Kinematics and Dynamics
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Core notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Kinematics
Describing Movement - how is something moving?
Dynamics
Cause of Movement - why is something moving?
Scalars
Magnitude only (num values only) e.g. distance
Vectors
Magnitude and Direction e.g. Displacement
Distance
Distance of path, denoted as d, measured ONLY in m/km
Displacement
Direct distance from point a to b, denoted as s
Include exact true bearing and exact distance, measured ONLY in m/km
Speed
Scalar Quantity, measured in kmh^-1 or m^s-1, denoted as v
Formula: Vav = total d/t (v=d/t)
Velocity
Vector Quantity, measured in kmh^-1 or m^s-1. Denoted as u or →v.
Formula: uav = total s/t (u = s/t)
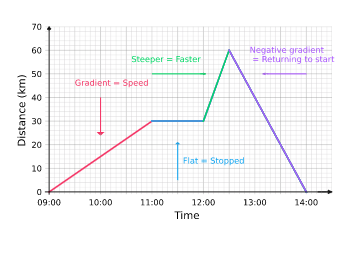
Distance / Time Graph
y-axis: Distance
x-axis: Time
Tip: the slope of the distance time graph gives instantaneous speed, and it can NEVER be negative.
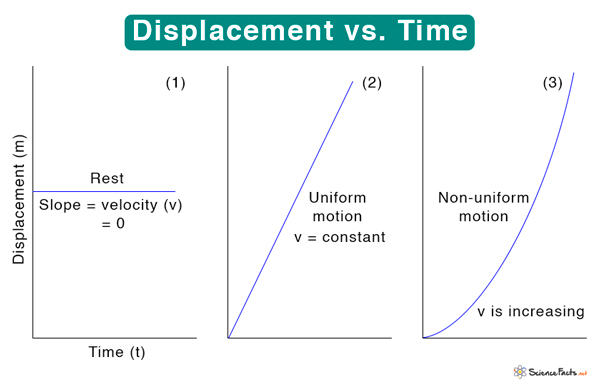
Displacement / Time Graph
y-axis: Displacement with given direction
x-axis: Time
Tip: the slope of the displacement time graph gives velocity, and it CAN be negative (negative velocity).
If it is not moving, there are NO direction (N/A)
Instantaneous Speed
Speed of an object at an exact time, t (the slope of the distance time graph). Can be in decimals.
Acceleration
Vector quantity, denoted as a.
Formula: Overall change in velocity/total time (a = Δu/Δt)
Second Formula: a = v-u/t, where v = final velocity, u = initial velocity, and t = time.
Third Formula: a = F/m, where F = net force, m = mass
Unit: ms^-2 (m/s²) e.g. 5m/s² = 5m / sec increase in velocity
Tip: Time = v-u/a
Veloctiy Time Graph
y-axis: Velocity
x-axis: Time
Tip: like displacement graph, any vector quantity graph can be negative, just like this one (negative velocity)
Slope = acceleration, Area (trapezium / triangle) = displacement
Positive Area = distance (get rid of negatives as it can’t be negative) = A1 + A2
Displacement (can accept negative) = A1 - A2 + direction (Negative = reverse direction, Positive = direction facing.)
Relationships of Graph that can be drawn from other
Distance - Time graph: can be drawn from Displacement - Time graph (but NOT reverse as there is not direction).
Speed - Time graph: can be drawn from distance time graph, and in reverse (no direction needed as both are scalars)
Displacement - Time graph: can be drawn from velocity - time graph, also in reverse (both are vectors).
Inertia: Newton’s 1st Law
An object remains at rest/constant motion, unless acted on by a net unbalanced external force.
Newton’s 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object produced by net force is directly proportional to acceleration and inversely proportional to mass.
Formula: F = ma, m = mass (kg), and a = acceleration (m/s²), F = net force (Newton, N).
Newton’s 3rd Law
Every force in nature has and equal and opposite reaction.
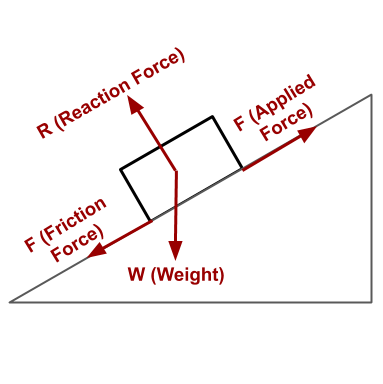
Force Diagram
Arrows from the centre of the object, depending on direction and amount of force, are in different sizes.
Friction: f=Fapplied−Fnet
Terminal Velocity
An object’s maximum velocity depends on several factors, such as air resistance, but the object is still moving.
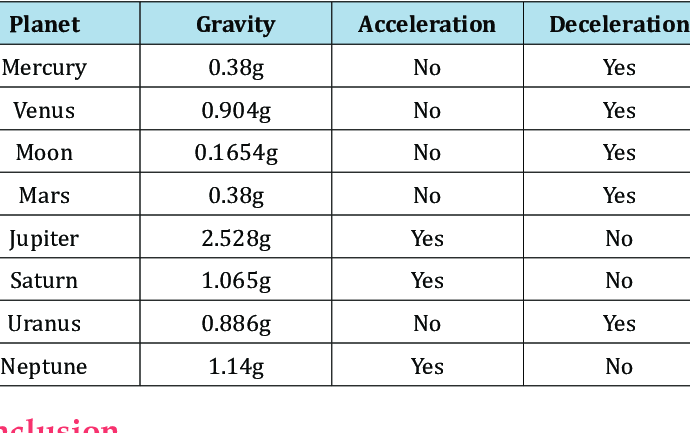
Gravity Net Force
Relates to Newton’s 3rd Law, denoted as Fg
Formula: Fg = mg, where m = mass and g = gravitational acceleration on Earth (constant and varies on different planets, ~ 9.8m/s²)