Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Last updated 2:39 PM on 9/28/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy
the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts and their relationships to one another
2
New cards
Gross Anatomy
the study of large, easily observable structures such as the heart or bones
3
New cards
Anatomy
the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts and their relationships to one another
4
New cards
Gross Anatomy
the study of large, easily observable structures such as the heart or bones
5
New cards
tomy
meaning "to cut"
6
New cards
ana
means "apart"
7
New cards
Anatomy
related most closely to gross anatomical studies because in most studies, preserved animals or their organs are dissected (cut up) to be examined
8
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
the study of body structures that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, for example, cells & tissues of the body can only be seen through a microscope
9
New cards
Physiology
the study of how the body and its parts work or function
10
New cards
physio
"nature"
11
New cards
logy
"the study of"
12
New cards
Neurophysiology
the branch of neuroscience that studies the workings of the nervous system
13
New cards
Cardiac Physiology
studies the function of the heart
14
New cards
Structure
determines what functions can take place
15
New cards
Atoms
Cells
Tissues
Organ
Organ System
Organism
Cells
Tissues
Organ
Organ System
Organism
the six levels of structural organization that make up the human body
16
New cards
Atoms
tiny building blocks of matter that combine to form molecules such as water, sugar, and proteins, like those that make up our muscles
17
New cards
Cells
the smallest units of all living things
18
New cards
Tissues
consist of groups of similar cells that have a common function
19
New cards
Organ
is a structure composed of two or more tissue types that performs a specific function for the body
20
New cards
small intestine
digests and absorbs food, is composed of all four tissue types
21
New cards
organ system
is a group of organs that work together to accomplish a common purpose
22
New cards
organism
made up of organ systems & represents the highest level of structural organization- the organismal level
23
New cards
organismal level
is the sum total of all structural levels working together to keep us alive
24
New cards
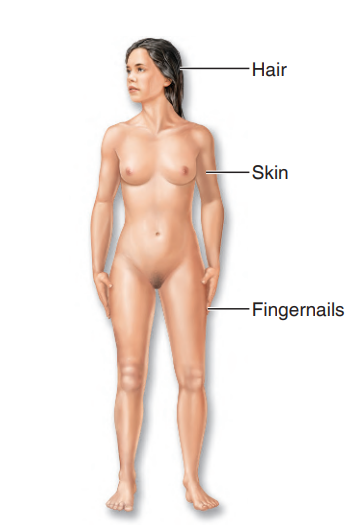
Integumentary System
the external covering of the body, or the skin, including the hair and fingernails
25
New cards
Integumentary System
it waterproofs the body and cushions and protects the deeper tissues from injury
26
New cards
Integumentary System
with the help of sunlight, it produces vitamin D
27
New cards
Integumentary System
it excretes salts in perspiration and helps regulate body temperature
28
New cards
Integumentary System
organ system where sensory receptors are located to alert us to what is happening at the body surface
29
New cards
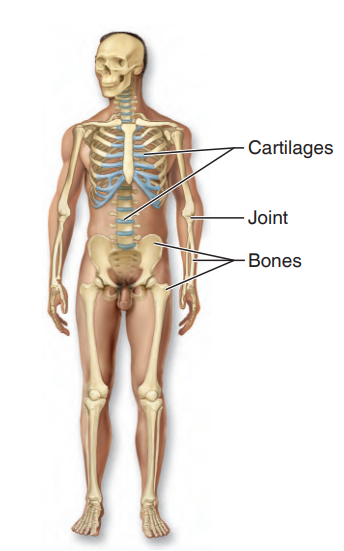
Skeletal System
organ system that consists of bones, cartilages, and joints
30
New cards
Skeletal System
supports the body and provides a framework that the skeletal muscles use to cause movement
31
New cards
Skeletal System
Organ system that has also protective functions (for example, the skull encloses and protects the brain), and the cavities of the skeleton are the sites where blood cells are formed. The hard substance of bones acts as a storehouse for minerals.
32
New cards
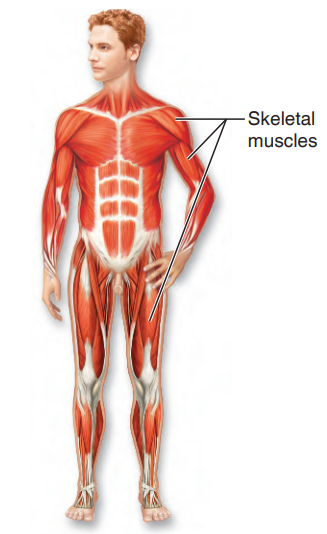
Muscular System
organ system that has only one function— to contract, or shorten
33
New cards
skeletal muscles
the large, fleshy muscles attached to bones
34
New cards
skeletal muscles
When these contract, you are able to stand erect, walk, jump, grasp, throw a ball, or smile
35
New cards
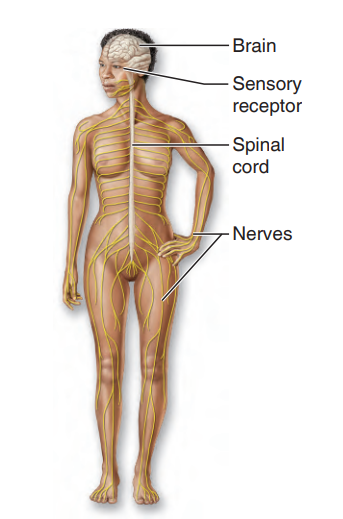
Nervous System
The body’s fast-acting control system. It consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors.
36
New cards
sensory receptors
detect changes in temperature, pressure, or light, and send messages (via electrical signals called nerve impulses) to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) so that it is constantly informed about what is going on
37
New cards
central nervous system
assesses information and responds by activating the appropriate body effectors (muscles or glands, which are organs that produce secretions)
38
New cards
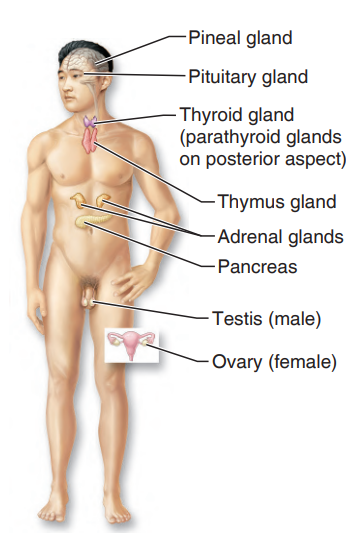
Endocrine System
like the nervous system it controls body activities, but it acts much more slowly
39
New cards
Endocrine glands
produce chemical molecules called hormones, and release them into the blood to travel to distant target organs
40
New cards
endocrine glands
include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, thymus, pancreas, pineal, ovaries (in the female), and testes (in the male)
41
New cards
endocrine glands
What they have in common is that they all secrete hormones, which regulate other structures
42
New cards
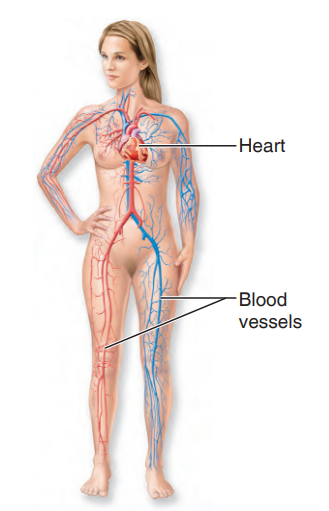
Cardiovascular System
its primary organs are the heart and blood vessels
43
New cards
Cardiovascular System
organ system that uses blood as a carrier, delivers oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other substances to, and picks up wastes such as carbon dioxide from cells near sites of exchange
44
New cards
heart
propels blood out of its chambers into blood vessels to be transported to all body tissues
45
New cards
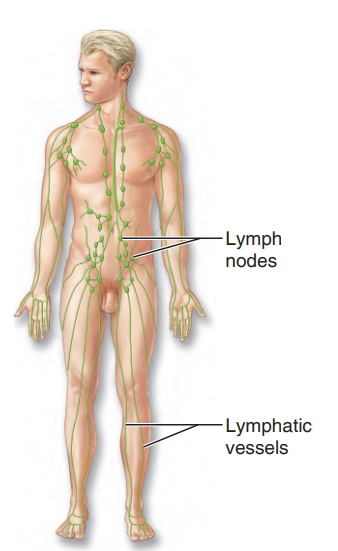
Lymphatic System
complements the cardiovascular system. Its organs include lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid organs such as the spleen and tonsils
46
New cards
lymphatic vessels
When fluid is leaked into tissues from the blood,
_____ return it to the bloodstream so that there is enough blood to continuously circulate through the body.
_____ return it to the bloodstream so that there is enough blood to continuously circulate through the body.
47
New cards
lymph nodes
The _____ and other lymphoid organs help to cleanse the blood and house white blood cells involved in immunity.
48
New cards
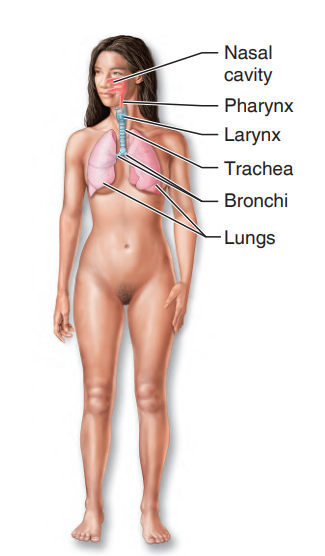
Respiratory System
keeps the body supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
49
New cards
respiratory system
It consists of the nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
50
New cards
alveoli
tiny air sacs within the lungs
51
New cards
gases
are exchanged with the blood through the thin walls of the alveoli
52
New cards
digestive system
basically a tube running through the body from mouth to anus
53
New cards
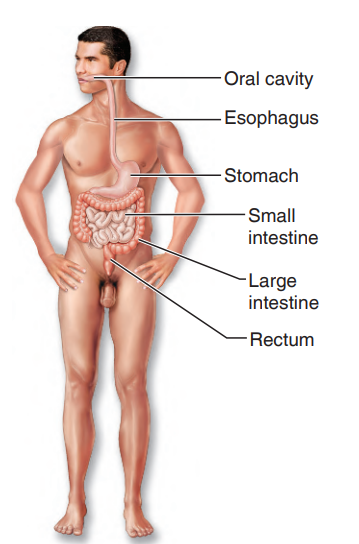
digestive system
include the oral cavity (mouth), esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and rectum plus a number of accessory organs (liver, salivary glands, pancreas, and others)
54
New cards
Digestive System
break down food and deliver the resulting nutrients to the blood for dispersal to body cells
55
New cards
small intestine
The breakdown activities that begin in the
mouth are completed in the _____.
mouth are completed in the _____.
56
New cards
Digestive System
its major function is to absorb nutrients and reabsorb water
57
New cards
liver
is considered a digestive organ because the bile it produces helps to break down fats
58
New cards
pancreas
delivers digestive enzymes to the small intestine, has both endocrine and digestive functions
59
New cards
nitrogen
One type of waste contains _____ (examples
are urea and uric acid), which results when the body
cells break down proteins and nucleic acids, which
are genetic information molecules.
are urea and uric acid), which results when the body
cells break down proteins and nucleic acids, which
are genetic information molecules.
60
New cards
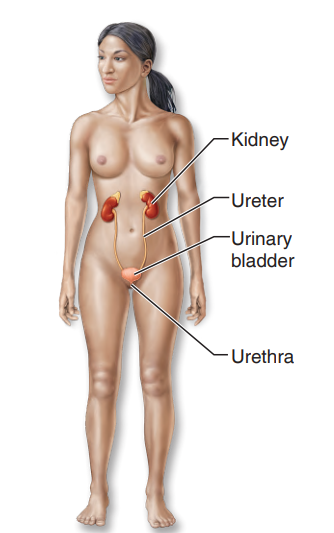
urinary system
removes the nitrogen-containing wastes from the blood and flushes them from the body in urine
61
New cards
urinary system
often called the excretory system, is composed of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
62
New cards
urinary system
functions of this system include maintaining the body’s water and salt (electrolyte) balance, regulating the acid-base balance of the blood, and helping to regulate normal blood pressure
63
New cards
reproductive system
organ system that has a role to produce offspring
64
New cards
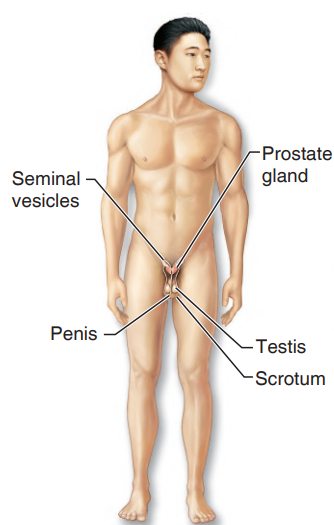
male testes
produces the sperm
65
New cards
male reproductive system
structures are the scrotum, penis, accessory glands, and the duct system, which carries sperm to the outside of the body
66
New cards
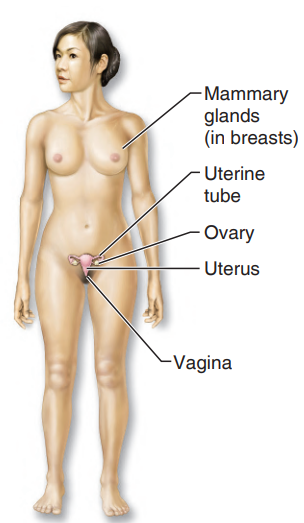
female ovaries
produce eggs, or ova
67
New cards
female reproductive system
consists of the uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
68
New cards
uterus
provides the site for the development of the fetus (immature infant) once fertilization has occurred
69
New cards
Integumentary System
Skeletal System
Muscular System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Cardiovascular System
Lymphatic System
Respiratory System
Digestive System
Urinary System
Reproductive System
Skeletal System
Muscular System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Cardiovascular System
Lymphatic System
Respiratory System
Digestive System
Urinary System
Reproductive System
11 organ systems
70
New cards
integumentary system
what system is this?
71
New cards
skeletal system
what system is this?
72
New cards
Muscular System
what system is this?
73
New cards
Nervous System
what system is this?
74
New cards
Endocrine System
what system is this?
75
New cards
Cardiovascular System
what system is this?
76
New cards
Lymphatic System
what system is this?
77
New cards
Respiratory System
what system is this?
78
New cards
digestive system
what system is this?
79
New cards
Urinary System
what system is this?
80
New cards
male reproductive system
what system is this?
81
New cards
female reproductive system
what system is this?
82
New cards
Maintain boundaries
Take in and digest nutrients
Carry out metabolism
Dispose of wastes
Reproduce themselves
Grow
Take in and digest nutrients
Carry out metabolism
Dispose of wastes
Reproduce themselves
Grow
what a highly organized human body do
83
New cards
Organ Systems
work together to promote the well-being of the entire body
84
New cards
Maintain boundaries
Every living organism must be able to _____ so that its “inside” remains distinct from its “outside.”
85
New cards
Movement
includes all the activities promoted by the muscular system, such as propelling ourselves from one place to another (by walking, swimming, and so forth) and manipulating the external environment with our fingers
86
New cards
Movement
also occurs when substances such as blood, foodstuffs, air, and urine are propelled through the internal organs of the cardiovascular, digestive, respiratory, and urinary systems, respectively
87
New cards
Responsiveness (or irritability)
the ability to sense changes (stimuli) in the environment and then to react to them
88
New cards
Digestion
the process of breaking down ingested food into simple molecules that can then be absorbed into the blood
89
New cards
Metabolism
refers to all chemical reactions that occur within the body and all of its cells
90
New cards
Metabolism
includes breaking down complex substances into simpler building blocks (as in digestion), making larger structures from smaller ones, and using nutrients and oxygen to produce molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy-rich molecules that power cellular activities
91
New cards
Metabolism
depends on the digestive and respiratory systems to make nutrients and oxygen available to the blood and on the cardiovascular system to distribute these needed substances throughout the body
92
New cards
Metabolism
is regulated chiefly by hormones secreted by the glands of the endocrine system
93
New cards
Excretion
the process of removing excreta, or wastes, from the body
94
New cards
Excretion
digestive system rids the body of indigestible food residues in feces, the urinary system disposes of nitrogen-containing metabolic wastes in urine, and the skin disposes of various waste products as components of sweat
95
New cards
Reproduction
production of offspring, can occur on the cellular or organismal level
96
New cards
cellular reproduction
the original cell divides, producing two identical daughter cells that may then be used for body growth or repair
97
New cards
Reproduction
the task of the organs of the reproductive system, which produce sperm and eggs
98
New cards
Reproduction
its function is regulated very precisely by hormones of the endocrine system