W3 - Gas exchange
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
pulmonary gas movemnet and exchange
in the conducting zone, has moves fown a pressure gradient via bluk flow
in the respiratory zone gas diffuses across the respiratory membrane: (img)
direction of gas movement depends on the relative concentration of each gas in the alveoli compared with the blood
relative concentration of each gas expressed as partial pressure (PO2 and PCO2)
Pulmonary gas exchange
movement of O2 and CO2 across the respiratory membrane is infleunced by a number of factors:
partial pressure gradients
how soluble the gas is in alveolar fluid and plasma (CO2 is 20x for soluble than O2)
structural characteristics of the respiratory emmbrane
matching of alveolar ventilation and pulmonary blood perfusion (blood flow)
Gas diffusion at the alveoli
diffusion of O2 from the alveoli to pulmonary capillaries
due to large difference in partial pressure
diffusion of CO2 from the capillaries to alveoli
equivalent to amount of O2 diffusion (amount of O2 in = CO2 out)
CO2 is 20x more soluable than O2
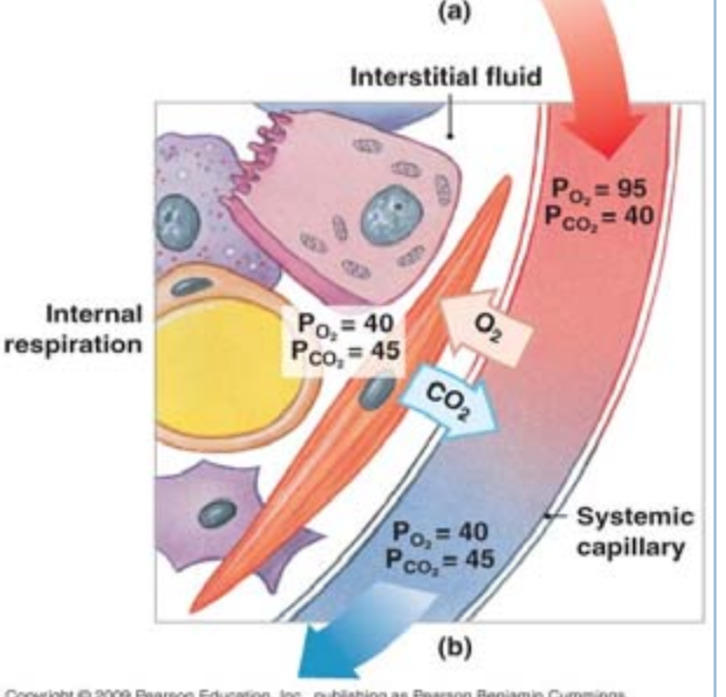
Gas diffusion at the tissues
O2 moves from the blood to tissues
due to large difference in O2 partial pressure
CO2 moves from tissue to plasma
at teh same at as O2 despite small differences in partial pressures
CO2 is 20x more soluble than O2
the respirator membrane
diffusion efficiency depends on:
width of respiratory membrane
very thin membrane
rapid gas exchange
surface area
very large (75m2/lung)
large amount of gas exchange area
ventilation-perfusion coupling
efficient gas exchange required matching gas flow (ventilation rate) with blood flow (perfusion)