Clinical diagnosis of ruminants
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What information is gathered from a history?
Animal details & history —> age, production stage, clinical signs
Herd history
Farm and the client
On-farm stage of examination
Full clinical examination
general inspection, vital signs, specific exam
Sampling for laboratory exam if required
Environment
Further history e.g. housing, nutrition
Rest of the herd?
How to approach clinical exam of cows
Cows are head shy —> used to being approached from behind:
Tail end
Udder
L side (abdomen & chest)
R side (abdomen & chest)
Head
Vaginal &/or rectal exam
What is checked at the tail end?
Temp, abdominal symmetry, vaginal discharge?, metritis, endometritis, bulling, faecal staining/faeces, BCS, coat condition (no rectal yet because it will introduce air —> gives false “ping” on RHS)
Temperature of adult vs calf
Adult = 38.5
Calf = 39
push thermometer to side so touches rectal wall and gives accurate reading
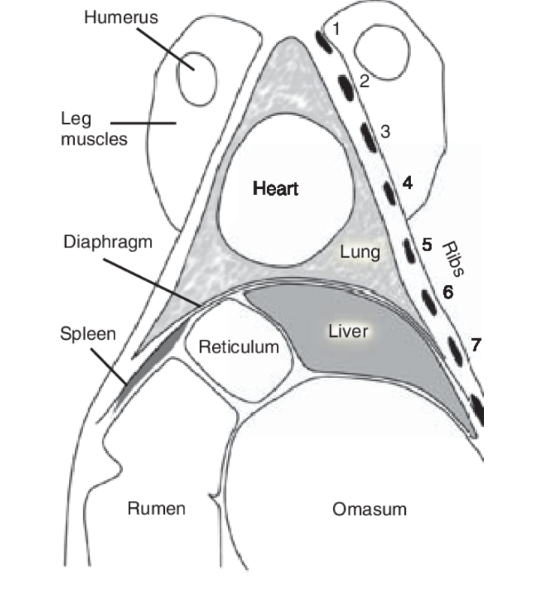
What is examined in the chest area?
Heart —> listen under elbow, rib spaces 3-5
murmurs = endocarditis
quiet/absence/splashing = traumatic pericarditis
Lungs
small lung field —> listen in several different areas (triangular, see image)
examine both sides
abnormal sounds = damage been there a while
heat stress at in warmer temps
DO ON BOTH LEFT AND RIGHT
HR in adult vs calf?
Adult = 60-80bpm
Calf = 80-120 bpm
RR in adults vs calves?
Adult = 15-30 breaths per min
Calf = 24-36 breaths per min
What is examined on the left abdomen?
Rumen
fill (score 1-5)
gas/bloat
consistency of contents
3 turnover movements in every 2 mins —> use bent fingers in L sub-lumbar fossa
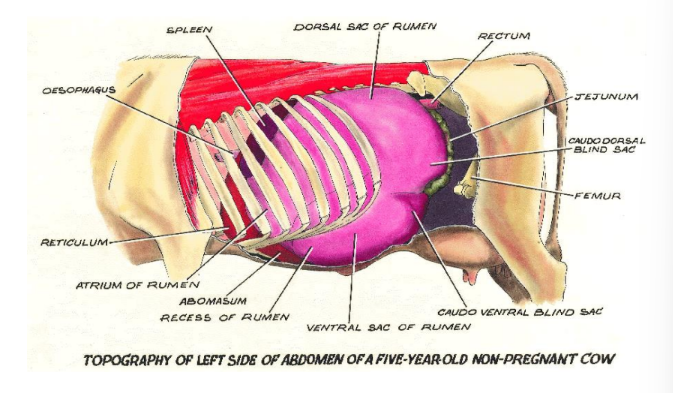
What is the Eric Williams test?
Palpation of rumen & auscultation of trachea
Primary cycle = no sound, feel rumen contract (mixing)
Secondary cycle = eructation sounds
Grunt before primary contraction = peritonitis caused by wire
Turnover + nothing then turnover + burp sound = normal
Describe displaced abomasum (“pinging”)
Spontaneous = tinkling & gurgling
Ping = tap rib hard —> resonate ping, indicates gas fluid interface, map out area of “pings”
Absence of rumen sounds over displaced abomasum
Fat cows = no ping
What is examined in the head?
Eye
Conjunctiva colour e.g. pink, red, white, petechiae
Discharges
Lesions
Keratoconjunctivitis
Iritis
Nose
Palpate LNs e.g. submandibular
Symmetry
CRT & skin tent for dehydration
Mouth
pull tongue out to side
lesions
ulcers/vesicles
What is examined on the right abdomen?
Ping & listen but no need to do Eric Williams test (done on left)
What to examine in udder?
Palpate (care with suckler cow)
Take milk sample from lactating animals, clots & colour (only if reason in dry cow or suckler cow)
California milk test
Sterile milk sample for bacteriology
What is examined in vaginal exam?
Discharge (calving date)
Vaginal wall
Cervix —> open/closed uterus & contents
Uterus & contents
What is examined in rectal exam?
Faeces consistency
Presence of blood?
Rectal tone
Rumen
Uterus & ovaries
L kidney (midline or on RHS) —> kidney infection painful
Distended abomasum/caecum
Gut contents
Skeletal examination
Lameness
Mostly foot but can get higher limb issues
What is examined in calves?
Initially won’t have a functioning rumen
Have neonate specific things to check for —> joint/navel ill, congenital abnormalities
Calving history —> colostrum intake (how much, how quickly)
What is the “Blunderbuss” approach?
Examine top to toe
Get every conceivable test carried out
Fit results to textbook model/vets own database of disease
What is the hypethetico-deductive model
Generation of hypotheses
Testing of hypotheses