Econ 200 Midterm #1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Economics
The study of how scarce resources are allocated (Choices are necessary due to scarcity)
Scarcity
The property of being deficient in quantity compared to demand; not plentiful or abundant
Economic models
simplified versions of reality used to analyze economic situations
What are the three key principles of economics?
1) People are rational
2) Optimal decisions are made by calculating opportunity costs and are made at the margin
3) People respond to incentives
Describe the first key principle (people are rational)
Rationality, rational consumers/firms weigh costs and benefits to each possible action to try and make the best decision possible. Example - Why are most social media networks free?
Describe the second key principle (optimal decisions are made by calculating opportunity costs and are made at the margin
opportunity cost, trade off, marginal costs, and marginal benefit
Describe the third key principle (People respond to incentives)
Incentives drive peoples responses
Rationality
using all available information to achieve one’s goals
Opportunity cost
the true cost of a choice is the value you could have gained by choosing the next best alternative instead. this is always a number
Trade off
What I have to give up in order to get something else. This is a thing, not a number
Marginal cost (MC) and Marginal benefit (MB)
The additional cost or benefit associated with a small amount (one unit) increase of some action or input
Give an example of a marginal cost
you run a lemonade stand and you want to produce one additional gallon of lemonade. Each gallon of lemonade costs $3 to produce. So marginal cost of producing an additional gallon of lemonade is $3.
Give an example of Marginal Benefit (MB)
Each hour of studying increases by final exam score by 10% (up to some threshold). MB of an hour studying is a 10% increase to my final exam.
Incentive
something that influences behavior by changing trade offs
Opportunity cost example:
You have $20, you can either buy 5 apples that costs you $4 each, or 10 bananas that cost you $2 each
The opportunity cost of apple in term of banana is 1 apple = 2 banana
The opportunity cost of banana in term of apple is 1 banana = ½ apple
Sunk cost
a cost that has already been incurred and cannot be recovered. Only want to compare additional benefits of choice against additional costs. Don’t want to consider costs that are sunk (or benefits)
Give a few examples of sunk costs:
gym joining fee
time spent waiting for something
dinner you purchased (assuming they won’t refund you if you don’t like it)
Give examples of incentives (positive and negative)
1) Group lending - if one member of the group defaults, nobody can borrow again (negative incentive)
2) If you finish your peas you get a piece of cake (positive incentive)
Microeconomics
The study of how consumers and firms make choices, how they interact in markets, and how the government attempts to influence their choices.
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth (GDP growth)
Econometrics
The study of statistics used in economics (regression analysis, machine learning.)
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that may be produced or purchased with available resources and current technology
Points along the PPF line are ________.
attainable
Points below the PPF line are ________.
inefficient
Points above the curve are _________.
unattainable given current resources
Production possibilities frontier
a set of efficient and feasible production between two goods given a budget constraint. Often called the the maximum resource allocation
What are some things that PPFs can show?
efficiency, trade-offs, growth, opportunity cost, etc.
What are the different types of PPF?
Increasing opportunity cost, and constant opportunity cost
Increasing opportunity cost
As you produce more of one good, the opportunity cost of producing additional units increases.
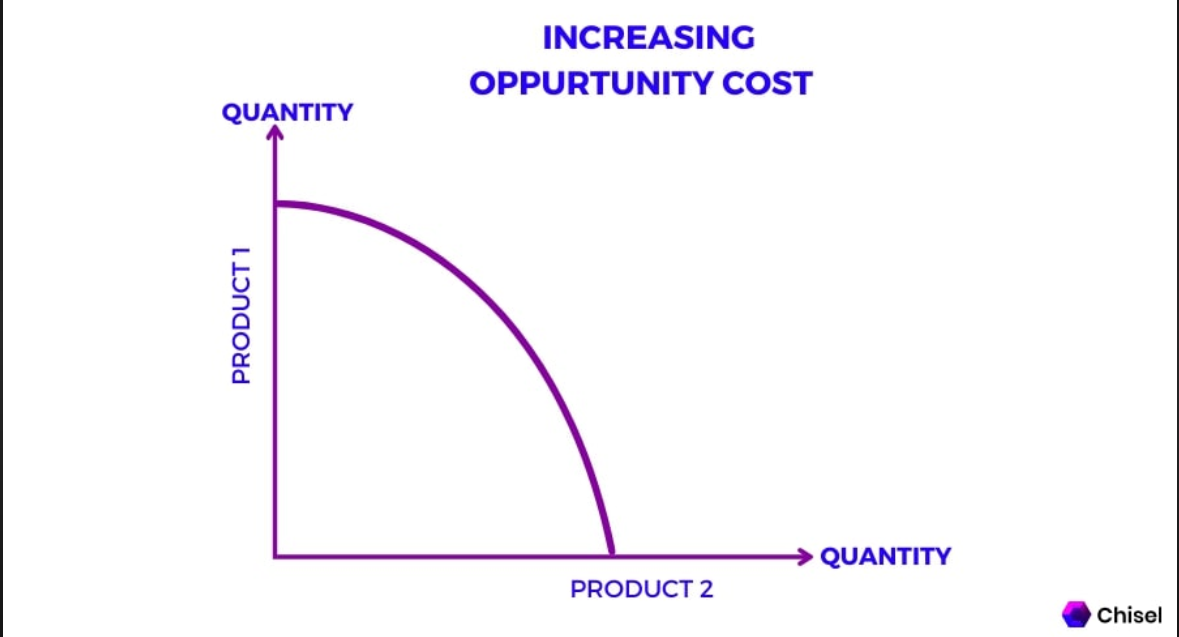
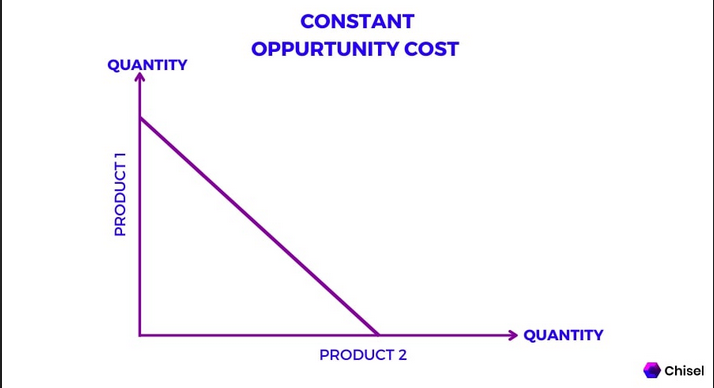
constant opportunity cost
The opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of the other remains the same, no matter how much you produce.
Why can a PPF shift outwards?
PPF can shift outward due to increase in budget constraint or technology innovation that boosts production
What does economic growth mean in terms of PPF?
More resources mean we can produce more
Economic growth
The ability of an economy to increase production, which is measured by GDP
What is invisible hand?
It's the idea that markets incentivize individuals, acting in their own self-interest, to produce what is societally necessary.
What is Autarky?
A situation with no trade, where a country must produce what it consumes.
Absolute advantage
the person or country that produces a good with a smaller quantity of inputs, or that produces more output per unit of input, is said to have absolute advantage in producing that good.
Comparative advantage
the person or country that has the smaller opportunity cost of producing a good is said to have a comparative advantage in producing that good. Comparative advantage determines which country will specialize in which good.