Chapter 21 Homework: Blood Vessel and Circulation
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is the pump that provides the major force for moving blood through blood vessels?
Heart
Name the type of vessel that carries blood from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart.
Pulmonary Vessel
Arteries, capillaries, and veins are types of blood _______
Vessels
Name the tunics of blood vessel walls.
Tunica M
Arteries carry blood Blank______ the heart.
Away from
True or false: The underlying function of the circulatory system is to deliver adequate blood flow to tissues to meet their needs.
True
Blood vessels that consist of only a single layer of endothelial cells resting on a basement membrane are ______.
Capillaries
Pulmonary vessels transport blood from the heart through the ______.
Lungs
Place the types of veins through which blood flows from the capillaries to the heart in order. Start with the smallest at the top.
Venules
Small veins
Medium Veins
Large Veins
Which is not a type of blood vessel?
Nerve
Small arteries and arterioles are innervated to a ______ extent than other blood vessel types.
Greater
The outmost layer of a blood vessel wall is the tunica Blank______.
Externa
Blood ejected by the right ventricle and returned to the left atrium flows through the ______ circuit of the circulation.
Pulmonary
The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are
Arteies
Systemic circulation begins at the heart when the ______ ventricle ejects blood into the aorta.
Left
Describe the structure of capillaries.
Single layer of simple squamous endothelium resting on a basement membrane
Starting at the left ventricle list the segments of the aorta in order.
ascending aorta, arch, thoracic aorta, abdominal aorta
Venules collect blood directly from ______.
Capillaries
Name the arteries that branch off of the ascending aorta.
Coronary Arteries
Sympathetic stimulation of vascular smooth muscle causes ______ while parasympathetic stimulation of vascular smooth muscle of the penis and clitoris causes ______.
vasoconstriction, vasodilation
The right subclavian artery branches directly off the ______.
brachiocephalic artery
Deoxygenated blood is carried to the lungs via pulmonary ______. Oxygenated blood is carried from the lungs to the heart via pulmonary ______.
Arteries: Vein
The order of arteries carrying blood to the arm is ______.
subclavian to axillary to brachial arteries
The system of vessels that carries blood from the left ventricle to the body and back to the right atrium is called ______ circulation.
Systemic
Arterial blood supply to the structures of the chest cavity arises from ______.
Thoracic Aorta
True or False: The only branches of the ascending aorta are the coronary arteries.
True
Shortly after leaving the aortic arch, the brachiocephalic trunk branches to form the ______.
right common carotid artery
right subclavian artery
The ______ divides into the right and left common iliac arteries.
Abdominal Aorta
The subclavian artery delivers blood directly to the ______ artery.
Axillary
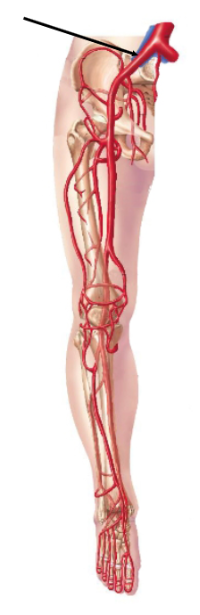
The blood vessel indicated in the figure of the leg is the ______ artery.
Common Iliac
Blood supply to organs of the thoracic cavity comes from branches of the _____-aorta.
Thoracic or descending
Indicate the veins carrying blood into the right atrium.
Coronary sinus
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
The three unpaired arteries arising from the abdominal aorta are the ______.
celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery
Name the arteries that branch off of the ascending aorta.
Coronary Artery
Cardiac veins carry blood from the walls of the ______.
Heart
At what level does the abdominal aorta divide into two common iliac arteries?
5th lumbar vertebra
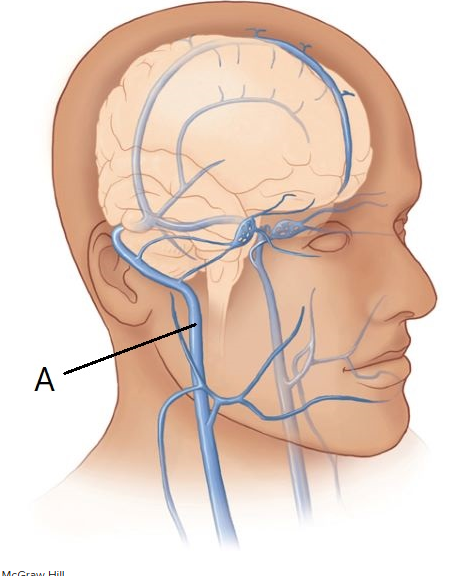
The vein indicated in this figure of the head is the Blank______ vein.
Internal Jugular Vein
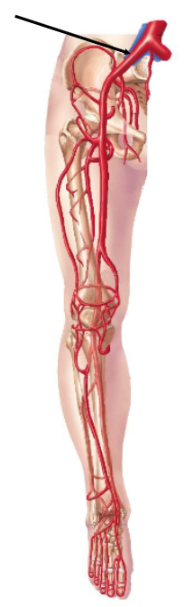
The blood vessel indicated by the arrow in the figure of the leg is the common _____ artery
Iliac
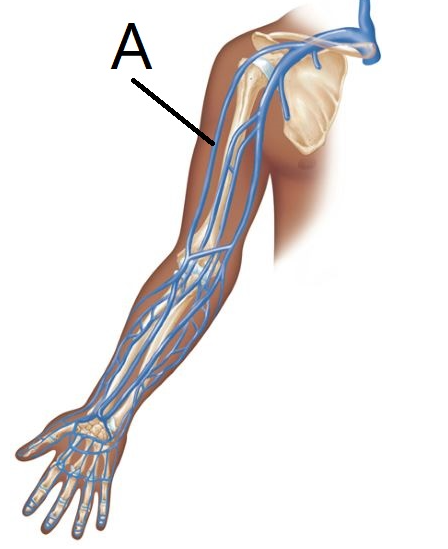
The vein of the arm designated by the letter A in this figure is the ______ vein.
Cephalic
What type of blood is carried by the vena cavae to the right atrium?
Deoxygenated
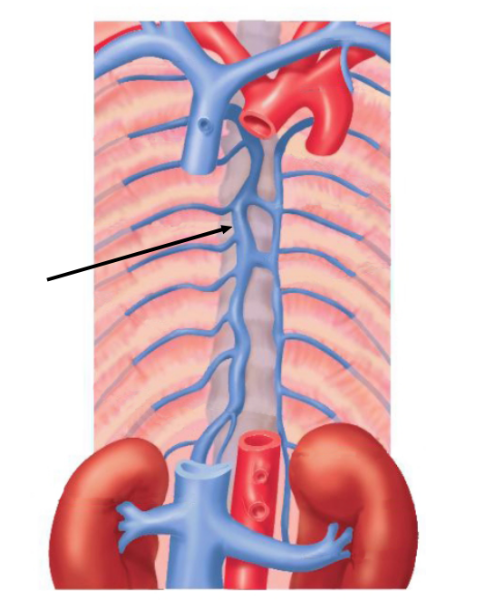
The vein of the thoracic cavity indicated in this figure is the____vein
Azygos
Choose the three unpaired arteries that arise from the abdominal aorta.
Celiac trunk
Superior mesenteric artery
Inferior mesenteric artery
Name the veins that merge to form the common iliac vein.
External iliac and internal iliac
The vessels that transport blood from the walls of the heart to the coronary sinus and right atrium are called____veins
Coronary
The popliteal vein continues as the ____ vein in the thigh
Femoral
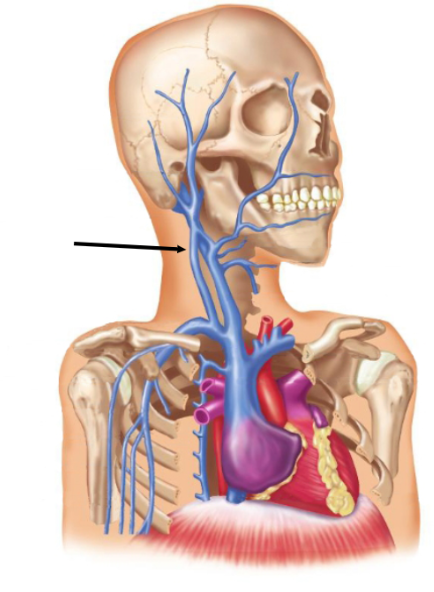
The neck vein indicated in the illustration of the head is the ______ vein.
External Jugular Vein
True or False: The brachial veins are medial to the cephalic vein.
True
Normal blood flow through healthy, unbranched vessels is usually ______, while ______ blood flow can occur through abnormally constricted vessels.
laminar, turbulent
The azygos vein drains blood directly into the ______.
Superior Vena Cava
What is blood pressure?
A measure of the force that the blood exerts against a vessel wall
The internal and external iliac veins merge to form the___iliac vein
common
Choose the two variables that will increase blood flow.
Increased pressure difference (P1-P2)
Decreased resistance (R)
In the lower limb, the ______ vein becomes the femoral vein.
Popliteal
What is an aneurysm?
An area of arterial wall that has weakened and formed a bulge
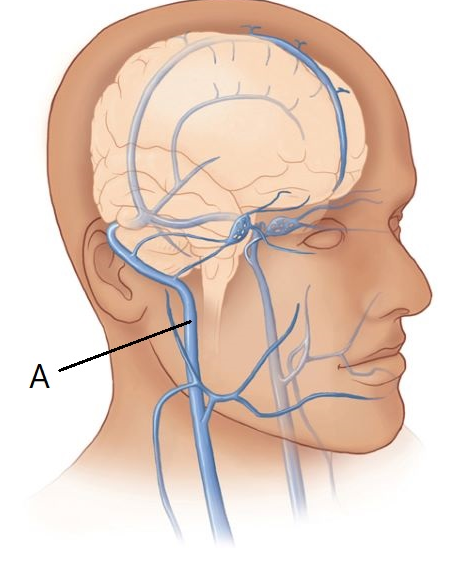
The vein of the neck indicated by the letter A in this figure is the ____ jugular vein
Internal
Blood vessels with small compliance stretch______ easily.
less
How would you describe the streamlined movement of blood through a vessel?
Laminal Flow
he cross-sectional area of all capillaries is ______ than the cross-sectional area of the aorta.
greater
The force that the blood exerts against a vessel wall is called ______.
Blood Pressure
The greater the resistance in a blood vessel, the more rapidly the blood pressure ______ as blood flows through it.
Decreases
The term ______ includes any opposition to blood flow.
Resistance
Heart rate can be determined by taking a ______.
pulse
An area of arterial wall that has weakened and forms a bulge is called a(n)
aneurysm
During capillary exchange, in the arterial end of the capillary there is a net movement of fluid ______ the capillaries and at the venous end of the capillary there is a net movement of fluid ______ the capillaries
Out of; Into
he tendency for the volume of a blood vessel to increase as the blood pressure increases is known as______. It is a measure of how easily the vessel wall stretches
Compliance
A factor that influences blood flow in veins is ______.
Blood Volume
The segment of the circulation that has the greatest total cross-sectional area is/are ______.
Capillaires
The compliance of veins is ______ than the compliance of arteries.
Greater
True or false: As blood flows from the aorta through the capillaries and veins to the right atrium, the blood pressure drops. This pressure drop is due to a decrease in blood volume.
False
The pulse is used to determine
Heart Rate
Mechanisms that regulate blood flow through tissues include local control,_____ control and _____control.
Nerve and hormonal
At the ______ end of capillaries, capillary exchange results in net filtration of fluid.
Arterial
Venous blood flow affects cardiovascular functioning by affecting ______.
Preload
Indicate the processes used to adjust blood flow to local tissues.
Adjustment of the precapillary sphincters to the capillary beds in the tissue
Adjustment of the arteriolar diameter leading to the tissue
Explain the drop in blood pressure that occurs when one goes from lying down to standing up.
Venous compliance allows blood to pool in the legs, decreasing venous return. This causes a drop in cardiac output and blood pressure.
True or false: Neural regulation of blood flow through tissues is primarily the function of the sympathetic nervous system.
True
The greater the resistance in a blood vessel, the more rapidly the blood pressure ______ as blood flows through it.
Decreases
As one ages, mean arterial pressure ______
Increases
The nervous system ______ blood flow through tissues.
Helps to control
During capillary exchange there is a net movement of fluid into the capillaries at the ______ end of the capillary and a net movement of fluid out of the capillaries at the ______ end of the capillary.
Venous; Arterial
The adrenal medullary mechanism is an example of a ______-term mechanism controlling blood pressure.
Multiple choice question.
short
Short
Indicate what changes are made in order to regulate the amount of blood flow to a tissue.
Adjustment of arteriolar diameter and capillary sphincters
The conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I is catalyzed by the enzyme ______.
Renin
Which system regulates control of blood flow throughout the body?
Sympathetic
The ______ is slightly less than the average of systolic and diastolic pressures.
Mean Arterial Pressure
Name the mechanisms which control blood flow through tissues.
Hormonal control
Local control
Nervous control
Neural and hormonal mechanisms are involved in the ______-term regulation of blood pressure.
Short
The hormone ______ is released by cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
Renin