Introduction to Art History and Its Key Concepts
1/514
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
515 Terms
How is art defined in contemporary art history?
Art is defined broadly to include objects previously dismissed as 'craft,' such as textiles, pottery, tattoos, mass-produced posters, advertisements, and even ordinary household items.
What is the primary goal of art history as an academic discipline?
The primary goal is to reconstruct the social, cultural, and economic contexts in which an artwork was created to understand its meaning in its historical moment.
What factors do art historians consider when analyzing a work of art?
They consider formal qualities, the function of the artwork in its original context, the goals and intentions of the artist and patron, and the social position and perspectives of the audience.
Which other disciplines are closely related to art history?
Art history is closely related to anthropology, history, sociology, aesthetics, and art criticism.
What does formal analysis focus on in art history?
Formal analysis focuses on the visual qualities of the artwork and assumes that the artist's decisions reveal aspects of meaning intrinsic to the work.
What does contextual analysis involve in the study of art?
Contextual analysis involves examining the social, cultural, and historical contexts surrounding the creation of the artwork.
How can the meaning of a work of art change over time?
The meaning can shift based on different perspectives, social status, education, and historical context.
Give an example of how different viewers may perceive Michelangelo's Sistine Chapel paintings differently.
The Pope, who commissioned the work, would have a sophisticated theological understanding, while a worker cleaning the chapel might have a low level of literacy, leading to different interpretations.
What is the impact of social factors on the interpretation of art?
Factors such as social status, education, religious background, race, and gender can significantly influence how a work of art is understood.
What is the significance of the audience's perspective in art history?
The audience's perspective can lead to multiple interpretations of the same artwork, highlighting that meaning is not fixed.
What is the traditional focus of art historians compared to contemporary definitions of art?
Traditionally, art historians focused on 'fine art' like paintings and sculptures, while contemporary definitions include a wider range of visual materials with special meaning.
What is the relationship between art history and aesthetics?
Art history sometimes overlaps with aesthetics, which is the philosophical inquiry into the nature and expression of beauty.
What role does art criticism play in relation to art history?
Art criticism explains current art events to the general public, often through the press, and can inform the understanding of art history.
What is a key assumption of formal analysis in art history?
A key assumption is that the artist's visual decisions reveal intrinsic meaning about the artwork.
How do art historians approach the study of mass-produced items?
Art historians now include mass-produced items in their inquiries, recognizing their aesthetic value and cultural significance.
What is the importance of case studies in art history education?
Case studies help students apply theoretical concepts to specific artworks, enhancing their understanding of art historical inquiry.
What does the term 'craft' refer to in the context of art history?
'Craft' refers to objects like textiles and pottery that were historically dismissed as art but are now considered within the broader definition of art.
Why is it important to consider the historical context of a work of art?
Considering historical context allows for a deeper understanding of the artwork's meaning and significance at the time it was created.
How can the same artwork be admired differently by diverse audiences?
Different audiences, such as a twenty-first-century Protestant or a sixteenth-century Catholic, may admire the aesthetic value but interpret the meaning based on their own cultural and religious backgrounds.
What is the significance of the artist's intention in art historical analysis?
The artist's intention is crucial for understanding the purpose and meaning behind the artwork in its original context.
What does the phrase 'invested with special meaning' imply about art?
It implies that art is not just visually appealing but also carries significance and value beyond its aesthetic qualities.
How does the definition of art impact the study of art history?
A broader definition of art allows for a more inclusive study of various visual materials and their cultural implications.
What is the role of the patron in the creation of a work of art?
The patron's goals and intentions can influence the artwork's creation and its interpretation in art history.
What is formal analysis in art history?
Formal analysis requires excellent skills in observation and description, focusing on the object itself.
Why do art historians often study reproductions of artworks?
Due to practical constraints, such as damaged or lost works, art historians may rely on reproductions.
What does contextual analysis involve in art history?
Contextual analysis examines the cultural, social, religious, and economic context in which a work of art was produced.
What types of issues do art historians consider in contextual analysis?
Art historians consider patronage, viewer access, physical location, cost, and subject matter in relation to other artworks.
What types of written sources do art historians use for contextual information?
Art historians use letters, documents about commissions, and contemporary art criticism stored in archives or libraries.
How might an art historian study the function of a work of art?
By researching documentation about materials used, their cost, and how the artwork was used in rituals.
What role do interviews play in art historical research?
Interviews with artists and consumers provide insights, especially in cultures that rely on oral history.
What method might art historians use to understand the context of a work of art?
Methods such as participant observation, guided by anthropology, to document events related to the artwork.
How does art history emphasize chronological development?
It assumes that one generation of artists impacts the following generations within a cultural setting.
What is the purpose of comparative study in art history?
To contrast different artworks, such as Gothic and Renaissance, to understand stylistic changes and historical context.
When did art history emerge as an academic discipline?
Art history arose in the mid-eighteenth century.
Who was Pliny the Elder and what was his contribution to art history?
Pliny the Elder was an ancient Roman historian who analyzed historical and contemporary art in his text Natural History.
What is the significance of situating artworks in their cultural and historical context?
It connects artworks to the long history of events leading up to the present culture.
What are some challenges art historians face when studying artworks?
Challenges include dealing with reproductions, damaged works, and the need for contextual understanding.
What is the importance of understanding associated studies like sketches in art history?
They provide insight into the artist's process and the development of the final artwork.
How do art historians use archival sources?
To find historical documents that provide context and information about the artwork and its creation.
What is participant observation in the context of art history?
A method where art historians engage in cultural practices to better understand art traditions.
How does art history contribute to understanding contemporary culture?
By placing artworks in context, it reveals connections to historical events and cultural developments.
What are some examples of contexts that might be examined in art history?
Cultural, social, religious, and economic contexts surrounding the creation of a work of art.
Why is the study of art history considered important?
It provides insights and background that enhance the meaning and significance of artworks.
What is the relationship between art history and other disciplines?
Art history intersects with literature, music, theater, and history to provide a comprehensive understanding.
What can be learned from contrasting different art movements?
It helps clarify unique features and stylistic changes between movements, enhancing historical understanding.
How do practical constraints affect the study of art history?
They may limit access to original works, forcing reliance on reproductions and historical descriptions.
Who gathered the biographies of great Italian artists during the Renaissance?
Giorgio Vasari
What is the title of Giorgio Vasari's influential work on artists?
The Lives of the Artists
Why is direct examination of a work of art preferred over reproductions?
Much is lost in terms of scale, three-dimensional qualities, and texture when viewing reproductions.
How has the field of art history expanded in recent years?
It has become broader, more international, multicultural, and inclusive, incorporating Marxist, feminist, and psychoanalytic methods.
What has lessened in the focus of art history according to recent trends?
The concern with great artistic geniuses and masterpieces.
What does the brief overview of Western art aim to provide?
A basic understanding of important art historical periods and key artistic innovations.
Who was Johann Joachim Winckelmann and what was his contribution to art history?
A German scholar who shifted focus from biographical emphasis to the study of stylistic development in historical context.
What major philosophical movement influenced modern art history?
Eighteenth-century Enlightenment philosophy.
What materials are most likely to survive from early cultures?
Enduring materials such as stone, metal, or fired clay.
How do environmental conditions affect the preservation of artifacts?
Hot dry climates, like that of Egypt, aid preservation, while humid climates, like West Africa, hinder it.
What bias has been noted in traditional art history?
It has largely focused on white men as artists or patrons.
What have feminist historians contributed to the field of art history?
They have revised traditional narratives to highlight the contributions of women and address biases.
What is the significance of the changing roles of artists during the Renaissance?
It reflects the developing concept of artistic genius and the artists' roles in society.
What is one reason for the greater emphasis on Western cultures in art history?
The survival of artifacts from Western cultures compared to those from Nonwestern cultures.
What does the study of art history reveal about the earliest life on earth?
It provides insights through the study of enduring artifacts from early cultures.
What is the impact of the humid climate of West Africa on art preservation?
It means that objects made of perishable materials have had little chance of survival.
What is the relationship between the formal qualities of a work of art and its context?
Art historians emphasize understanding this interrelationship in their analyses.
What does the term 'visual culture' encompass in contemporary art history?
It includes a range of visual media from advertisement posters to film and television imagery.
What does the abbreviation 'c.' stand for in the context of dates, such as in 'c. 1567'?
It stands for 'circa,' indicating an approximate date.
What is the role of art historians in analyzing a work of art?
They begin with a close examination of the work to understand its context and significance.
What does the term 'artistic genius' refer to in the context of art history?
The evolving concept of exceptional talent and creativity in artists.
How has the focus of art history changed over time?
From a concentration on masterpieces to a broader view of visual culture.
What is one challenge faced by art historians studying Nonwestern cultures?
The lack of surviving artifacts due to environmental conditions.
What are the civilizations most often studied in art history courses based on?
They are based on the preservation and discovery of their art, not necessarily on the quantity or quality of art produced.
What has often happened to important civilizations' sites in Central and South America?
They have been exploited and destroyed, with artifacts being taken for sale on the international antiquities market.
What is significant about the cave paintings found in Chauvet Cave?
They are the oldest known works of art, dating from approximately 30,000 BCE.
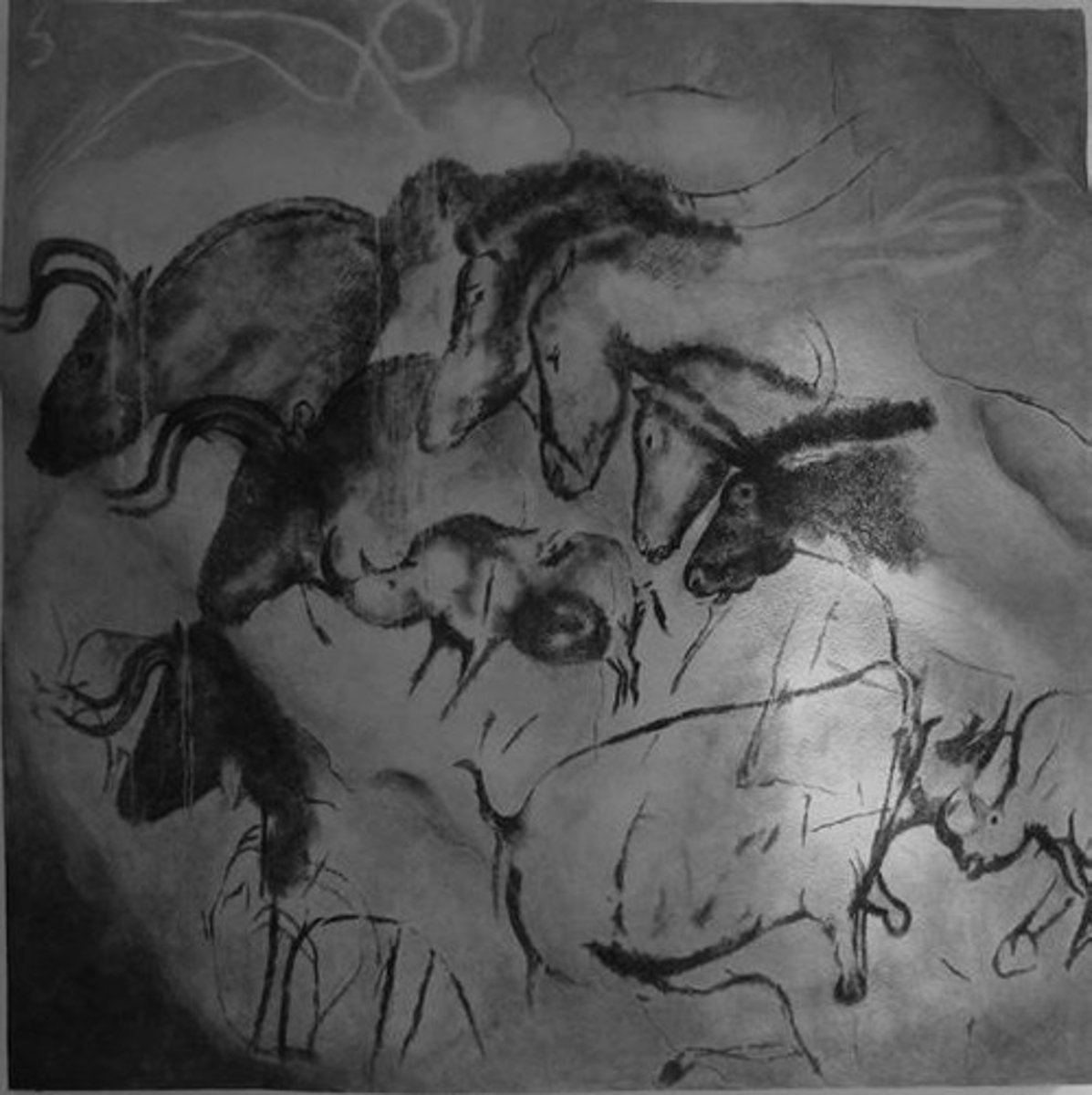
What materials were primarily used in the cave paintings of Chauvet Cave?
Red ochre and black charcoal.
What types of animals are depicted in the Chauvet Cave paintings?
Horses, rhinoceros, lions, buffalos, and mammoths.
What is the estimated time frame for the creation of rock shelter paintings during the Middle Stone Age?
From around 7000 BCE until 4000 BCE.
How do rock shelter paintings differ from cave paintings?
Rock shelter paintings include depictions of human figures, while cave paintings primarily depict animals.
What is one possible purpose of the cave paintings created during the Old Stone Age?
They may have been created as part of hunting ceremonies or other ritual behaviors.
What is the Venus of Willendorf, and when was it created?
It is a small stone female figure with exaggerated features, created around 28,000-25,000 BCE.
What is the significance of the artistic tradition observed in cave paintings?
They were created by skilled artists working within an established tradition, rather than being mere spontaneous scribbles.
What does the term 'Upper Paleolithic Period' refer to?
It refers to the later part of the Old Stone Age, during which the Chauvet Cave paintings were created.
What is the importance of the dating of artworks in art history?
Art historians use the best available information to date works, which may be contested and revised as new information arises.
What is depicted in the rock shelter paintings found in eastern Spain?
Animal figures and human figures, often emphasizing scenes where humans dominate animals.
What is one characteristic of the figures found from the Old Stone Age?
They often have exaggerated features, particularly in female figures.
What is the significance of the paintings in Lascaux and Altamira?
They are among the most famous cave paintings, showcasing the artistic skills of prehistoric humans.
What was the initial scholarly view of cave drawings before further study?
They were considered spontaneous scribblings of primitive cavemen.
What role did climate change play during the Middle Stone Age?
It led to a warming climate that allowed cave dwellers to move out of caves and use rock shelters.
What is the significance of the human figure in rock shelter paintings?
It represents a shift in artistic focus, showing humans in various scenes, unlike the earlier cave paintings.
What is the estimated height of the Venus of Willendorf?
About four and one-eighth inches high.
What does the term 'Mesolithic Period' refer to?
It is the Middle Stone Age, characterized by the development of new cultures and art forms.
What is the main theme of the art created during the Old Stone Age?
The depiction of animals and, in some cases, human figures, often in ritualistic contexts.
What is the significance of the Chauvet Cave paintings in the context of art history?
They provide insight into the early artistic expression and cultural practices of prehistoric humans.
What is the role of scholars in understanding ancient artworks?
They debate and analyze the dating and significance of artworks to better understand historical contexts.
What conditions typically allow for the creation and survival of artworks?
Art thrives in highly organized cultures with stable population centers, usually great cities, supported by ruling classes.
How does the protection of art in inaccessible locations affect its survival?
Civilizations that protect their art in inaccessible locations are more likely to have their works survive for study in art history.
What are the primary art forms associated with the New Stone Age (Neolithic Period)?
The primary art forms are rings or rows of rough-hewn stones, often referred to as megaliths.
What is the significance of Stonehenge in the context of New Stone Age art?
Stonehenge, built around 2100 bce, is the most well-known megalithic structure featuring concentric rings of sarsen stones and bluestones.
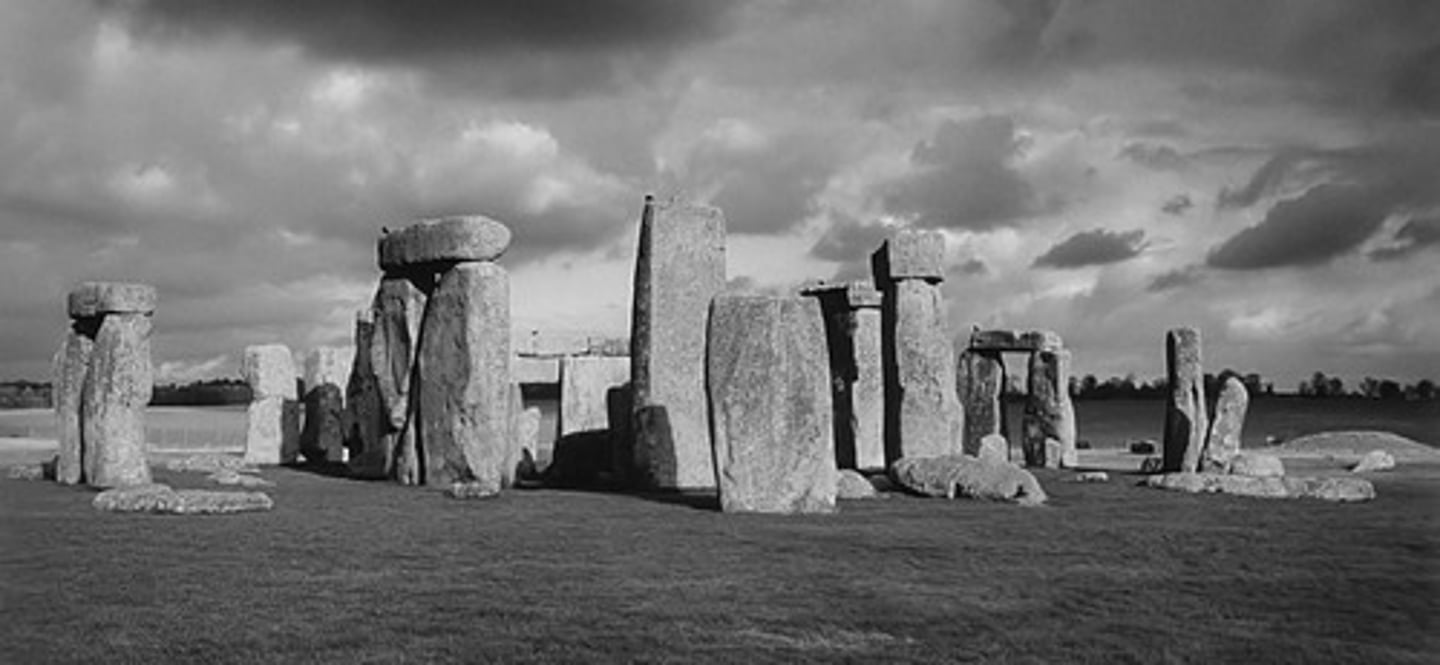

What construction technique is used in the outermost ring of Stonehenge?
The outermost ring is constructed using post and lintel construction with huge sarsen stones.
What does the 'heel-stone' at Stonehenge mark?
The 'heel-stone' marks the point where the sun rises on the midsummer solstice.
What geographical features made Mesopotamian civilizations vulnerable?
Mesopotamian civilizations lacked natural barriers like deserts and mountains, making them susceptible to invasion.
What is the significance of the Code of Hammurabi in Mesopotamian art?
The Code of Hammurabi is the oldest legal code known in its entirety, and its artwork includes a stone stele depicting Hammurabi receiving inspiration from the sun-god, Shamash.