*****6666 Ankle and Foot!
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
foot function
weightbearing and ambulation
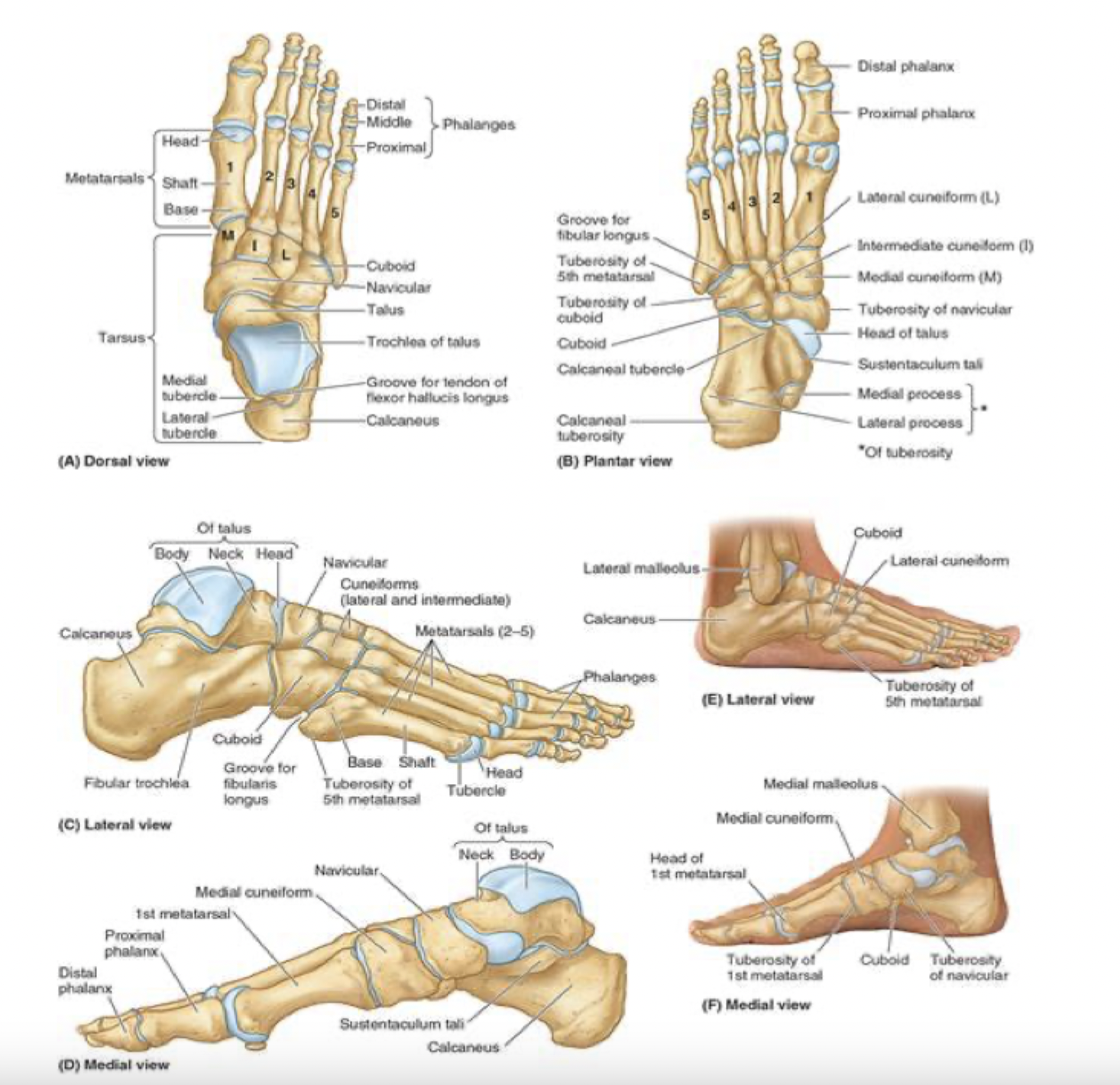
anatomical parts of the foot
hindfoot: talus and calcaneus
midfoot: navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms
forefoot: metatarsals and phalanges
regions of the foot
sole of foot (plantar)
dorsum of the foot
heel
ball of foot
big/great toe and little/5th toe
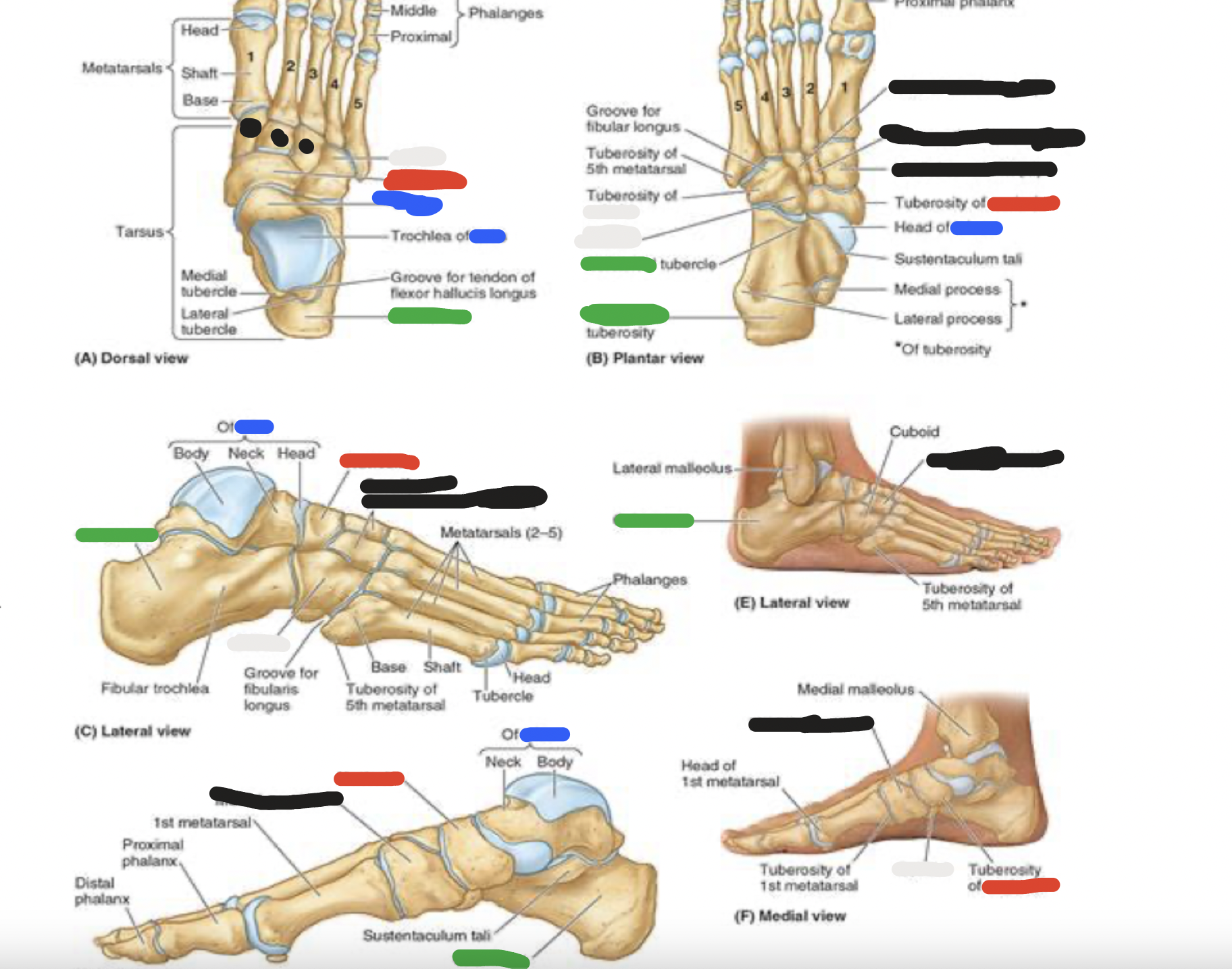
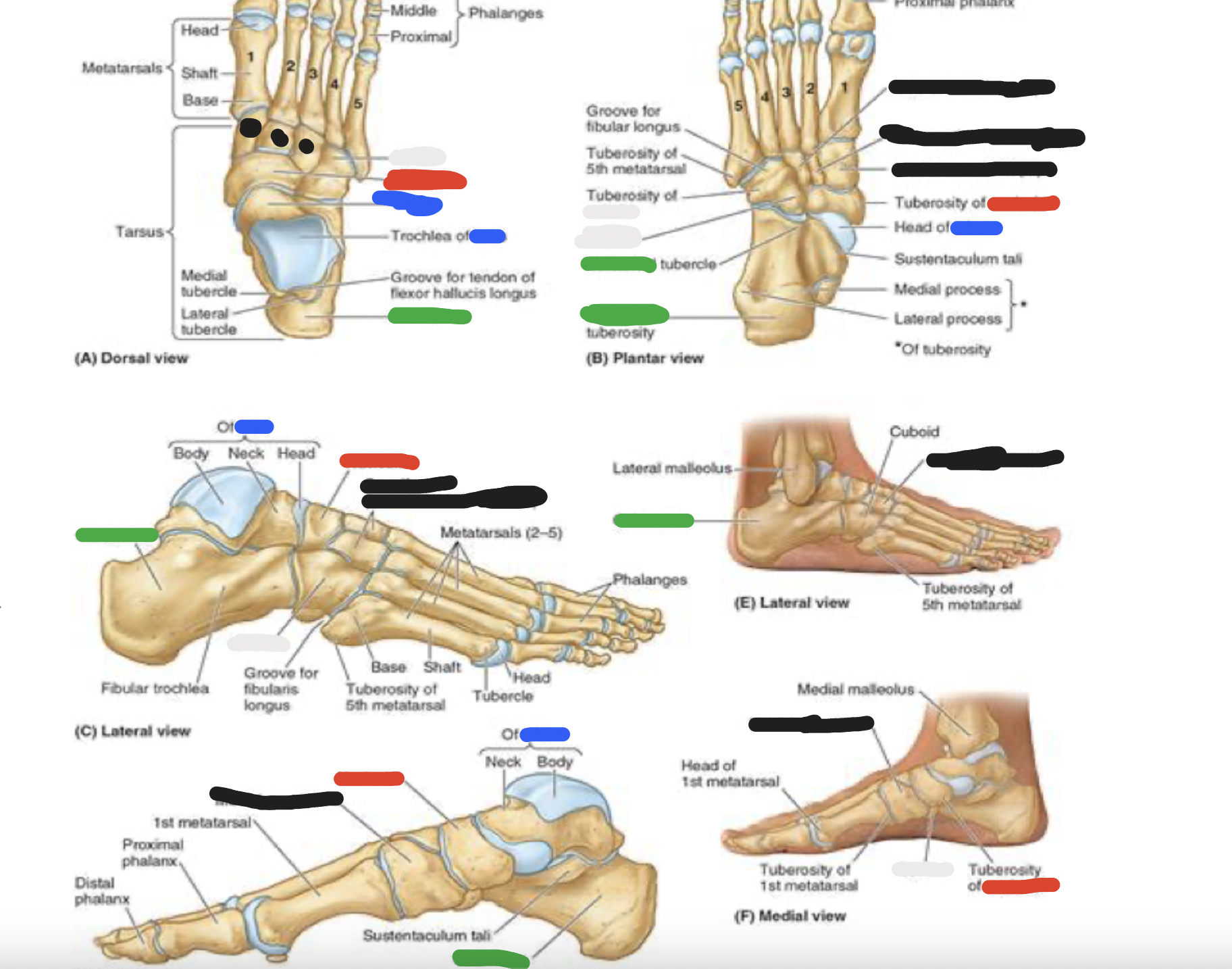
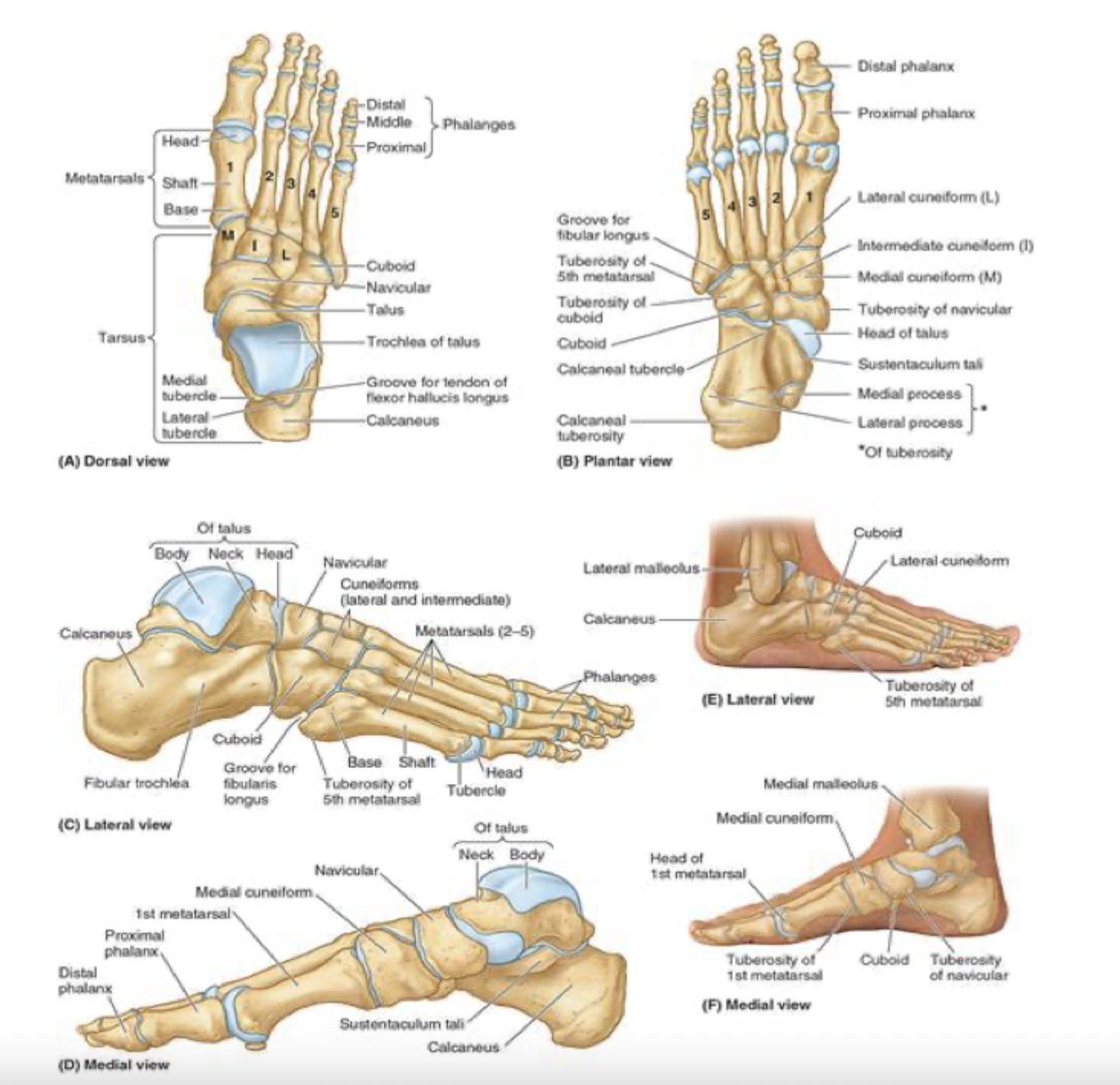
7 tarsal bones: blue
talus:
articulates with the fibula and tibia
medial to calcaneus
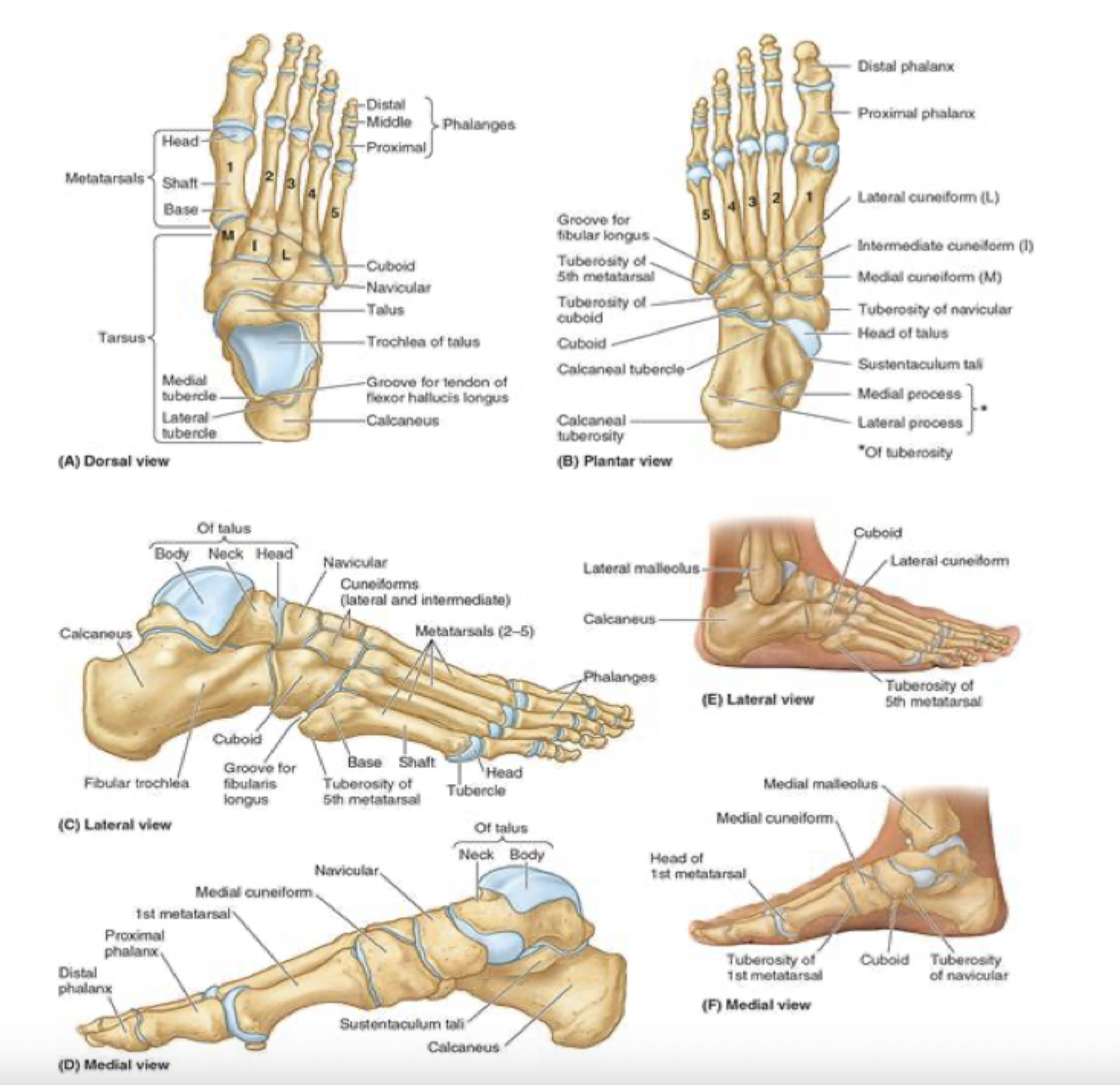
7 tarsal bones: green
calcaneus:
known as the heel bone
strongest of the heel bones
large calcaneus tuberosity on posterior aspect
articulates with the talus
7 tarsal bones: red
navicular:
looks like a boat- or a rectangular bridge
navicular tuberosity prominent on medial aspect of the foot and can be the source of foot pain
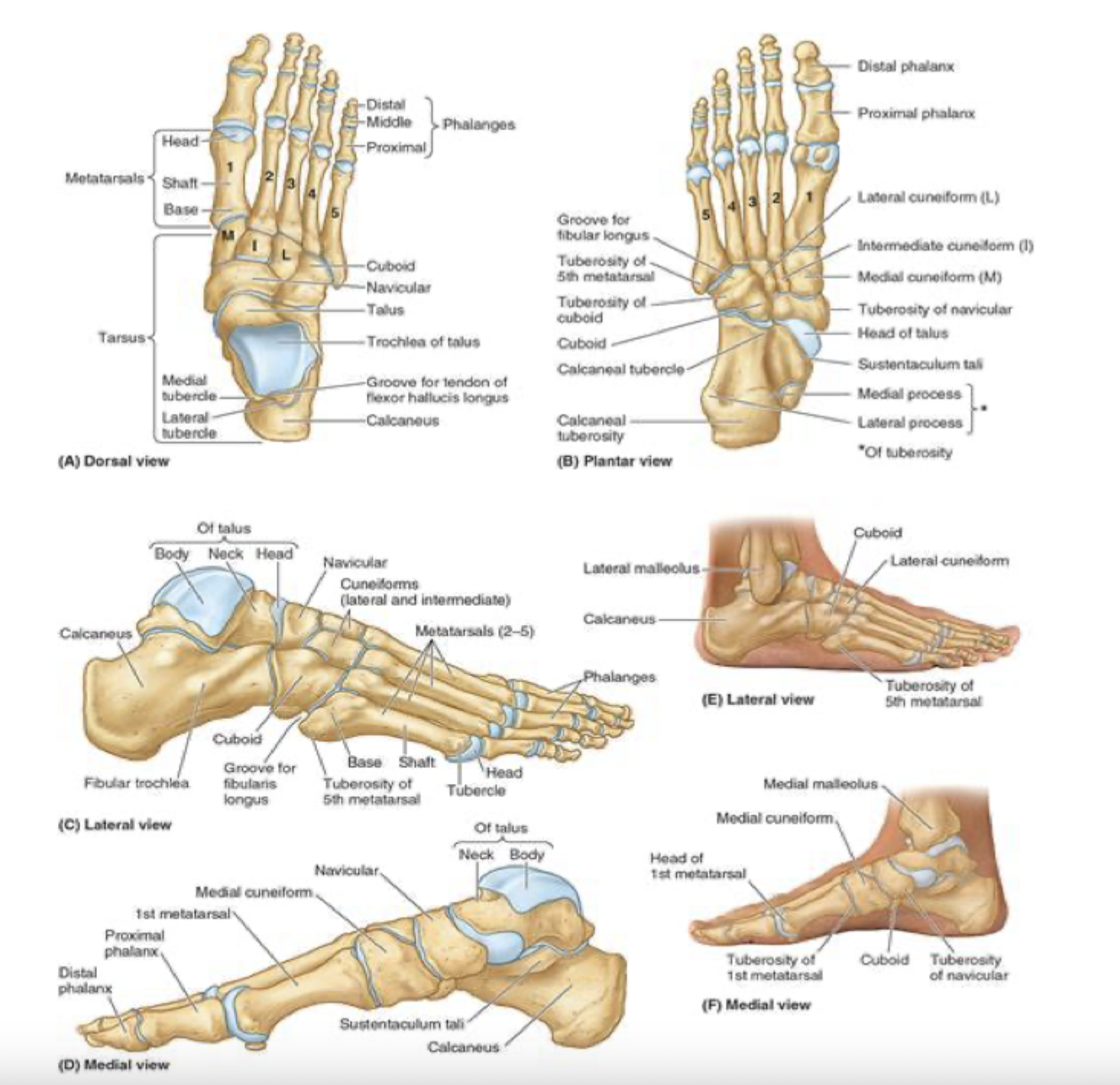
7 tarsal bones: white
cuboid
most lateral of the tarsal bones
in distal row with 3 cuneiform bones
the cuboid articulates with metatarsals 4 and 5
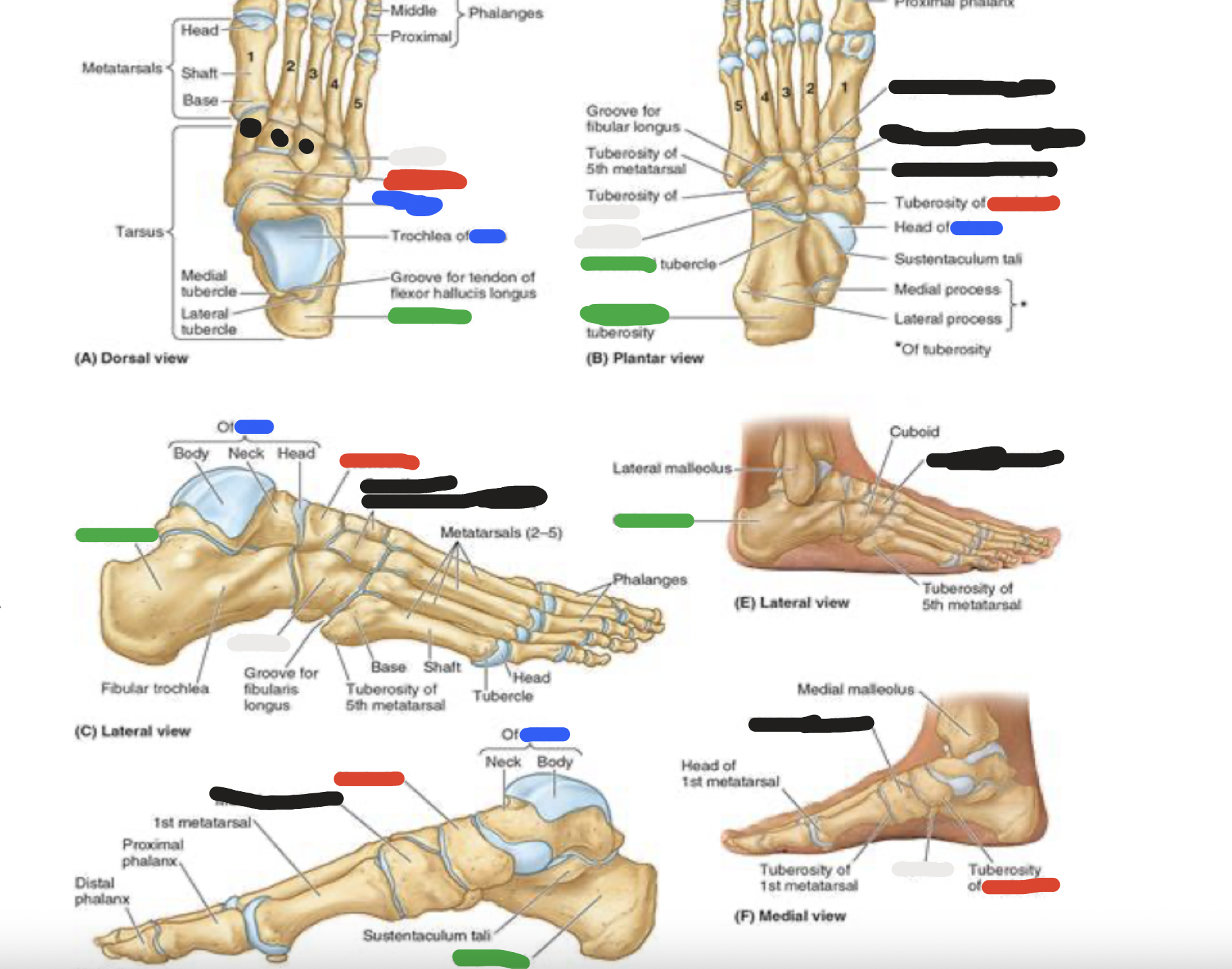
7 tarsal bones: black
cuneiform bones (3):
distal row-medial
intermediate
lateral
articulate posteriorly with the navicular bone and distally with metatarsals 1, 2, and 3
blue; green; red; white
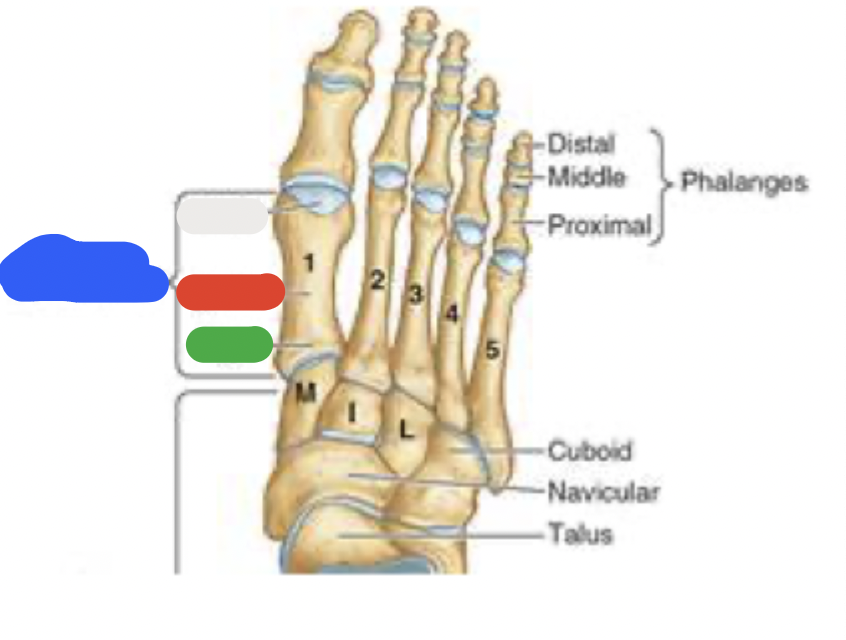
metatarsals
5 metatarsals: most medial is metatarsal #1, then progresses to #5
metatarsals
green: base (most proximal)
red and white: shaft and head (distally-articulates with phalanges)
*note that the 5th metatarsal has a prominent tuberosity that projects laterally
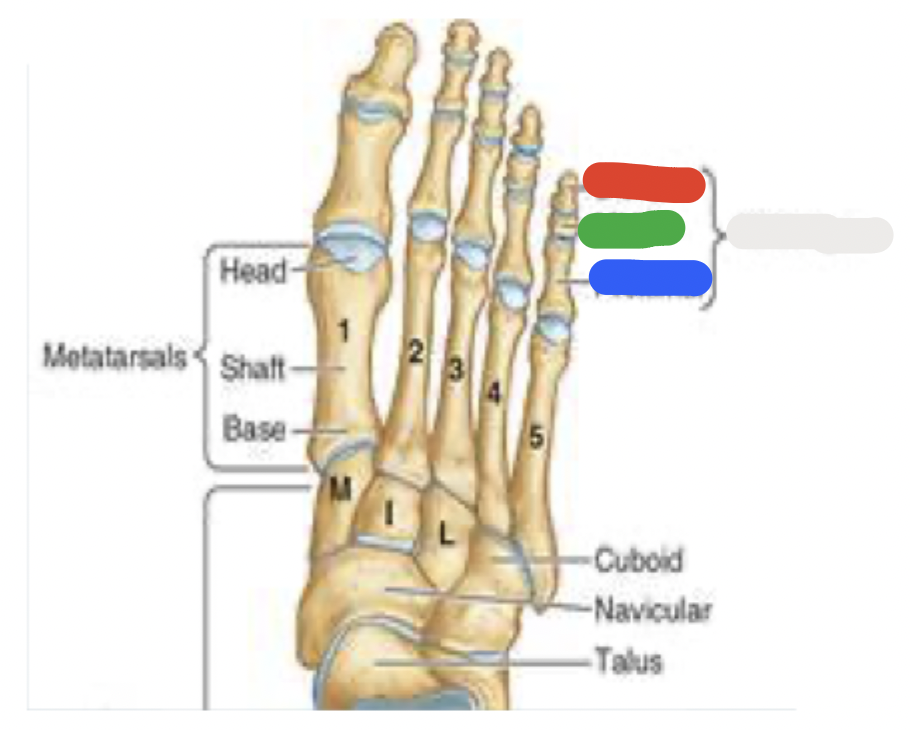
white; blue; green; red
phalanges
big (great) toe
proximal
distal phalanges
toes 2-5:
blue: proximal
green: middle
red: distal phalanges
each phalange has a base (proximal), shaft and head (distal)
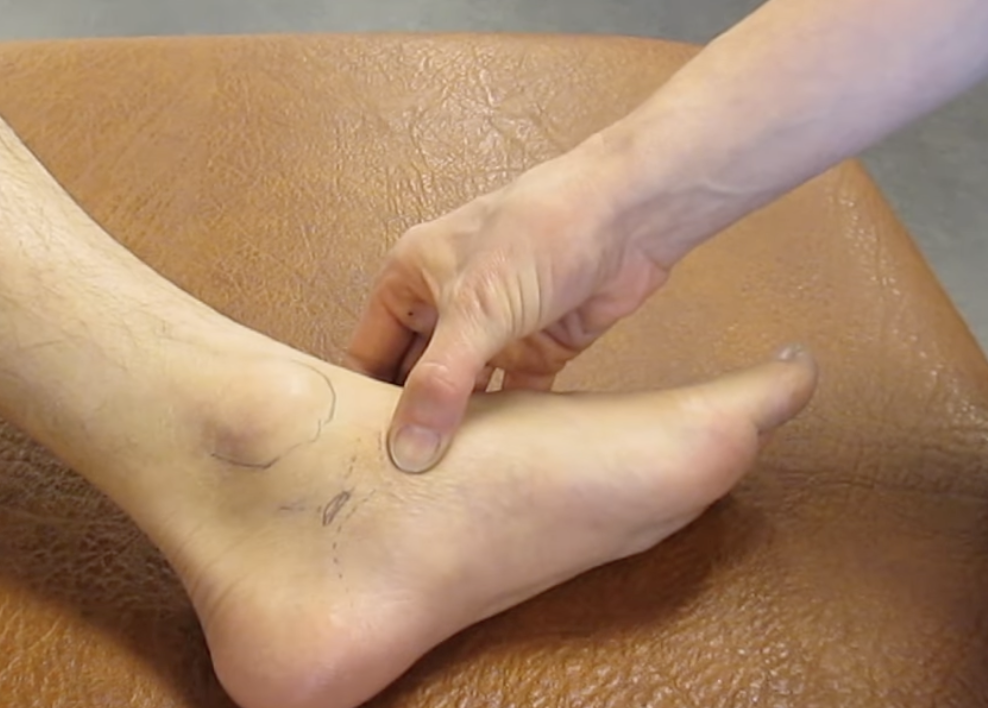
palpate:
navicular tubercle
from the tip of the medial malleolus, go 2 ½ cm anteriorly and inferiorly
feel for a raised bony surface
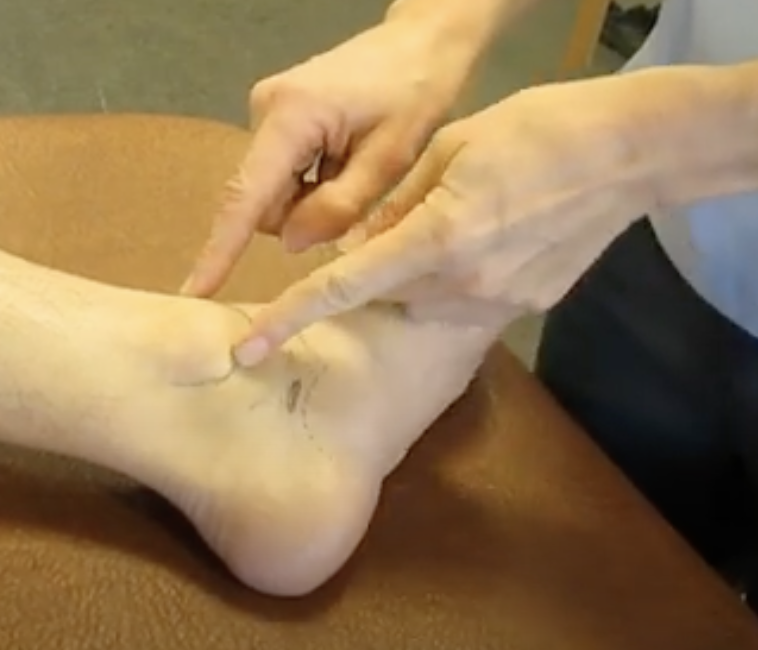
palpate:
medial malleolus
at distal end of fibula
big bony prominence
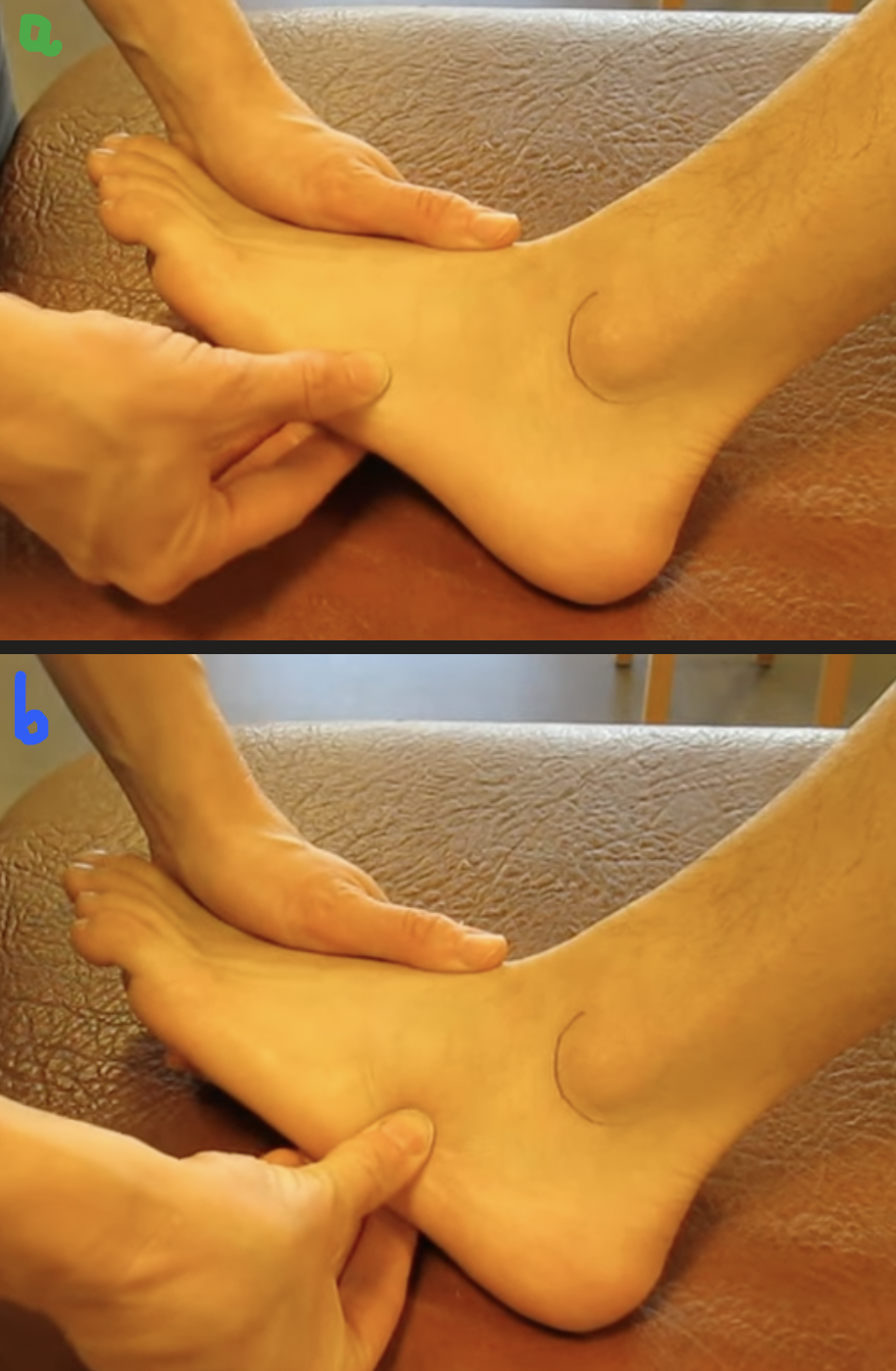
palpate: a. and b.
a. tubercle of 5th metatarsal
palpate along the metatarsal on the lateral aspect of the foot and feel for a rounded edge
b. cuboid
drop your finger off ^ the above
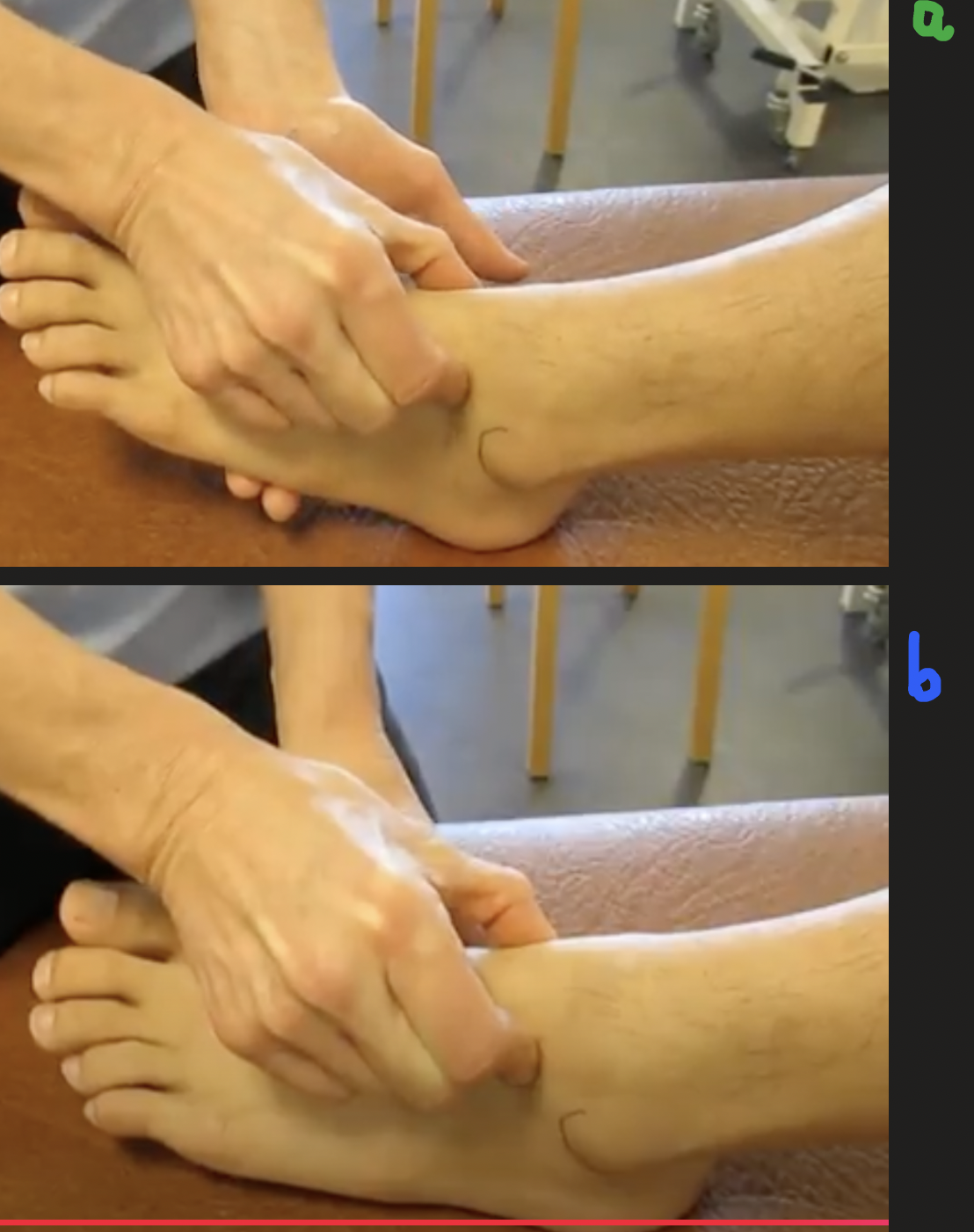
palpate: a. and b.
a. head of talus
find tips of malleoli
put thumb on medial malleolus and index finger on lateral malleolus
move anteriorly until you feel a dip
b. neck of the talus
slightly plantar flex the foot to feel
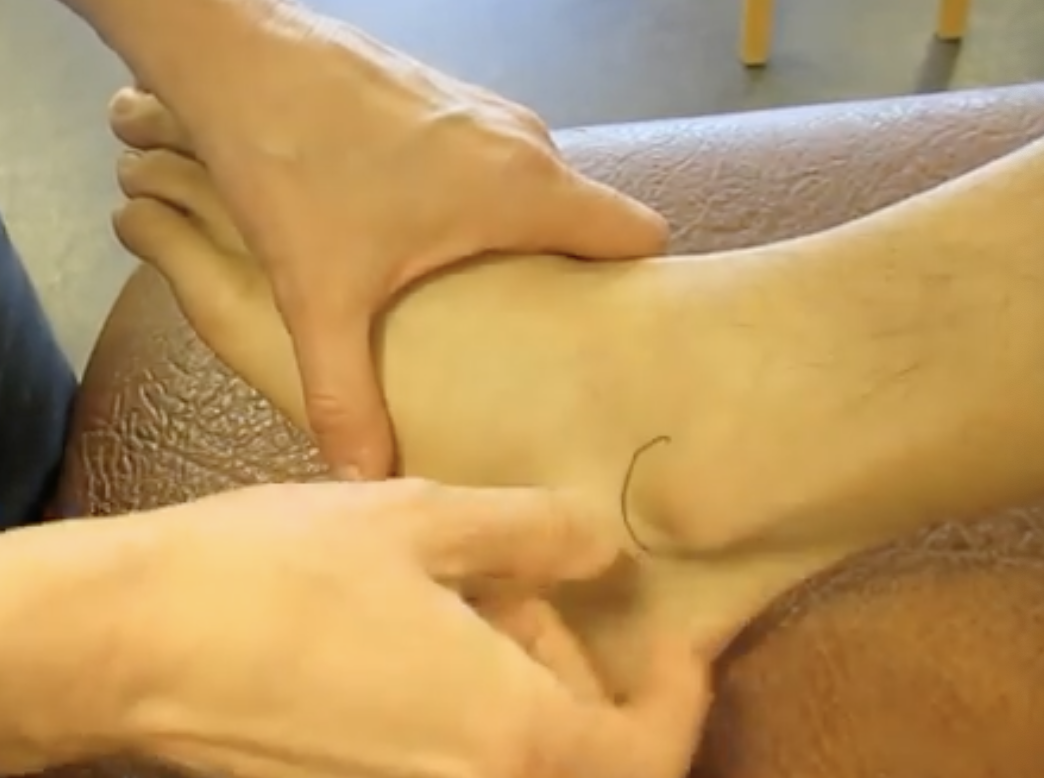
palpate:
lateral malleolus
at distal end of fibula
big bony prominence
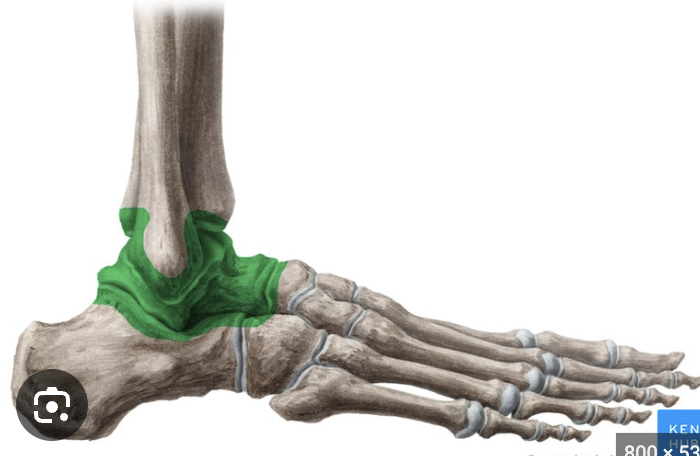
joints:
(upper) ankle joint/talocrural
distal fibula and tibia articulating with the superior talus
somewhat unstable during plantar flexion
movements: plantarflexion, dorsiflexion
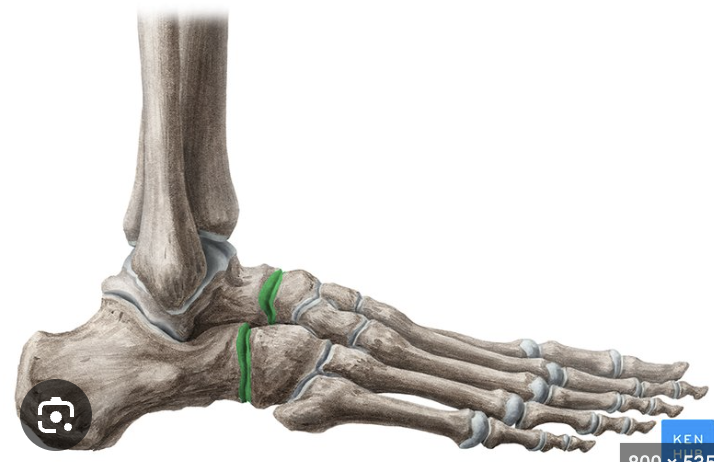
joints:
subtalar and transverse tarsal
inferior talus and superior calcaneus
formed by calcaneus and cuboid, and talus and navicular
movements: inversion (big toes goes in), eversion (big toe goes out)
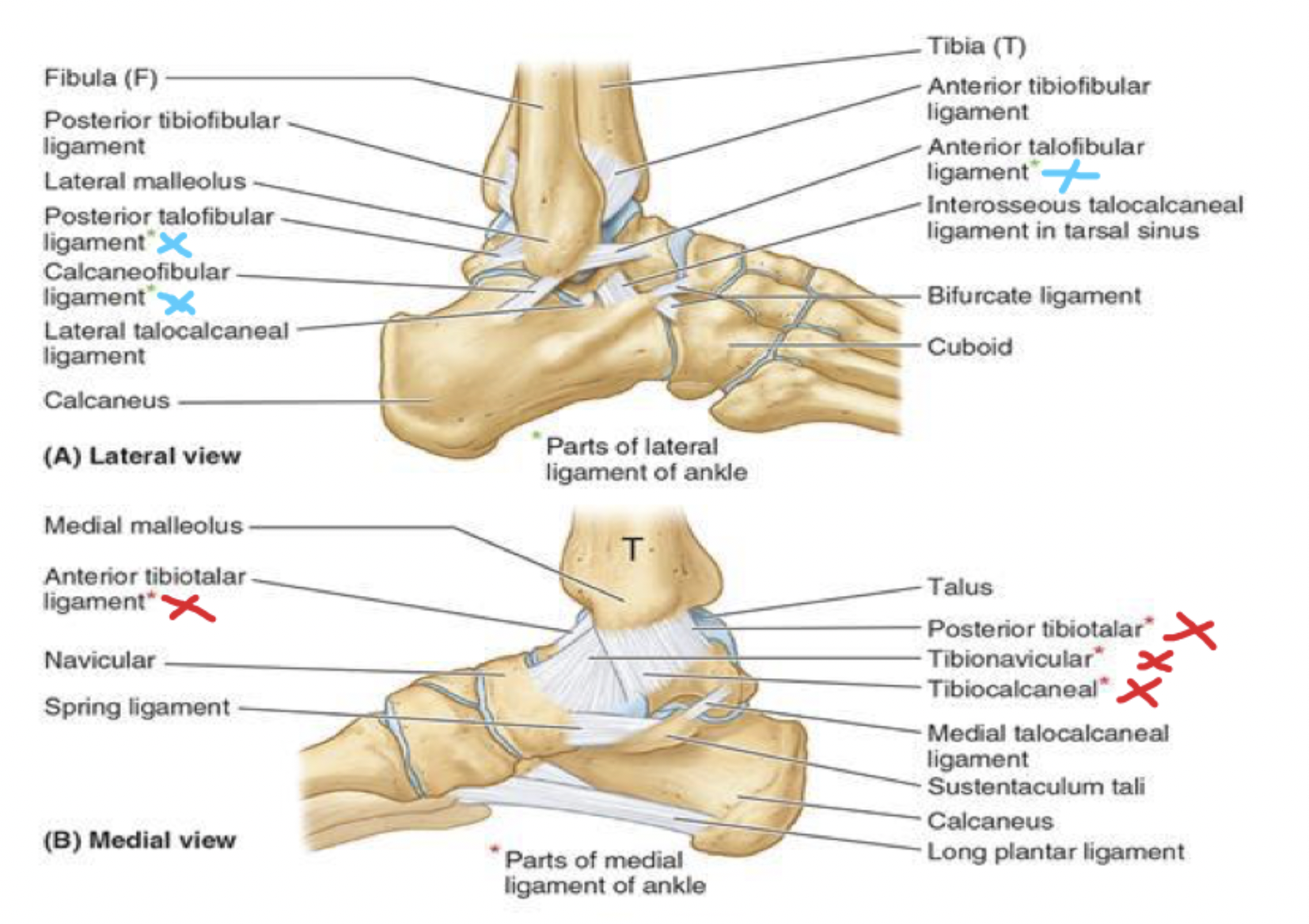
joints: ligaments
blue- lateral: 3 parts
red- medial: 4 parts
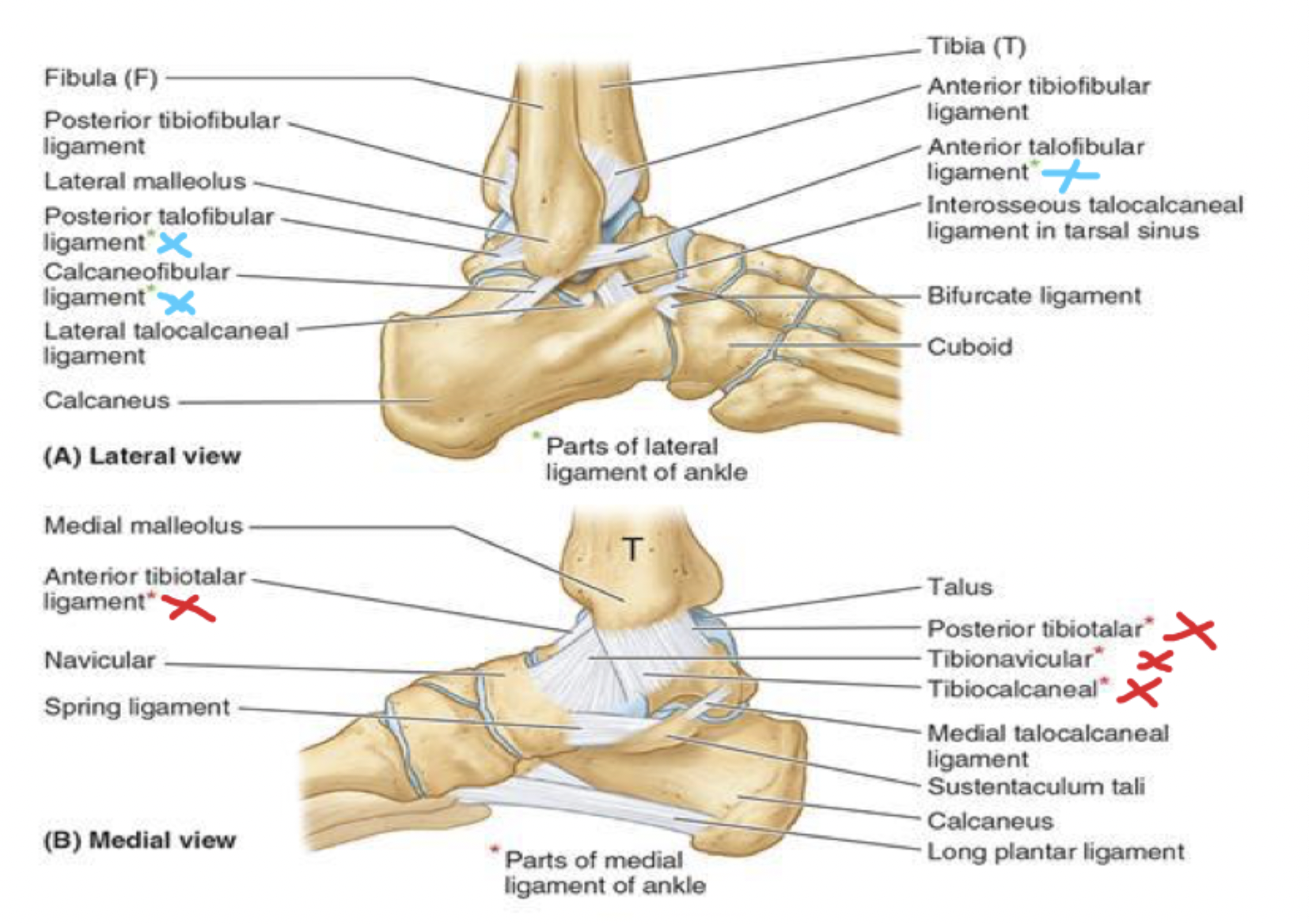
blood supply to the foot
thigh
femoral artery through the adductor canal —> out the adductor hiatus and adductor magnus —> to the back of the knee, where it becomes the popliteal artery
popliteal artery passes the popliteal fossa and then divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
in the anterior lower leg:
anterior tibial artery
in the foot, continues as dorsalis pedis artery
in the posterior lower leg:
posterior tibial artery
posterior to medial malleolus: becomes medial and lateral plantar arteries
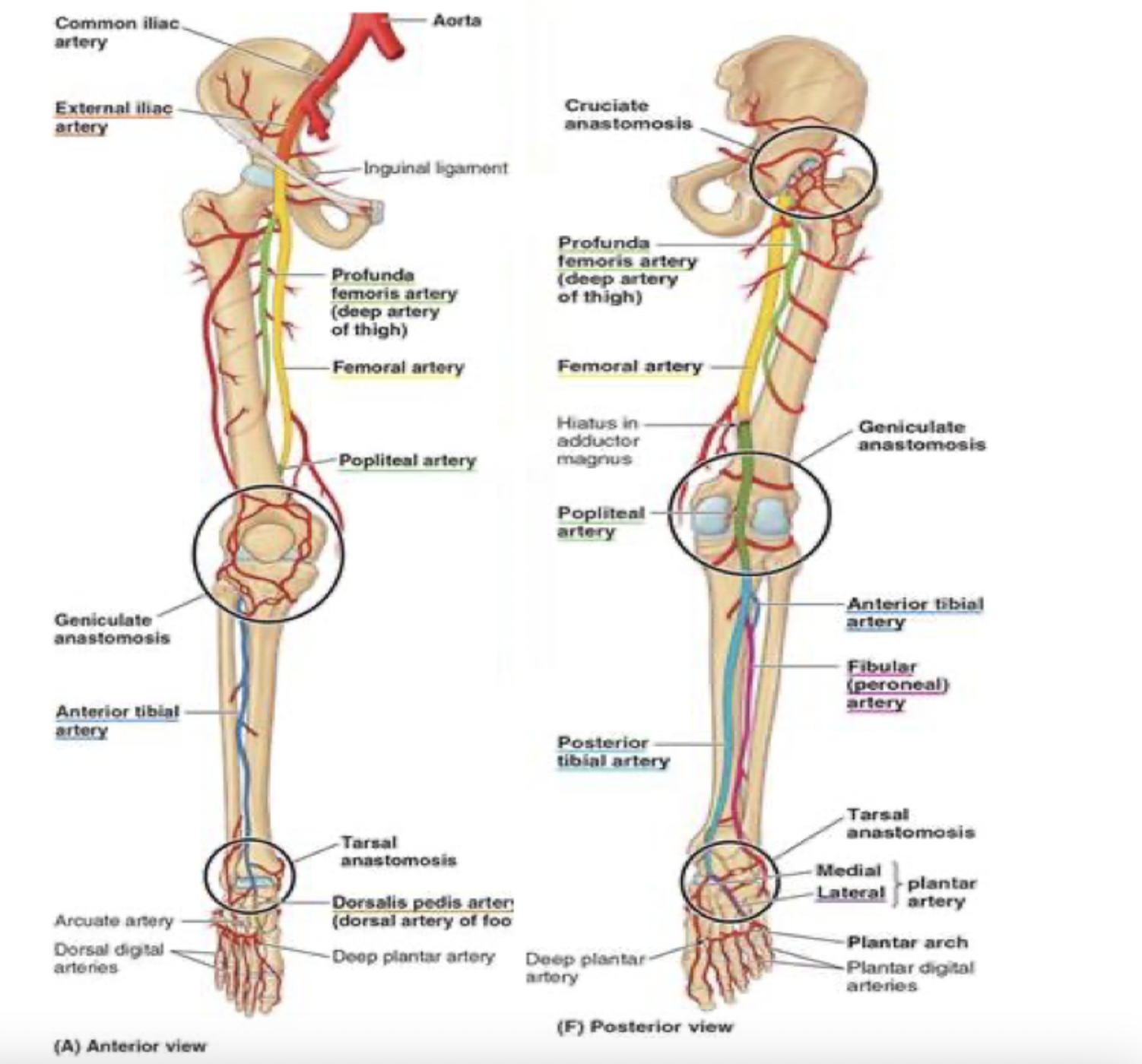
__ pulse
posterior tibial pulse
in between medial malleolus and heel
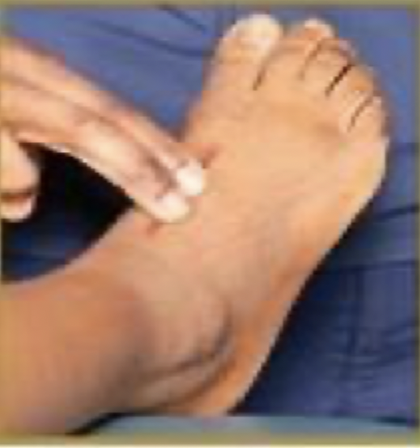
__ pulse
dorsalis pedis pulse
1st tendon of extensor digitorum —> move slightly laterally
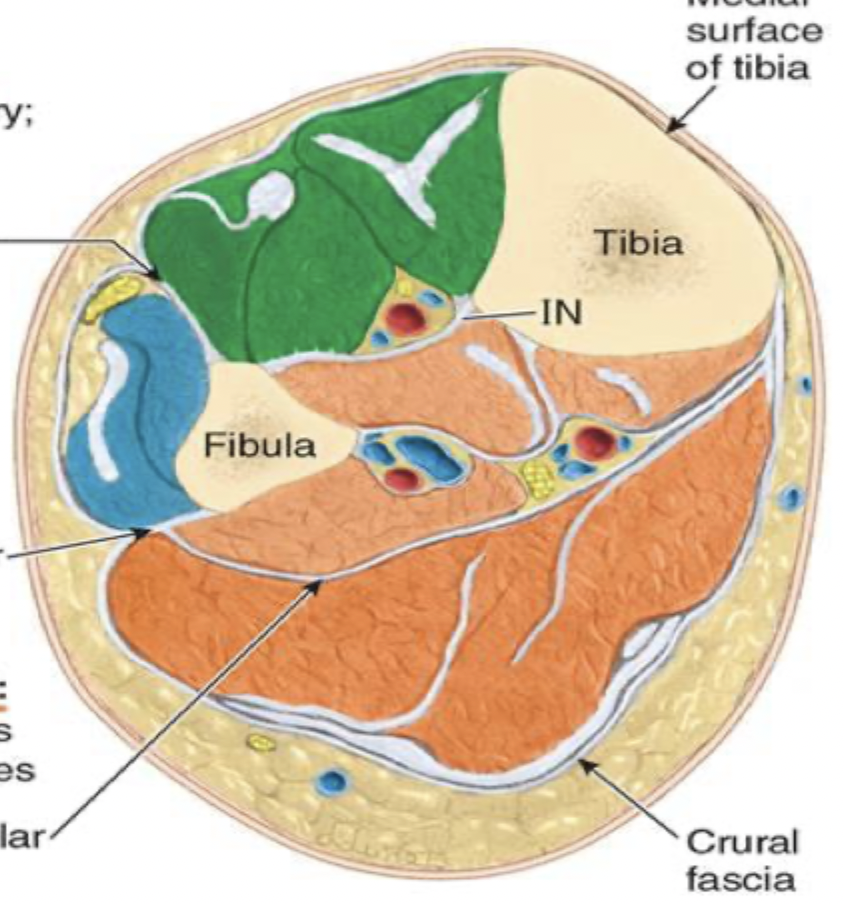
muscles of the lower leg: green; blue; orange
green: anterior compartment
innervated by deep fibular nerve
dorsiflex ankle
extend toes
blue: lateral compartment (fibular side)
innervated by superficial fibular nerve
everts foot
orange: posterior compartment
innervated by tibial nerve
plantarflexes ankles
flexes toes
superficial muscles of posterior leg: gastrocnemius; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
lateral head: lateral condyle of femur
medial head: femur, superior to medial condyle
distal attachment
calcaneus via calneal tendon
innervation
tibial nerve
main actions
plantarflexes ankle
superficial muscles of posterior leg: soleus; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
fibula
tibia
distal attachment
calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
innervation
tibial nerve
main actions
plantarflexes ankle
superficial muscles of posterior leg: plantaris; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
inferior end of lateral supracondylar line of femur
distal attachment
calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
innervation
tibial nerve
main actions
plantarflexes ankle
deep muscles of posterior leg: popliteus; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation
proximal attachment
lateral condyle of femur
lateral meniscus
distal attachment
tibia
innervation
tibial nerve
deep muscles of posterior leg: flexor hallucis longus; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
fibula
distal attachment
great toe
innervation
tibial nerve
main actions
flexes great toe
deep muscles of posterior leg: flexor digitorum longus; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
tibia
distal attachment
bases of distal phalanges
innervation
tibial nerve
main actions
flexes lateral 4 digits
plantarflexes ankle joint
deep muscles of posterior leg: tibialis posterior; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
interosseous membrane
posterior surface of tibia
fibula
distal attachment
primarily to tuberosity of navicular
innervation
tibial nerve
main actions
plantarflexes ankle joint
when measuring hip flexion range of motion, palpate for this boney prominence
greater trochanter
when measuring hip abduction range of motion, palpate for this boney prominence
ASIS
when measuring knee range of motion, palpate for this boney prominence
lateral condyle
when measuring ankle dorsiflexion range of motion, palpate for this boney prominence
lateral malleolus
when measuring ankle plantarflexion range of motion, palpate for this boney prominence
lateral malleolus
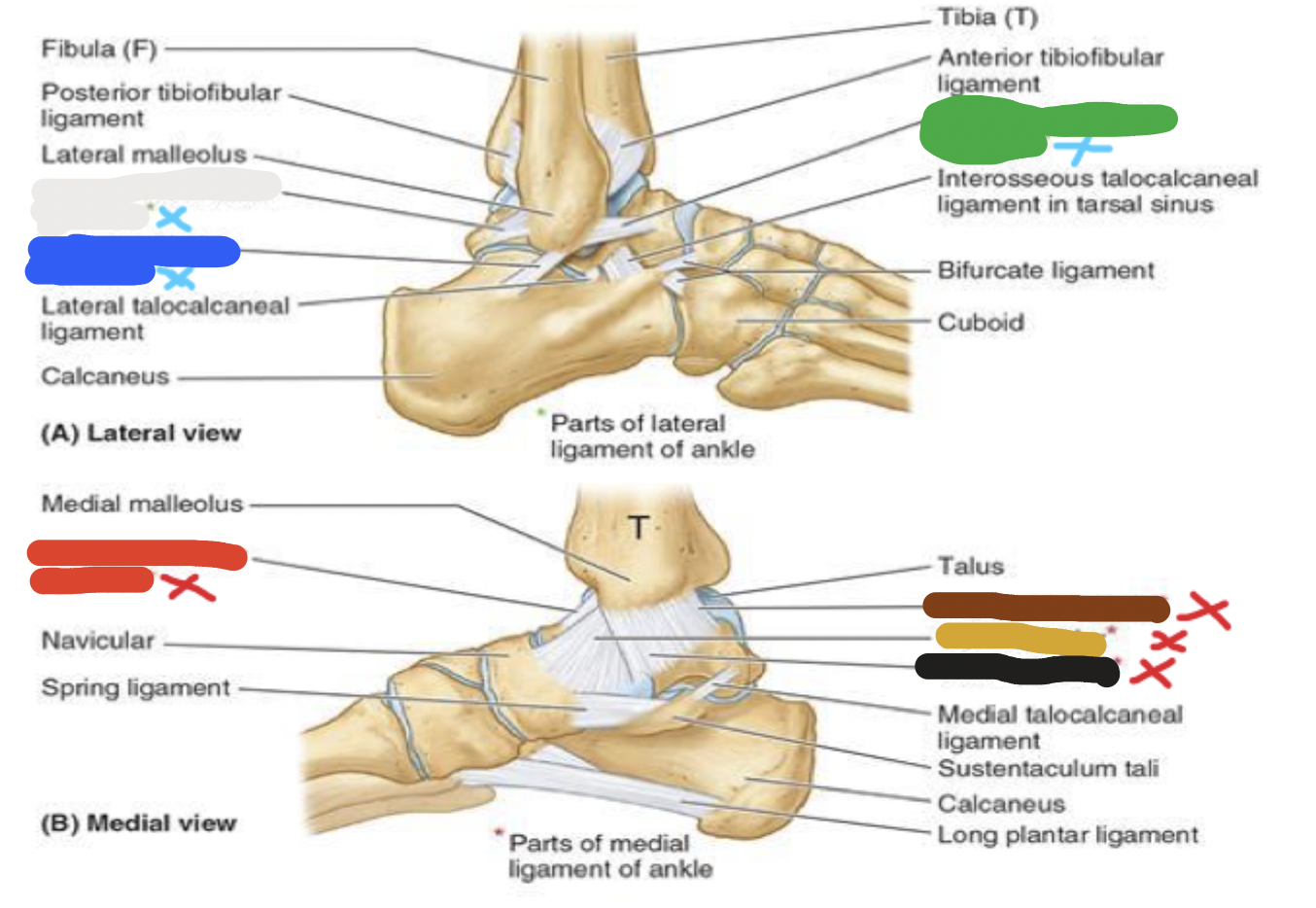
joint: white
lateral ligaments- posterior talofibular ligament
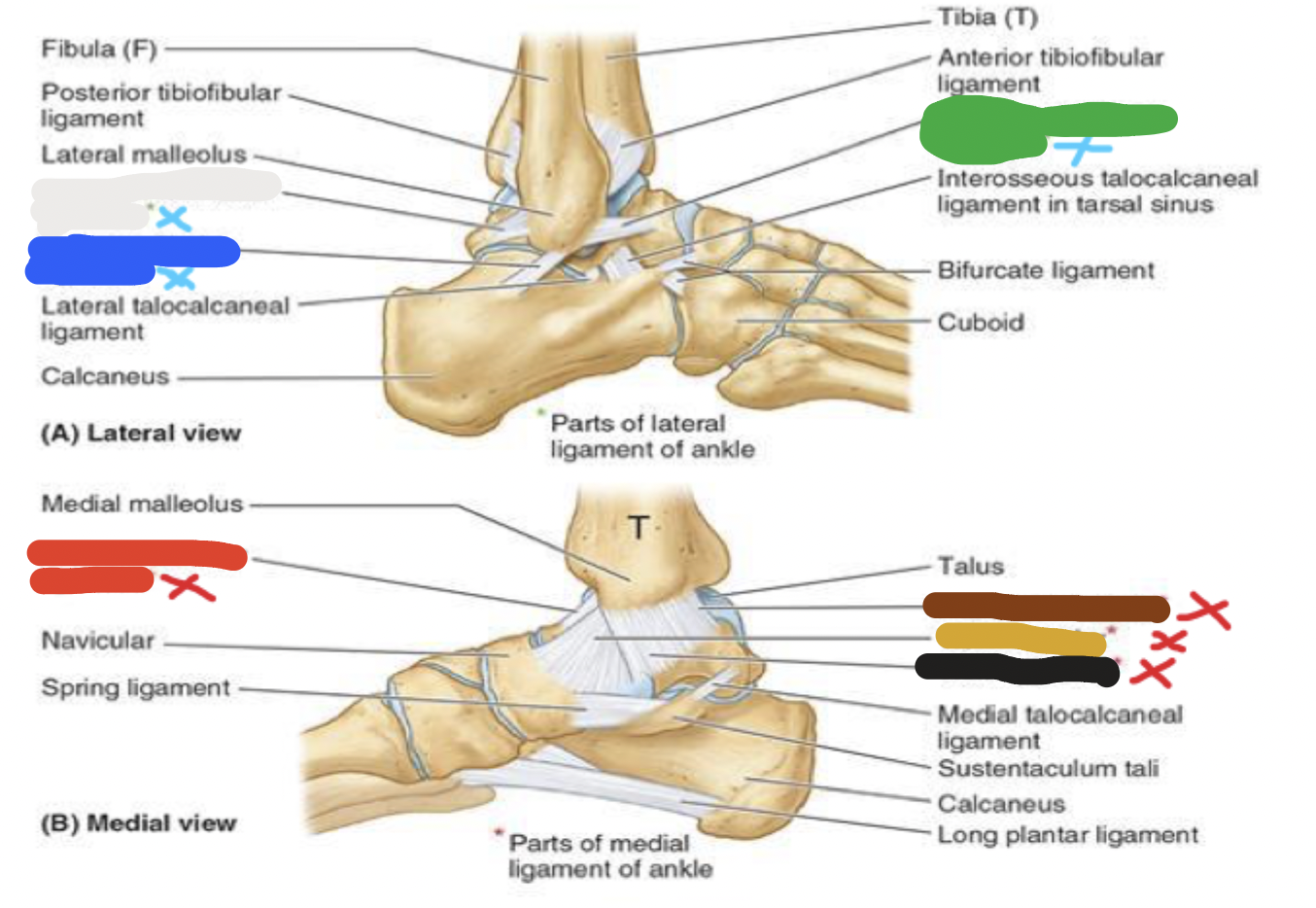
joint: blue
lateral ligaments- calcaneofibular ligament
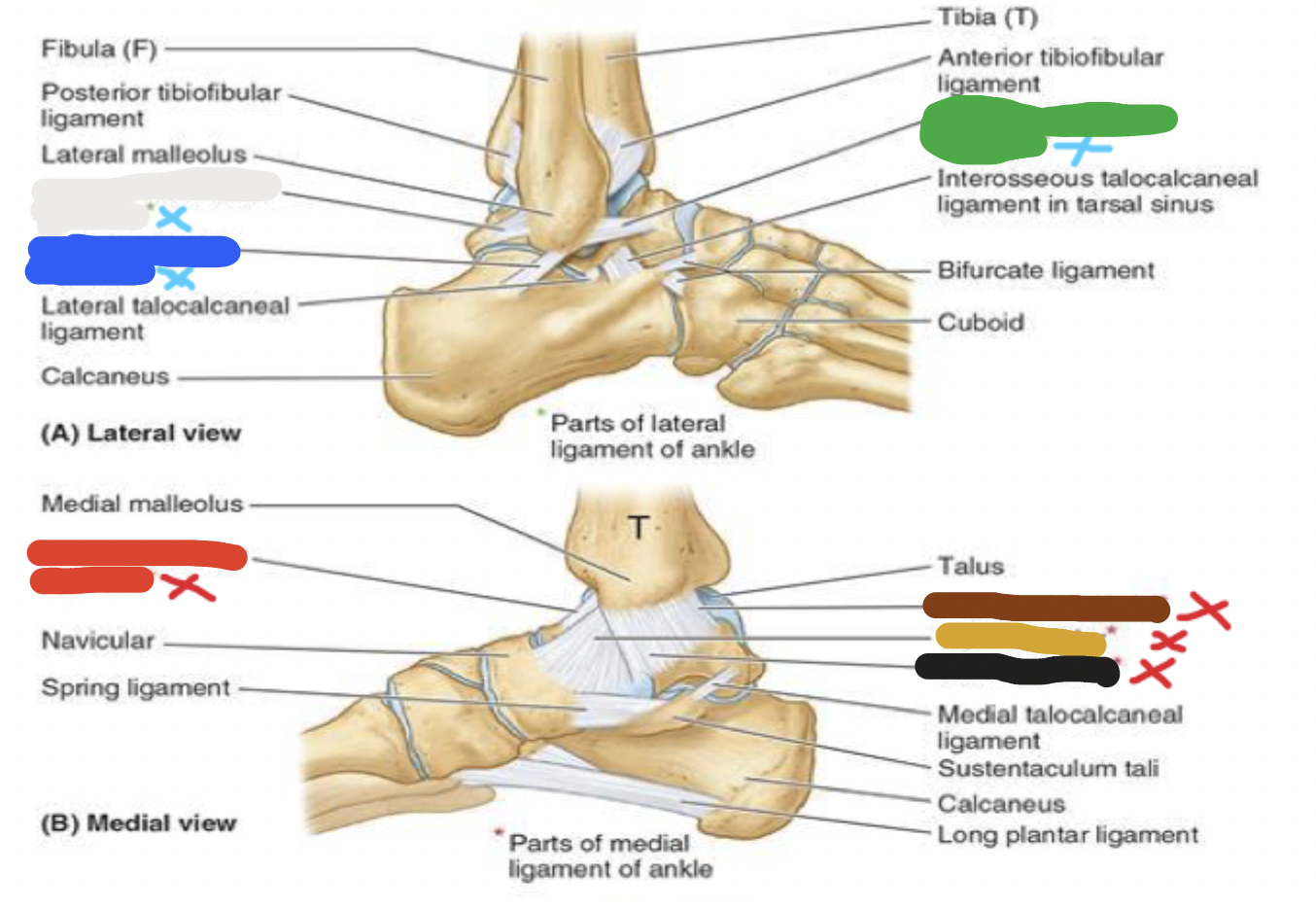
joint: green
lateral ligaments- anterior talofibular ligament
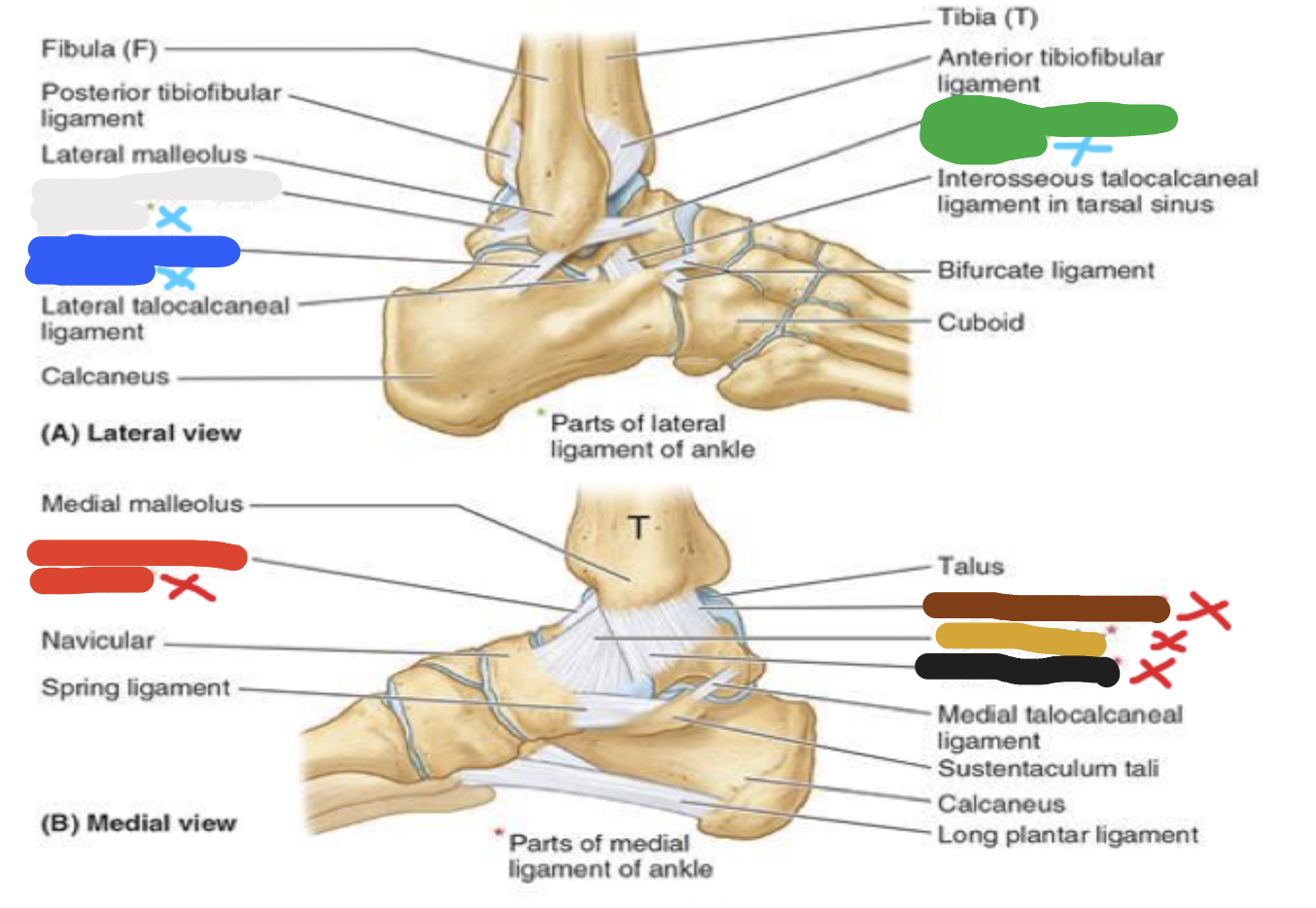
joint: red
medial ligaments- anterior tibiotalar ligament
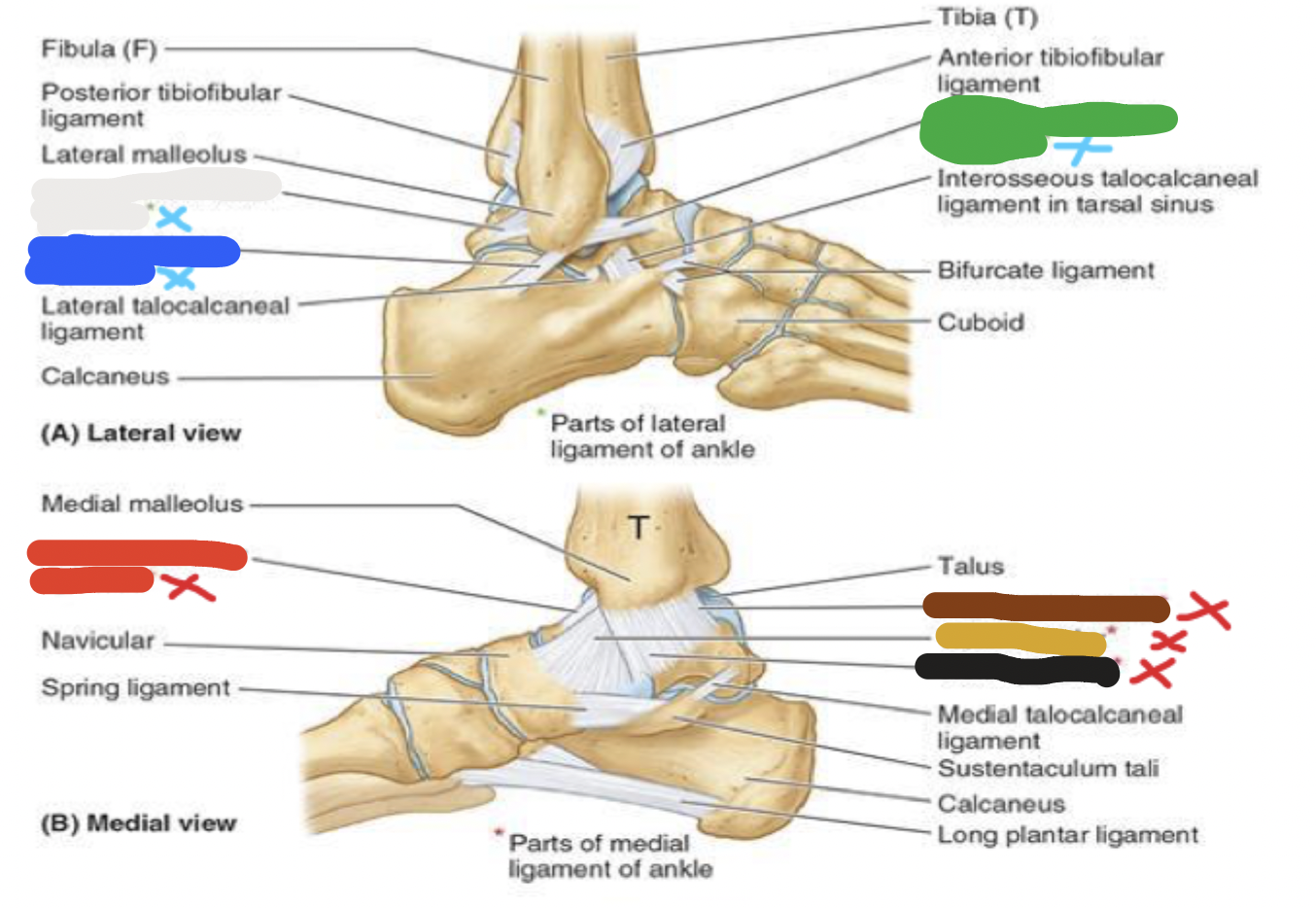
joint: brown
medial ligaments- posterior tibiotalar ligament
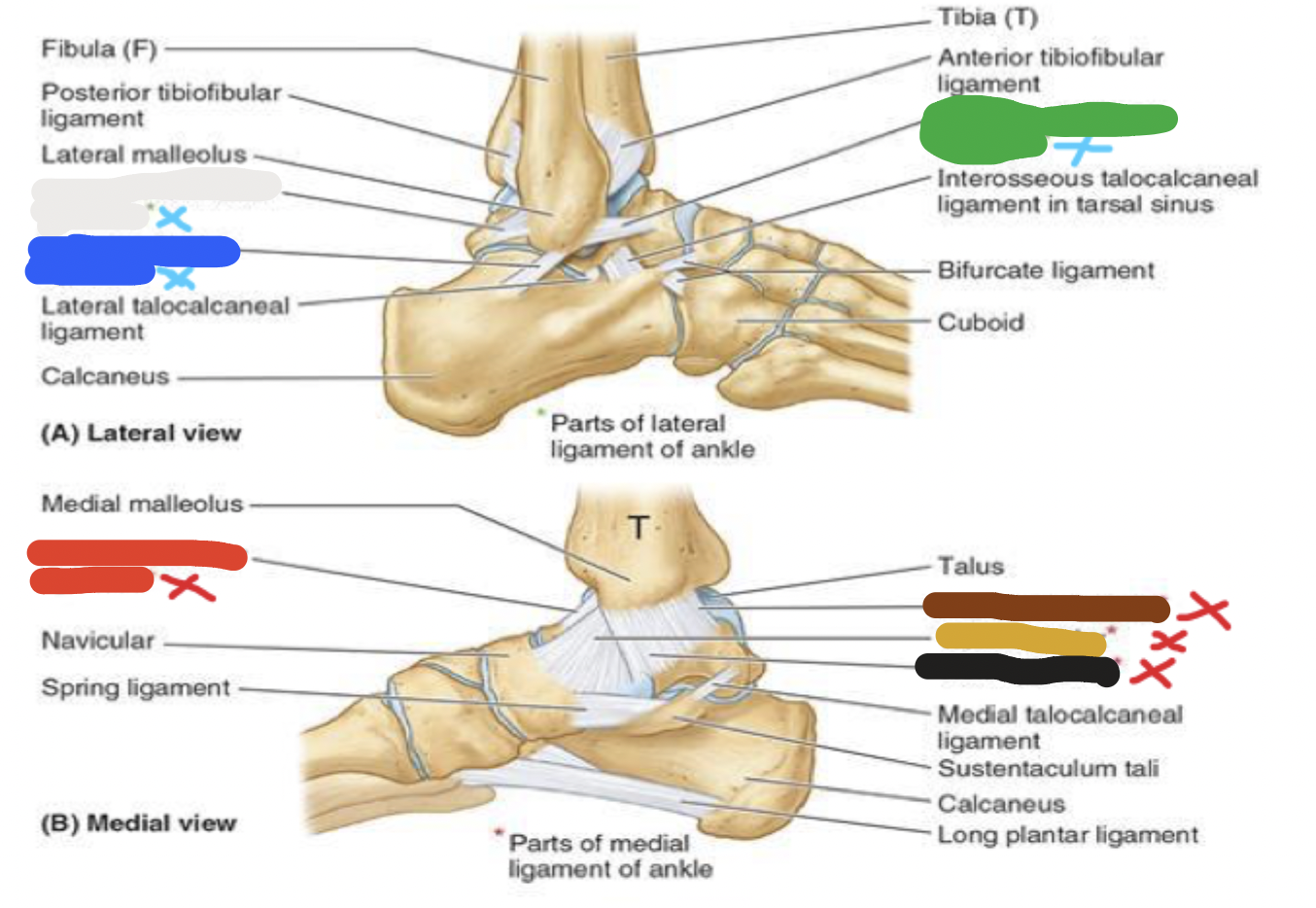
joint: yellow
medial ligaments- tibionavicular ligament
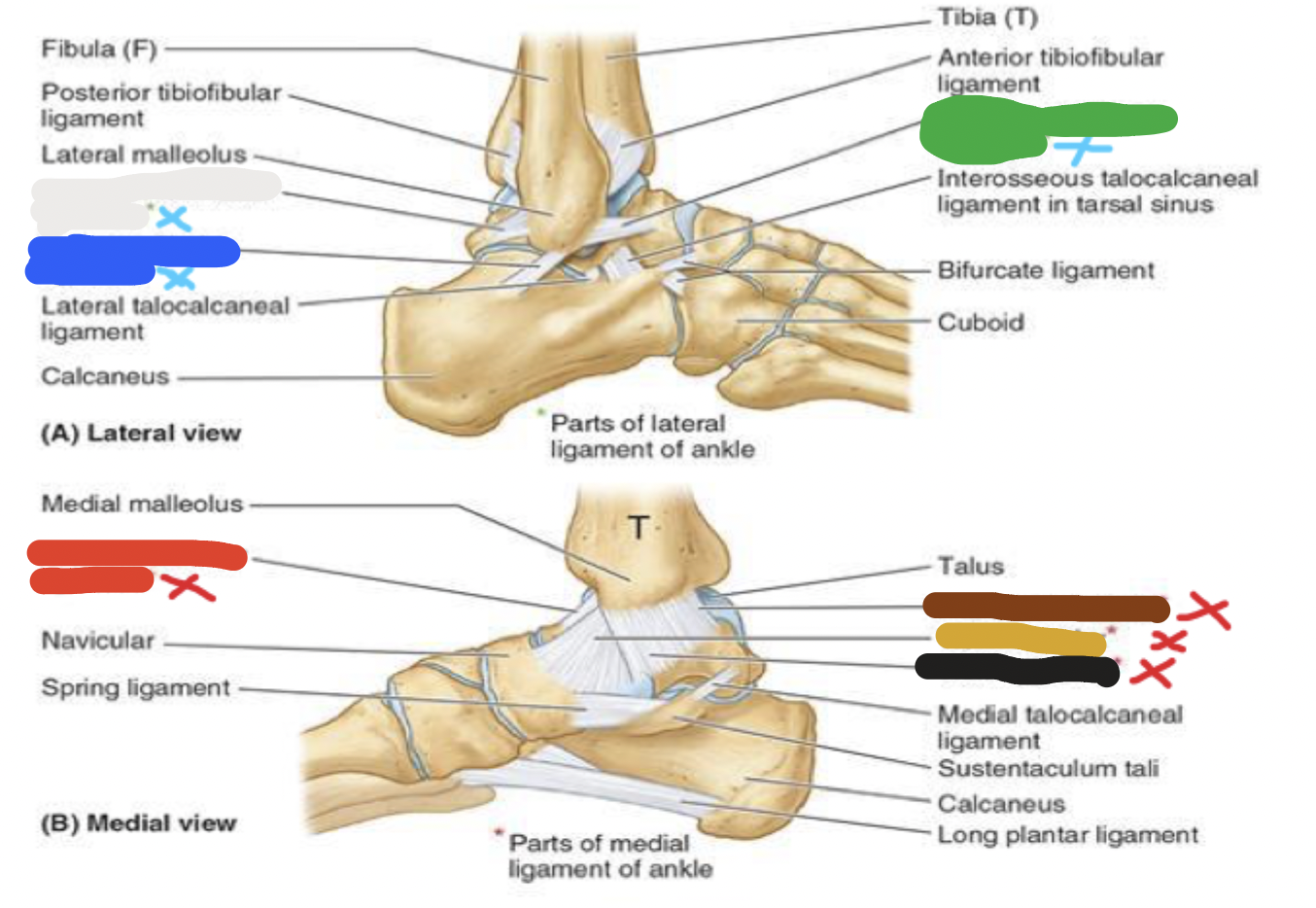
joint: black
medial ligaments- tibiocalcaneal ligament
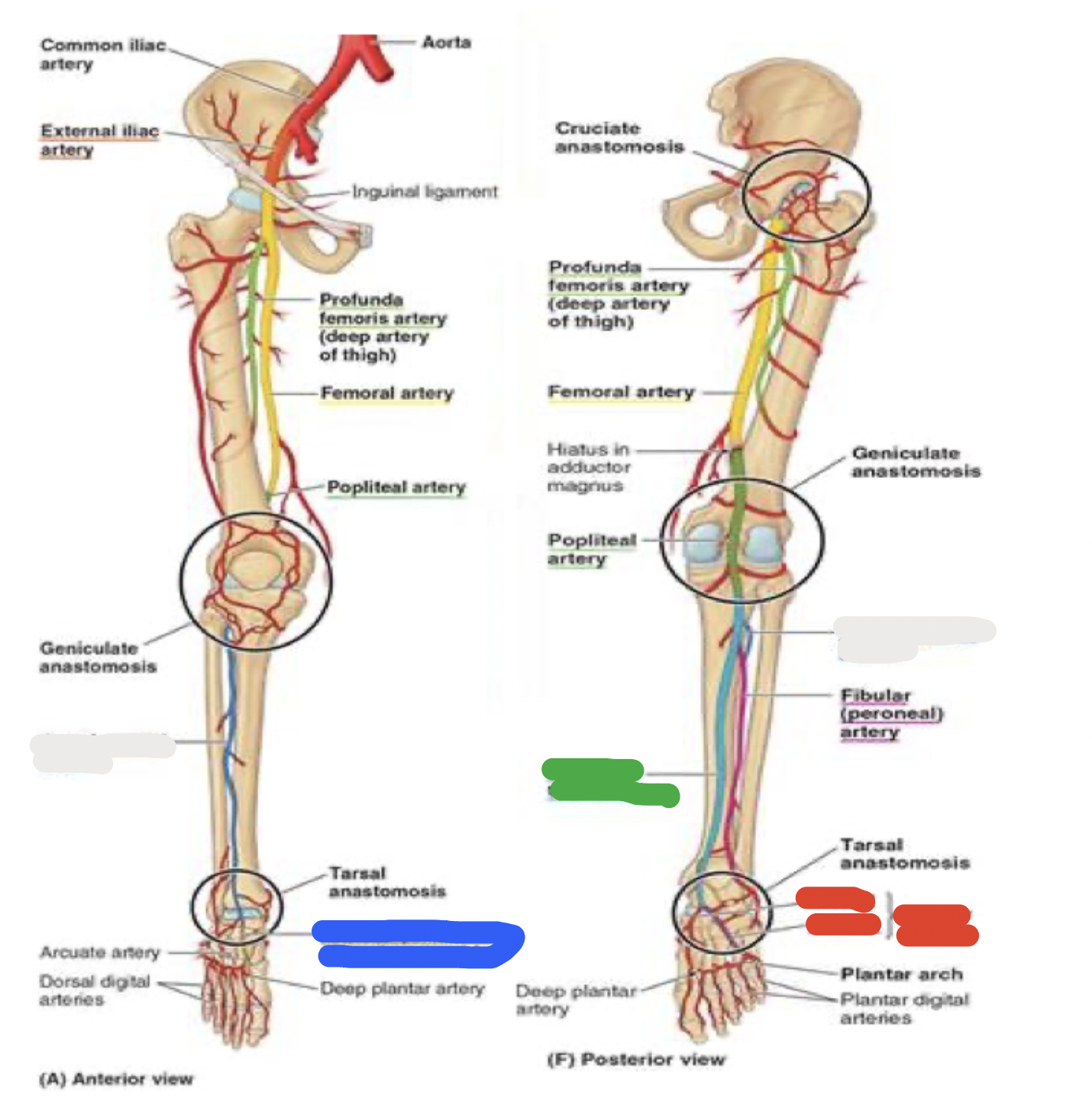
blood supply to the foot: white
anterior lower leg- anterior tibial artery
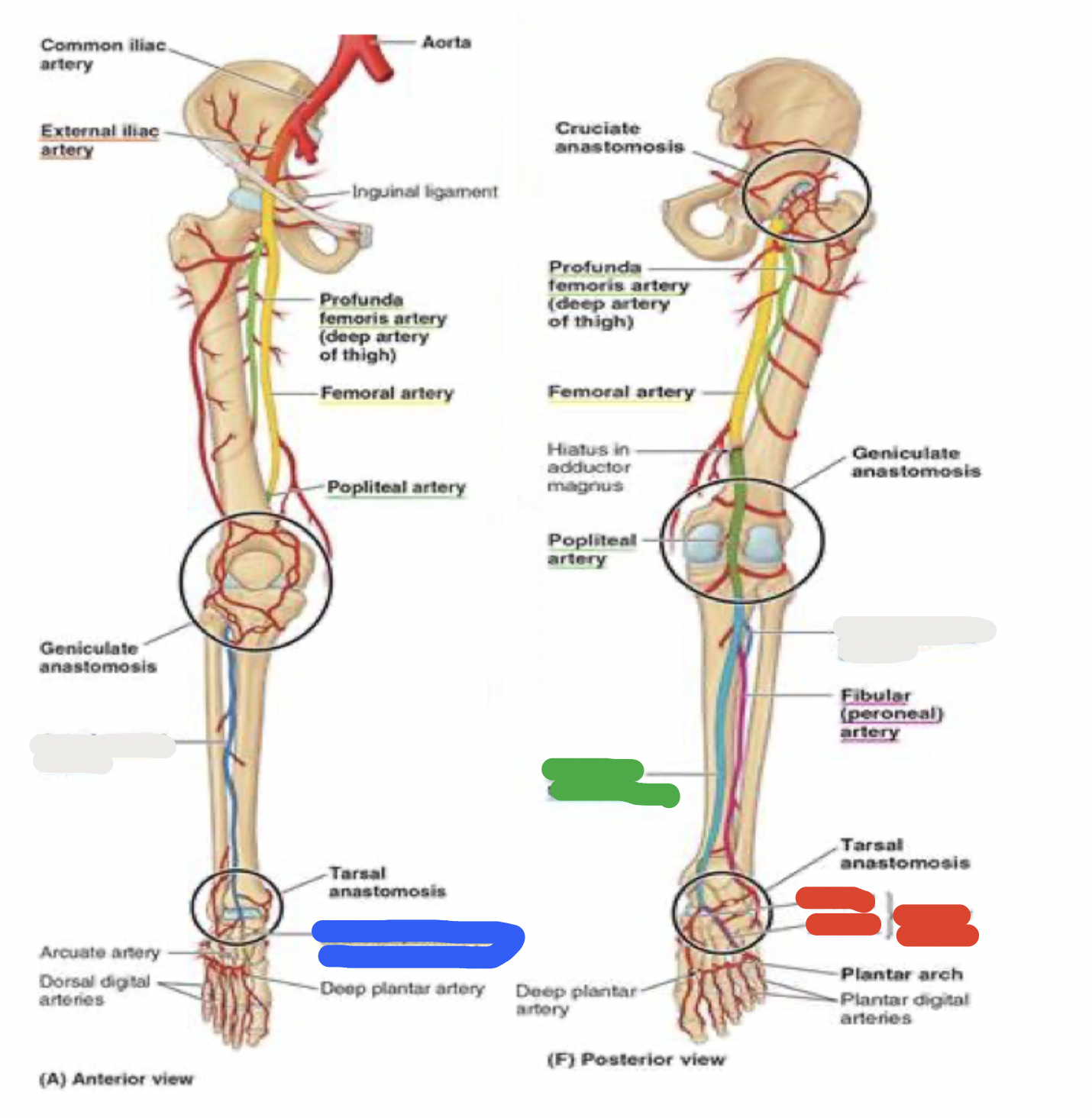
blood supply to the foot: blue
anterior lower leg- dorsalis pedis artery
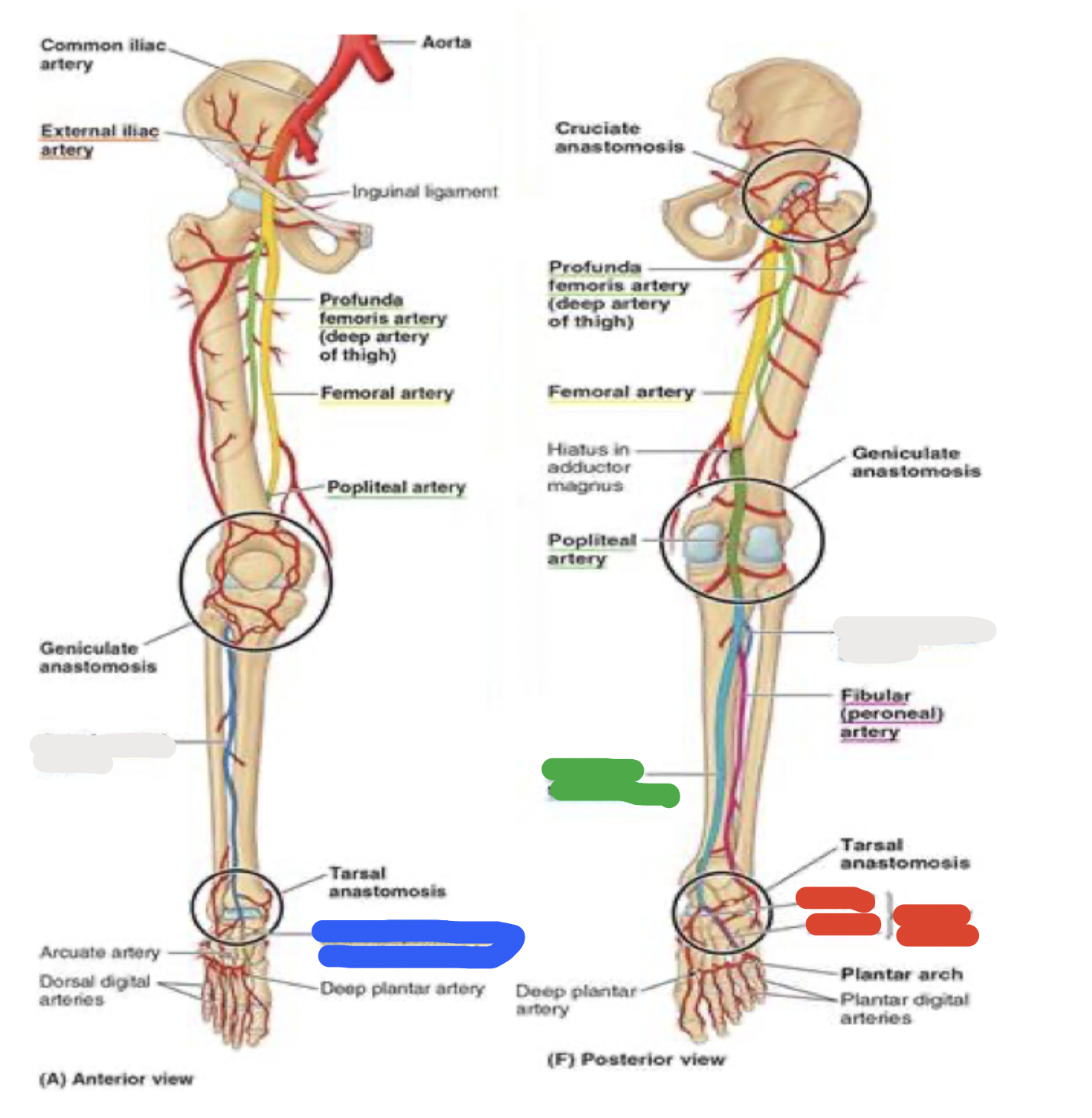
blood supply to the foot: green
posterior lower leg- posterior tibial artery
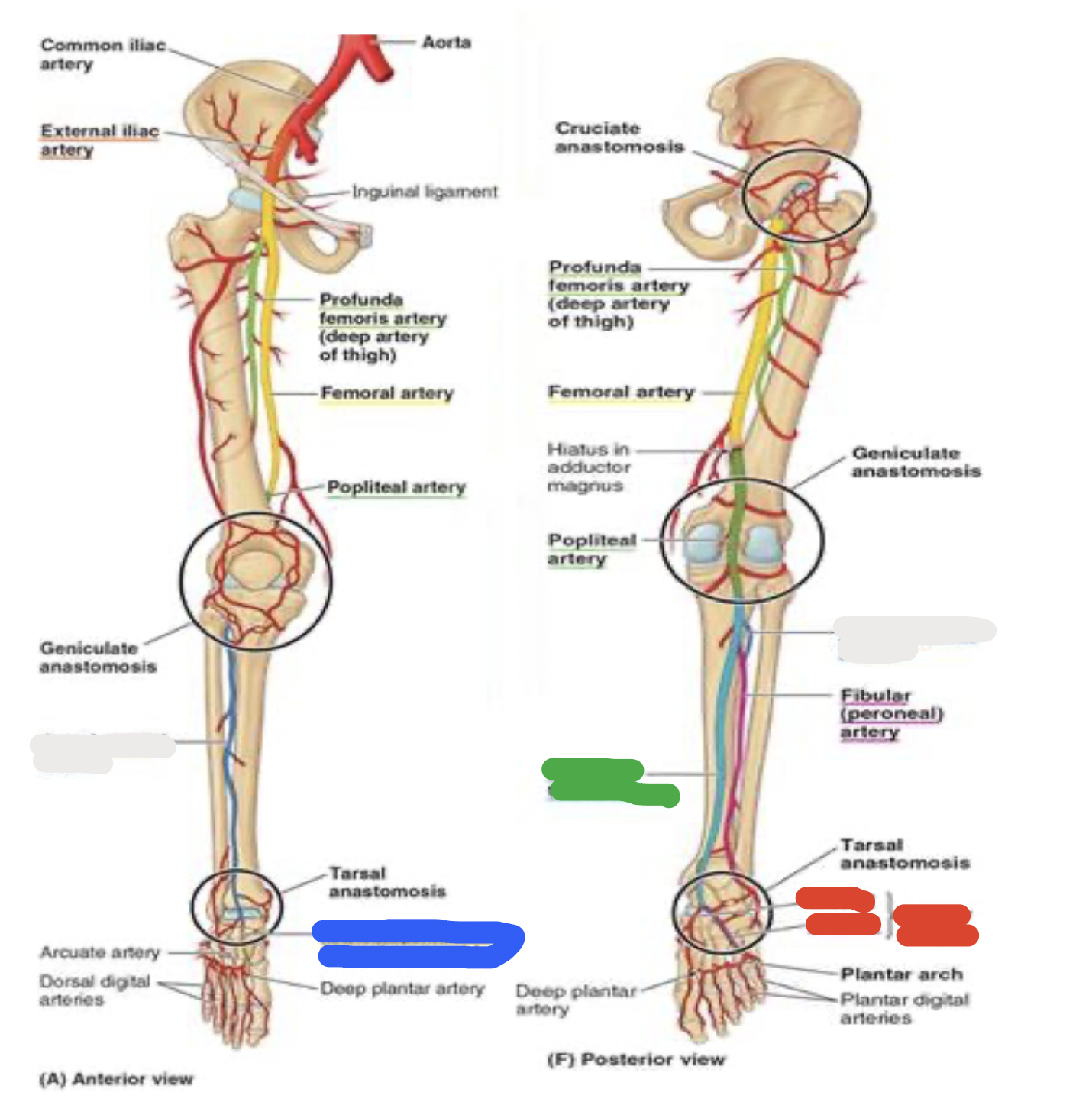
blood supply to the foot: red
posterior lower leg- posterior to medial malleolus: becomes medial and lateral plantar arteries
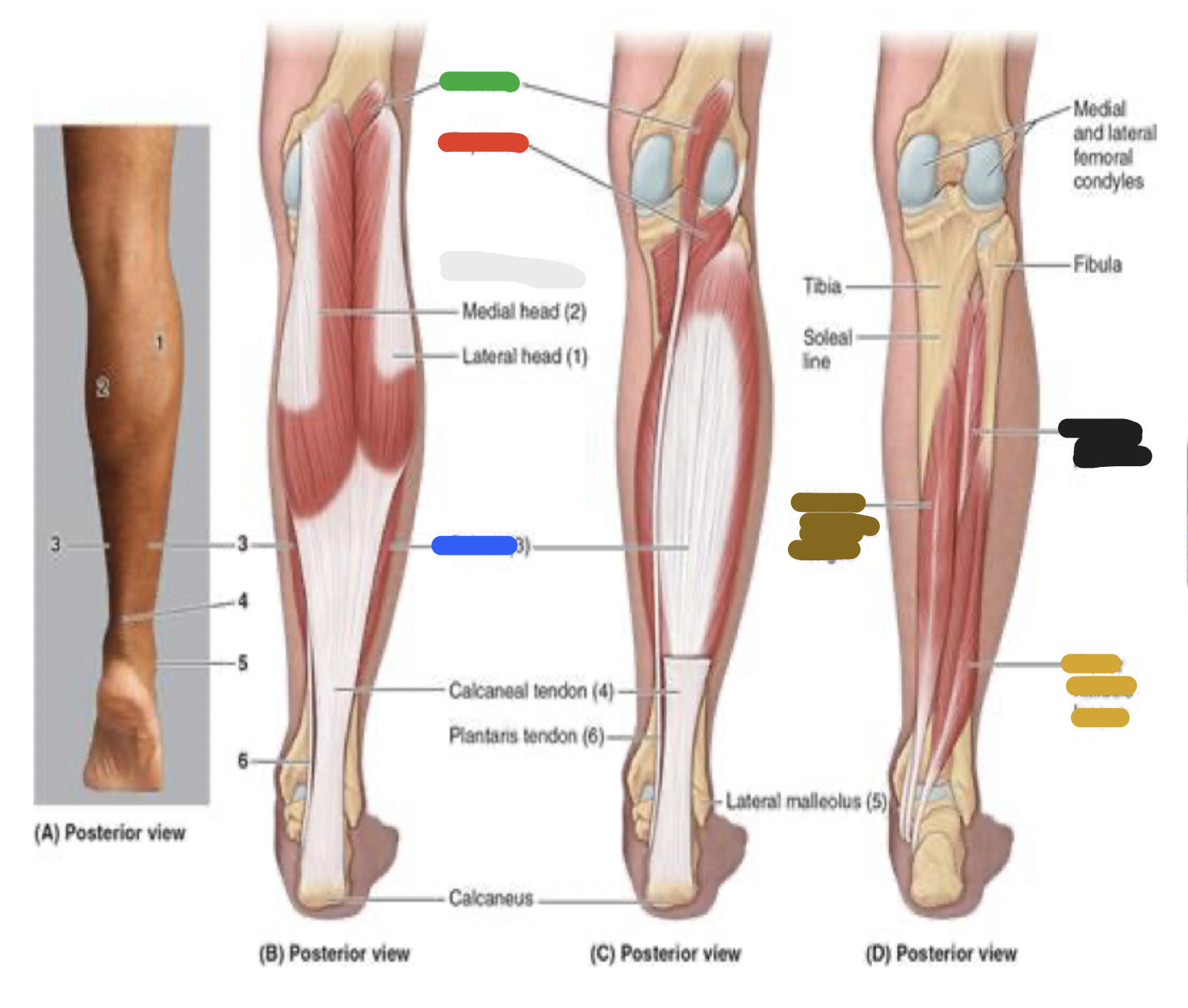
muscles of the posterior leg: white
gastrocnemius
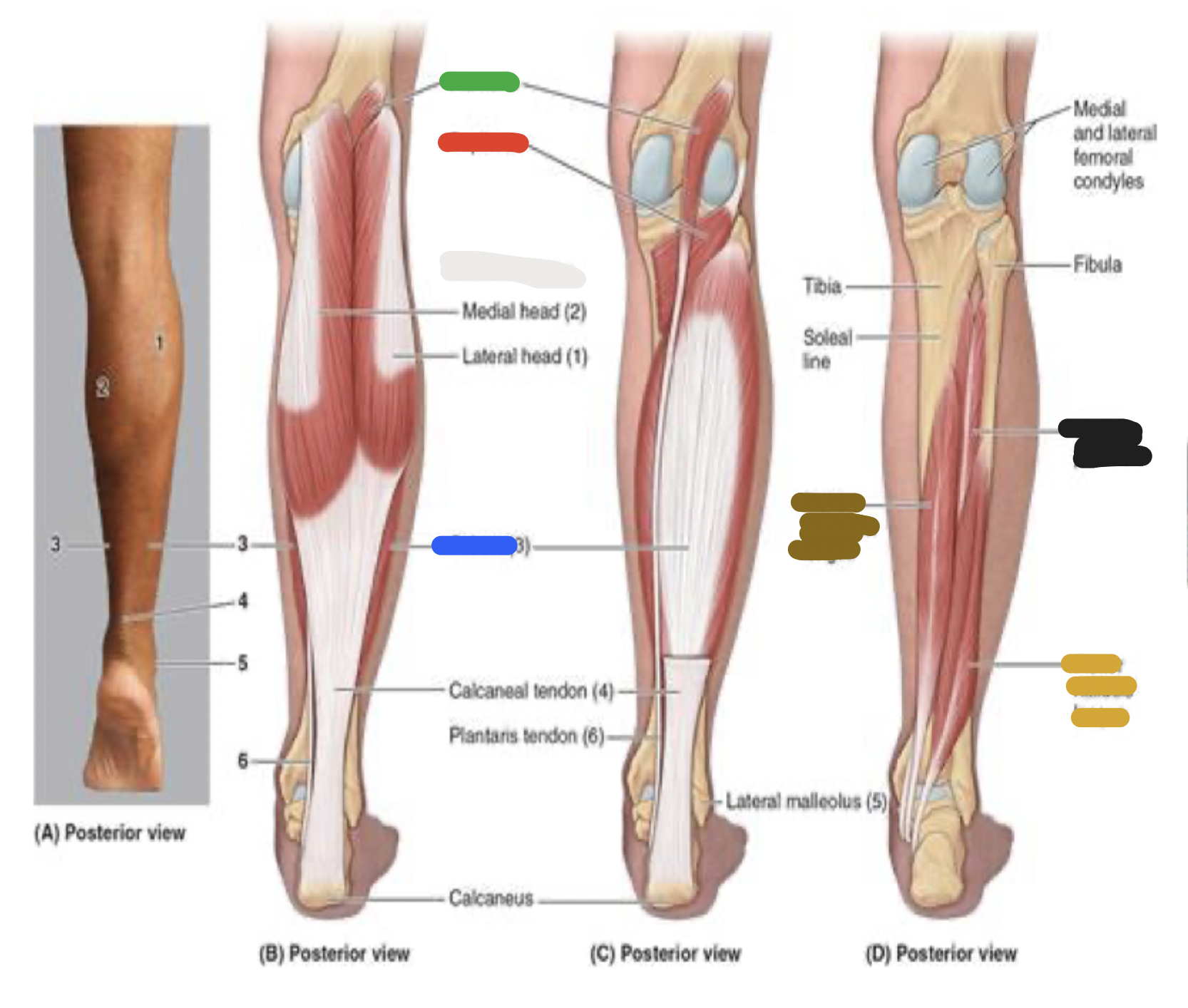
muscles of the posterior leg: blue
soleus
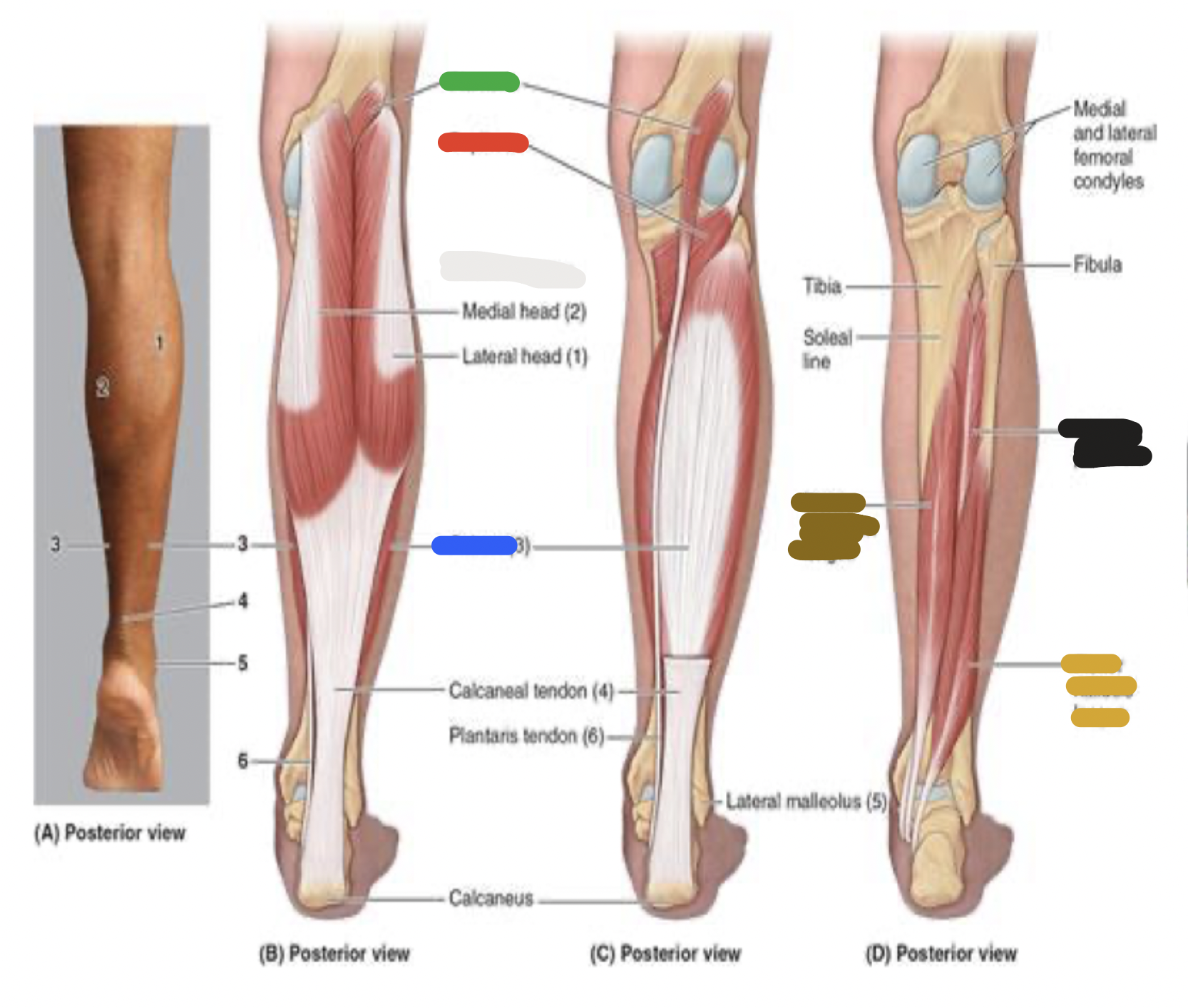
muscles of the posterior leg: green
plantaris
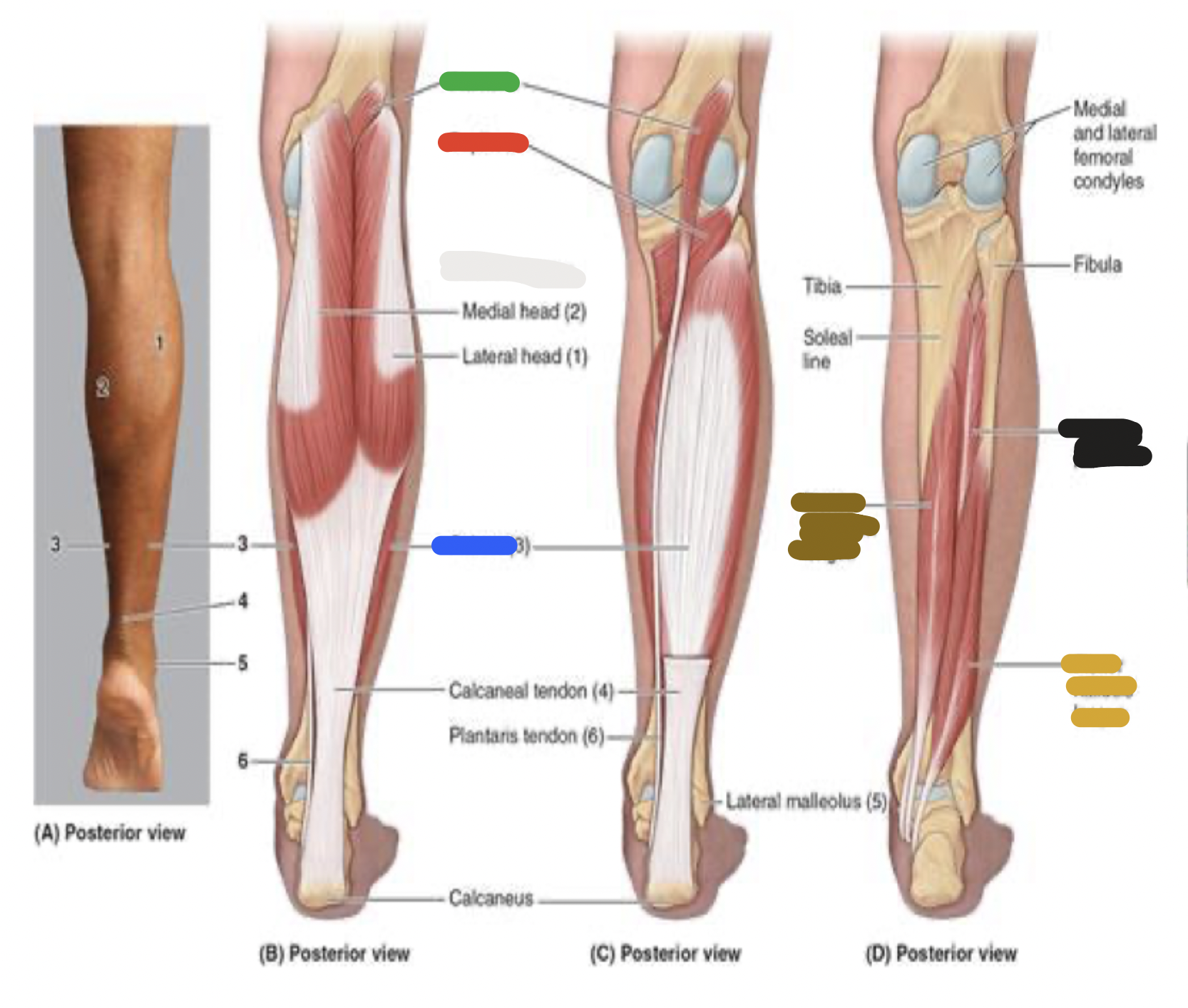
muscles of the posterior leg: red
popliteus
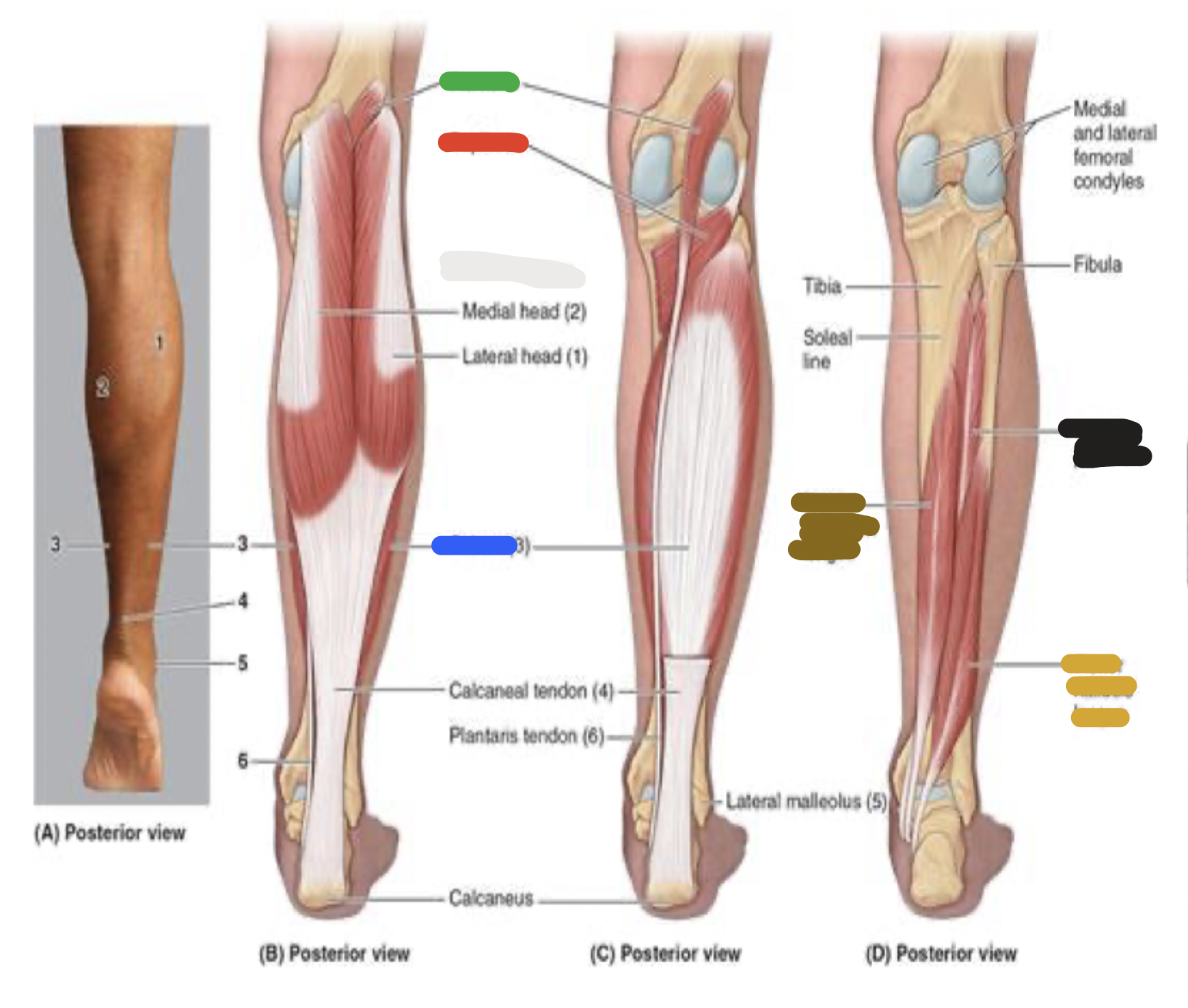
muscles of the posterior leg: yellow
flexor hallucis longus
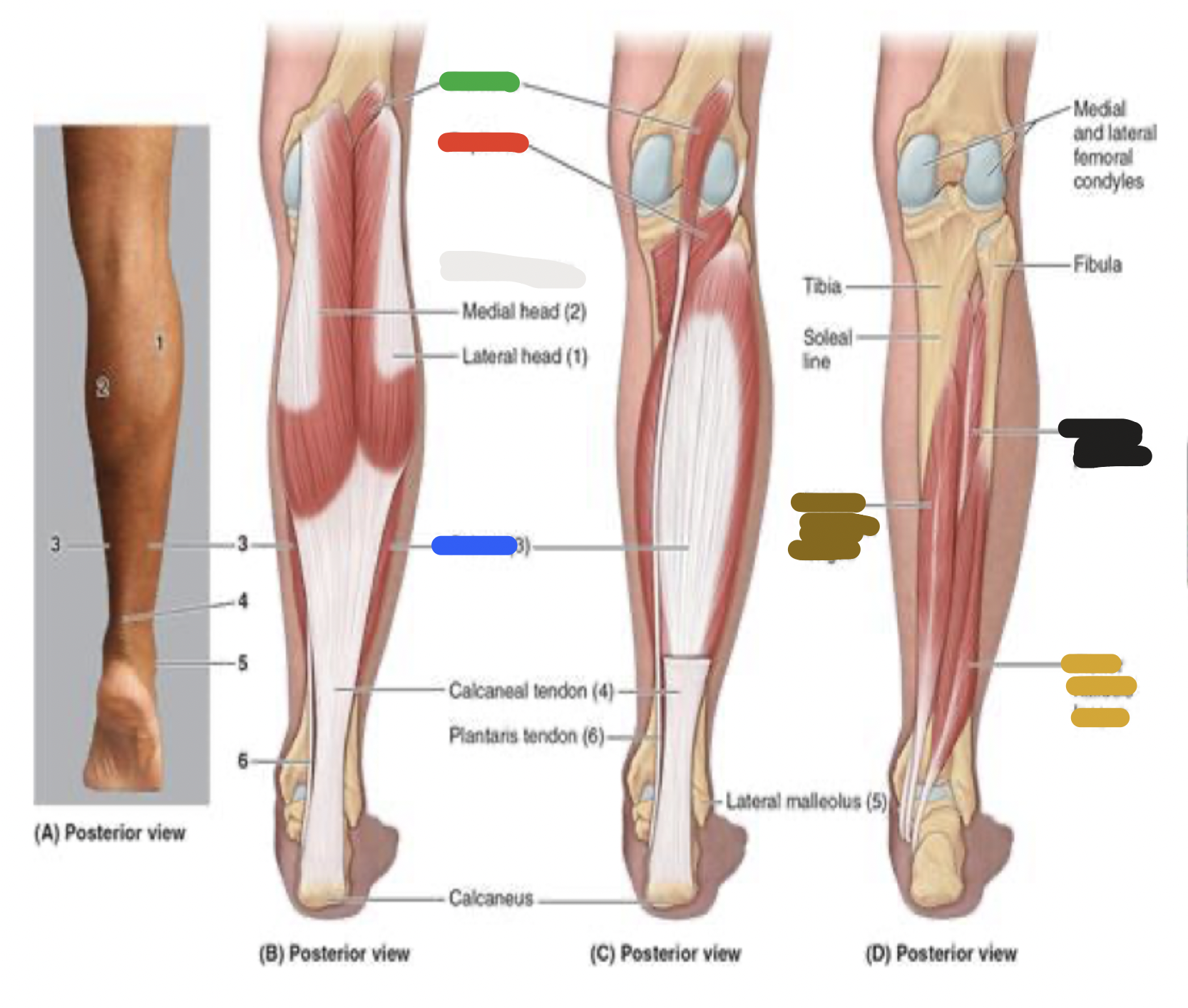
muscles of the posterior leg: brown
flexor digitorum longus
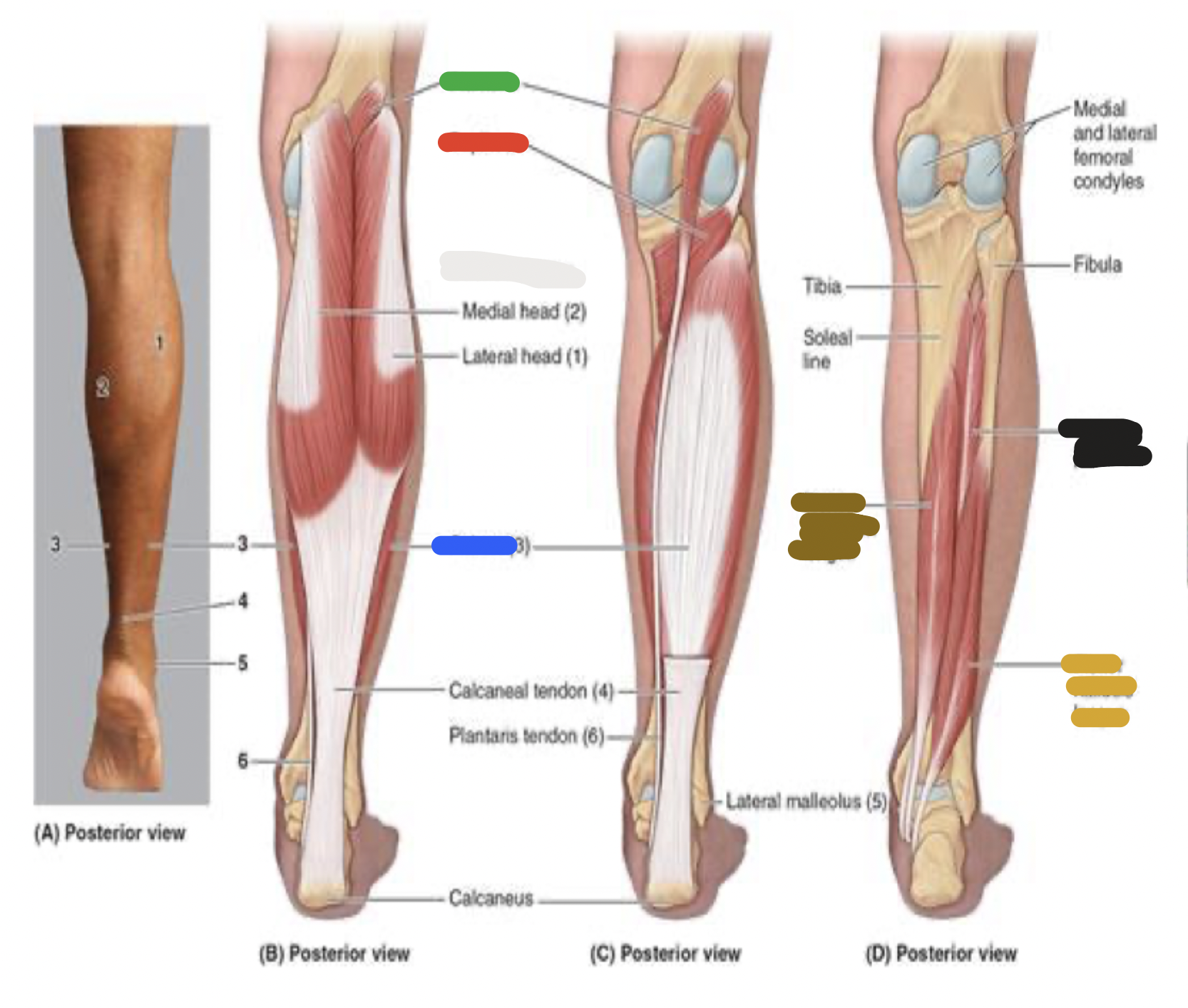
muscles of the posterior leg: black
tibialis posterior
posterior aspect of tibia and fibula
flexors of the foot (does plantarflexion)
anterior aspect of tibia and fibula
extensors of the foot (does dorsiflexion)
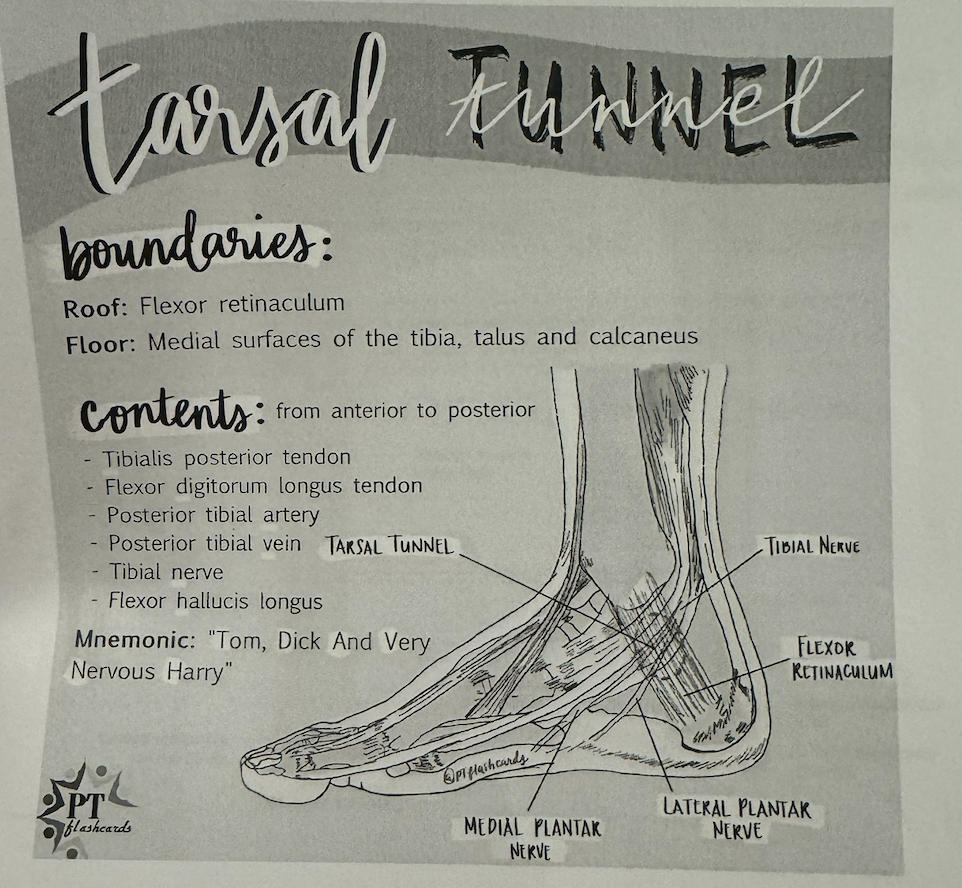
Tom, Dick, Harry
(most of) muscles of the anterior leg
(most of) deep muscles of the posterior leg
T: Tibialis anterior and posterior
D: extensor/flexor Digitorum longus
H: extensor/flexor Hallucis longus
Tom, Dick, And Very Nervous Harry
“tarsal tunnel”
blood supply to the foot (in order from closer to the big toe —> closer to the heel)
T: Tibialis posterior tendon
D: flexor Digitorum longus tendon
A: posterior tibial Artery
V: posterior tibial Vein
N: tibial Nerve
H: flexor Hallucis longus