Module #10
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Organism is anaerobicl; nutrients or conditions more favorable at the bottom of the tube
What does th eterm Hydrophilicity mean
The tendency of a molecule or surface to repel water; non-polar molecules are hydrophobic.
Cell morphology describes microscopic shape, size, and arrangement of individual cells; cultural morphology describes macroscopic appearance of colonies on media
Well-isolated colonies are about the same size colonies close together may be smaller due to nutrient competition
Nutrients get used up; metabolic waste products build up
A film of growth on the surface of liquid media often formed by aerobic bacteria or fungi
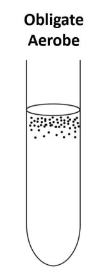
Grows only at the surface
Grows on the surface because it needs air
Grows just below the surface
Little air not a lot

Grows throughout the medium, but greatest growth at the surface
grows a little more with air

Grows with or without oxygen, dispersed equally throughout the medium
Doesnt care if there is air

Grows only at the bottom of the medium
it has no air so it goes to the bottom and die

Staphylococcus