Neuro Lab Practicum 2
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
Experimental Neuro
measures how nervous system functions by manipulation/ measuring activity in standard lab conditions; relies on empirical techniques
Theoretical/ Computational
uses models and simulations
Cognitive/ Clinical
measures behavior and mental processes
Molecular Neuro
most elementary level
individual cells that make up neurons and glial cells
DNA, RNA and neurotransmitters
Cellular Neuro
special properties of neuro
characteristics:
neuron types, functions, how they form connections
System Neuro
visual and motor systems
how neurons are wired together to preform a shared functions
Behavioral Neuroscience
Behaviors
specific regions of the brain that are related to specific behavior
Cognitive Neuroscience
Neural Mechanisms: self-awareness, imagination, language
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
all species come from a common ancestor and share some physiological similarity
Why is studying the brain difficult?
Its unethical to study on live humans
Have to study humans after death
Uses animal models; are quite the same (in genetic makeup and complexity)
How many genes and neurons do humans have?
20,000 genes
billions of neurons
Most common Neuroscience model?
rats and mice
inexpensive, reproduce quickly, share many similar structures with humans
How many genes do mice have?
25,000
How many genes do zebrafish have?
24,000
Why are zebrafish used?
they are transparent, neurons and internal organs are easy to visualize
How many genes do fruit flies have?
15,000
Why are fruit flies better?
simple genome and short life
How many genes and cells and neurons do nematode have?
19,000 genes
1,000 total body cells
302 neurons
Who’s physiology is closet to humans?
Rhesus Monkey
developmental neurobiologist
analzyes the development and maturation of the brain
molecular neurobiologist
uses the genetic material material of neurons to understand the structure and function of the brain molecules
Neuroanatomist
studies the structure of the nervous system
Neurochemist
studies the chemistry of the nervous system
Neuroethologist
studies the neural basis of species-species animal behaviors in natural settings
neuropharmacologist
examines the effects of drugs on the nervous system
neurophysiologist
measures the electrical activity of the nervous system
Physiological psychologist
studies the biological basis of behavior
Psychophysicist
quantitatively measures perceptual abilities
Why is animal testing important?
can be tested to find further unknown information that computers cannot do
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC)
a committee that reviews and approves animal research protocols to ensure ethical and humane treatment of research animals.
Dose = 25 mg/kg BW Cefazolin
Rat body weight = 479 grams = 0.478 kg
Calculate dose to administer:
0.478 kg x 25 mg/kg = 11.95 mg
Calculate volume to inject:
Cefazolin concentration = 100 mg/mL
11.95 mg / 100 mg/mL = 0.12 mL
All antibiotics cross the BBB
false, some antibiotics cannot enter the BBB or CSF due to their molecular size or charge
What antibiotic are animals normally given after surgery?
Cefazolin
What are cell walls made out of?
Peptidoglycan, a polymer consisting of sugars and amino acids, which provides structural support to bacterial cell walls.
Name the stages of anesthesia
1) Analgesia
2) Excitement/ Delirium
3) Surgical Anesthesia
4) Medullary Paralysis
Analgesia
-From start of anesthesia to loss of consciousness
-Normal stats; dream-like state
Excitement/ Delirium
-from loss of consciousness to start of regular breathing
-may vocalize, struggle, respiration, heart and blood pressure may increase
Surgical Anesthesia
-From beginning of regular respiration to stopping of respiration
-Plane 1: spontaneous respiration, loss of eyelid and conjunctival reflex
-Plane 2: intermittent stopping of respiration, loss of corneal and laryngeal reflex
-Plane 3: Loss of function of intercostal and abdominal muscles, loss of pupillary light reflex. True surgical anesthesia
-Plane 4: Irregular respiration, loss of diaphragm function, apnea, loss of cranial reflex
Medullary Paralysis
-From stopping respiration until circulatory failure and death
-Anestetic overdose
What is Consciousness and what is it made up of?
regulated by a network of brain regions rather than a single structure. The key areas include the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem reticular formation, which work together to maintain awareness and arousal.
What areas are responsible for high-order awareness, perception and decision making?
The cerebral cortex, especially the prefrontal, parietal, and temporal association areas
What does the Thalamus do?
central relay that integrates sensory input and maintains communication between cortical regions. Disruption of thalamocortical signaling leads to loss of consciousness, as seen in deep anesthesia or coma.
Damage causes loss of consciousness
What is the Reticular activating system critical for?
arousal; releases acetylcholine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine that keep the cortex active and responsive
Damages cause less wakefulness/ awareness
Consciousness is dependent on what?
continuous signaling between the brainstem (which controls arousal), the thalamus (which integrates and distributes signals), and the cerebral cortex (which generates awareness and cognition).
What does anesthesia do in the brain?
altering ion channel activity and synaptic transmission
increases GABA receptors
decreases transmission of glutamate receptors like NMDA and AMPA
Ketamine and nitrous oxide do what?
suppressing cortical and thalamic excitatory circuits
violate isoflurane; increases potassium and decreases sodium and calcium channels
Sodium pentobarbital does what?
anesthetic that acts as a potent central nervous system depressant through its interaction with GABA-A receptors
causes hyperpolarization
high amounts can increase GABA without it even being present
Name the gauges and its associated color
30G → light yellow
26G → brown
25G → orange
24G → purple
23G → blue
22G → black
21G → green
20G → yellow
19G →.creamy yellow
18G → pink
16G → white
Is 26G or 18G bigger?
18G
What is the bevel?
tip of the hypodermic needle
always faces up
What angle is intramuscular?
90 degrees
in muscle
What angle is subcutaneous?
45 degrees
in fat
What angle is intravenous?
25 degrees
in vein
What angle is intredekmal?
10-15 degrees
in skins surface
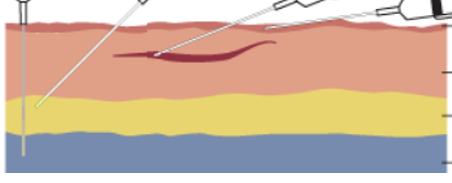
Name each layer
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous tissue
muscle
Is drug absorbed faster in fat or muscle?
Drug is absorbed faster in muscle/vein rather than fat due to blood flow
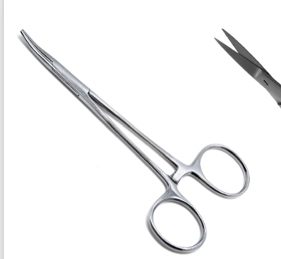
Name instrument and purpose
Hemostatic forceps (hemostat)
clamp blood vessels and stop bleeding
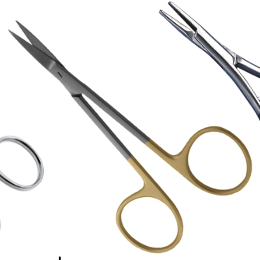
Name instrument and purpose
iris scissors
cutting
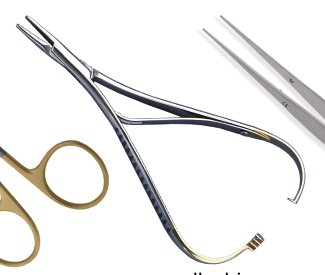
Name instrument and purpose
needle driver
to hold needles while suturing

Name instrument and purpose
thumb forceps
to grasp and hold tissue
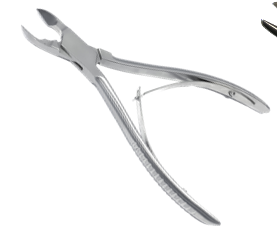
Name instrument and purpose
bone cutting forceps
cutting bone
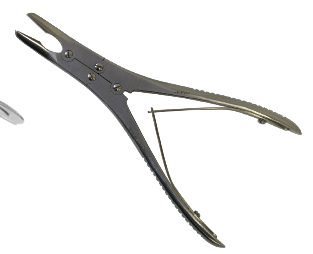
rongeur
to remove bone

Name instrument and purpose
suture needles
stitching
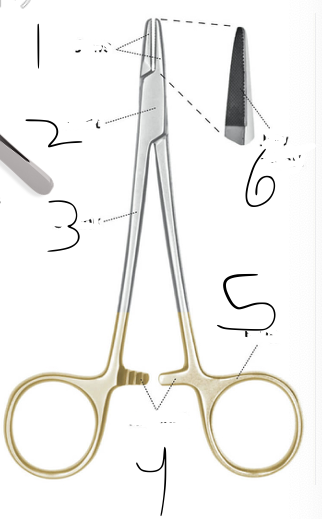
Name instrument pieces in order
1) Jaws
2) Joint
3) Shank
4) Rachet
5) Ring
6) Jaw insert
Difference between absorbable and nonabsorbable sutures
Absorbable are made of cat gut and uses on internal organs and slowly dossolve
nonabsorable is made of silk, nylon, polypropylene, and polyester, must be removed later and are used for skin or areas requiring long-term support
What determines the size of a suture?
1-2 without zeros are thicker while 6-0 and 7-0 are fine sutures for nerves
simple continuous suture
single strand of suture material passed back and forth along the incision
simple interrupted suture
most basic and widely used pattern. Each stitch is tied individually, which provides strong closure and allows for adjustment of tension at each point. If one stitch fails, the others still hold.
horizontal mattress suture
greater strength across the incision and helps distribute tension over a wider area of tissue. It is often used in areas where skin edges are under more tension.
vertical mattress suture
both deep and superficial closure in one stitch, helping to evert wound edges and promote better healing. It is useful in thicker tissue or where precise edge alignment is needed.
Ford interlocking suture
lock stitch, resembles the simple continuous pattern but includes small loops that lock each pass in place. This provides extra security while still being relatively quick to place.
running subcutaneous suture
placed beneath the skin surface to close deeper tissue layers or to produce a more cosmetic closure.
proper scrubbing techniques
1) apply soap to the palm of hand
2) dip fingertips of other hand and decontaminate area under nails
3) spread remaining solution from wrist to elbow
4) apply in circular movement until forearm is covered
5) covers all aspects of hands, up to wrists
6) rub backs of hands and palms
7) interlace fingers to reach interdigital spaces and apply to thumbs
8) Allow hands to dry before donning gloves and gown
What and why are the anesthetic gases used in animal surgeries?
isoflurane or halothane
instantly control the flow
Proper scrubbing surgical site technique
Scrub incision with chlorohexidine, starting and the midline, then left then right side, only swiping from top to down, not rubbing
Repeat same steps with povidone-iodine
What does Chlorhexidine do?
broad-spectrum antiseptic that destroys bacteria
What does Povidone-iodine do?
releases free iodine, which rapidly penetrates and oxidizes microbial proteins, killing bacteria, viruses, fungi, and some spores.
how to identify a question and form a hypothesis
-Observe and identify a specific question
• Review what is already known
• Focus the question so it is testable
• Predict an outcome (form a hypothesis)
• Make sure the hypothesis can be
demonstrated or rejected
control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment, used for comparison
cofound
unintended variable that changes along with the independent variable and therefore could provide an alternative explanation for the results
How to chose a sample of animals
select animals that reflect the general characteristics of the population so that the results can be generalized beyond the specific individuals tested. What is observed in that group is assumed to reflect how most animals of the same species would respond under similar conditions
Variation
natural differences that exist among individuals within a population. No two animals are exactly the same
What is a power analysis?
statistical calculation that estimates how many animals are needed to detect a meaningful difference between groups with a given level of confidence
Randomization
Randomization means that each animal has an equal chance of receiving any of the treatment
Replication
repeating the experiment or having multiple animals within each group so that results can be verified and not attributed to chance.
random number table
list of digits arranged in no predictable order, often generated by a computer or mathematical algorithm
assigns randomly for certain uses (1-no dose 4- high dose)
read in order
induced disease
most widely used
reproduce symptoms & biological changes
pharmacological (induced disease)
injecting chemicals
lesion (induced disease)
damaging certain brain region
stress (induced disease)
expose to high stress to activate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
studies mental health issues
biological (induced disease)
injecting bacteria and viruses
spontaneous change
natural biological changes without any stimulation
genetically modified animals
adding, removing or editing specific genes
negative model
resistant to diseases that affect other species
healthy animals
gain baseline data
between subjects
different groups get different treatments
Within-subjects
same animals used across all conditions
Factorial
tests effects of two or more variables
Repeated-measures
measures the same subjects over time
Mixed
combines between- and within-subjects approaches