Cellular Processes
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for cell biology exam review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Unicellular Organism
An organism that consists of one independent cell.
Multicellular Organism
An organism that consists of more than one cell. Each cell has different functions and structures.
Prokaryote
A cell type without a nucleus.
Eukaryote
A cell type with a nucleus.
Specialized cells
Cells in multicellular organisms adapted for specific functions.
Plant cells
Eukaryotic cells present in green plants. Plant cells have certain features like chloroplasts, cell walls, and intracellular vacuoles.
Cell Wall
Tough external outer covering. It provides support and strength; prevents excess water uptake
Chloroplast
The site of photosynthesis in plant cells; gives the cell its characteristic green color.
Large Central Vacuole
Assists with storage and structure in plant cells.
Animal Cells
Eukaryotic cells that make up the tissues and organs of animals.
Cell Membrane (Animal Cell)
Surrounds the animal cell and controls the passage of nutrients and chemicals; flexible and allows the cell to change shape.
Enzyme
A biological catalyst that speeds up the rate of reactions or allows reactions to take place.
Enzyme Action
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions because they reduce the stability of bonds in the reactants, providing an alternative energy pathway with lower activation energy.
Substrate
The molecule that fits into an enzyme
Active site
The place on the enzyme that the substrate fits
Enzyme Specificity
Enzymes are specific meaning they only work on one type of reaction due to the shape of their active sites.
Denaturation
Loss of an enzyme's three-dimensional structure, resulting in loss of catalytic activity.
Enzyme Optimum pH
The pH at which an enzyme will work best.
Substrate Concentration
Affects enzyme activity; the greater the substrate concentration, the higher the rate of reaction until all enzyme is 'busy'.
Enzyme Concentration
Affects the rate of reaction; as the amount of enzyme increases, activity will increase if there is sufficient substrate available.
Co-factor
Cannot be made in the body but interacts with enzymes so the substrate can bind better and the enzyme can function (helpful).
Inhibitors
Competitive: Similar shape to substrate so it blocks the active site and alter its shape.
Semipermeable Membrane
Allows small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules to move through easily by diffusion.
Diffusion
The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration, along the concentration gradient until they are equal.
Simple Diffusion
Molecules can freely move through a membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion
for big and charged particles they can pass through protein channels.
Facilitated Diffusion is used when large particles can’t diffuse freely through the phospholipid bilayer
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from where water is in higher concentration to where it is in lower concentration.
Active Transport
Moving ions and molecules from an area of low concentration to high concentration using energy, through a protein pump.
Active transport is used when cells need to transport a substance into the cell against it’s concentration gradient.
Photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen.
Photosynthesis stages
The light-dependent reactions (also called the light phase) take place in the grana, which are stacks of thylakoids inside the chloroplast.
The light-independent reactions (also called the Calvin cycle or dark phase) occur in the stroma, which is the fluid-filled space surrounding the grana inside the chloroplast.
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is the pigment that gives plants their green color. Plants use chlorophyll to trap light needed for photosynthesis
Light Dependent Reaction
It occurs in the thylakoid membranes. Water enters and the energy from light splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. Oxygen is released and ATP (energy) is also produced.
Light Independent Reaction
It occurs in the stroma of chloroplast. Hydrogen from light dependent enter the chloroplast and combine with the Carbon dioxide (CO2) carbon + hydrogen and leave the reaction as glucose, there will be excess Hydrogen and carbon released. ADP is converted to form ATP.
Respiration
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP + Heat
Aerobic Respiration
This takes place in the mitochondria.
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (36ATP)
Glycolysis - Enzyme Controlled reaction that involves Aerobic Respiration.
Occurs in the cytoplasm, it happens in the first stages of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. One molecule of glucose and 2ATP is used to produce two pyruvate molecules, hydrogen ions, and 4ATP
Krebs Cycle - Enzyme Controlled reaction that involves Aerobic Respiration.
Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria, it happens in the 2 stage of aerobic respiration. It uses pyruvate from glycolysis and produces Carbon dioxide, ATP, and water
Electrons transfer chain - Enzyme Controlled reaction that involves Aerobic Respiration.
Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane – cristae, it happens in the 3rd stage of aerobic respiration and it uses energy from the kerb cycle and oxygen so it can produce ATP and Water.
Anaerobic respiration
It occurs in the cytoplasm
Glucose → Lactic Acid + Energy (2ATP)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aerobic
Advantages
More efficient in producing ATP
No lactic acid build up which can cause muscle fatigue and soreness.
Disadvantages
Oxygen dependent, so it cannot occur in anaerobic environments
It’s a slow process that requires multiple steps to produce ATP which is why it cannot meet immediate energy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Anaerobic
Advantages
It can produce energy quickly making it useful for short bursts of high-intensity.
No oxygen needed which makes it useful in anaerobic environments.
Disadvantages
It is less efficient in producing ATP because it uses small amount of energy from glucose
Produces lactic acid, which can lead to muscle fatigue, soreness and decreased performance.
Cell Cycle
Is a regulated sequence of events that occur between one cell division and the next. It has two phases: Interphase and Cell division (mitosis)
Interphase
The cell increases in mass and size and carries out its normal cellular functions. Interphase consists of 3 phases G1, S phase, G2 phase
G1 Phase
It occurs prior to DNA replication. During this phase the cell is actively growing and preparing for DNA synthesis.
The cell also checks for damage to its DNA and other cellular components before proceeding to the next phase of the cell cycle. If damage is detected, the cell undergoes repair or cell death
S phase
During the G1 phase a signal is received telling the cell to divide again. DNA in the nucleus replicates resulting in each chromosome consisting of 2 identical sister chromatids
G2 Phase
In this phase, the cell contiues to grow and prepare for cell division. Then the cell undergoes a final check for DNA damage and makes any necessary repairs before entering mitosis
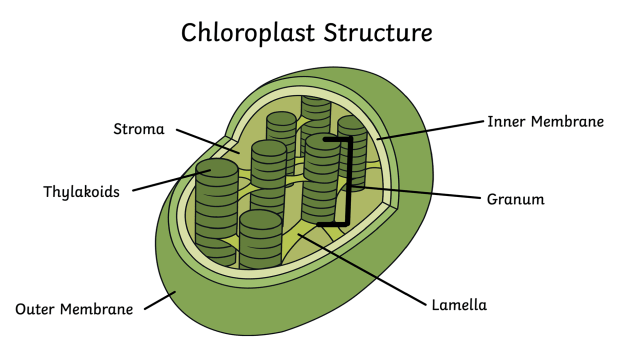
Chloroplast Diagram
Outer Membrane - Is clear and allows light to pass through. Controls what goes in and out of chloroplast.
Thylakoids - Stacks within the chloroplast.
Grana - Stacks of thylakoids.
Inner Membrane - Inside of chloroplast
Stroma - Liquid filled space where CO2 is captured and is used to make sugars (food for plants).
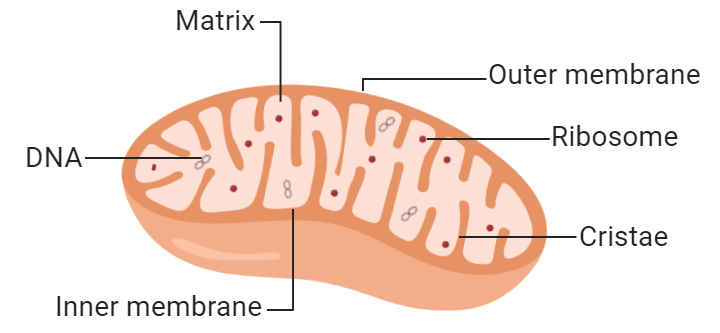
Mitochondria Diagram
Outer Membrane - Is smooth
Inner Membrane - Is folded
Cristae - Inside Folds, the wiggles of the cristae increase the surface area of the inner membrane, where lots of reactions happen.
Which means mitochondria can convert more sugar into ATP energy the same amount of time.
Matrix - Liquid filled space inside the inner membrane which contains many enzymes for respiration.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is when DNA replicates itself so that chromosomes can be replicated prior to cell division
Replication ensues that all cells formed have a copy of the genetic code which gives them the instructions needed to grow and carry out their essential cell process.
STEPS of DNA REPLICATION
Unwinding
The enzyme helicase unwinds the DNA double helix and separates the two strands.
Base Pairing
DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides (A with T, C with G) to each original strand.
Bond Formation
The sugar-phosphate backbone is sealed by DNA ligase, forming two new DNA strands.
Result
Two identical DNA molecules are formed, each with one original strand and one new strand (semi-conservative replication).
Mitosis
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other - these news cells thus can continue essential life processes.
Rate of Mitosis can be influenced by:
Cell type - Each has different rates of mitosis e.g. skin cell divide faster than nerve cells
Age - Mitosis rates are generally higher in younger organisms and tend to decline with age.
Hormones - Oestrogen can increase the rate of mitosis in breast tissues.
Growth Factors - Can stimulate cell division and increase the rate of mitosis.
Environmental Factors - Such as temperature, pH, and availability of nutrients can also affect the rate of mitosis.
Genetic Factors - Leading to conditions such as cancer
Surface area:volume ratio
Cells may increase their surface area to volume ratio by:
having a long thin shape
folding the surface of an object (cell membrane)
Cells need to be small because they rely on diffusion for getting substances into and out of their cells.
As cells grow, the volume increases more than the surface area.
smaller SA:Vol ratios are not effective at transporting key material
Key takeaway: Small cells are more efficient at diffusion as they have a HIGH SA:V ratio