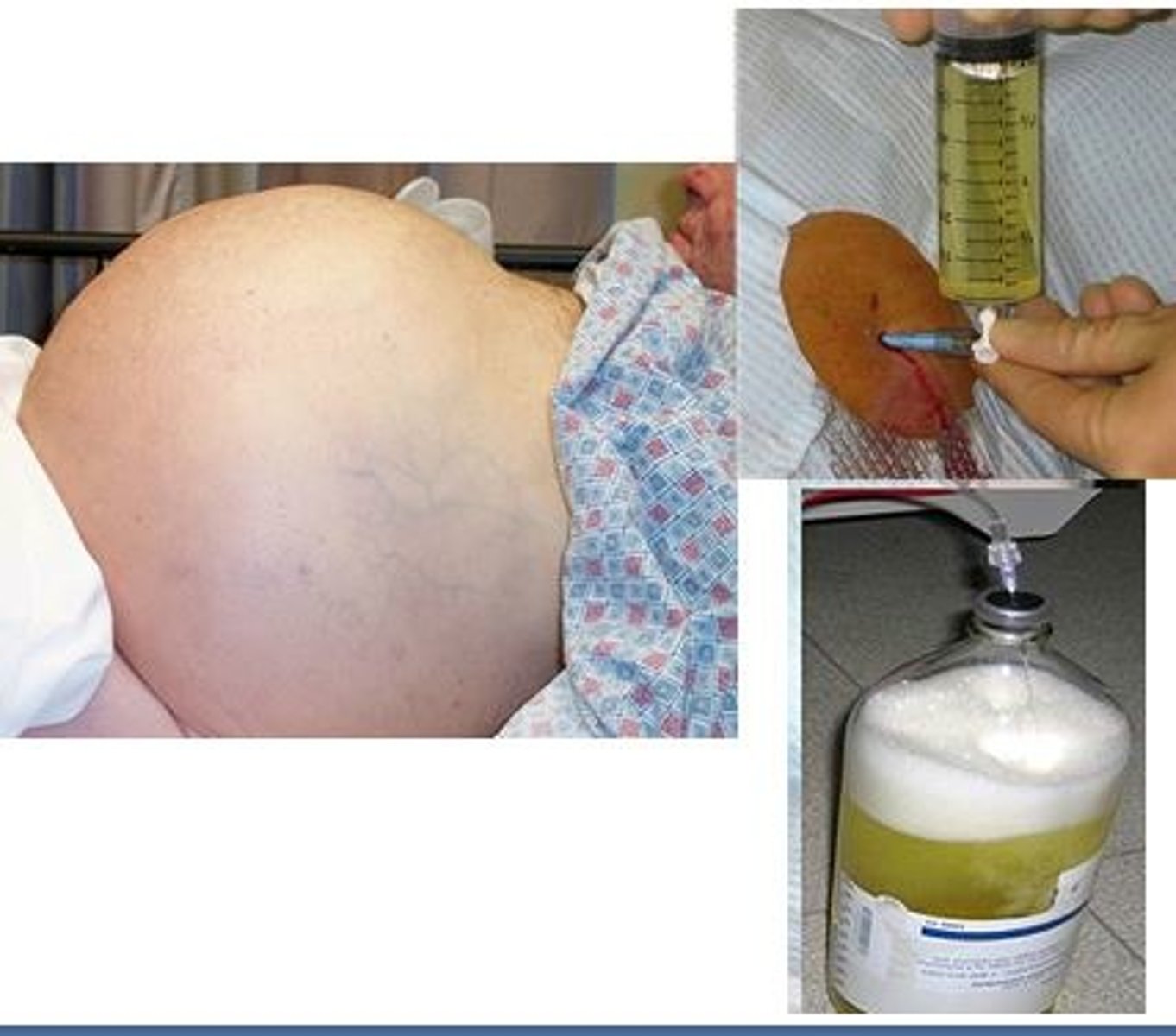
Paracentesis (insertion of the catheter in the abdomen/liver to remove the fluid)
Patient needs to be NPO for 4 to 6 hours
Assess output
Monitor VS
Pre-procedure—assess coagulation studies, void prior to procedure.
- PPT and INR because liver makes coagulants
- If this is compromised, pt will require platelet or plasma replacement before the surgery is done
- Need to void prior to procedure so there is a decrease risk in puncturing the kidney
Educate the patient on what to expect
2x2 in the stomach, stay in bed for 2 hr
Cirrhosis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions -
SBP
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) [kupner cell compromsied]
Monitor for low-grade fever
Loss of appetite
Assess bowel sounds [hypoactive] & abdominal rigidity
TX: IV cefotaxime, third-generation cephalosporins, fluroquinolones
Cirrhosis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - dyspnea and F/E
Respiratory support
- Dyspnea from increased abdominal pressure
- Fluid build up in the stomach
- Auscultate lungs sounds every 4-8 hours for crackles
Monitor F&E status
- BUN/CR, serum protein, HCT
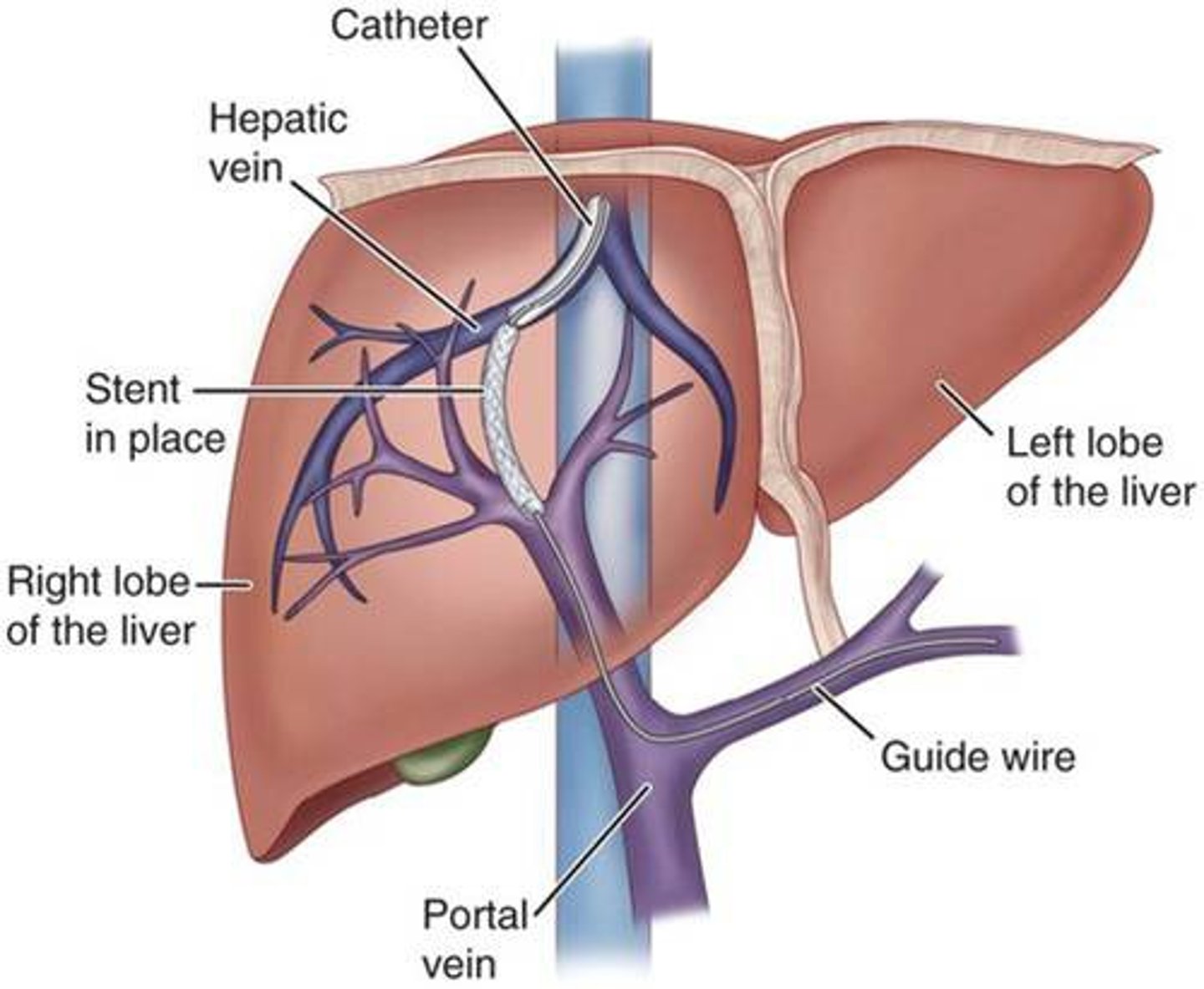
Trans jugular intrahepatic portal-systemic shunt (TIPS)
cirrhosis
preventing & managing hemorrhaging
Used to control long term ascites & reduce variceal bleeding
Helps to DEC pressure in the hepatic vein by putting a shunt in it
Bc there is too much pressure in the portal vein, connect shunt into the hepatic vein to decrease the pressure
Post OP
→ FU US to check patency of shunt
→ used to treat portal hypertension
CX of procedure & management
Hepatic encephalopathy
lactulose
INC in PAP
Diuretics
Bleeding
NG tube to assess bleeding
PRBC, plasma, dextran, albumin, platelets through 2 large bore IV catheters
**Monitor VS Q1H→ PT+PTT, INR & platelet count.
Cirrhosis: Medical Management and Nursing Interventions - Esophageal varices
→ dilated distended esophagus & gastric veins c/b INC portal HTN
Preventing bleeding
Beta-blocker (propranolol)
Sandostatin (octreotide)
DEC blood flow to GI to reduce pressure
AVOID!!→ Cough, Valsalva maneuver bc it DEC abd pressure
IF Rupture or bleed occurs…
MONITOR→ hypovolemic shock, fluid resuscitation [2 large bore IV caths]
Blood products: PRBC, plasma, albumin
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Endoscopic variceal ligation (banding)
small o shape band placed around varices
Sclerotherapy→ Inject blood to varicose vein to shrink
TIPS→ portal vein stent to relieve pressure from portal vein & DEC PAP
Sengstaken-Blakemore tube (Emergency tube to stop bleeding)
- NG tube to evacuate the stomach and put a stomach to stop the bleeding
TIPS (Hepatic vein to portal vein shunt)
Hepatic encephalopathy
Medical Management and Nursing Interventions
Encephalopathy (craziness because of ammonia in their brain, build up of metabolites in the brain)
Nutrition therapy
Moderate protein and fat and simple carbohydrates
If you give them a lot of protein, the more ammonia they will build up
- Bc liver is not taking care of ammonia in the body
Monitor drug therapy
Opioid, sedatives, and barbiturates
Opioids are metabolized in the liver
Medication therapy
Lactulose (will cause patient diarrhea)
- Helps promote excretion of ammonia in stool
- Bowel movement is expected
- Potassium will drop
- Monitor for hypokalemia and dehydration
Antibiotics
- Neomycin, rifaximin, metronidazole
Monitor for changes in LOC, asterixis, fetor hepaticus
Thiamine and benzodiazepines if patient at risk for alcohol withdrawal.
- Benzodiazepines if the medication of choices for alcohol withdrawal
- Give them thiamine bc liver is the powerhouse of vitamins and they are not making them vitamins
Cirrhosis: Evaluation
Patient Verbalizes knowledge of disease process
States prevention of complications
Discuss common therapeutic modalities
Splenomegaly Mx [cirrhosis]
→ spleen enlarged due to portal HTN
Causes destruction of
WBC, RBC & platelets→ thrombocytopenia
MONITOR: petechia, hemorrhage, bruising & bleeding
RISK 4: falls
Edema & ascites Mx [cirrhosis]
INC P HTN & DEC albumin→ decreases colloidal osm. pressure→ edema
free fluid in peritoneal cavity [“third spacing”] → ASCITES
causes sodium & water retention
Managment
Paracentesis
Monitor→ I&O, abd girth, VS, electrolytes, BS
CX→ SBP
SPB s/s: low grade fever, loss of appetite, reduced UO, INC urine osm. & INC BUN/Cr, change in mental stat.
Drug Tx
cephalosporins
fluroquinolones
Diuretics
2 types: Furosemide & Aldactone
Monitor!! Hypotension, DEC B/p due to fluid loss
Diet
low sodium diet!!
Paracentesis (NOT CURATIVE)
Pre-OP
→ check weight, VS, VOID! to avoid kidney damage
→ check PT,PTT → Give albumin tranfusion
to avoid hypotension & renal dysfunction
Post-OP Teaching
position→ sitting
Drainage amount & specimen collection
VS, weight, hypovolemia s/s [dec b/p, inc HR, thready pulse]
HOME Mx
plleurX
Hep enceph Cues
Etiology→ ammonia buildup
c/b liver being unable to convert ammonia into urea after protein breakdown.
Cues
changes in mood
hyperflexia
confusion
hallucinations
Worsening s/s
fetor hepaticus
asterixis
HPE Mx- diet & drug
Goal: lower NH4 levels
Diet: mod protein, INC CHO & mod fat
Meds:
Lactulose: excretes ammonia
Neomycin: antibiotic: antiseptic
Levodopa: mx for hyperflexia
Assess
LOC
Serum ammonia & dec/absent asterixis.
Hepatorenal syndrome
Redistribution of BF from kidneys to periphery
→ azotemia & oliguria
CUES:
DEC UO
INC BUN/Cr & dilutional hyponatremia
UA: INC urine specific gravity
Nursing MX goals for cirrhosis
SAFETY!
Mx/prevent hemorrhage
Mx/prevent HPE
Mx FVO
Hep A route of transmission
Fecal-oral
Contaminated water or food
Hep B+C route of transmission
Percutaneous or mucosal
Blood, body fluids, needles or sharp instruments
Same way you get HIV
HepB: HbsAg
Immunoglobulin
vaccines available
Hep A acute or chronic
acute
Hep B acute or chronic?
both
Hep C acute or chronic
chronic
Hepatitis vaccines?
Hep A and Hep B
no vaccine for C, but there is a cure
Hep treatment
A - Symptomatic
- treated on when symptomatic
B - Interferon and antivirals
Hepatitis - clinical manifestations
Symptoms intermittent or ongoing
- Low-grade fever
- Malaise
- Fatigue
- Myalgia/arthralgia
- Right upper quadrant tenderness
- Enlarged liver
- Nausea, vomiting
- Pruritus
- Dark urine
- jaundice
hepatitis acute phase
Sick and max infectivity
Hepatitis convalescent phase
Begins as jaundice is disappearing
Lasts weeks to months
Major complaints
Malaise
Easy fatigability
Hepatomegaly persists
Splenomegaly subsides
hepatitis recovery phase
most recover; some relapse
what causes jaundice?
when the liver is damage, it is not able to take the uncongugated billirubin in the blood stream and congugated it for it to be released by in bile
Hemolytic Jaundice
Caused by: Transfusion reactions, Sickle cell dz, Hemolytic anemia
Liver unable to handle increase load of unconjugated bilirubin in the blood
Hepatocellular jaundice
Caused by: hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver unable to take up bilirubin from blood, to conjugate it, or excrete it. Also caused from damaged hepatocytes
Might be from liver cancer
Obstructive jaundice
Caused by: Hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular cancer, common bile duct obstruction, pancreatic cancer
Liver flow decreased or obstructed by intrahepatic or extrahepatic blockage
Hepatitis - Complications
- 5 complications
Acute liver failure: Acute liver failure is loss of liver function that occurs rapidly — in days or weeks — usually in a person who has no preexisting liver disease
Chronic hepatitis-inflammation of the liver that lasts at least 6 months
Cirrhosis: is a late-stage liver disease in which healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue and the liver is permanently damaged
- Irreversible unless you get a liver transplant
Portal hypertension: Portal hypertension is elevated pressure in the portal venous system. The portal vein is a major vein that leads to the liver
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Primary liver cancer—cancer that starts in the liver—is called hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
Hepatitis: NSG Analysis / Diagnostics
Antigen vs. Antibody-
- What is the difference?
- Antigen is the disease
- Antibody is the immune system that copes with the disease
Liver biopsy
Diagnostic lab findings (liver panel)
Hepatitis: NSG Diagnosis/Planning
Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements
- Adequate calories
- Care with fat because of bile production decreased
- Vitamin supplement especially B complex and K
- Fluid and electrolyte balance
Activity intolerance
Risk for impaired liver function
- When the patient does not have liver problem
- Ex. they are heavy drinkers
Hepatitis: IP & NSG Care - acute and chronic
Rest
- Degree and strictness varies
Avoid alcohol intake and drugs detoxified by liver
Notification of possible contacts
- Maryland law requires they notify their person of contact without saying the patient name (case manager)
- Use a condem with Hep B
Drug Therapy
- Acute HAV infection: no specific
- Acute HBV infection: only if severe
- Acute HCV infection
- Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs)
Supportive drug therapy
- Antihistamines
- Antiemetics
Hepatitis: IP & NSG Care - nutrition and teaching
Nutrition Care
- Well-balanced diet; maybe low fat – why?
- Vitamins B-complex and K
-- If the patient has anemia the patient needs vitamin B 12
- IV glucose or enteral nutrition
Teaching – Ambulatory Care
Fatigue
Transmission
S&S to report
ID complications
No alcohol
No blood donation
Med admin (subcut) teaching
Chronic hepatitis B
Blood borne pathogen
Focus on decreasing viral load and slowing rate of dz progression
Drug Rx will not eradicate the virus but rather suppress vial replication
- Nucleoside and nucleotide analogues - Lower viral load by affecting viral DNA synthesis
- Interferon - Immune modulator
-- Will need liver function tests every 4-6 weeks
-- Need to be screened for depression and other mood disorders
Long term goals
- Preventing development of cirrhosis, Portal hypertension, liver failure, and hepatocellular cancer
Chronic Hepatitis C
Based on specific genotype
Care focused on preventing other concurrent health problems
Treatment primarily with direct active antivirals to block proteins necessary for HCV viral replication
- No vaccination
Hepatitis: Medical Management & Nursing Intervention drugs
Hep B
Tenofovir
- Monitor kidney function
- Can cause bone de-mineralization
Adefovir
- Monitor kidney function
Lamivudine
- Monitor kidney function
Entecavir
- Monitor kidney function
Hep C
Telaprevir
- Monitor CBC for anemia
Boceprevir
- Monitor kidney function
- Monitor liver function
- Monitor electrolytes
PegIFN/RBV
- Patient’s cannot miss a dose
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
People who have diabetes or overweight
Most important thing for them is to lose weight and not drink too much alcohol
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
causes
diagnosis
treatment
Causes:
- DM
- Obesity
- Elevated lipid profile
DX: Elevated AST and ALT
TX: Weight loss, glucose control, lipid-lowering agents
- Monitor LFTs