straight line graphs
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what can you do when 2 equations are intersecting?
set them equal to each other
substitution
when do you substitute when 2 lines are intersecting?
when the equation doesn’t have y as the subject
gradient of parallel lines are …
The same
gradient of perpendicular lines are …
negative reciprocals
what is the product of the gradients of 2 perpendicular lines?
-1
when finding the negative reciprocal of the gradient, what do you have to ensure?
that y x 1
how do you prove a quadrilateral is a rectangle?
2 pairs of parallel sides
how do you prove a quadrilateral is a trapezium?
1 pair of parallel sides
how do you prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram?
2 parallel sides
…. what’s a trapezium …..
you should be ashamed of yourself
what’s a parallelogram …
sigh
how do you find the distance between 2 points?
pythagoras
how do you answer this? (Example 14, 5.3)
what does congruent mean?
of the same length
how do you find the point of intersection?
make sure y is the subject
set equal to each other / substitute
rearrange for x. this gives u the x coord at the p.o.i
substitute ur x value into one of the equations for the y coord
what is the shortest distance between parallel lines?
the perpendicular distance between them
how do you answer this? 5g 6d
how do you answer this 5g 7 also ask teacher abt it
how do you prove a triangle is a scalene?
the length of all 3 sides are different
what is a scalene triangle?
a triangle with each side being of a different length
how do you answer this? 5g 8 (b)
what is an equilateral triangle?
a triangle where each side is the same length
how do you prove a triangle is an equilateral?
all sides (the distance between points) are the same length
what is an isosceles triangle?
a triangle where 2 sides are the same length
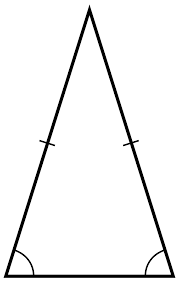
how do you show a triangle is an isosceles?
2 sides (the distance between points) are the same length
when are 2 quantities in direct proportion?
increase at the same rate
straight line
through the origin
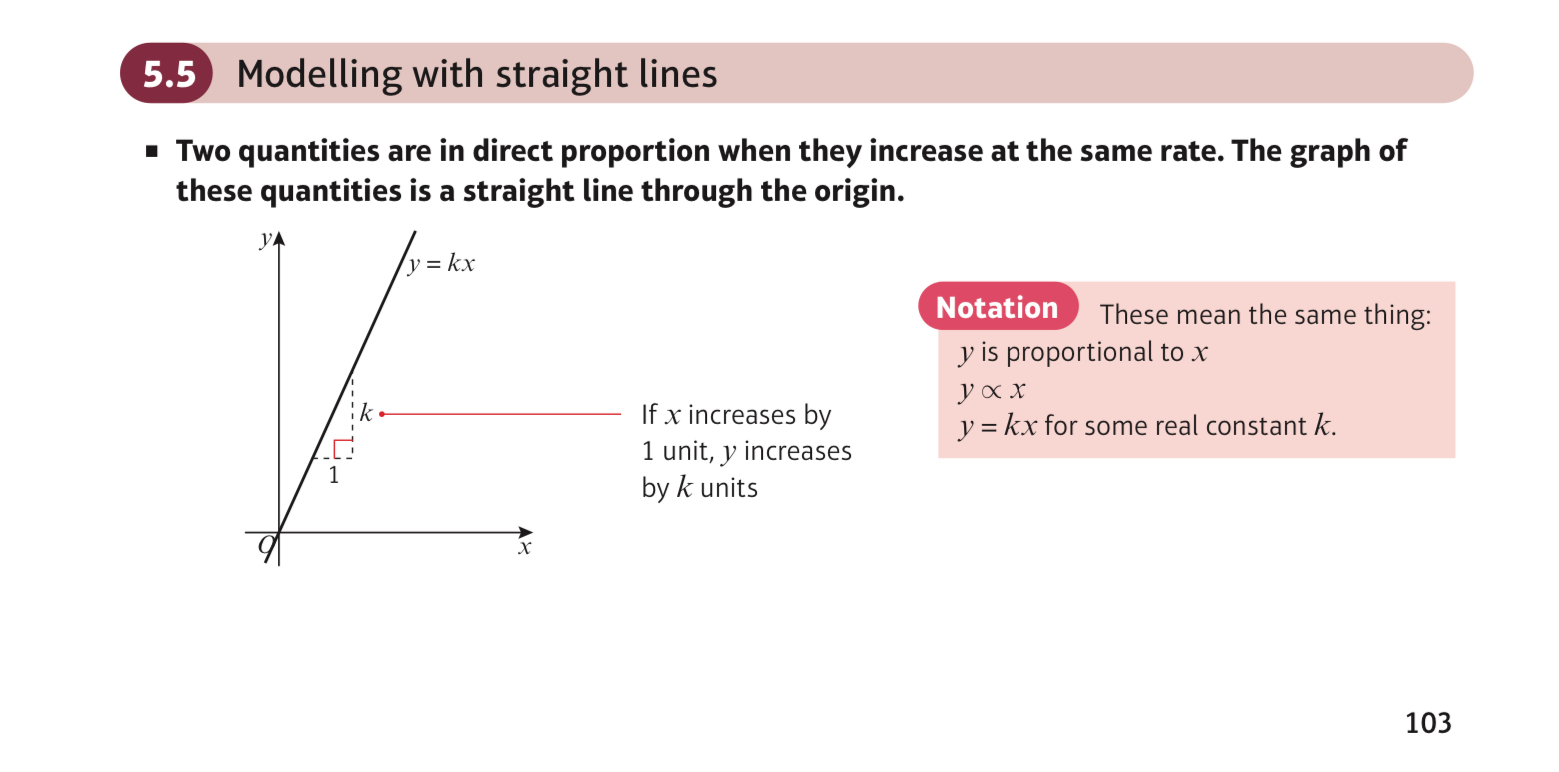
does a direct proportion graph go through the origin or not?
yes, it does
why is the y-int of a direct proportion graph 0?
because it goes through the origin
why is a direct proportion graph straight?
because they are increasing at the same rate
what is the equation of a direct proportion graph?
y = kx
why is the equation of a direct proportion graph y = kx?
y ∝ x
y = kx
y-int = 0 because it goes through the origin
what does the gradient of a direct proportion mean in straight line modelling?
if x increases by 1 unit, y increases by k units
HERE
what is a linear model?
a model showing the relationship of 2 variables that aren’t directly proportional
what is the difference between a linear model and a direct proportional model?
direct proportion model goes through the origin, y = kx
linear model may not go through the origin, y = kx + c
what is the equation for a linear model?
y = kx + c
for a linear model, do all values need to lie on the line?
no, but they must be close to the line
sometimes a linear model is not appropriate for modelling. what determines this?
the proximity of the values to the line - the further away, the less appropriate a linear model is
what is the gradient in a linear model? (example answer)
the amount the [y variable] increases by in [units] when the [x variable] increases by 1 [unit]
when explaining a linear model, what must you remember to include?
to include the units of measurement (e.g., the amount the [variable] increases in [units])
what does it mean in linear modelling when the gradient is negative?
the y variable is decreasing when the x variable increases by 1 unit
what does it mean in linear modelling when the gradient is positive?
the y variable in units is increasing when the x variable increases by 1 unit
what is the y-intercept in linear modelling?
the initial y value
when asked to see if a linear model is appropriate, what should you include?
a conclusion statement, saying that ‘the points do / don’t form a straight line, therefore a linear model is / isn’t suitable’
when asked to find the equation for a linear model, what should you include?
what the values represent (e.g., the x variable represents the time)
what should you do throughout all of modelling?
add a conclusion explaining what everything represents
in linear modelling, what does the x value increase by in the gradient?
always 1 unit, regardless of the scale
what is a common assumption we make in linear modelling?
that the y value will increase by the same amount each 1 x variable unit
in linear modelling, how do you find the value when the y value = x value? exercise 5h 6d
algebra here
what does this mean; ‘find the equation in terms of y and x only’?
not including any constants or unknown values
how do you solve this? mixed exercise 12 b
when asked to prove if 2 lines are perpendicular, what do you do?
compare their gradients (don’t do anything about magnitude since it’s not gradient) and prove they are negative reciprocals of each other by multiplying them together to get -1
how to find;
gradient
distance
here
mixed exercise 17 a