Parturition: Dystocia’s (Cram)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
True or false: Generally outside interference in a normal parturition should be avoided.
True. If an owner is concerned they should observe the birth, remove afterbirth if it is obstructing the airway, ensure the newborn can suckle, and maybe disinfect the navel
Feet of uniparous feti appear with each contraction and disappear after each contraction, without any progress of the fetus through the passage. What could be the problem?
The fetus could be stuck in a hip or shoulder lock. Assistance is warrented
Fill in the blank: If there’s no progress ___ hour(s) after the rupture of the amnionic water bag, assistance is warrented in farm animals.
1
Fill in the blank: Assistance is warranted when the first stage of labour extends beyond ___ - ___ hours in sow, ewe, or cow. Or beyond ___ hours in mare
6, 12, 4
Fill in the blank: Assistance is warranted when the second stage of labour is more than ___ - ____ hours in the sow, ewe, or cow. Or beyond ___ - ___ minutes in the mare.
2, 3, 20, 30
Term for the earliest stools of a neonate
Meconium
Note: Black, green, or yellow
Meconium is sometimes expelled into the amniotic fluid prior to birth or during labor and delivery. What can this indicate?
Usually a sign of fetal distress
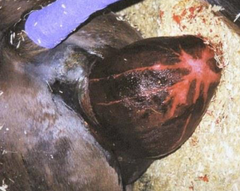
What is this condition called in mares? It involves premature placental separation
Red bag
Note: This occurs when the allanto–chorion fails to break before delivery of the foal
What needs to be done in the case of a mare with red bag?
The allanto-chorion will need to be cut through to deliver the foal. This needs to be done ASAP, as the tissue is ischemic and the mare can suffer permenant damage
Term for the birth of offspring from more than one sire in the same pregnancy
Superfecundation
Term for a condition where a pregnant female with one or more live fetuses, comes into heat again, is bred again, and another conception occurs
Superfetation
Note: This looks like the simultaneous occurrence of more than one stage of developing embryo in the same animal
True or false: Superfetation is relatively common in sheep and goats.
False. It is VERY RARE in all species except marsupials. It most commonly occurs in embryo transplantation
Term for false pregnancy. It is a display of maternal behavior and physical signs of pregnancy by a non–pregnant female
Pseudocyesis
Note: Most commonly occurs in dogs and mice, sometimes in cats
Term for a condition where the embryo or zygote is free in the abdomen at a very early stage in development and it develops a relationship with an organ other than the uterus and undergoes some embryonic development
Extra-uterine pregnancy
Term for the condition where the fetus starts out with a normal endometrial relationship and then escapes from the uterus. It is usually the result of uterine rupture
Secondary–uterine pregnancy
Term for a condition characterized by a gradual enlargement or filling of the placental membranes and/or fetus with excessive fluid
Hydrops
What are the two types of hydrops?
- Hydrops allantois
- Hydrops amnion
Which type of hydrops is more likely to result in death of the fetus?
Hydrops amnion

What condition could this goat have?
Rupture of the prepubic tendon
Note: The tendon of the rectus abdominus muscle can tear away from the pubis
True or false: Hydrops and rupture of the prepubic tendon both have a poor prognosis. Treatment options are limited.
True
Which outcome of fetal death is this? The only external sign is a return to heat. It is the result of very early embryonic death
Reabsorption
Which outcome of fetal death is this? The only external sign is prolonged period of anestrous, and the passage of a ‘mummy’ upon termination of pregnancy
Mummification
Which outcome of fetal death is this? Externally evidenced by sight of the fetus in a non-decomposed or completely decomposed state
Abortion (with or without maceration)
Fill in the blank: One cause of abortions in domestic animals may be the use of some _____ ____ virus vaccines.
modified live
Term that means present at birth
Congenital
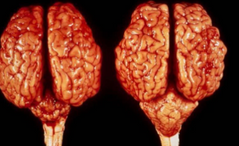
What is wrong with the brain to the left? What is the causative infectious agent of this congenital defect?
Cerebellar hypoplasia, caused by bovine viral diarrhea
What are the four causes of congenital defects?
- Inheritance
- Infectious Agents
- Drugs
- Nutritional Deficiencies

True or false: Cleft palate can be hereditary or caused by toxic plants the mother ingested, or viruses
True
Examples: Locoweed, lupine, tobacco, poison hemlock, akabane virus, bluetongue virus
Term for the condition where the uterus become twisted on its long axis. This can be due to violent movement or falls
Uterine torsion
In cattle and llamoids, uterine torsion might occur at term. In which species can torsion occur at around 7–9 months gestation?
Mares. They are always corrected by laparotomy
Note: Cattle torsions may be corrected by a detorsion rod
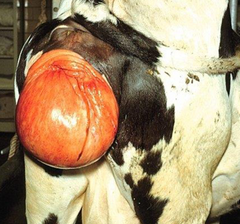
What condition is this?
Vaginal prolapse
Vaginal prolapse has a hereditary componant, which breed of cattle is especially prone to this conditon?
Hereford cattle
Term for a vaginal prolapse that only occurs when the animal is lying down
Dynamic vaginal prolapse
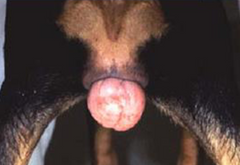
What is this condition in dogs? It is different from vaginal prolapse
Canine vaginal hyperplasia
Note: If it doesn't regress on its own, amputation may be needed
Which species is most prone to mammary neoplasia. 45% of these tumors are malignant
Dogs
Which species, while not as frequently affected as dogs, will have mammary tumors with a 90% chance of being malignant
Cats
When should you spay your dog to drastically reduce the likelyhood of mammary neoplasia?
Before their first estrus. This reduces the risk of mammary neoplasia to 0.5% of the risk in intact bitches
Note: Ovariectomy after 1st estrus will only reduce the risk to 8% of that in intact bitches
Which species is most likley to get a vaginal prolapse postpartum?
Dogs
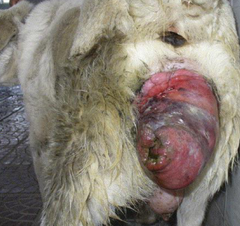
Treatment of vaginal prolapse can involve caudal epidurals, sutures, or raising the hindlimbs of a patient. What is a method of reducing vaginal edema that utilizes a common pantry item?
Sugar can be used to reduce edema by osmotic pressure
Which is more serious (a true veterinary emergency!): A vaginal, or uterine prolapse?
Uterine prolapse
Note: These usually occur during the first day or postpartum
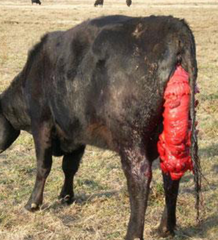
Why is a uterine prolapse so dangerous and potentially deadly?
There are large arteries inside the uterus that may rupture as the cow moves around. This would result in the cow bleeding to death internally. Replacing the uterus back into the animal needs to occur ASAP for the best outcome!
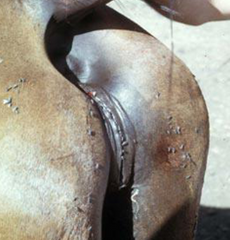
This mare is old and thin, she has faulty closing of the vulvar lips. What condition could result?
Pneumovagina (ie. windsucking)
Note: This condition can also affect mares with good conformation because of an injury doing foaling/breeding
What surgery is used to treat pneumovagina?
Caslick's surgery
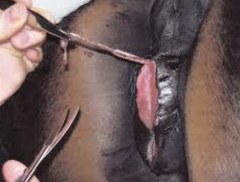

You see a pregnant ewe go down. She is weak, and unable to stand. What could be causing this?
Pregnancy toxemia. The ewe has a negative energy balance and has gone into ketosis trying to sustain her pregnancy (breaking down fat stores as energy)
True or false: Lambing should be induced (or C–section performed) in ewes with pregnancy toxemia.
True. She should also recieve glucose IV, and increased energy rations


You see a cow in sternal or lateral recumbancy. She is excited, drowsy, or at worst comatose. What nutritional deficiency can cause these clinical signs?
Hypocalemia (ie. Milk fever)
Note: Also called parturient paresis
How does the temperature change in cattle suffering from 2nd or 3rd stage milk fever?
They become hypothermic, especially their extremities. Despite the name milk "fever"

What stage of milk fever is this?
Stage 2

What stage of milk fever is this?

What stage of milk fever is this?
What position should a cow be in for the treatment of milk fever?
Sternal. Then deliver IV (slow), or SQ calcium
What type of hay is ideal for lactating cattle for the prevention of milk fever?
Alfalfa (high in calicum and potassium)
Which species typically have the least occurence of dystocias?
Cats
Defined as the lack of normal physiologic uterine contractions during or after parturition
Uterine inertia
Note: Primary inertias can be caused by disease, obesity, lack of hormone release, or stress due to confinment. While secondary inertias occur due to long unproductive labour
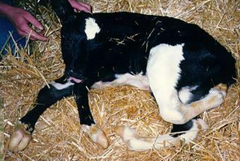
This hereditary condition of the fetus can be a cause of dystocia, what is it called?
Arthrogryposis (ie. twisted joints)
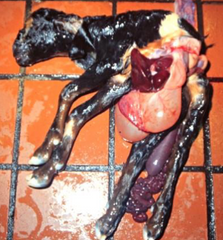
This hereditary condition of the fetus can be a cause of dystocia, what is it called?
Schistosomus reflexus

This condition of the fetus can be a cause of dystocia, what is it called?
Hydrocephalus
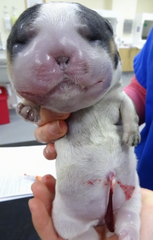
This condition of the fetus can be a cause of dystocia, what is it called?
Anasarca
Defined as those operations by which a fetus is returned to anormal presentation, position and posture
Mutation
Note: Mutations are not often possible in cats and dogs due to size limitations
Consists of pushing the fetus out of the pelvis, into the abdominal cavity where more room is available for adjustments
Repulsion
Defined as the turning or rotating of the fetus on its long axis
Rotation
Defined as the rotation of the fetus on its transverse axis
Version
Fill in the blank: In the anterior presentation, when both ______ [joints] are out of the vulva about ___ [#] hand’s distance, both shoulders should be in the pelvis. Extraction is possible.
fetlocks, 1
Fill in the blank: In the posterior presentation, if the _____ [joints] are out of the vulva, the hips have entered the pelvis. Extraction is possible.
hocks
True or false: There are no conseqeunces for indiscriminate assisted vaginal delivery in cattle.
False. If the assistance isn't warrented you risk fracturing the cow's pelvis, or obturator nerve paralysis. The calf can have degloved limbs or dislocated vertebrae
Name some indications for C-section
Uterine inertia, pregnancy toxemia, obstructive dystocia, and rupture of the uterus
Defined as those operations performed on the fetus for the purpose of reducing its size by division or removal of certain of its parts
Fetotomy. This can be complete or partial depending on how many cuts have to be made to extract the fetus
