Week 11- DMS 212 Fetal Head, Neck, and Spine
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
AFP is produced by the fetal ____________ and ________________
liver and yolk sac
AFP is found in the...
maternal serum and amniotic fluid
AFP peaks at ___________ weeks
15-18
elevated AFP can indicate
underestimated ges age
multiple fetuses
open neural tube defect
abdominal wall defect
cystic hygroma
fetal demise
low AFP can indicate
overestimated ges age
chromosomal abnormality
GTN
long-standing demise
maternal HTN or diabetes
when is the maternal AFP test taken
15-17 weeks
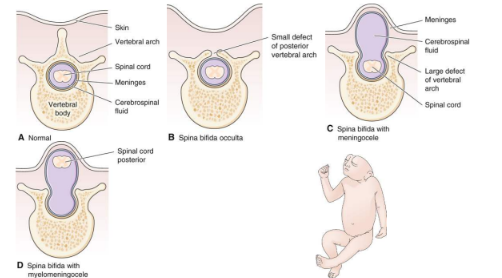
example of neural tube defect
spina bifida
example of abdominal wall defect
omphalocele
in the early 1st trimester most of the amniotic fluid comes from the _____________
maternal blood
later in the 1st trimester amniotic fluid comes from the ___________________
fetus excreting urine
how is amniotic fluid created
fetus swallowing the fluid and urinates it
when does the ability to swallow begin
8-11 weeks
swallowing the fluid helps to develop the __________________ system
GI
inhaling small amounts of fluid helps to develop the _______________ system
respiratory
keritization
exchange of fluid through permeable fetal skin
urine output accounts for nearly ________________ of fluid in the second half of pregnancy
total volume
after _______ weeks the fetus becomes the major producer of the amniotic fluid
16
quantity of fluid is directly related to _____________ function
kidney
if there is a renal anomaly you might expect to see
oligohydramnios
functions of the amniotic fluid
protection
temp reg
enables fetal movement
lung and genitourinary development
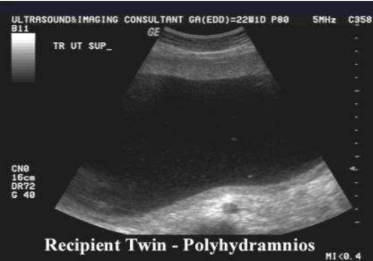
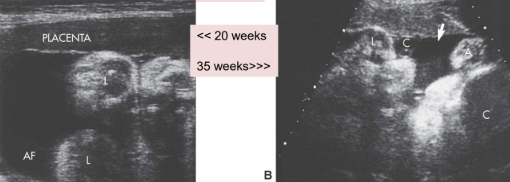
polyhydraminos
too much fluid
polyhydraminos is assoc with
TTTS
oligohydramnios
too little fluid
anhydramnios
no fluid
sono appearance of anhydramnios
no window to see baby
from __________weeks there will be a generous amount of fluid
20-30
volume of fluid stops increasing at _______ weeks
33
when does fluid become scanty
late third trimester
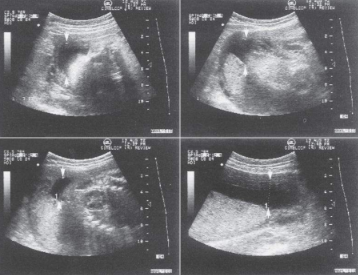
how is AFI determined
in the maternal sag plane four quadrants of fluid are measured
AFI of oligohydramnios
less than 5cm
largest single pocket less than 2cm
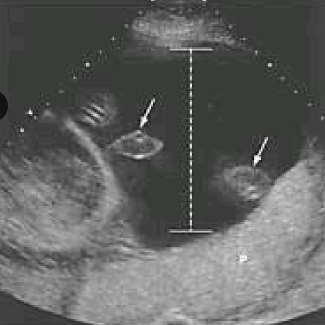
AFI of polyhydramnios
more than 24cm
largest single pocket more than 8cm
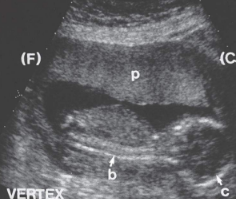
cephalic presentation
head down toward cervix
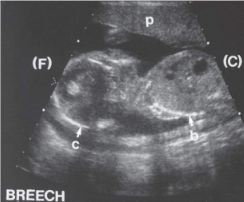
breech presentation
head up
transverse lie maternal right
head toward right
transverse lie maternal left
head toward left
complete breech
both knees bent feet down
incomplete breech
one leg up one leg down
frank breech
both legs up
oblique presentation
head and body are 45 degrees angle to the maternal sag plane
how many bones are in the feta head
8
the fetal head bones are connected by
sutures
________________________ exist between the forming bones
fontanelle spaces
abnormal head shapes can develop because
bones of the skull are moveable and malleable
fontanelles ramin unossifies through the __________ of life to allow...
1st year, vaginal delivery and expansion of growing brain
what are the forces that can cause a mishappen head
external pressure
gravitational forces
early fusion
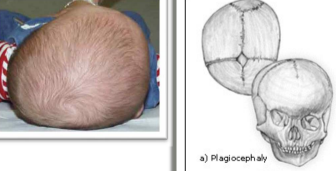
plagiocephaly
uneven shaped forehead
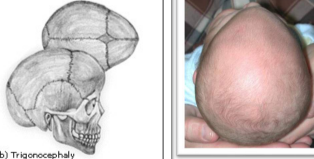
trigonocephaly
triangular shaped forehead
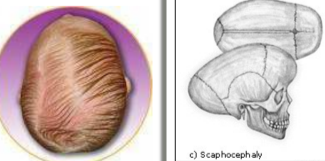
scaphocephaly
long narrow head
scaphocephaly is caused by
craniosynostosis
brachycephaly
short wide head
dolichocephaly
Long narrow head
dolichocephaly is caused by
pressure or premature fusion of sagittal suture
what are the two divisions of the fetal head
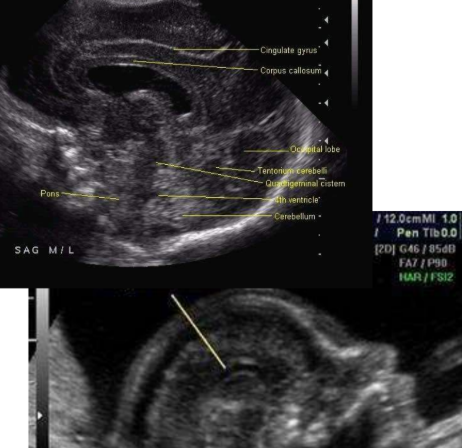
cerebrum
posterior fossa
the cerebrum contains the
interhemispheric fissure
falx
corpus callosum
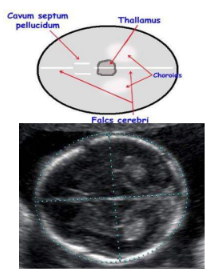
CSP
thalamus
ventricular system
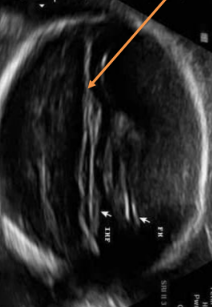
corpus callosum
provides communication between the two hemispheres
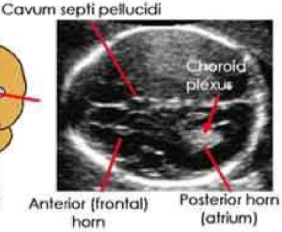
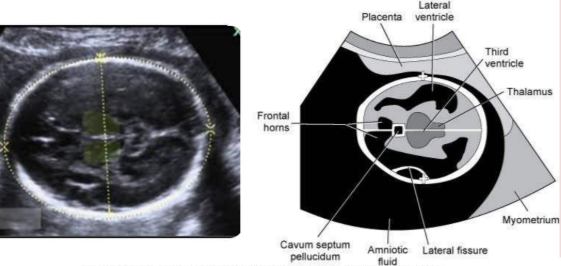
location cavum septum pellucidum
between the frontal horns of lateral ventricles
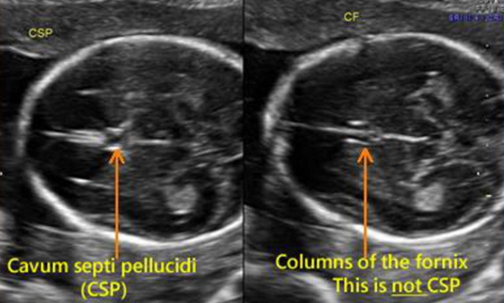
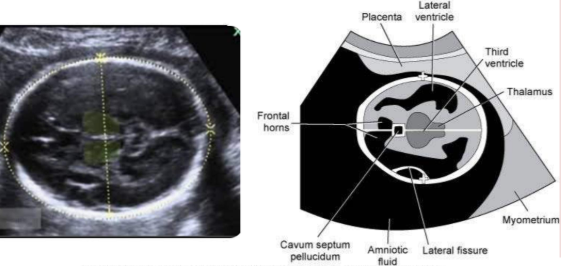
location of thalamus
either side of the third ventricle
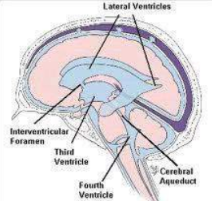
function of the ventricular system
cushioning for the brain
the ventricular system contains the _______________
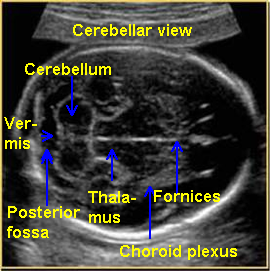
choroid plexus
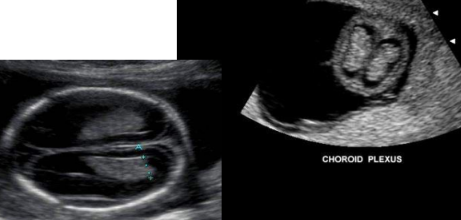
choroid plexus function
produces CSF
echogenicity of the choroid plexus
echogenic
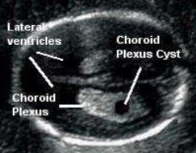
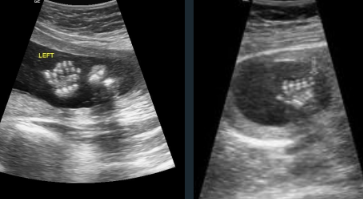
choroid plexus cysts
isolated
contain CSF
resolve between 24-26 weeks
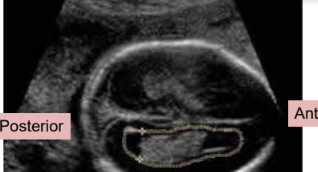
measurement of the lateral ventricles
less than 10mm
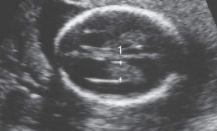
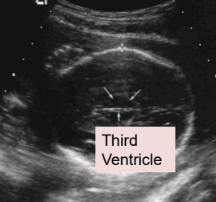
location of the 3rd ventricle
slit between lobes of the thalamus
posterior fossa
cerebellum
cisterna magna
forth ventricle
the cerebellum grows ______mm per week between _________ weeks
1, 14 and 20
shape of the cerebellum
figure 8
where is the cerebellum measured
level of cisterna magna and thalamus
what is the banana sign
cerebellum is banana shaped
brian is being pulled down into spinal canal
normal measurement of cisterna magna
3-10mm
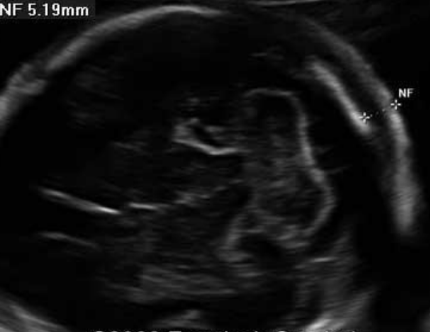
normal measurement of nuchal fold
less than 6mm
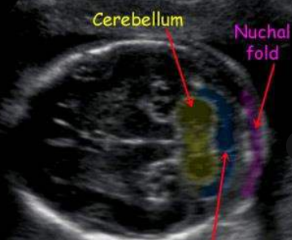
when is the nuchal fold identified
17-20 weeks
thickened nuchal fold indicated
down syndrome
trisomy 21
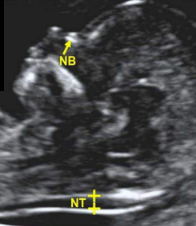
when is NT measured
11-13.5 weeks

normal measurement of NT
2.5-3mm
equal sign
top- skin
bottom- nasal bone
level of BPD, HC, and OFD
falx
CSP
thalami
CI of dolichocephaly
less than 75
CI of brachycephaly
more than 85
normal CI
80
when do the nasal bones first appear
11-13 weeks 6 days
CRL of 42mm
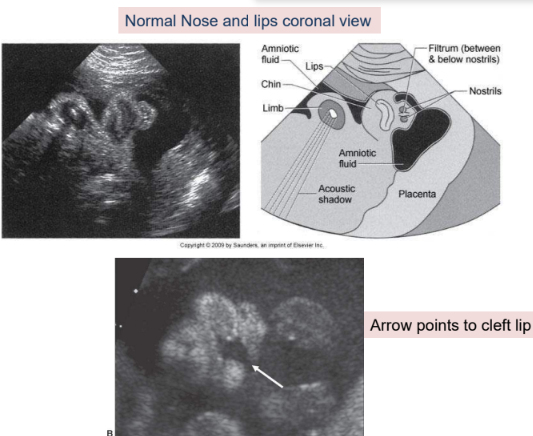
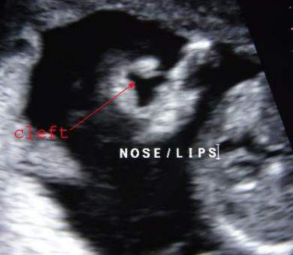
why is the nose/lips view so important
to rule out cleft lip/palate
anophthalmia
absence of one or both eyes
colpocephaly
migrational defect of the occipital horns of the lateral ventricles leading to ventricular enlargement
dysgenesis
abnormal formation
dysmorphic
Malformation of an organ or structure
ectasia
dilation or distension of hollow structure
nares
nostrils
neuropore
rostral or caudal end of neural tube
rostral
toward the head
teratogen
anything that interferes with development
vermis
central portion of cerebellum assoc with posture and locomotion
maternal serum AFP ________________ across placenta
diffuses
anencephaly
no cranium or brain tissue
sonographic features of anencephaly
abnormally shaped cephalic pole
absent neural tissue
loss of normal head contour
froglike appearance
spinal defects
omphalocele
clubfoot
cleft lip/palate
polyhydramnios
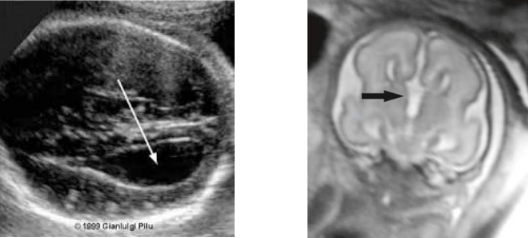
agenesis of corpus callosum (ACC)
complete or partial albescence of corpus callosum

ACC is assoc with
trisomy 13 and 18
hydrocephalus
dandy-walker syndrome
arnold-chairi malformation
holoprosencephaly
dandy-walker syndrome
absence of cerebellar vermis and enlarges 4th ventricle
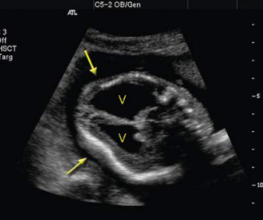
lemon sign
frontal deformities assoc with arnold chiari malformation
growth of long bones is from __________________ to ______________________
proximal to distal