Concept 1: The Nervous System - Study Guide
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Describe the overall functions of the nervous system and summarize the overall process used to accomplish these functions.
The ultimate control center of the body, overseeing all communication among the organ systems. Sensory Input, Motor Output, and integration.
Differentiate between the two main types of cells that make up nervous tissue.
Neurons: Excitable cells that respond to stimuli by conducting impulses to transmit signals.
Neuroglia: Supportive cells that provide nutrition, insulation, and help with signal transmission.
Draw a picture of a neuron and label its key parts.
See picture
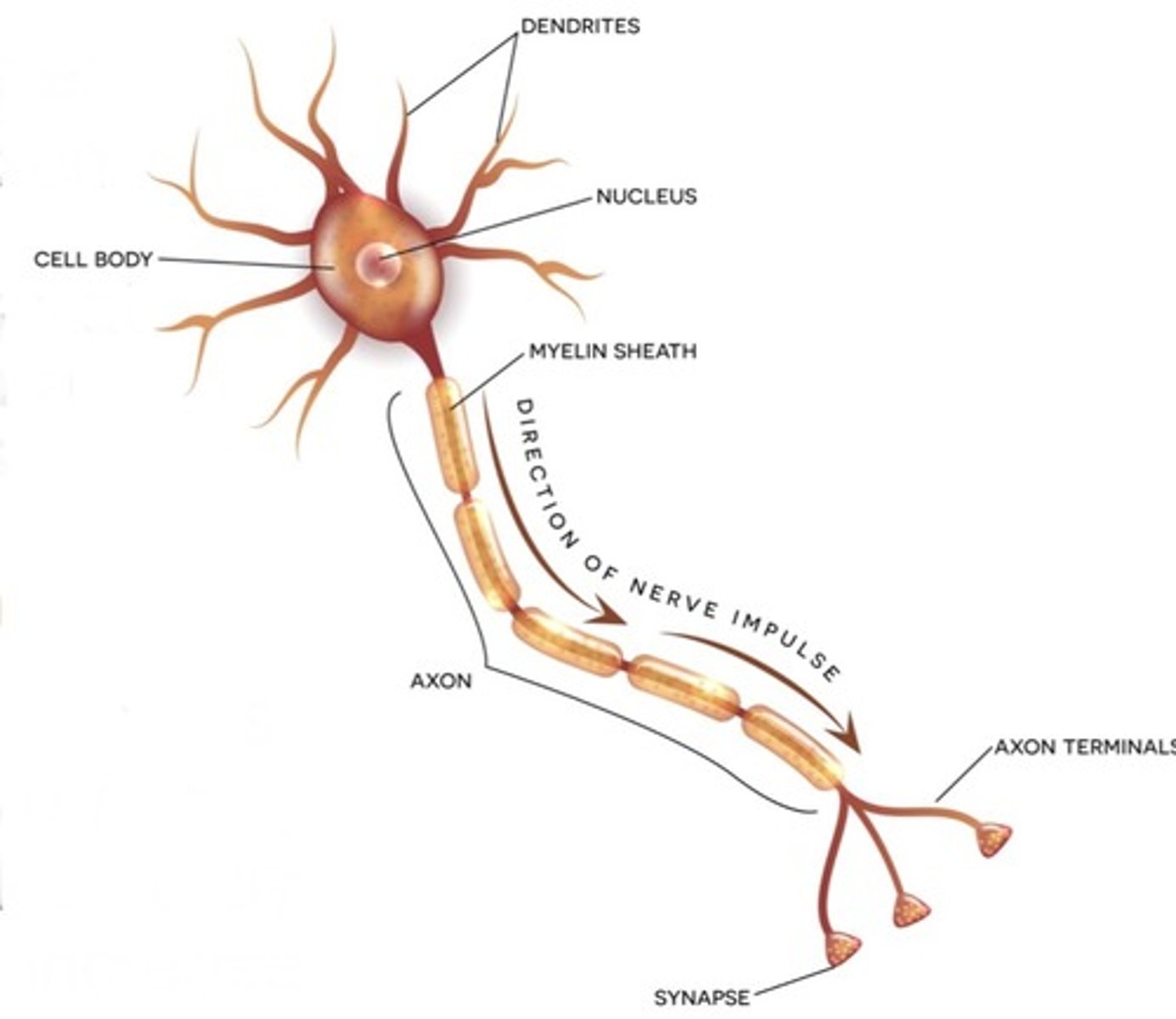
Summarize how a signal is transmitted from one neuron to another, including what happens at a synapse and how to increase the strength of the signal.
Dendrites - Cell Body - Axon - Axon terminals - Synapse
Explain how neurons can be classified based on their structure and/or their function.
Neurons can be classified by their structural differences, based on the number of processes (extensions) from the cell body.
Explain the role of protein channels, specifically including the Na+/K+ pump, in the conduction of a nerve impulse
Allows transport into the cell membrane, both positively and negatively charged.
Differentiate between the three main ways protein channels can be gated.
Voltage-gated channels: Open and close in response to changes in the membrane potential.
Lingand-gated channels: Only open when a specific chemical (ligand), such as a neurotransmitter, binds to the channel.
Mechanically gated channels: Only open if the membrane is stretched or physically deformed.
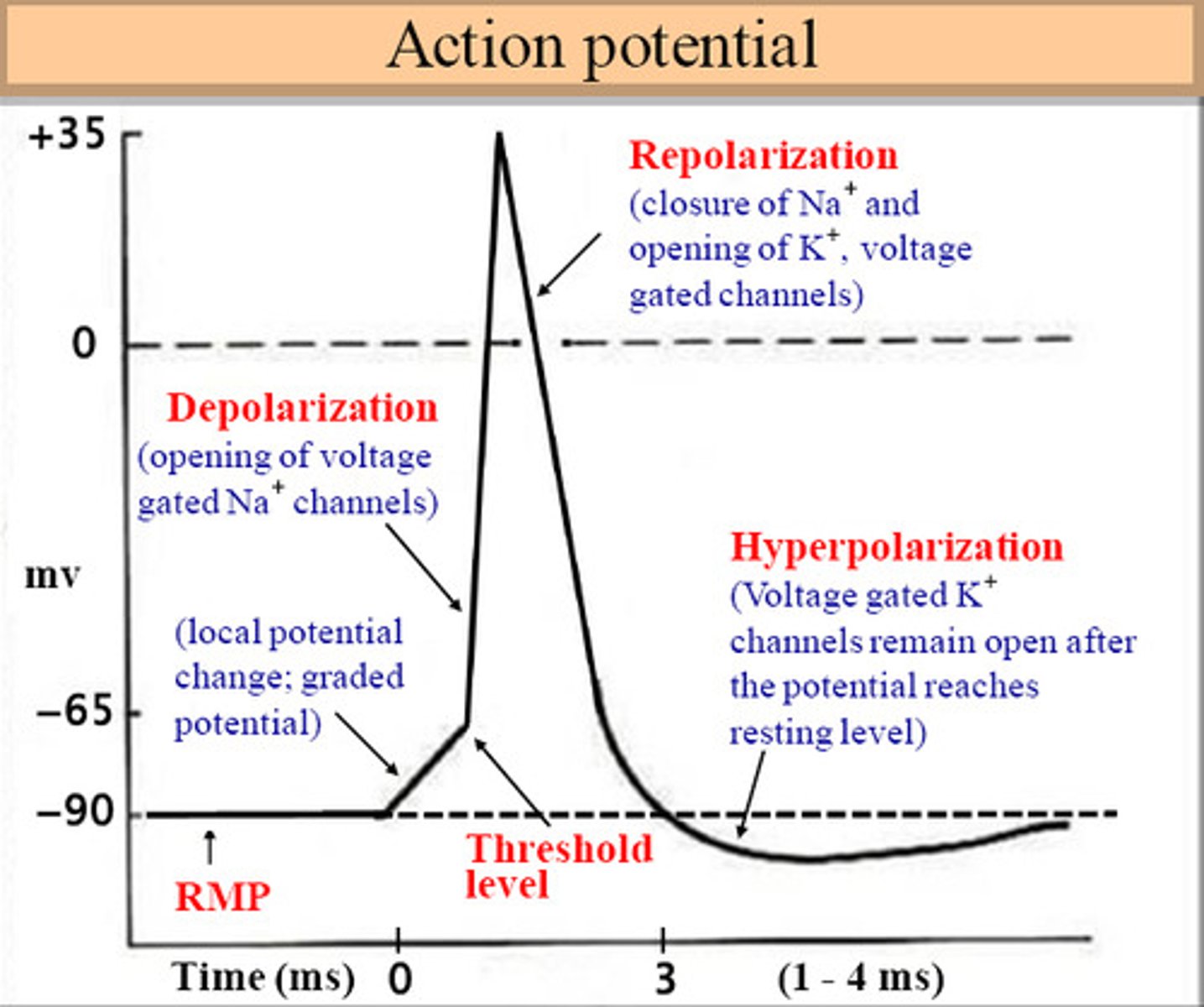
Sketch a graph of how the voltage changes across the cell membrane during an action potential. Label and briefly explain what each section of the graph shows in terms of what is happening.
see image
Explain how excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters function differently.
Excitatory neurotransmitters pen the ion channels and depolarize the postsynaptic neuron, causing the action potential to be sent on.
Inhibitory neurotransmitters can hyperpolarize the postsynaptic neuron so it can't send on the action potential
Sketch a flowchart showing the organization of the different divisions of the nervous system. Include short phrases or pictures under each division to help you remember their differences.
See image
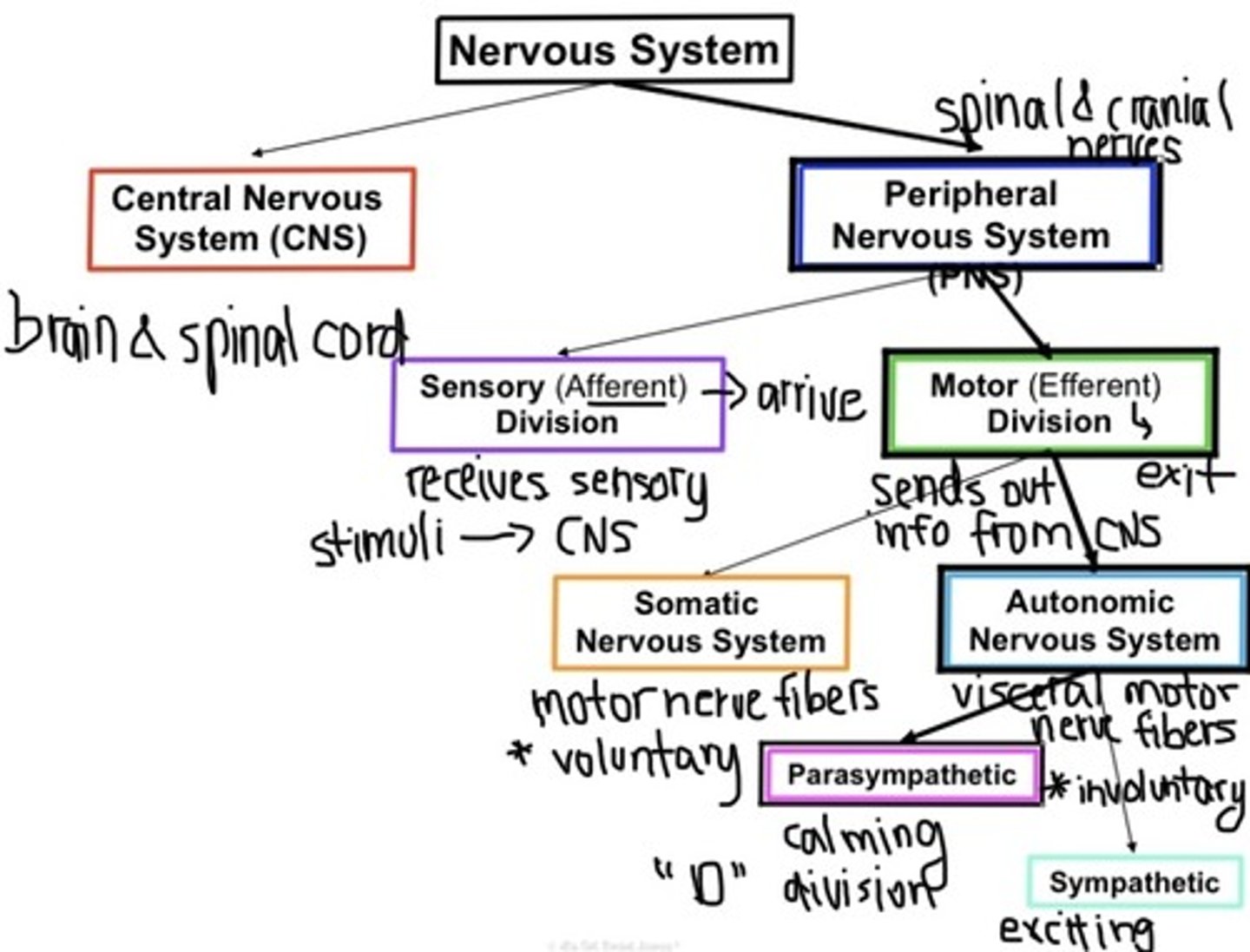
Distinguish between the roles and components of the central and peripherl nervous systems.
Central Nervous System
- brain and spinal cord
- Integration & control center
Peripheral Nervous System
- spinal and cranial nerves
- communication system between CNS & rest of body
Summarize the location and role of the three main parts of the brain.
Cerebrum (main part, 4 lobes): Functions in learning, speech, emotion, reasoning, vision, hearing, and fine movements.
Cerebellum (under the cerebrum): posture & balance, coordinates timing and patterns for smooth and agile subconscious movements.
Brain stem (base of the cerebrum & anterior to the cerebellum): relays info between rest of the brain and the spinal cord; coordinates a lot of automatic functions like respiration, circulation, body temperature, sleep, digestion, and swallowing
Distinguish between the sensory and motor divisions of the peripheral nervous system.
Sensory (Afferent) Division —> Receives sensory stimuli to send back to CNS/brain
Motor (Efferent) Division —>Sends out information from the brain to effector organs like muscles (so they will contract) and glands (so they will secrete)
Distinguish between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems of the motor division.
Somatic Nervous System (somatic motor nerve fibers)
- Conduct impulses from CNS→ skeletal muscles
- Controls voluntary movements
Autonomic Nervous System (visceral motor nerve fibers)
- Conduct impulses from CNS →smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands
- Controls involuntary movements of the heart, lungs, stomach, etc.
Explain how the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system work in opposition to one another.
The parasympathetic division aka "rest and digest" division maintains the body and conserves energy for later. It essentially helps the body calm down and recover, especially after becoming aroused by the sympathetic aka "fight or flight" division, that focuses on what body needs immediately and prepares body to take action sad respond quickly.
Explain the difference between an innate and learned reflex.
Innate reflex (intrinsic): a rapid, predictable motor response to a startling stimulus.
Learned reflex (acquired): a response resulting from practice, repetition, or experience
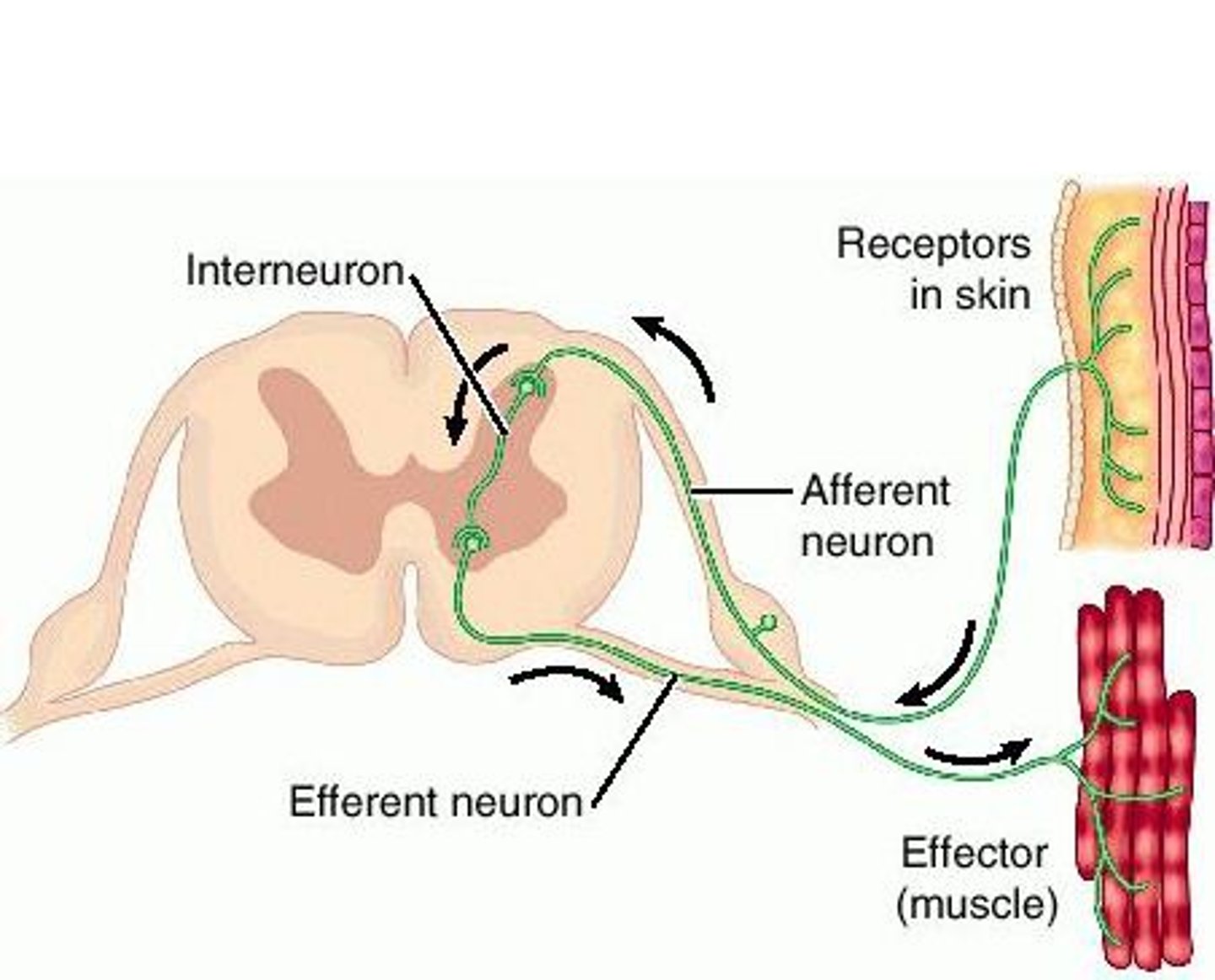
Draw and interpret or describe an example of a reflex arc. Within your drawing or description, identify the 5 essential components of all reflex arcs.
Receptor: site of stimulus
Sensory neuron: transmits impulse from PNS to CNS
Integration center: "decodes" the signal at a synapse (or multiple synapses)
Motor neuron: conducts impulses to an effector organ
Effector: responds by contracting (if a muscle cell) or secreting (if a gland)
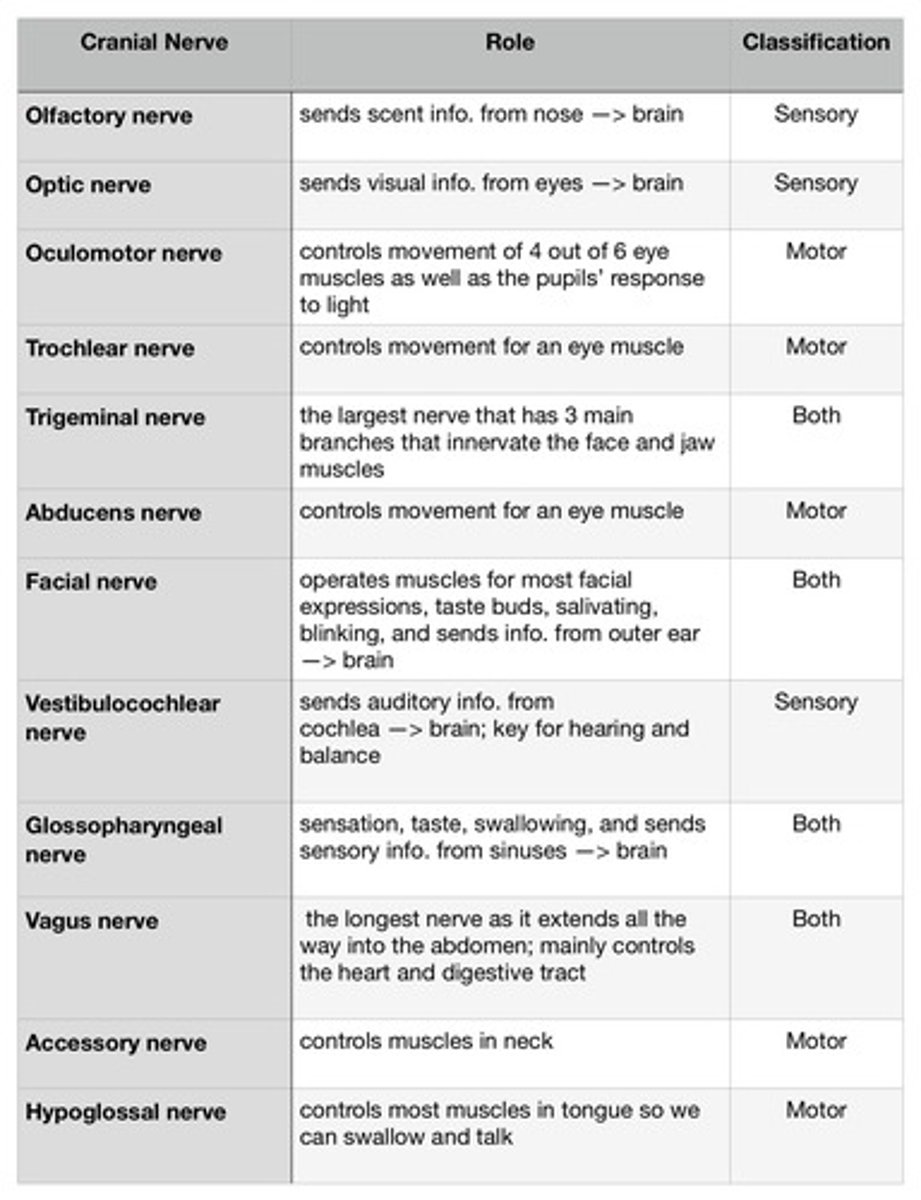
Summarize the role of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves. Include their classifications.
see image
Soma(Cell Body)
contains the nucleus and other structures common to living cells.
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Ganglion
collection of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
Nerve
a whitish fiber or bundle of fibers that transmits impulses of sensation to the brain or spinal cord, and impulses from these to the muscles and organs.
Axon terminal
The very end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters and makes synaptic contact with the next neuron in the chain.
Mylelin Sheath
a greatly extended and modified plasma membrane wrapped around the nerve axon in a spiral fashion
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
Sensory Neurons
Neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
Motor Neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs, with other neurons.
Resting Membrane Potential
An electrical potential established across the plasma membrane of all cells by the Na+/K+ ATPase and the K+ leak channels. IN most cells, the resting membrane potential is approximately -70 mV with respect to the outside of the cell.
Graded Potential
Any change in electric potential of a neuron that is not propagated along the cell (as is an action potential) but declines with distance from the source.
Threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Action Potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Nerve Impulse
the message carried by a neuron
Depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
Repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell.
Hyperpolarization
The movement of the membrane potential of a cell away from rest potential in a more negative direction.
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Meninges
membrane surrounding the spinal cord and brain
Ventricle
lower chamber of the heart
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
Brain Stem
Connection to spinal cord. Filters information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain.
Neurotransmitter
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Hormone
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
Mechanoreceptors
Sensory receptors responsible for sensing distortion in body tissues.
Thermoreceptors
respond to changes in temperature
Photoreceptors
respond to light
Chemoreceptors
respond to chemicals
Nociceptors
pain receptors
Reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response