Trusts
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
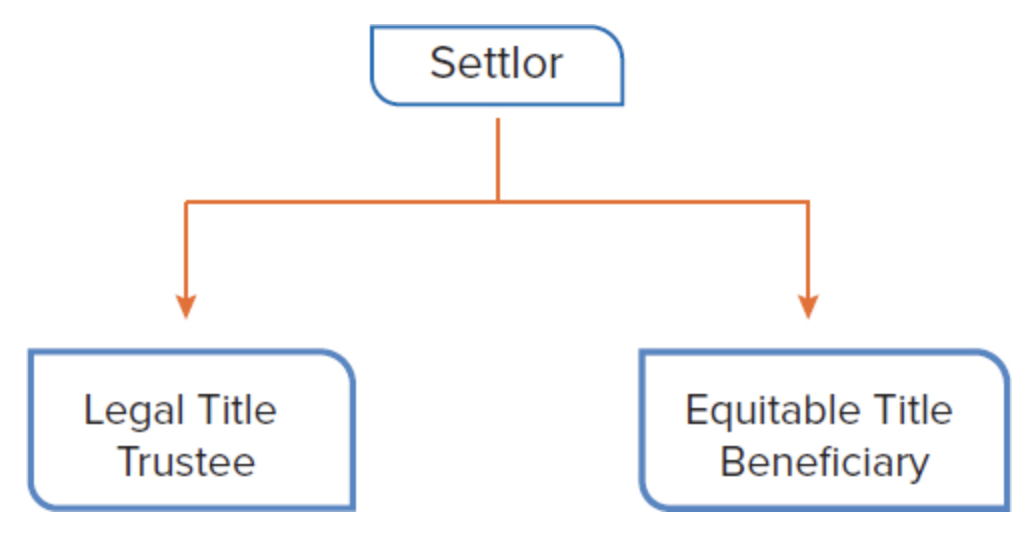

Trustee
Holds legal title
Owes fiduciary duties to beneficiaries
Duty of care and loyalty
Personally responsible if their conduct falls beneath required standards
Beneficiary
Holds equitable / beneficial title to property
Enforces fiduciary duties
Settlor
Creates the trust
May be called trustor, grantor, or donor
Trust Property Required
May be called principal, corpus, trust estate, or res
Purposes and Uses of Trusts
Protect and provide for beneficiaries
Flexibility of Asset Distribution
Protection Against Settlor’s Incompetence
Professional Management of Property
Probate Avoidance
Tax Benefits
Basic Classifications of Trusts
Express Trust
Trust created through express intent of settlor
Private → private beneficiaries
Charitable → charitable beneficiaries
Trusts created by Operation of Law
Resulting Trust
Attempt to carry out settlor’s intent
Constructive Trust
Equitable remedy
Trusts Validity
Trust not stated to be valid → ALWAYS start here
Requirements
Intent
Identifiable corpus
Ascertainable beneficiaries
Proper purpose
Trustee
Mechanics and formalities
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Intent
2 Types
Intent to split legal and equitable title
Intent to impose enforceable duties on holder of legal title
Issues
Settlor Must Have Capacity
Capacity required to create an inter vivos trust → same as to make an inter vivos gift
Capacity to make a testamentary trust → same as that required to make a will
Intent may be manifested by written or spoken words or by the conduct of the settlor
Unless the Statute of Wills or the Statute of Frauds applies
No formal words required
Communication of intent to the beneficiaries is not necessary
Settler must have present intent to create trust
Promise to create trust in future is unenforceable unless there is binding contract
Once an outright transfer of property occurs, it is too late for the alleged settlor to go back and claim the transfer was really one in trust
Precatory Language: expression of hope, wish, or suggestion
Generally doesn’t create trust
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Intent
Split of Title
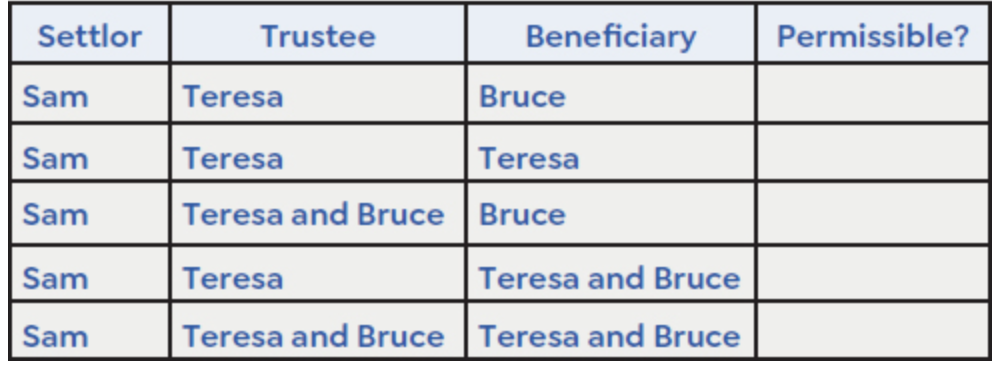
Any split of title into legal and equitable portions is permissible if the same person doesn’t own all the legal and equitable title
Sole trustee and sole beneficiary are the same person → equitable and legal title merges → trust terminates
Example:
Yes
No
Yes
Yes

Trusts Validity
Requirements
Identifiable corpus
Property must be ascertainable with certainty
Any property the settlor can transfer can be held in trust
Property settlor can’t transfer or doesn’t yet own can’t be trust property
Must be separated from other property
But it can be a portion of specific property
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Ascertainable beneficiaries
Qualified Beneficiary: beneficiary who is current or first line remainder beneficiary
Any person or entity capable of taking and holding title to property
Need not be competent
May disclaim interest if they haven’t accepted any benefits
Anti-Lapse Statutes
Some States → apply to interest in trusts
If requirements are met, trust interest will go to predeceased beneficiary’s descendants
Final Divorce
Revokes all trust provisions in favor of ex-spouse
Class Gifts
Beneficiaries may be unascertainable when trust created
But must be ascertainable when property is to be distributed
Settler may allow trustee or third party to select which class members receive benefits
Failure to exercise the power gives rise to a resulting trust in favor of the settlor or their successors
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Proper purpose
Any purpose that is not
Illegal
Against public policy
Impossible to achieve
Intended to defraud the settlor’s creditors or based on illegal consideration
Doesn’t violate the Rule of Perpetuities
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Trustee
Trust will not fail for lack of trustee because court can appoint one
Acceptance of Trusteeship
Must sign trust instrument or written acceptance
If person starts acting like trustee, they will be deemed to have accepted
Must have real powers and duties
Compensation
Trust instrument can indicate compensation
If instrument is silent, trustee usually entitled to reasonable compensation
Removal
Grounds for removal include:
a serious breach of trust;
serious lack of cooperation among co-trustees;
unfitness, unwillingness, or persistent failure to administer; or
a substantial change in circumstances
Court has power to remove and appoint new one
Successor Trustee
all of the rights, powers, and privileges of the original trustee
subject to all of the original trustee’s duties, liabilities, and responsibilities
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Mechanics and formalities
Creation Methods
Inter Vivos Trust (Living Trust)
Declaration of Trust
Settlor and trustee are same person
Transfer or Conveyance in Trust
Settlor transfers legal title to someone else
Testamentary Trust (Created by Testator’s Will)
Secret Trust
Settlor agrees with will beneficiary that beneficiary will hold property in trust for someone else
Will does not state trust nature of gift
Courts allow trust beneficiary to present extrinsic evidence and seek constructive trust remedy
Semi-Secret Trust
Will makes gift in trust but fails to state beneficiary
Gift fails → trustee must give legal title back to settlor’s succession in interest (resulting trust)
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Mechanics and formalities
Requirement
Requirement: Convey the Property
Declaration of Trust
Personal Property → property segregated and identified
Real Property → deed land from settlor as individual to settlor as trustee
Conveyance in Trust
Real Property → deed land to trustee
Personal Property → physically deliver property to trustee
Pour Over Gift from Will to Trust
Will contains provision leaving property to inter vivos trust
Property governed by terms of trust → trust amendments govern poured-over property
Poured-over property can be initial trust funding if trust identified in will and trust executed before testator’s death
Trusts Validity
Requirements
Mechanics and formalities
Writing
But are there times when you can have a valid will without a writing?
Most states do not require a writing for a trust of personal property.
Oral trusts may be established only by clear and convincing evidence
If the holder of the legal title acts as if they are a trustee, part performance will preclude the Statute of Frauds defense
Transfer of Beneficiary’s Interest
General Rule: Interests freely transferable
Voluntary Transfers—Gifts and Sales
Involuntary Transfers—Creditors
Transfer of Beneficiary’s Interest
Discretionary Trust
Trustee determines how much beneficiary receives
Beneficiary has nothing to transfer until trustee decides to distribute money
So there is nothing for creditors to reach
Exception: claims for child or spousal support
Transfer of Beneficiary’s Interest
Spendthrift Provision
Characteristics
Beneficiary can’t transfer interest
Once the trustee pays the beneficiary, the beneficiary may transfer the property received
Creditors can’t attach beneficiary’s interest
Once the trustee pays the beneficiary, the creditors may reach the property
Limitations
Ineffective if settlor is beneficiary
Minority Rule: allow self-settled spendthrift trusts
Ineffective against certain claims such as child or spousal support
Transfer of Beneficiary’s Interest
Support Trusts
Use of trust property limited to beneficiary’s support
May be mandatory or discretionary
Impliedly spendthrift
Issues
Standard of support if not in instrument → lifestyle to which beneficiary accustomed
Creditors of the trustee cannot reach trust property to satisfy their claims
Have only a personal claim against the trustee
Modification and Termination of Trusts
General
Terminate automatically upon
the expiration of the term specified in the instrument OR
when all of the purposes of the trust have been accomplished or have become unlawful, contrary to public policy, or impossible to achieve
Duty Of Trustee Upon Termination
Trustee’s powers do not end immediately upon trust termination
May continue to exercise powers for a reasonable period of time necessary to wind up the affairs of the trust
Must then timely distribute trust property to the appropriate remainder beneficiaries
Modification and Termination of Trusts
Types
By express terms
By the settlor
May modify or revoke trust for any reason
Unless trust instrument expressly states it’s irrevocable
Some states → may revoke an irrevocable trust upon written consent of all living persons with vested or contingent interests
By the beneficiaries
With settlor’s consent → permitted
Without settlor’s consent → may if
All beneficiaries agree
Changes would not upset material trust purpose
Examples:
Support of beneficiary
Spendthrift provision
Payment at certain ages
Payment at certain dates
Discretionary trust
By operation of law
Property has been exhausted or if the legal and equitable titles have merged
By the court
Trust’s purpose accomplished, illegal, or impossible
Unanticipated circumstances
Value of trust too low
Some States → fix mistake if shown by clear and convincing evidence
By the trustee
Terminate uneconomic trust
Trust property is less than $50,000 and the amount is insufficient to justify the cost of administration
Combine or divide trusts
Powers of the Trustee
Sources of the Trustee’s Power
Express powers granted by settlor in trust instrument
Powers provided by state statute
Powers granted by court
Implied powers necessary or appropriate to carry out terms of trust
Examples:
Sell trust property (How else invest?)
Lease trust property (How else earn income?)
Incur reasonable expenses (How else carry out trust?)
Hire agents (How else carry out trust?)
Mortgage trust property (How else borrow money?)
Repair (How else keep trust property valuable?)
Joint Powers
Trustees can exercise power by majority decision
Types of Powers
Mandatory Power → trustee must exercise it
Discretionary Power → trustee may exercise power as trustee sees fit
Trustee liable only for abuse of discretion or failure to exercise discretion
No such thing as absolute discretion
Duties of the Trustee
Duty to Administer Trust
Duty to administer trust in good faith and in a prudent manner, according to its terms
Duty of Loyalty
Avoid self-dealing
Trustees cannot
Personally benefit from trust
Purchase property from trust
Sell own property to trust
Borrow from trust
Claim excessive compensation
Trustee’s good faith or fairness irrelevant
Duty to Report
Provide the qualified beneficiaries with the trustee’s name, address, and telephone number and
Respond to beneficiary requests for information about the trust’s administration and provide a copy of the trust instrument if requested; and
Furnish an annual accounting of the trust
Duty to Separate Trust Property and Keep Records
No Commingling
“Earmark” trust property by labeling it as trust, rather than individually owned, property
Duty to Enforce Claims and Defend Trust from Attack
Duty to Preserve Trust Property and Make It Productive
Investments
Prudent Investor Rule
Trustee must invest in same manner as prudent investor
Reasonable care, skill, and caution when investing and managing trust assets
Following phrases in a trust invoke the prudent investor rule:
“Prudent person rule”
“Prudent man rule”
“Legal investments”
What if the trustee has higher or lower skills?
Higher skills → duty to use those skills
Lower skills → must comply with prudent investor rule
Portfolio Approach: view investments together in context of entire trust portfolio and part of overall investment strategy
Factors considered in making investment decisions
Trust purposes
Economic conditions
Tax consequences
Role of each investment in portfolio
Income and appreciation
Other resources of beneficiaries
Need for liquidity, regularity of income, or preservation of capital
Asset’s special relationship to beneficiary
Must diversify investments
Unless trust purposes are better served without diversification
Duty to review trust property
Review of Conduct
Facts and circumstances existing at the time of the trustee’s decision or action
Loyalty and Impartiality
Must administer trust exclusively for beneficiary’s interest
Must act impartially and not favor one beneficiary over another
Delegation
May delegate investment and management functions
Protected from liability if acted prudently in
Selecting agent
Establishing scope and terms of delegation
Periodically reviewing agent’s actions
Liabilities of Trustee
Remedies
Damages Recoverable for Breach (Money Damages - Most Common)
Lost profits
Depreciation in value of trust property
Trustee’s profits from breach
Remedies for Self-Dealing
Affirm transaction if trust profitied
Set aside transaction if trust lost money
Trace profits from trustee
Removal of Trustee (Common Remedy)
Grounds
Incompetence
Unfit
Serious breach of duty
Serious conflict of interest
Insolvency
Extreme hostility between trustee and beneficiaries
Refusal to post bond
Refusal to account
Courts will consider the settlor’s intent
Liabilities of Trustee
Trustee Not Liable for Breach When:
Reasonably relied on terms of trust
Beneficiaries consented or ratified transaction
Settlor or instrument allowed conduct
Exculpatory clause relieves trustee from liability for breaches
Generally exculpate only negligent conduct
Liabilities of Trustee
Liability of Co-Trustees
Not liable for act of co-trustee if
trustee did not join in the action and exercised reasonable care in preventing the breach or compelling the co-trustees to redress it
Liabilities of Trustee
Trustee’s Liability to Third Parties
Contracts → trustee personally liable
But can avoid liability by contract provision or indicating role as trustee by signature
Trustee entitled to indemnification or reimbursement from trust
Tort → liable if personally at fault
Liability Of Third Parties To The Trust
Court can set aside transactions that are breaches of trust if
the property is not in the hands of a bona fide purchaser
Knowing participant in a breach of trust is liable for the resulting loss
Allocation Of Receipts And Expenses Between Income And Principal Accounts
Uniform Principal and Income Act
Describes how principal and income should be allocated
Settlor can alter rules
Trustee has adjustment power
Must consider many factors
Can’t be made if
Prohibited by trust instrument
Trustee is also beneficiary
It would cause adverse tax consequences
Allocation of Receipts
Principal
Money from selling asset
Eminent domain awards
Insurance proceeds if principal is destroyed
Stock dividend, stock split, or shares received because of reorganization
Sale of underproductive property
Income
Rent
Interest on trust investment
Cash stock dividend
Both
“Wasting assets” → 10% Income & 90% Principal
Allocation of Expenses
Principal
Capital gains tax
Extraordinary repairs and capital improvements
Income
Ordinary income tax
Ordinary repairs
Depreciation
Both
Trustee compensation and accounting expenses → 50% income & 50% Principal
Charitable Trust
Must have a purpose considered to benefit the public
Charitable purposes include:
The relief of poverty
The advancement of education or religion
The promotion of health
The accomplishment of government purposes (such as parks, museums, and playgrounds)
Settlor must be sufficiently altruistic in supplying benefits
May not be so narrow as to only benefit a few individuals whom the settlor wishes to aid personally
Just because some family members might be benefited does not keep the trust from being charitable.
Court can select a charitable purpose or beneficiary if none is specified in the trust instrument
So long as the selection is consistent with the settlor’s ascertainable intention
Cy Pres (“as near as possible”) Doctrine
If charitable purpose cannot be carried out, court may select alternate by ascertaining settlor’s primary purpose
Rule Against Perpetuities does not apply to charitable trusts
Enforcement
State AG enforces
Honorary Trust
No human beneficiaries and not for charitable purpose
Common example: trust to care for pet
Resulting Trust
Arise by implication from settlor’s conduct
Beneficiaries: settlor or settlor’s successors in interest if settlor has died
Purpose is to do what settlor would have done
Situations Giving Rise to Resulting Trust
Failure to create express trust
Express trust corpus and no provision for remainder
Purchase money resulting trust: supplier of purchase money gives money to seller who gives title to property to third party
Explanations why 3rd Party has title instead of purchaser
Gift
Law presumes gift when parties closely related
Loan
Purchase money resulting trust
Constructive Trust
Not a trust
But an equitable remedy to prevent unjust enrichment resulting from wrongful conduct
Must be requested as remedy in court action
Must show particular property was involved in improper conduct
Constructive Trustee’s Duty
Give legal title back to person who would have owned it but for wrongful conduct
Grounds to Impose
Fraud, duress, mistake, or breach of fiduciary duty
Homicide
In states that lack slayer statute
Abuse of confidential relationship
Can include attorney-client, doctor-patient, business partners, family relations, and friendships
Breach of promise