Quiz 3: Moles, EM Spectrum, and Quantum Theory
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
(1 x 22.990 amu) + (1 x 35.453 amu) = 58.443 amu
What is the Average Atomic mass of NaCl?
(1 x 32.065 amu) + (2x 15.999amu) = 64.063 amu
64.063 amu/1 molecule = 64.063 g/mol
What is the Molar Mass (MM) of SO2?
MM = 110.984 g/mol
5.12 x 10^-7 mol x (110.984 g / 1 mol) x (1 Mg / 10^-6 g)
= 56.8 Mg
5.12 x 10^-7 mol CaCl2 →
______ mass in Mg
Avogadro's Number (n)
6.0221 x 10^23 particles/1 mol
To convert moles into molecules, you must use ________________
Avagadros number (n)
What equation is this:
6.0221 x 10^23 particles/1 mol
0.166 mol CO2 x (6.0221 x 10^23 CO2 molecules) / 1 mol CO2
= 9.99 x 10^22 CO2 molecules
0.166 mol CO2 →
______ CO2 molecules
12.011 + (2 x 35.453) + (2 x 18.918) = 120.913 amu
120.913 amu/ 1 molecule →
120.913 g/mol
Molar Mass (MM) of CCl2F2?
5.48 kg x (10^3 g/ 1 kg) x (1 mol/ 120.913 g)
= 45.3 mol
5.48 kg ->
______ mols of CCl2F2
45.3 mol x (6.0221 x 10^23 molecules) / 1 mol
= 2.73 x 10^25 molecules
5.48 kg ->
______ molecules of CCl2F2?
speed of light = wavelength x frequency (m/s = m x s^-1)
To solve for wavelength, you must use ___________
Frequency (V)
_____________ is the number of oscillations per second, measured in Hz (s^-1)
Speed of Light (C)
What is this equation:
2.998 x 10^8 m/s
0.111 cm x 10^-2 m/1 cm
= 0.00111 m
C = wavelength x V
(2.998 x 10^8 m/s) = 0.00111m x V
V = 2.70 x 10^11 Hz
(2.70 x 10^11 Hz) x 1 MHz / (10^6 Hz)
= 2.70 x 10^5 MHz
0.111 cm → _____ MHz (megahertz)
1240 KHz x (10^3 Hz/ 1 KHz) = 124 x 10^6 Hz
C = wavelength x V
2.998 x 10^8 m/s = wavelength x (1.24 x 10^6 s^-1)
Wavelength = 242m
1240 KHz → ______ wavelength in m?
Amplitude
The ____________ is the brightness of light in electromagnetic waves
Continuous Spectrum
The _________________ is an unbroken distribution of light across wavelengths
Continuous Spectrum
The EM spectrum is an example of a ___________________
Atomic Spectrum
The _______________ is a group of unique wavelengths emitted by elements when excited
Atomic Spectrum
Black lines (Fraunhofer Lines) in the absorption spectrum correspond to wavelength of light in the _____________________
Quantized energies
The Atomic spectrum is evidence that electrons have __________________
Discrete energy
Quantized energy is ___________________
Energy of 1 photon = (plancks constant x speed of light) / wavelength
What does each variable in the equation stand for?
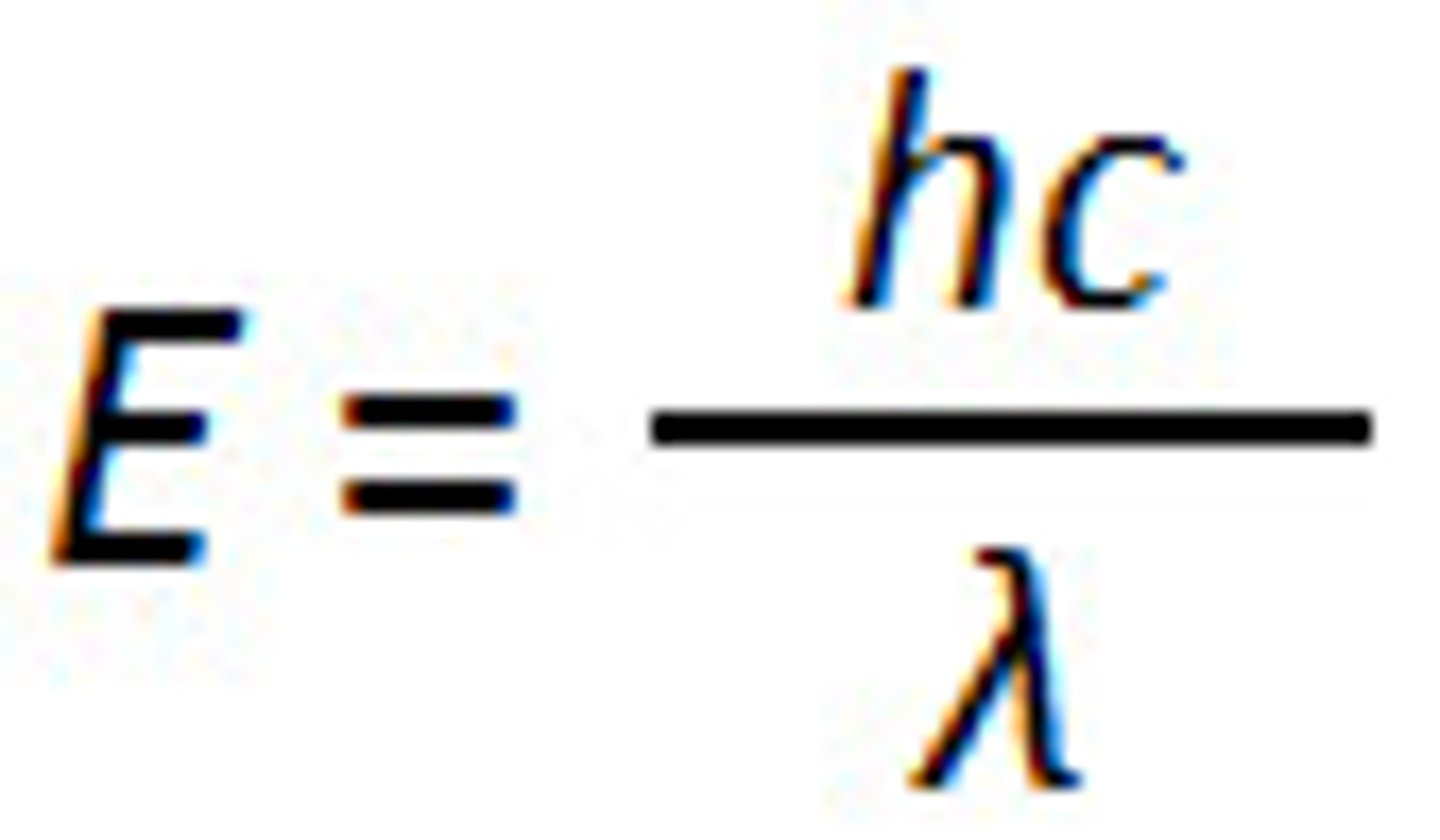
Planck's Constant (h)
What is this equation:
6.626 x 10^-34 JS
520 nm x (10^-9 m/1 nm) = 5.20 x 10^-7 m
E = (6.626 x 10^-34 JS) (2.998 x 10^8 m/s)/ 5.20 x 10^-7 m
E = 3.83 x 10^-19 J
Green laser pointer emits light at 520 nm
What is the energy of 1 photon of light at the wavelength?
Quantum Theory
The ________________ describes quantized energy levels of electrons
Bohr Model
The ______________ explains electron energy levels in hydrogen
Change in energy
Bohr model:
ΔE = -2.178 x 10^-8 J ( 1/n^2 Final - 1/n^2 Initial) solves for ____________
ΔE = -2.178 x 10^-8 J ( 1/1^2 Final - 1/2^2 Initial)
ΔE = -2.178 x 10^-8 J ( 4/4 Final - 1/4 Initial)
ΔE = -2.178 x 10^-8 J ( 3/4)
ΔE = -1.634 x 10^-18 J
Bohr model:
Electron gets excited from n = 1 to n = 2
What is the energy released when electron returns to n = 1
n Initial = 2 n Final = 1
True
True or False:
A negative outcome from the Bohr model tells us that energy has been released (positive - energy has been absorbed)
n = 1
_____________ is the lowest energy orbit
H (hydrogen)
E (energy) of transmission corresponds to a band on the atomic structure of __________ only
H has 1 electron, more than one electron makes things more complicated
Why does the E (energy) of transmission only work with H (hydrogen)?
- h -> Plancks constant
- m -> mass
- v -> velocity
h/mv is the De Broglie Wavelength
- h stands for ______________
- m stands for _______________
- v stands for _______________
momentum
mv (mass x velocity) --> __________________
Wavelength
As mass increases, ________________ decreases
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
- location
________________ states that you cannot know both the position and momentum of an electron at the same time. The focus in on the probable _____________ of the electron
1. Principle (n)
2. Angular momentum (L)
3. Magnetic (m L)
4. Spin (m s)
There are four Quantum numbers describing the electron's energy and position. What are they?
Orbital
Each __________ is described by 4 Quantum numbers
Principal (n)
Quantum numbers:
The _______________ tells us the size and energy level of an orbital
Angular Momentum (L)
Quantum numbers:
The ____________ tells us the shape of an orbital
0 to n-1
L can equal _______________
Magnetic (m L)
Quantum numbers:
The ________________ tells us the orientation of an orbital (divides the subshells and orbitals)
-L to +L (Integers)
m L can equal _____________
Spin (m s)
Quantum numbers:
The _____________ describes the electron spin
+½ or -½
m s can be _______________
Pauli Exclusion Principle
The ______________ Tells us that no electrons in the same atom can have identical quantum numbers
2
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that each orbital can hold a max of ________ electrons
Electrons (2 max)
______________ will have opposite spins if in the same orbital
True
True or False:
To find the max number in electrons multiply number of orbitals by 2 (max electrons)
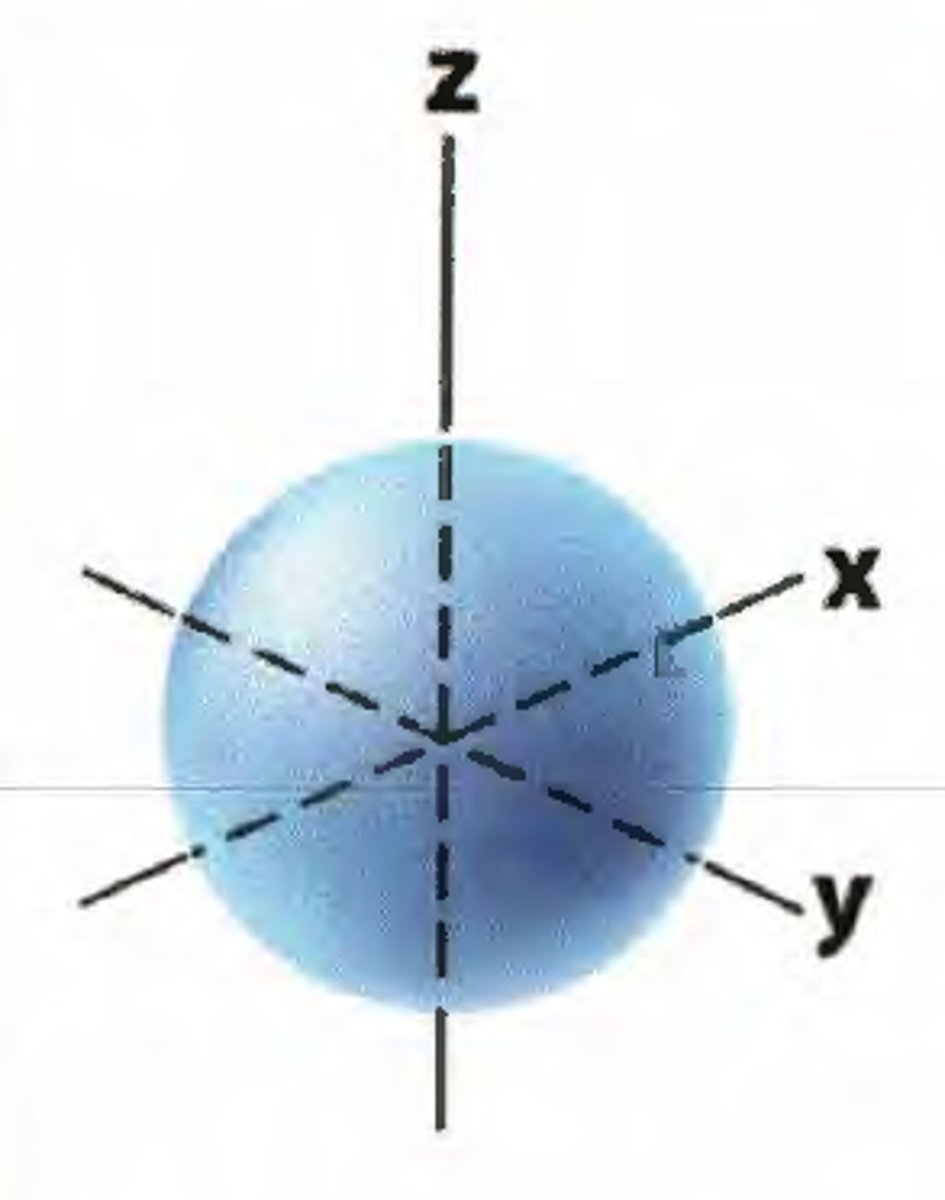
S orbital
Which orbital is shown here?
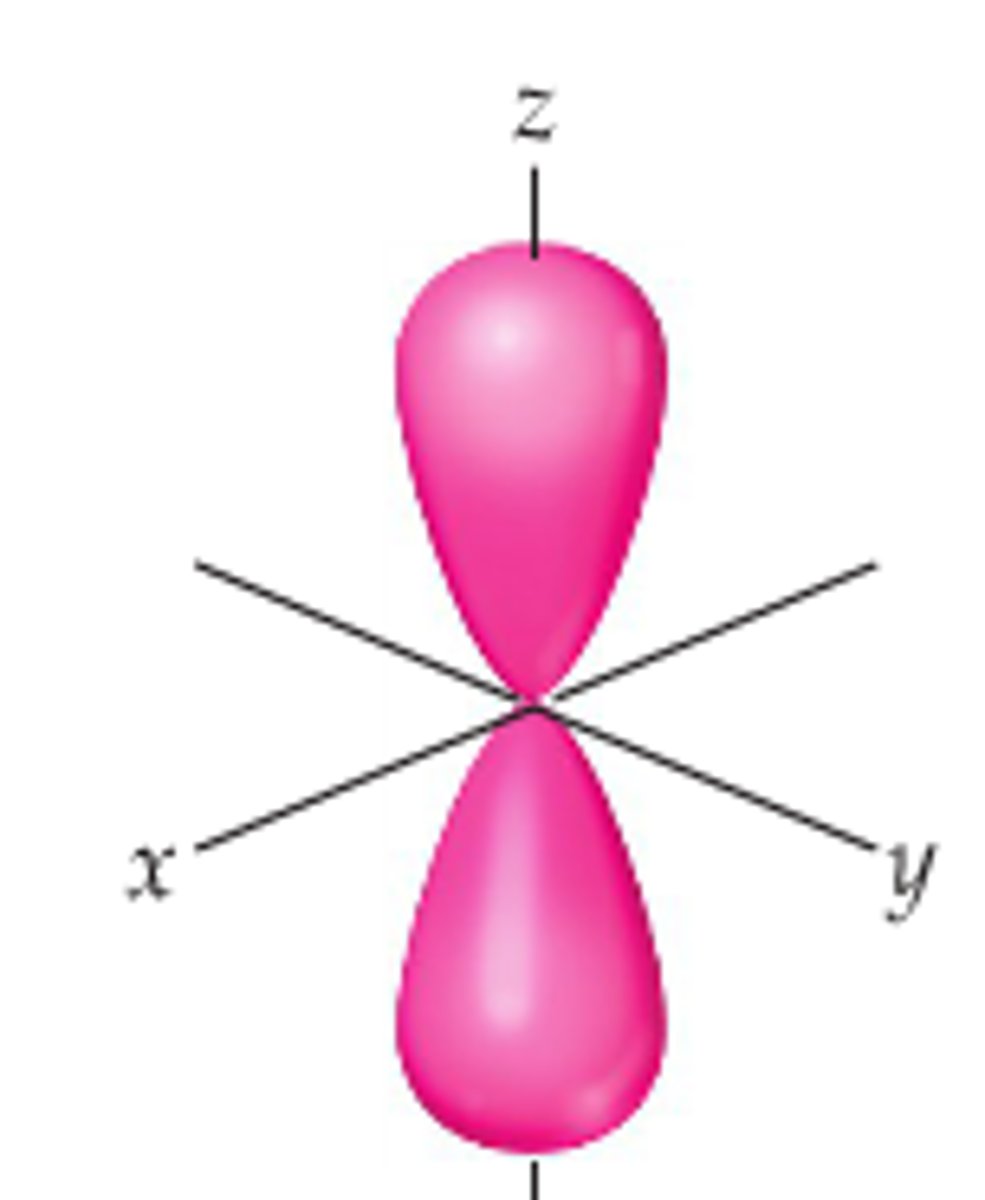
p orbital
Which orbital is shown here?
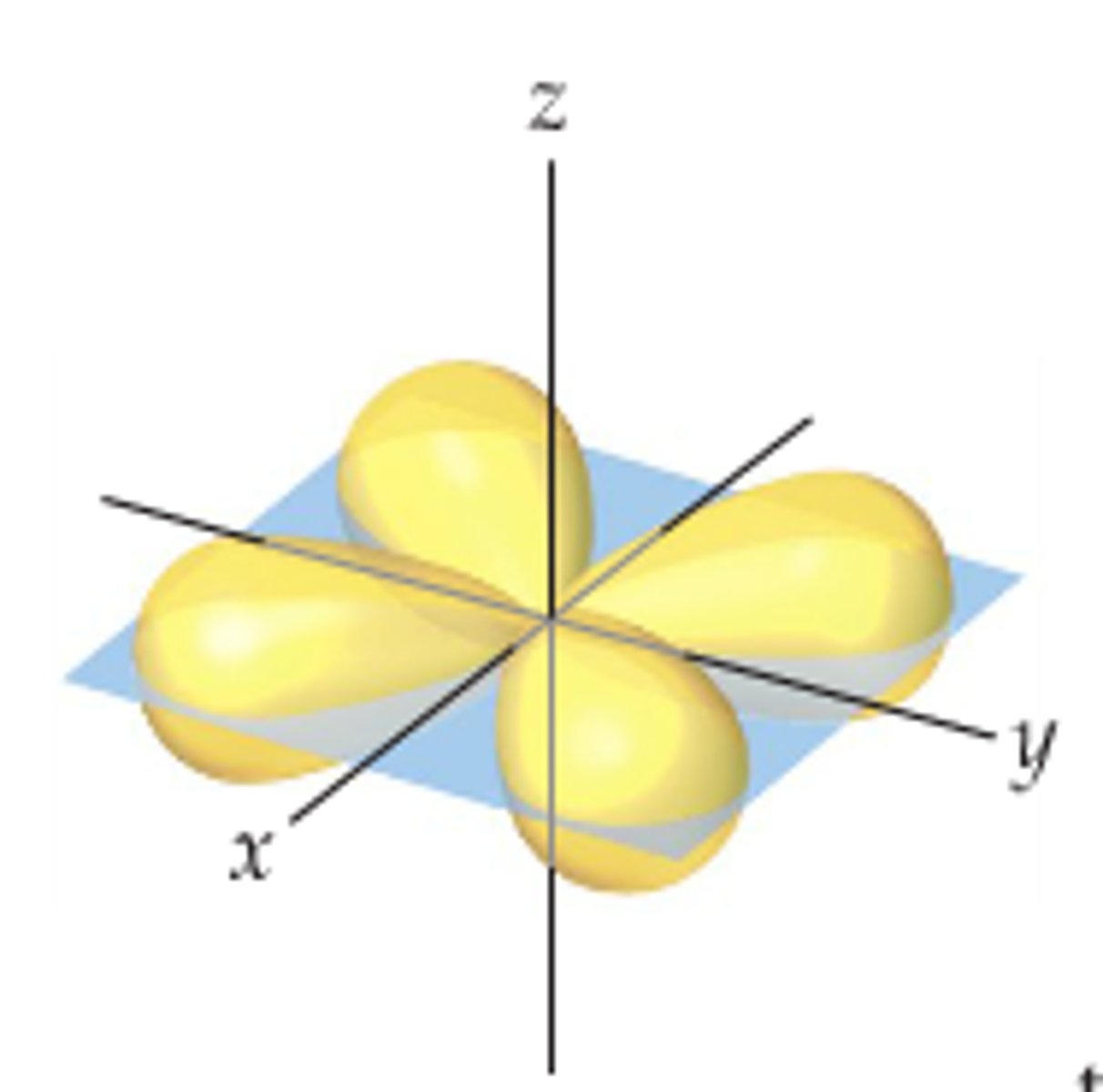
d orbital
Which orbital is shown here?
E -> Energy of one photon of light
h -> planks constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J S)
V -> frequency
E = hV is the ____________________
h stands for ______________
V stand for _______________
Photons
Light exists by waves and packets of energy called ____________