Quality Assurance
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
what is the definition for quality assurance?
all planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate assurance that a structure, system or procedure will perform satisfactorily in compliance with standards
what is the definition of quality control?
means the set of operations intended to maintain or to improve quality and includes monitoring, evaluation and maintenance at required levels of all characteristics of performance of equipment that can be defined, measured, and controlled
what legislation does quality assurance fall under?
IR(ME)R 2017, IRR 2017
what does IR(ME)R 2017 stand for?
ionising radiation (medical exposure) regulations
what does IRR 2017 stand for?
ionising radiation regulations
what are the main points of IR(ME)R17?
defines employer responsibilities
defines duty holders and their responsibilities
what are responsibilities of an employer as stated by IR(ME)R17?
an employer who has control over any equipment must implement and maintain a quality assurance programme
list the different duty holders defined in IR(ME)R17
employer, referrer, practitioner, operator, medical physics expert
what are the main points of IRR17?
sets basic safety standards for any establishment
protect the general public and works against dangers of ionising radiation
what does IPEM 91 stand for?
institute of physics & engineering in medicine report 91
published 2010
what is IPEM 91
a report which provides:
guidance for anyone responsible for diagnostic x-ray equipment
advice on which routine performance tests are essential and which are desirable
information on how to do QA tests, who should be doing them and how often they should be done
guidance as to when the results indicate further action should be taken
what are the different types of quality assurance tests?
critical exam, acceptance testing, commissioning
what is a critical exam?
when the supplier demonstrates to the purchaser that the designed safety features work properly; shows theres sufficient protection from ionising radiation exposure and the equipment is safe to use
what is acceptance testing?
test done by the department to verify the equipment and image quality is satisfactory and complies with manufacturers specification
when should acceptance testing be done
twice - before commissioning and one month before the end of the warranty period
what is commissioning?
tests which establishes baseline measurements for future QC checks
what are examples of quality control tests that can be done?
routine performance testing of the tube and generator and image quality
regular measurements in order to monitor radiation dose to the patient
what are examples of QC tests that can be done by radiographers?
beam collimation and alignment
radiation output
automatic exposure control
image quality
dose rate in fluoro
what is the purpose of a beam collimation QC test?
to check that the light field and radiation field are properly aligned and centred to the detector
what tool is used in a beam collimation QC test?
alignment test tool; after exposure the radiation field size in the resultant image is measured compared to the light field size and
what is the purpose of a beam alignment QC test?
to check the central ray of the radiation field is properly aligned
what tool is used in a beam alignment QC test?
glass tube shaped alignment test tool that is used in conjunction with collimator test tool
what is the purpose of a radiation output QC test?
to monitor the repeatability and reproducibility of radiation output
what tool is used for radiation output QC tests?
dosimeters under reproducible conditions (use predetermined exposure factors)
what is the purpose of AEC QC tests?
to check that the AEC is functioning correctly and the resultant detector dose indicator is consistant
what is the purpose of radiographic image quality QC tests?
to monitor the limiting spatial resolution and threshold contrast of the system
what tool is used for image quality QC tests?
TOR CDR
how is a image quality QC test done?
an image of a TOR CDR phantom is taken under reproducible conditions; count the number of contrast details and resolution groups visible

name this tool and what is it used for?
TOR CDR; used for image quality QC tests
why is there usually no suspension level fail requirements for an image quality QC tests?
it is a subjective analysis therefore cant be accurately measured
what do the lines on a TOR CDR test?
spatial resolution
what do the large grey discs on a TOR CDR test?
low contrast, large detail detectability
what do the small dots in the inner ring on a TOR CDR test?
high contrast small detail detectability
what do the medium sized circles on a TOR CDR test?
sensitometric measurements
what is the purpose of a fluoroscopy dose rate QC test?
to assess the dose rate reproducibility under automatic exposure control
how would you know a QA test is compliant with IPEM91 standards?
compare test date to time frequency baseline, positive if the test date is within the time frequency baseline
who can perform a level A test?
radiographers and medical physics expert
who can perform a level B test?
medical physics expert only
what are the characteristics of a level A test?
performed more frequently, quicker, less detailed
what are the characteristics of a level B test?
performed less frequently because highly detailed so takes significantly longer; might require complex equipment
what action would you take if a QC test fails (remedially or suspension level)?
repeat test then inform superintendent and medical physics expert
what are the different types of failures of a QA test?
remedial or suspension level failure
what does it mean if a machine has failed on a remedial level?
it does not meet standards of operation but is still useable by staff so machine is not taken out of action
what does it mean if a machine has failed on a suspension level?
the machine is not useable or safe so needs to be taken out of actions
what is the purpose of a fluorography image quality test?
to monitor the limiting spatial resolution and threshold contrast of a system
how would a fluorography image quality test be carried out?
screen the TOR 18FG phantom under reproducible conditions; count the number of resolution groups that are visible
what test tool is used for a fluorography image quality test?
TOR 18FG
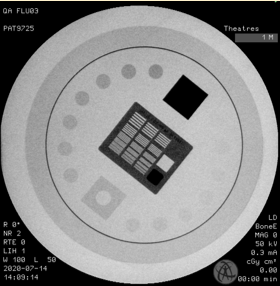
which test tool is shown?
TOR 18FG