Water, Aqueous Solutions, and Intermolecular Forces
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Water Molecule
Composed of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom.
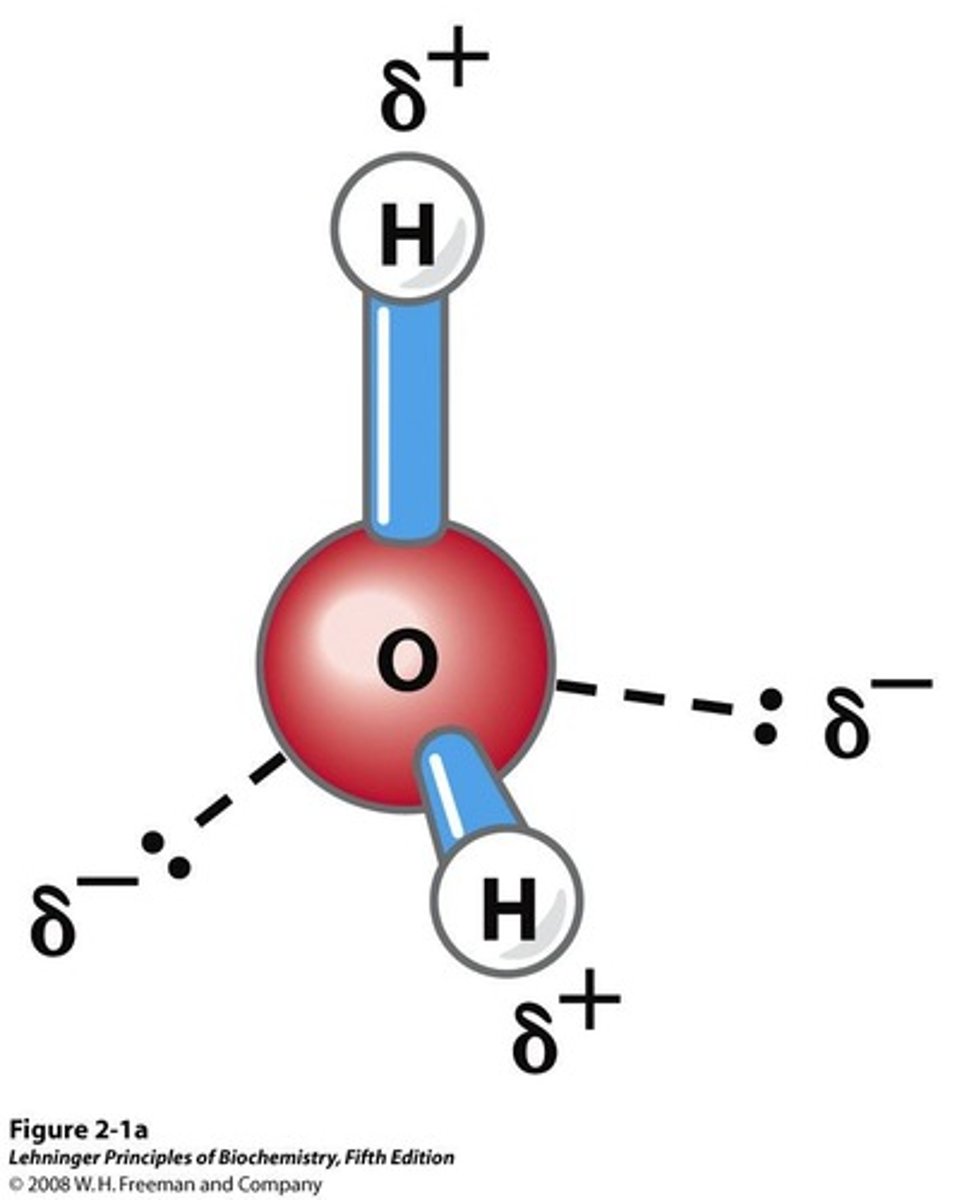
Dipole Moment
Unequal sharing of electrons creates partial charges.
Hydrogen Bond
Electrostatic attraction between H and O atoms.
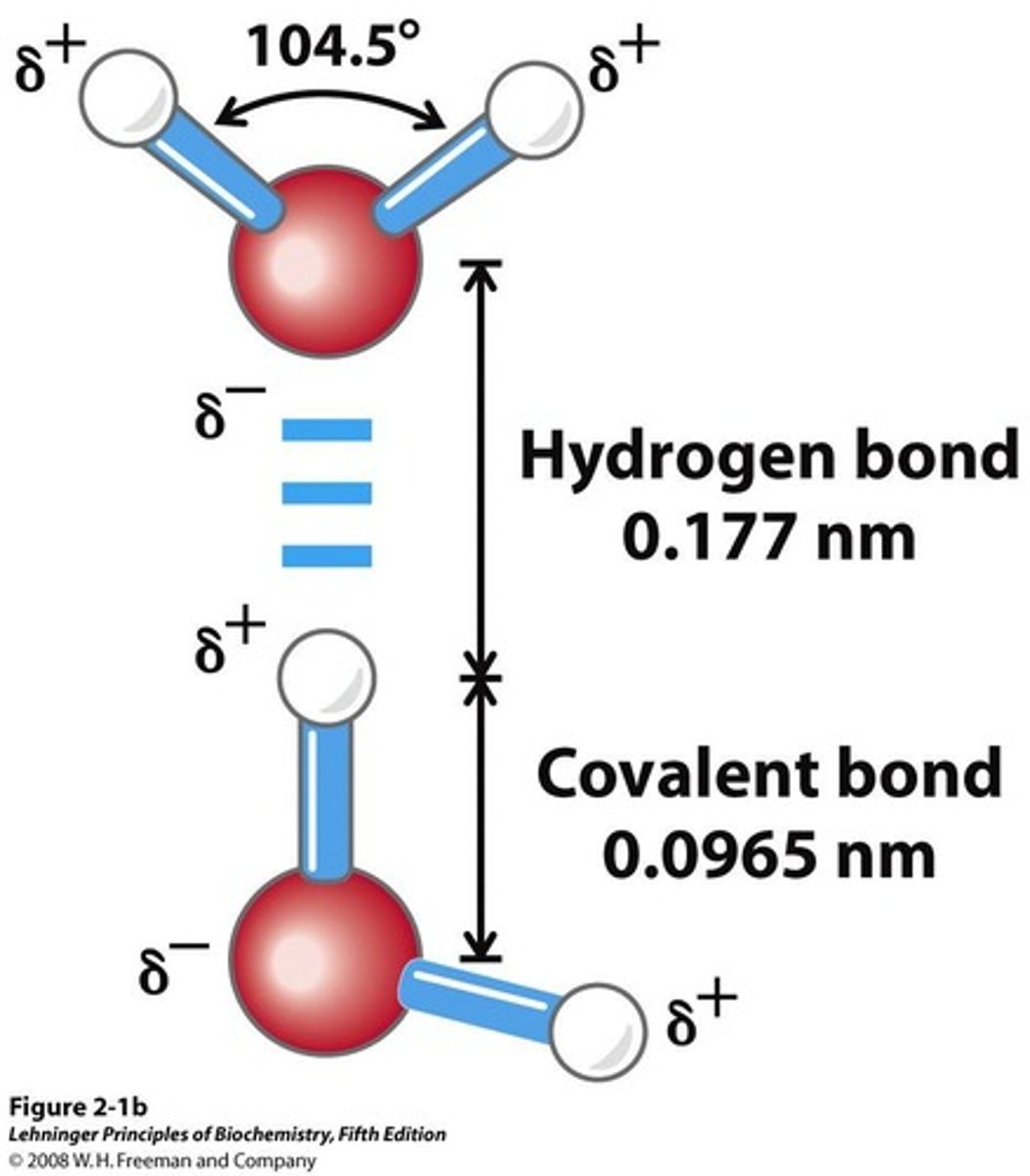
Boiling Point
Water's high boiling point due to hydrogen bonding.
Melting Point
Water's high melting point from strong intermolecular forces.
Surface Tension
Water's resistance to external force, due to cohesion.
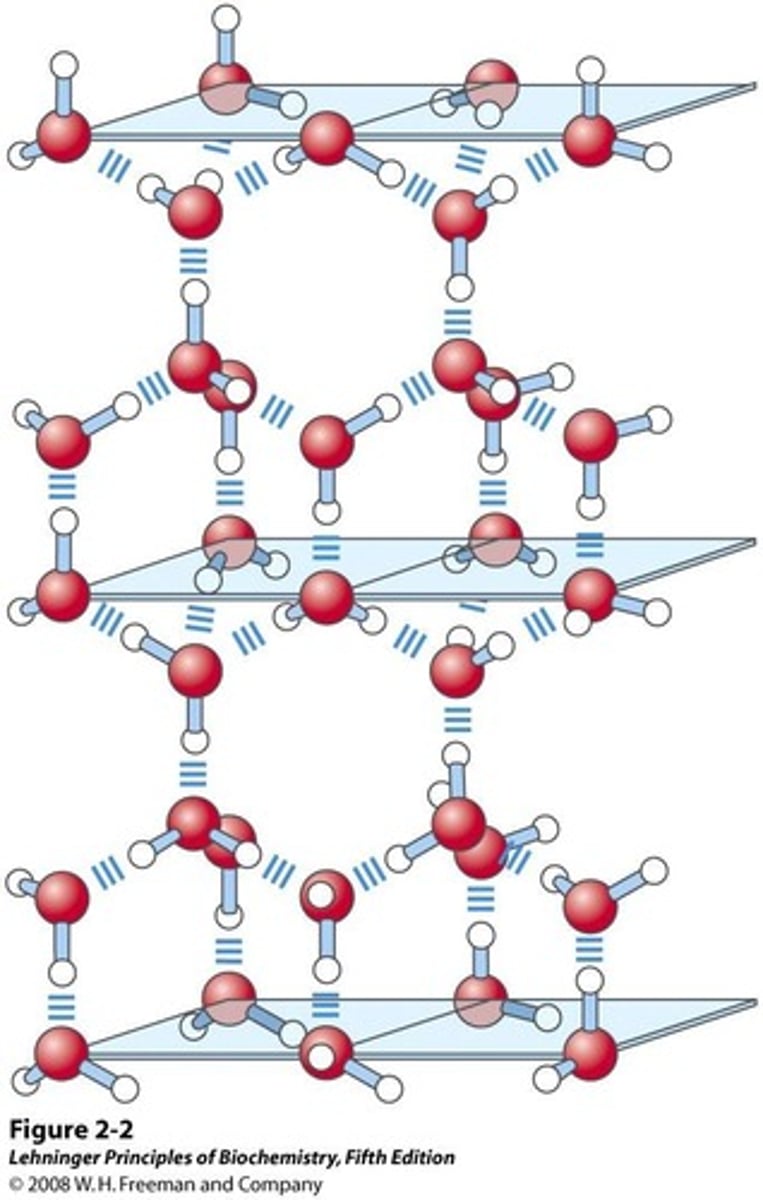
Hexagonal Ice
Common ice structure with low entropy and density.
Hydrophilic
Substances that easily dissolve in water.
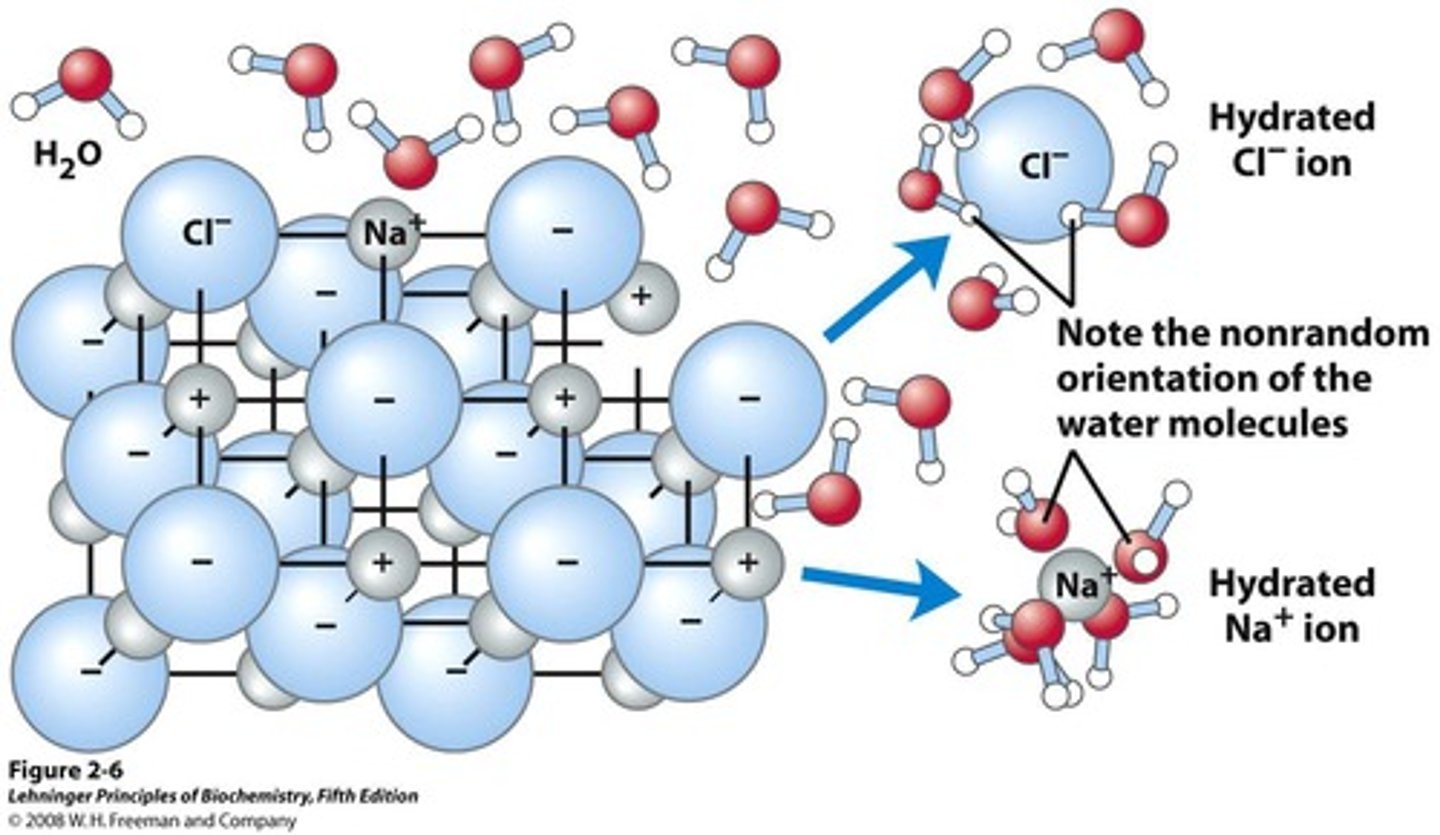
Hydrophobic
Nonpolar substances that do not dissolve in water.
Solvation
Process of surrounding solute particles with solvent molecules.
Electrostatic Interaction
Attraction between charged or polar molecules.
Entropy Increase
Dissolving salts raises disorder in the system.
Aqueous Environment
Water-based medium where biochemical reactions occur.
Weak Acid
Substance that partially dissociates in water.
Weak Base
Substance that partially accepts protons in water.
Crystal Lattice
Ordered arrangement of ions in solid state.
Proton Donor
Substance that releases protons in a reaction.
Proton Acceptor
Substance that gains protons in a reaction.
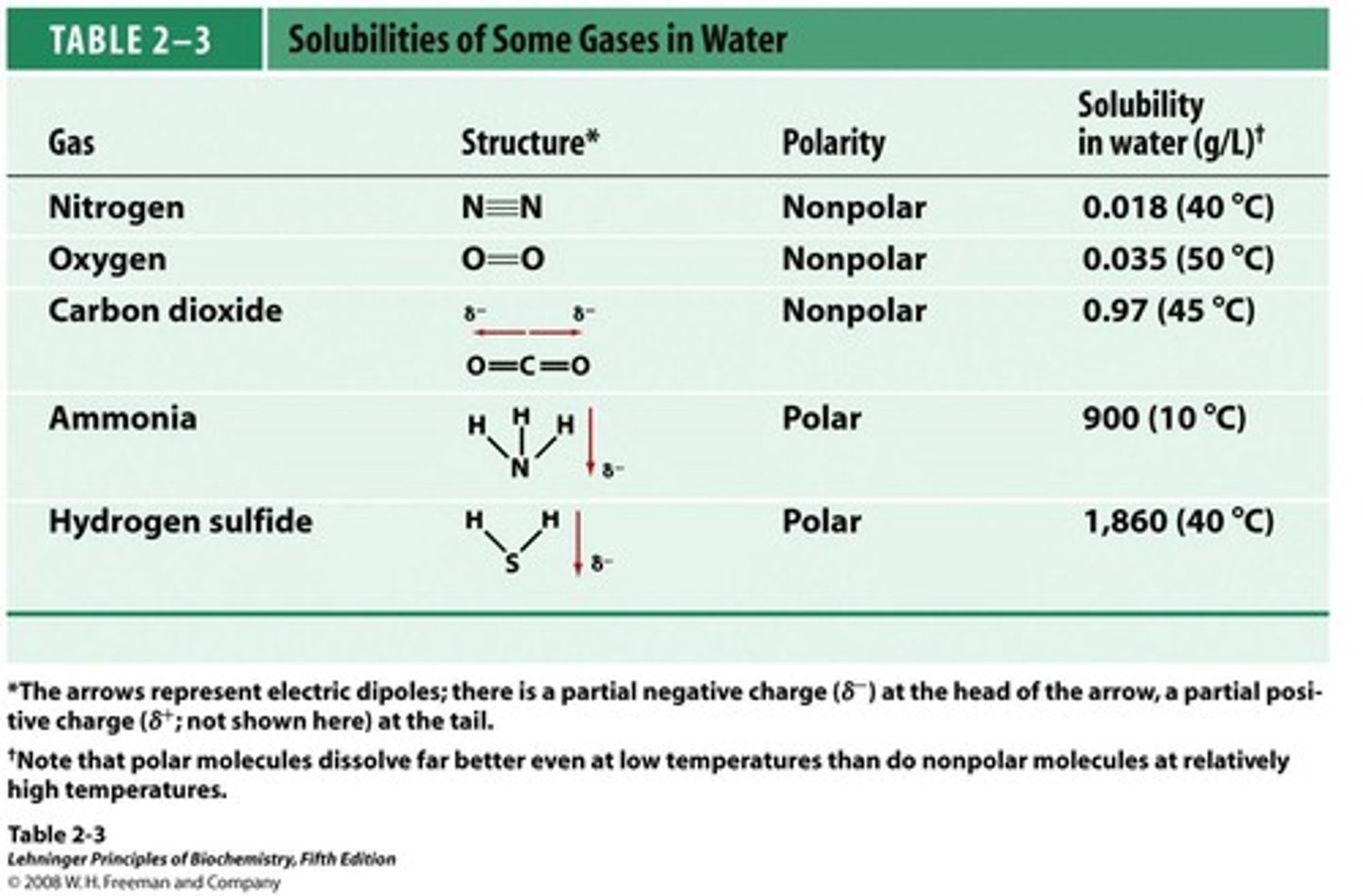
Nonpolar Gases
Gases with no charge separation, poorly soluble in water.
Electronegativity
Tendency of an atom to attract electrons.
Solubility
Ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
Molecular Interactions
Forces that affect how molecules interact in solutions.
Bulk Water
Water with high entropy and little order.
Hydrophobic Solute
Substance with low solubility in water.
Low Entropy
Thermodynamically unfavorable state in systems.
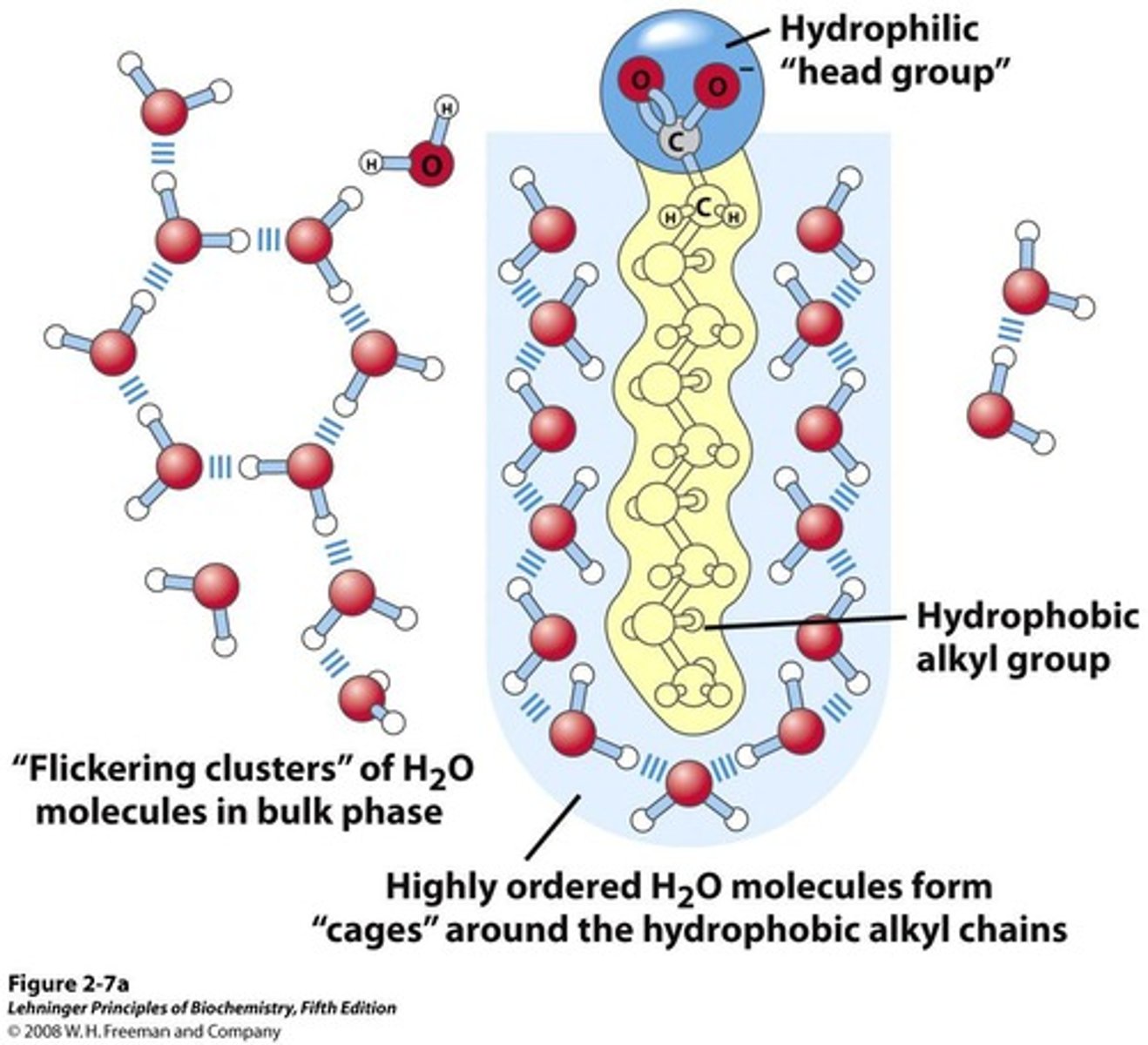
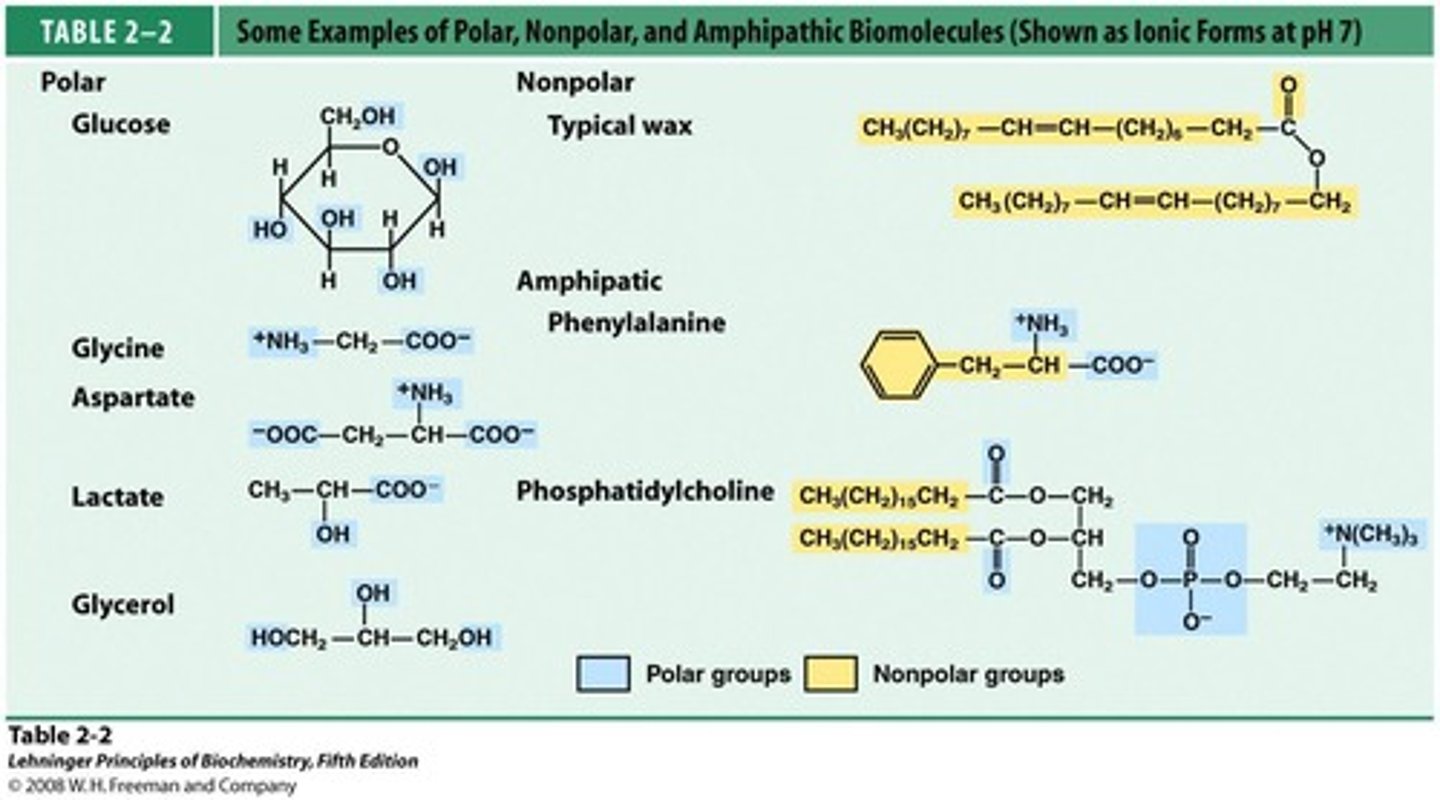
Amphipathic Lipids
Molecules with polar and nonpolar regions.
Ordered Water Molecules
Water molecules structured around nonpolar tails.
Entropy Decrease
Reduction in randomness, leading to unfavorable states.
Non-Polar Aggregation
Non-polar molecules cluster to minimize water interaction.
Hydrogen Bonds
Energetically favorable bonds formed by polar groups.
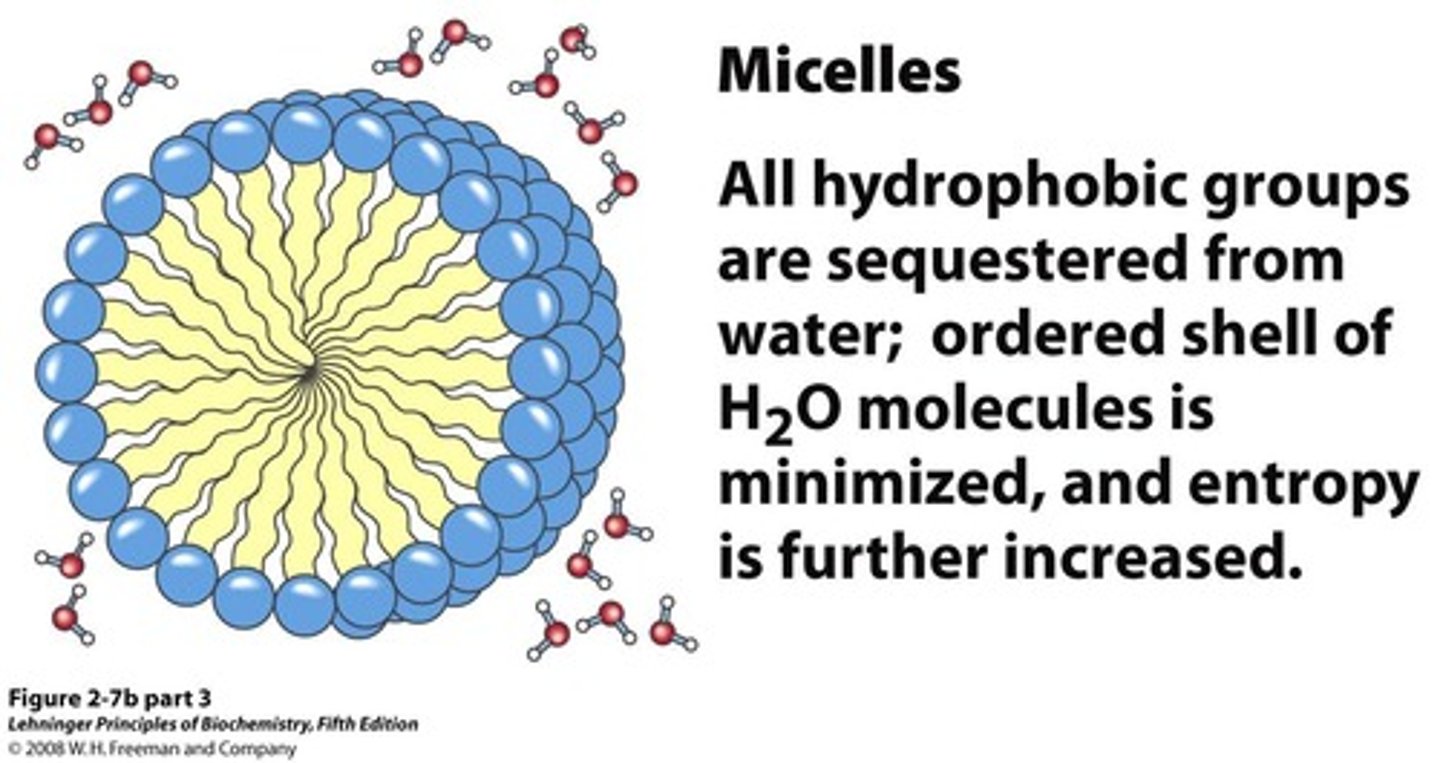
Lipid Micelles
Aggregates formed by amphipathic lipids in water.
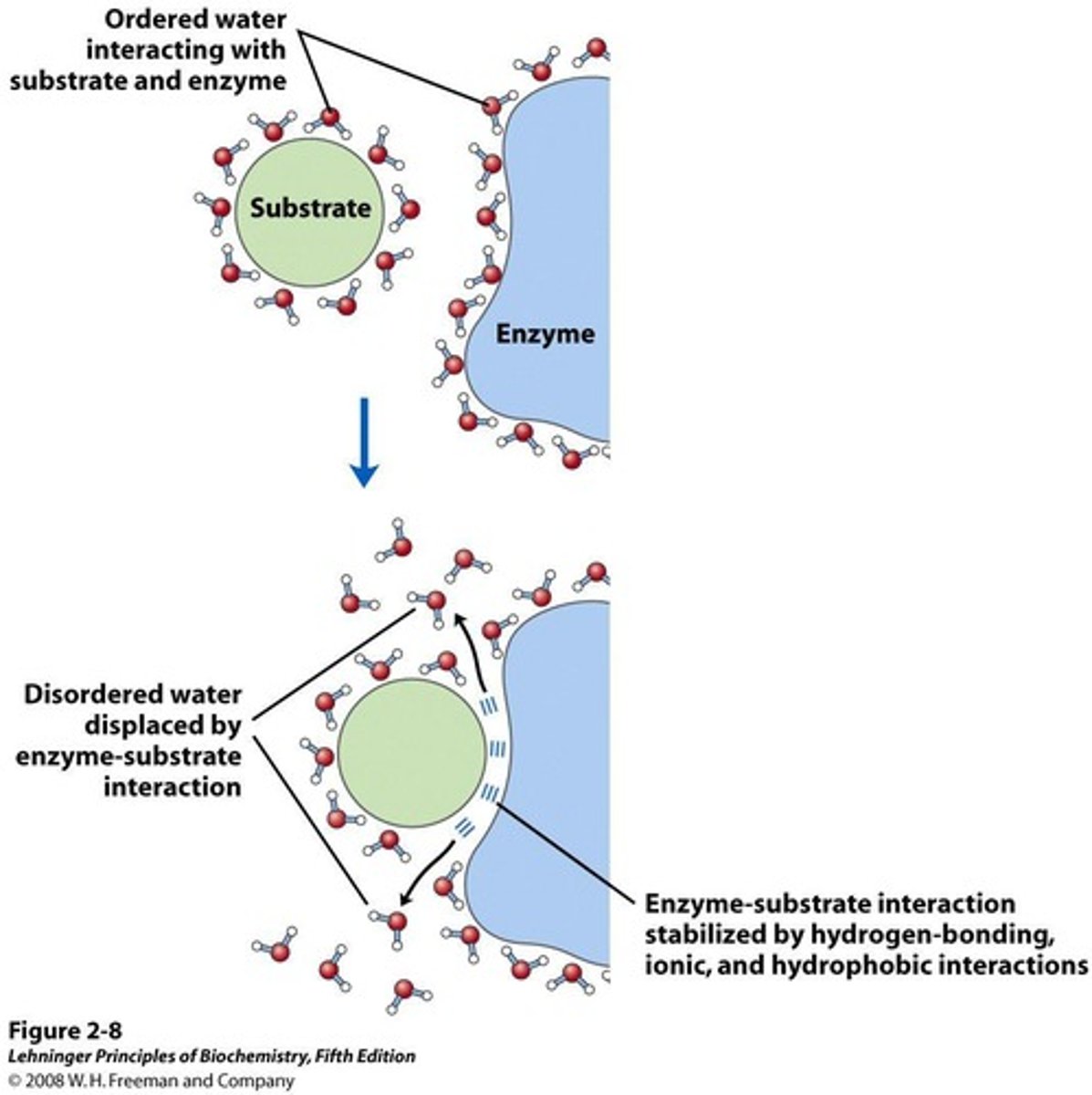
Ligand Binding
Interaction of hydrophobic substrates with proteins.
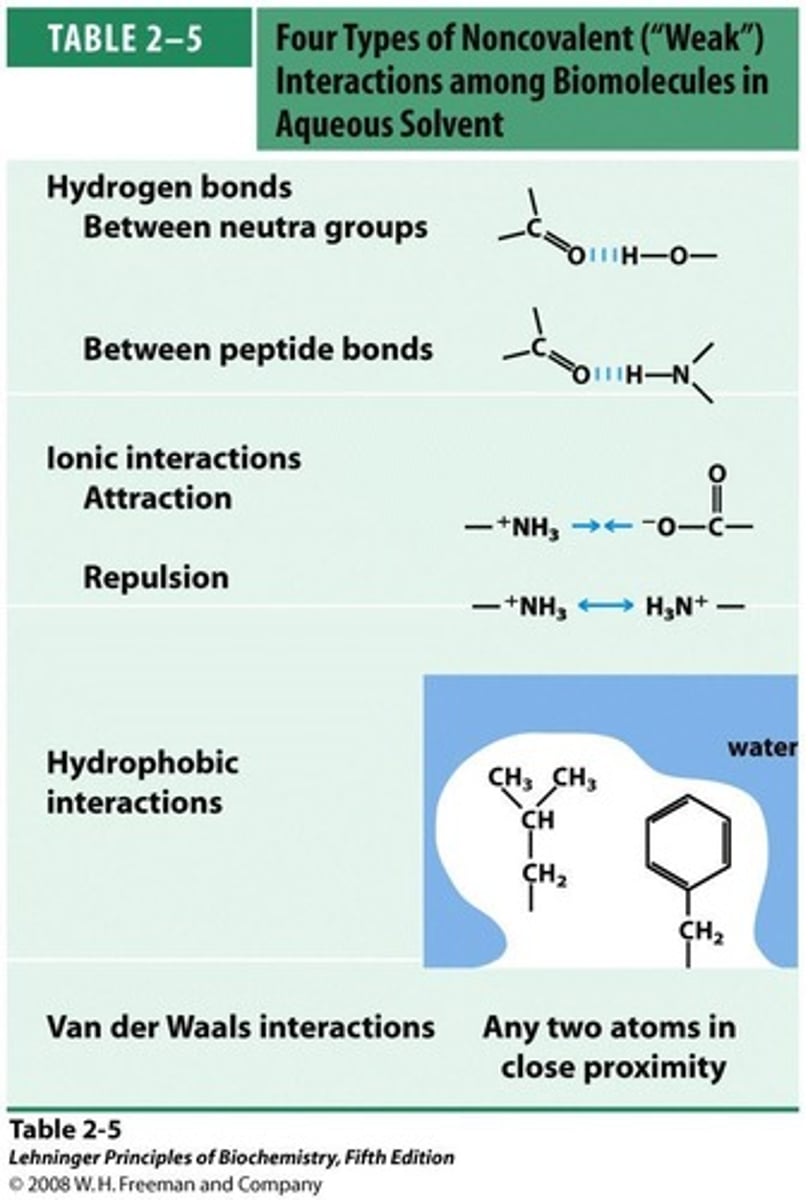
Van der Waals Interactions
Weak forces between nearby atoms.
London Dispersion Forces
Attractive forces due to transient dipoles.
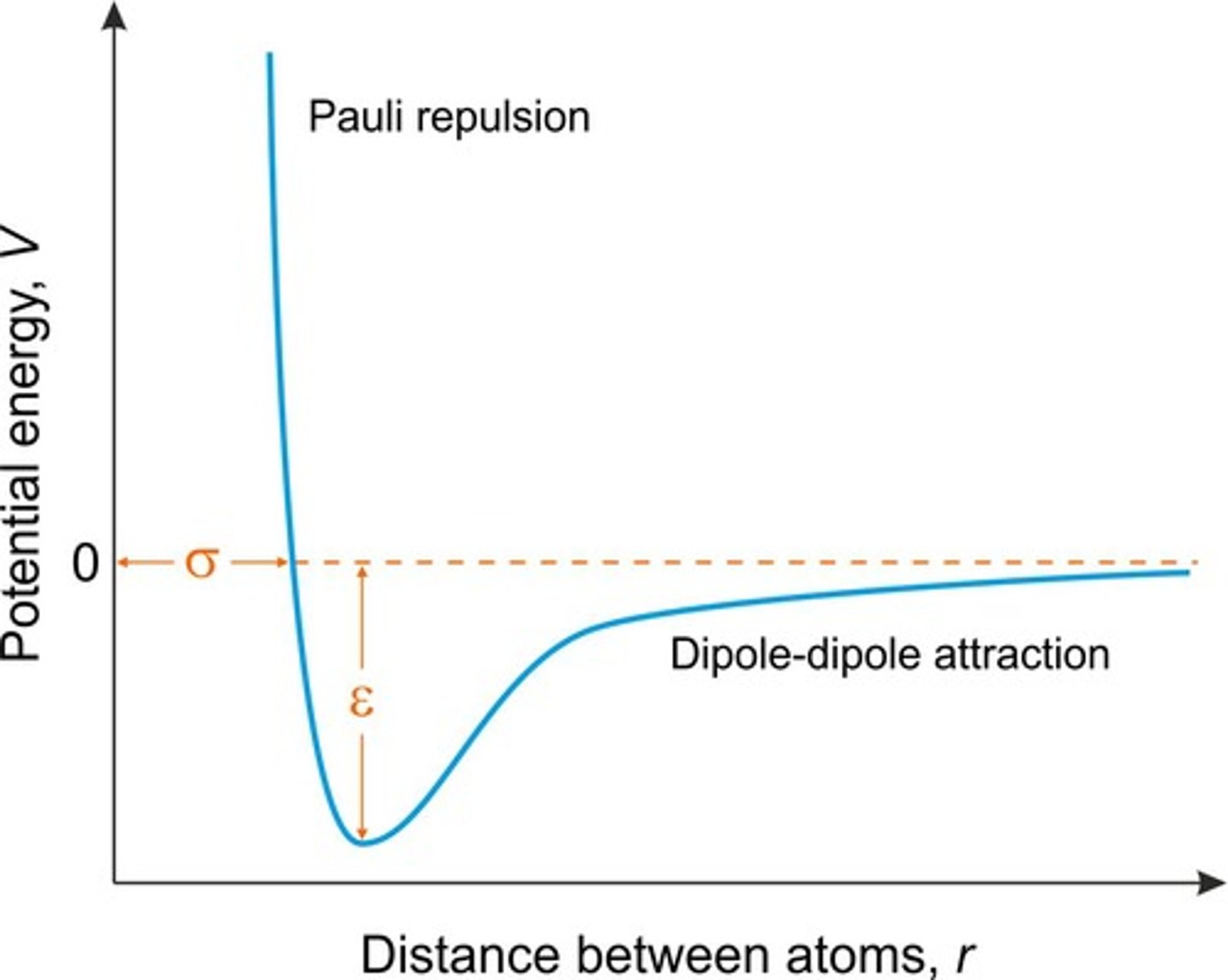
Steric Repulsion
Repulsive forces based on atomic size.
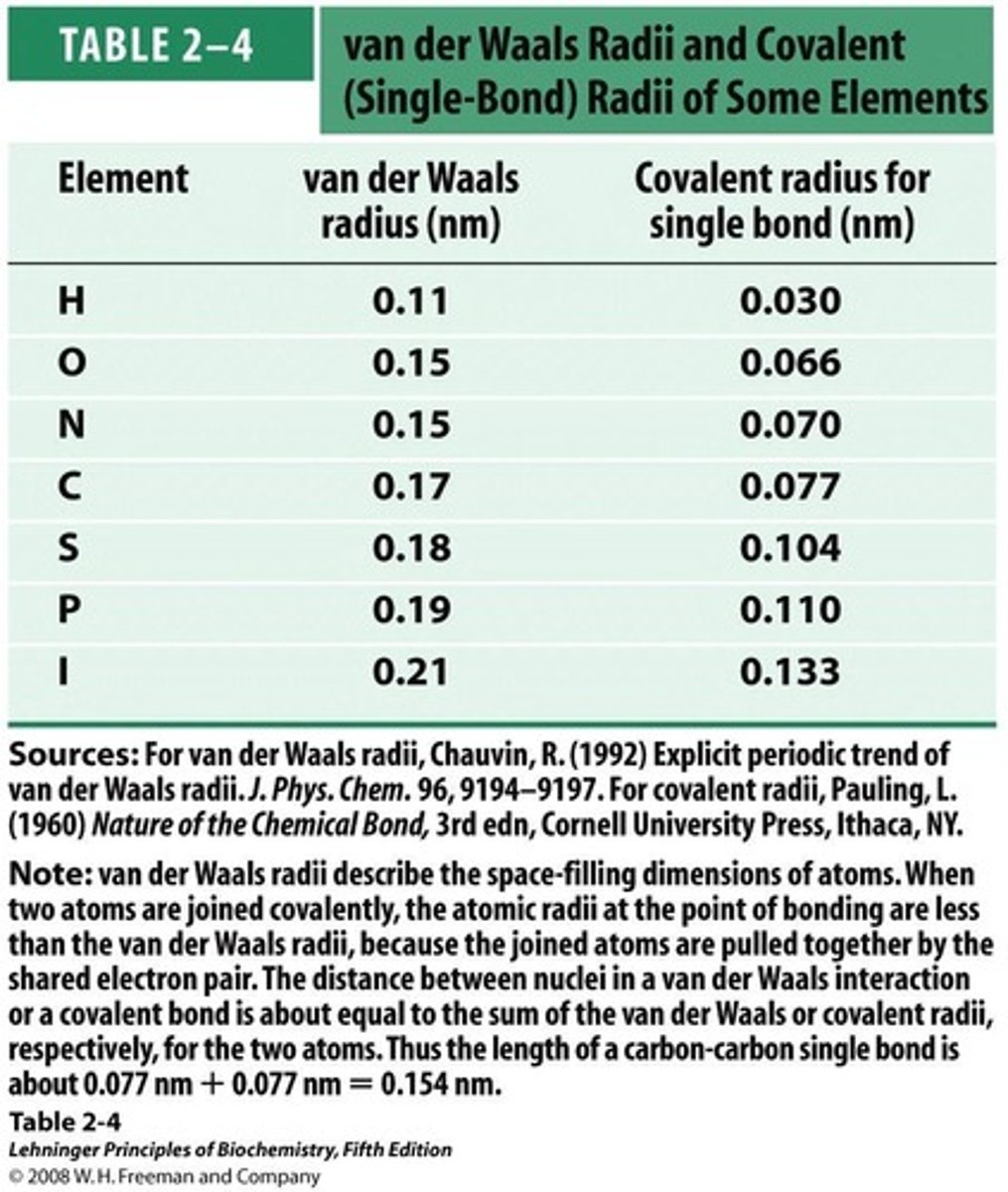
Van der Waals Contact Distance
Distance for maximal attraction between atoms.
Van der Waals Radius
Limit of atomic proximity without repulsion.
Steric Complementarity
Fit between shapes of interacting molecules.
Biological Macromolecules
Large molecules stabilized by non-covalent interactions.
Hydrophobic Effect
Spontaneous formation of non-polar aggregates.
Hydrophobic Binding Sites
Protein regions that attract hydrophobic ligands.
Drug Design
Utilizes hydrophobic effects for therapeutic compounds.
Non-Covalent Interactions
Forces not involving electron sharing.
Hydrogen bonds
Attractive forces between polar molecules' hydrogen atoms.
Ionic Interactions
Electrostatic forces between charged species or dipoles.
Hydrophobic Effect
Ordering of water around non-polar substances.
Van der Waals Interactions
Weak attractions between all atoms, regardless of polarity.
Cumulative Effect
Weak interactions significantly influence protein structure.
Ionization of Water
Water dissociates into H+ and OH- ions.
Proton Hopping
Rapid movement of protons in water via hydrogen bonds.
Electrical Conductivity of Water
Pure water conducts electricity via ion migration.
Hydronium Ion
H2O molecule that gains a proton, forming H3O+.
Osmotic Pressure
Pressure from water movement across semipermeable membranes.
Equilibrium Constant
Ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium.
Weak Acids
Substances that partially ionize in solution.
Weak Bases
Substances that accept protons in solution.
Solvent Properties of Water
Unique characteristics due to hydrogen bonding.
Macromolecular Conformations
Stable structures influenced by noncovalent interactions.
Hydrophobic Moieties
Non-polar parts of molecules that avoid water.
Dissociation of Water
Rapid reversible process producing H+ and OH-.
Semipermeable Membrane
Barrier allowing selective passage of substances.
Proton Concentration Measurement
Experimental determination of total H+ in solution.
Hydroxide Ion
An ion formed when water loses a proton.
Diffusion Rate Comparison
Proton movement faster than Na+ and K+ diffusion.
Water Molecule Structure
Two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
Hydronium Ion
A water molecule with an added proton.
Ionization of Water
Process where water dissociates into H+ and OH-.
Equilibrium Constant (Keq)
Ratio of concentrations at equilibrium for a reaction.
Water Density
Mass of water per unit volume, 55.5 M.
Ion Product of Water (Kw)
Product of [H+] and [OH-] concentrations.
Kw Value
1.0 x 10^-14 M² at 25 °C.
Neutral pH
Condition where [H+] equals [OH-], pH 7.
pH Definition
Negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration.
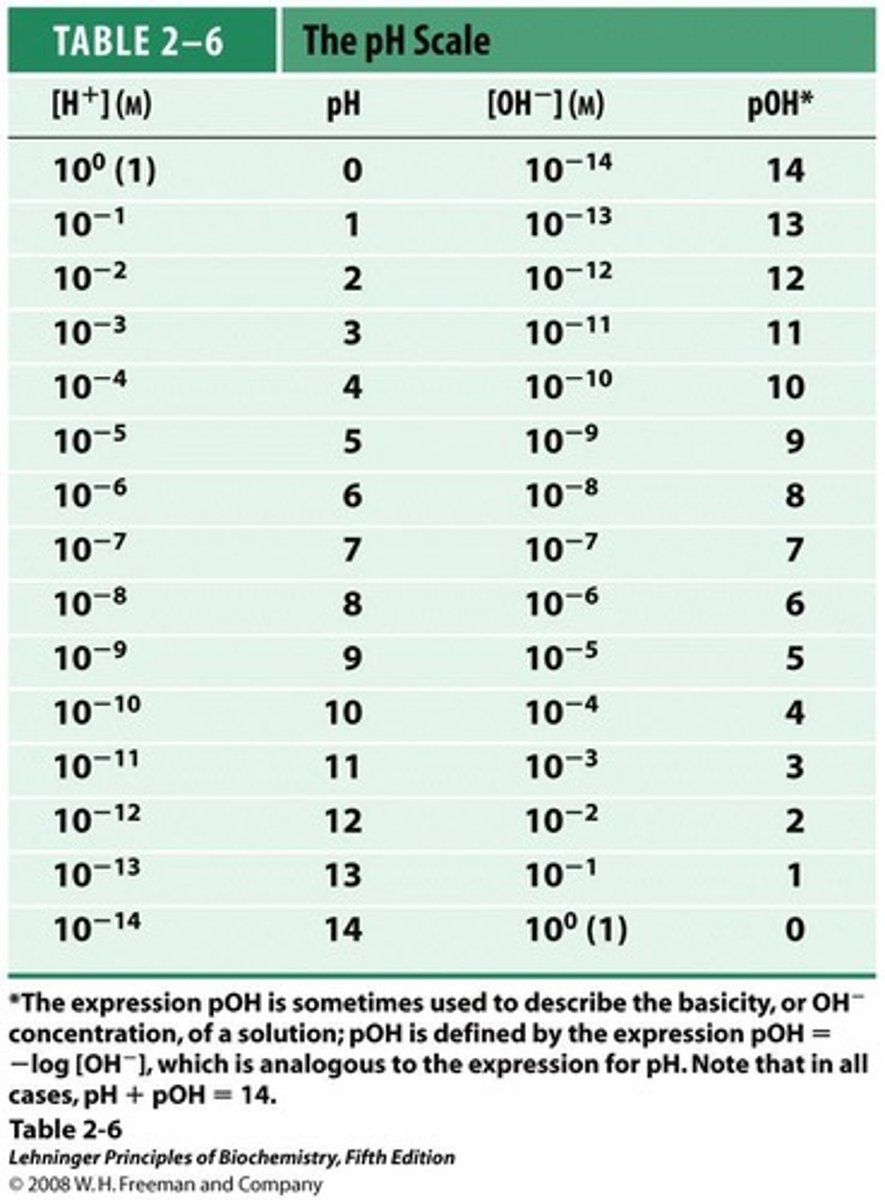
pH Scale
Logarithmic scale for acidity/basicity of solutions.
pH and pOH Relationship
pH + pOH = 14 in aqueous solutions.
Concentration of Water
55.5 M derived from water's density.
Acid-Base Reaction
Chemical reaction involving proton transfer.
Electrical Conductivity of Water
Measurement used to determine Keq value.
Hydrogen Ion Concentration
[H+] in pure water is 1 x 10^-7 M.
OH- Concentration
[OH-] in pure water is 1 x 10^-7 M.
Logarithmic Nature of pH
Each pH unit change represents tenfold concentration change.
Reversible Reactions
Chemical reactions that can proceed in both directions.
Dissociation of Water
Water splits into H+ and OH- ions.
Proton Hops
Rapid movement of protons through hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between water molecules facilitating proton movement.
Enzyme Functionality
Affected by pH levels, impacting biological processes.
Acidosis Symptoms
Drowsiness, nausea, and convulsions from low pH.
Diabetes Mellitus
Condition indicated by high blood glucose and acidosis.
b-Hydroxybutyric Acid
Ketone body elevated in diabetic acidosis.
Acetoacetic Acid
Another ketone body found in diabetic patients.
Plasma pH
Measure of acidity or alkalinity in blood.
Fasting
Condition leading to increased fatty acid usage.
Pepsin
Digestive enzyme active in acidic gastric juice.
Trypsin
Digestive enzyme active in neutral small intestine.
Alkaline Phosphatase
Enzyme aiding in bone mineralization, active at alkaline pH.
Enzyme Activity
Influenced by pH, affecting metabolic processes.
pKa
Measures a molecule's acidity and proton loss tendency.
Strong acids
Completely ionize in water, releasing H+.
Weak acids
Partially ionize in water, not fully dissociated.
HA
Generic formula for a weak acid.