Aromatic compounds
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what are aromatic compounds/arenes?
compounds which contain a benzene ring
what are aryl groups?
a group based on a benzene ring, where one hydrogen has been removed
what is a benzene ring?
cyclic hydrocarbon which contains 6 carbons in a ring, where the p orbitals overlap to form a pi system
kekule's model for benzene?
6 carbons in a ring, bonded together by alternating double and single bonds, each carbon has a H atom
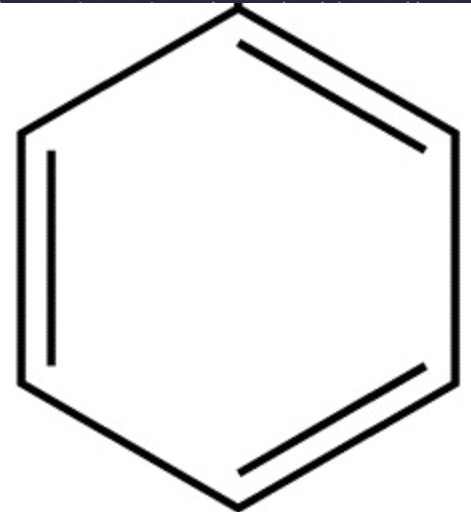
3 problems with kekule's model?
benzene doesnt undergo addition reactions with Br2 (unlike normal unsaturated molecules)
model suggests benzene should have 2 different C-C bond lengths, but theyre experimentally found to be the same, so theres not alternating single and double
enthalpy of hydrogenation is less exothermic than expected
actual model for bonding in benzene? (delocalised model)
1 each carbon forms 3 sigma bonds
2 a p-orbital from each carbon overlaps with 2 neighbouring p-orbitals = pi system
3 electrons are delocalised across the ring, in p orbitals that overlap
what is a pi system?
where electrons are delocalised across the ring
what compounds have delocalised electrons?
ones which have alternating carbon-carbon single and double bonds
why are compounds with more carbon bonds more stable?
more delocalised electrons from overlapping pi bonds = more stable and less likely to react
how are they more stable?
more p-orbitals, more delocalised electrons, electrons are more spread out, decreasing electron density, decreasing likelihood to attract other molecules to react
how does the delocalisation model explain why kekule's model is wrong about all C-C bonds being different in length?
all p orbitals overlap by the same amount = all C-C bonds are identical
how does the delocalisation model explain why kekule's model is wrong about benzene undergoing addition reactions with Br2 (it doesnt)?
benzene has delocalised electrons = lower electron density compared to alkenes = doesnt induce as large of a dipole in Br-Br = bad nucleophile
how does the delocalisation model explain why enthalpy of hydrogenation is less exo than expected?
delocalised electrons increase stability, more energy is needed to disrupt the pi system over breaking 3 bonds (bond breaking in hydrogenation is more endothermic)
valence bond theory?
if two atoms have orbitals which contain unpaired electrons, the orbitals will overlap with each other, forming a covalent bond
suffix for aryl groups?
-benzene
what is an aryl group?
contains a benzene ring
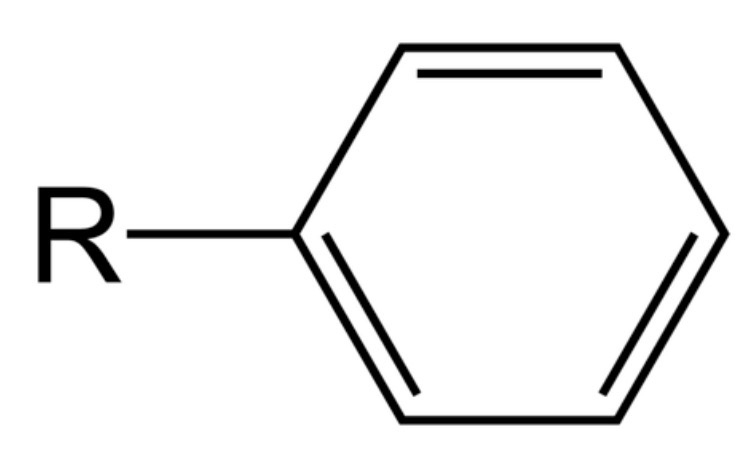
why do aromatic compounds have high melting points?
high stability of the delocalised ring
why are aromatic compounds insoluble in water?
they are non-polar
which mechanism does benzene undergo?
electrophilic substitution
where do electrophiles attack on benzene?
delocalised ring, which is an area of high electron density
what happens to the delocalised ring during electrophilic substitution?
it is partially destroyed, then restored
electrophilic substitution of benzene mechanism?
A = electrophile
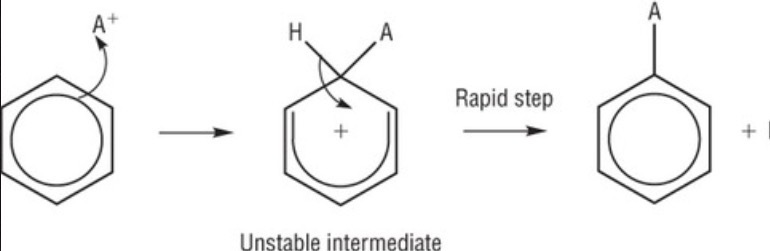
what can be produced from electrophilic substitution with benzene?
aromatic amines and nitrobenzene
electrophile used in the formation of nitrobenzene?
NO2+
where is NO2+ obtained?
produced in the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid with concentrated nitric acid
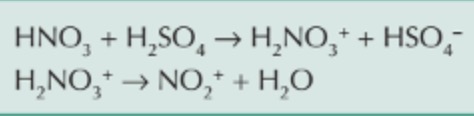
reaction between concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid?
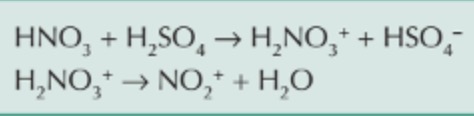
electrophilic substitution mechanism to form nitrobenzene?
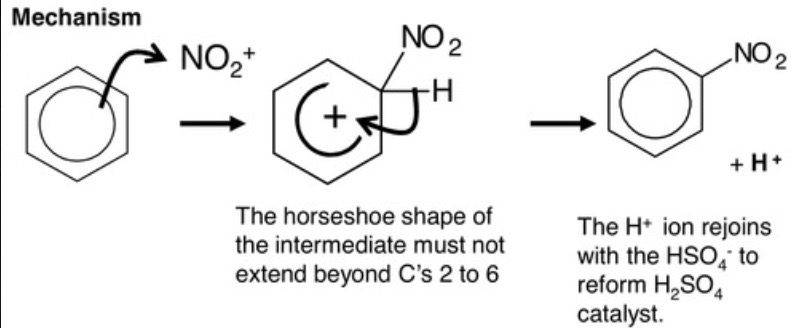
why is it vital for this reaction to occur a 55°C?
so only one substitution occurs for the production of aromatic amines
what is friedel crafts acylation?
When the delocalised electron ring acts as a nucleophile, leading to the attack on acyl chlorides.
conditions required for friedel crafts acylation?
reactive intermediate must be produced from the acyl chloride and an aluminum catalyst
what happens to the reactive intermediate?
its attacked by the benzene ring
friedel crafts acylation mechanism?
Electrophilic substitution
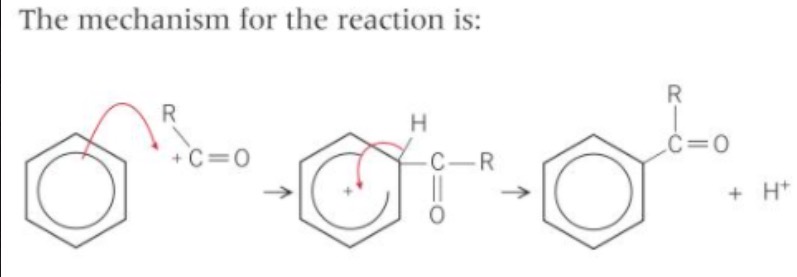
at the end of the reaction, what does the H+ ion removed from the ring do?
reacts with AlCl4- to reform the alumunium chloride (catalyst)
how is aluminium chloride seen to be a catalyst?
at the end of the reaction, the H+ ion removed reacts with AlCl4- ion to reform aluminum chloride
products of friedel crafts acylation?
phenylketone (phenyl functional group)
what is a phenyl group?
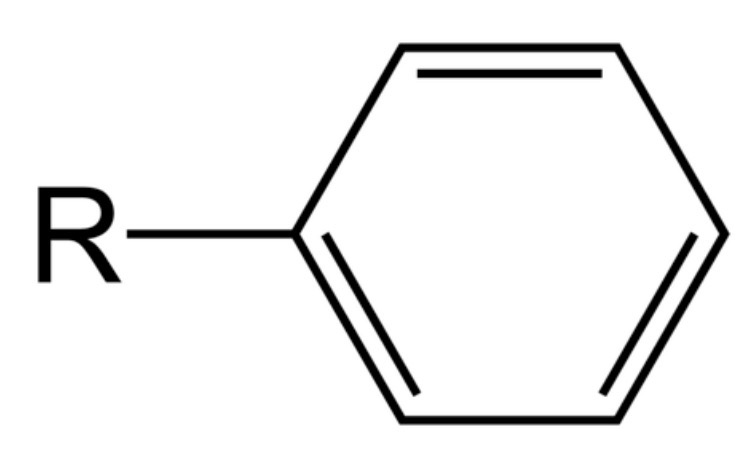
what are phenyls used for?
industrial production of dyes, pharmaceuticals and explosives
functional group order of priority?
1 carboxylic acid
2 nitrile
3 aldehyde
4 ketone
5 alcohol
6 alkene
7 benzene
8 halogenoalkane
9 alkane
10 nitro
suffix for when benzene is the highest priority functional group?
-benzene
prefix for when benzene isnt the highest priority functional group?
phenyl-
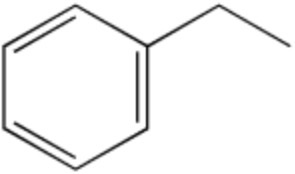
draw ethylbenzene
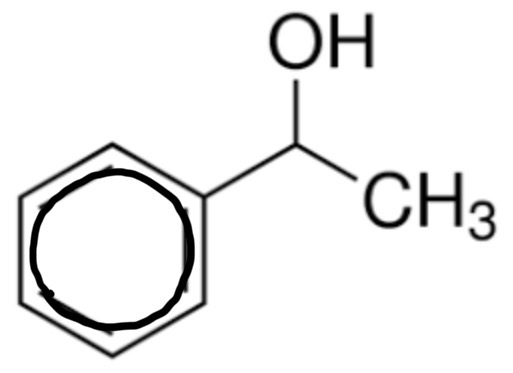
Draw 1-phenylethanol
ring instead of double bonds
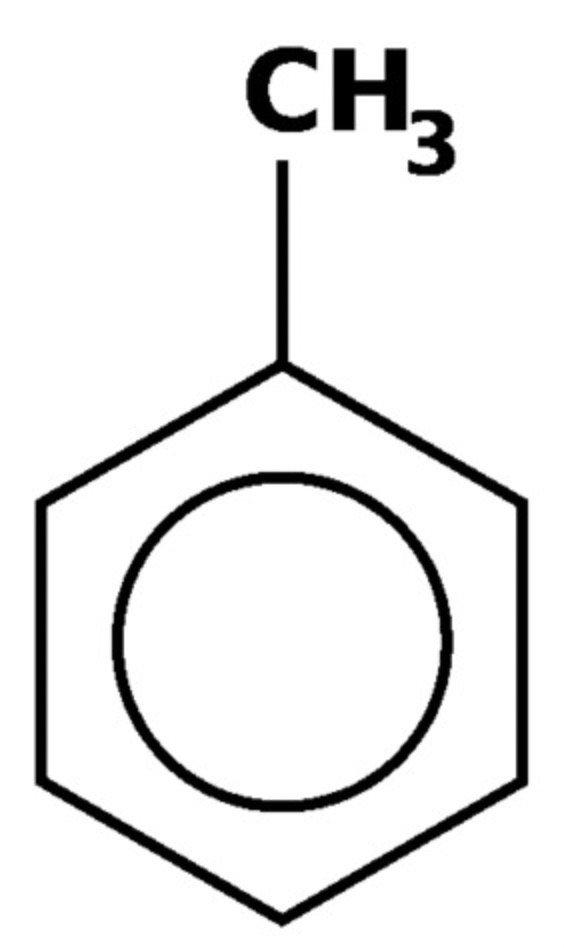
draw methylbenzene
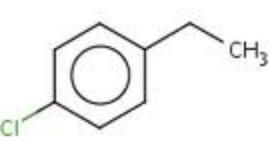
draw 1-chloro-4-ethylbenzene
nitro group?
R-NO2
prefix for nitro groups?
nitro-
draw 1,3,5-trinitrobenzene
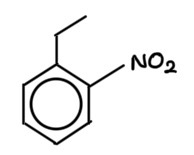
draw 1-ethyl-2-nitrobenzene
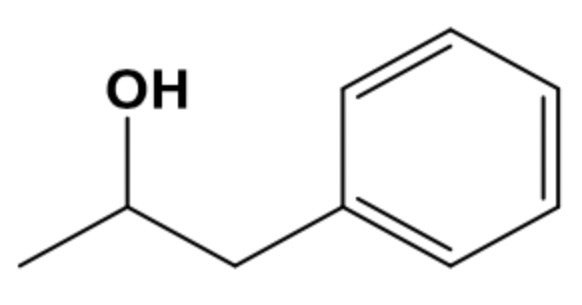
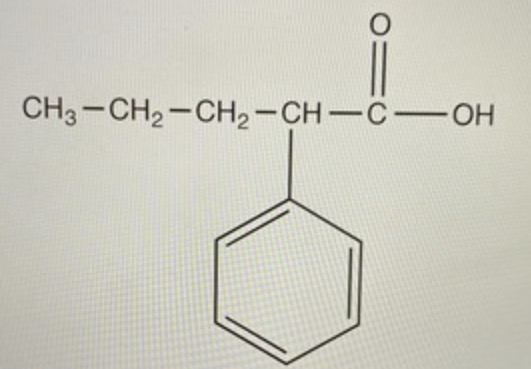
draw 1-phenylpropan-1-ol
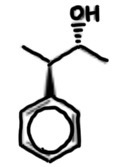
draw 3-phenylbutan-2-ol
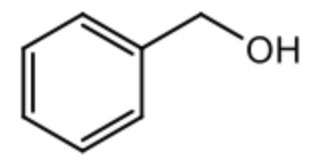
draw phenylmethanol
is the benzene ring included as a part of the longest carbon chain when naming molecules with an alcohol and benzene ring?
no x
draw 1-phenylpropan-2-one
ring-cH2-c(=O)-cH3
draw 4-phenylbutanal
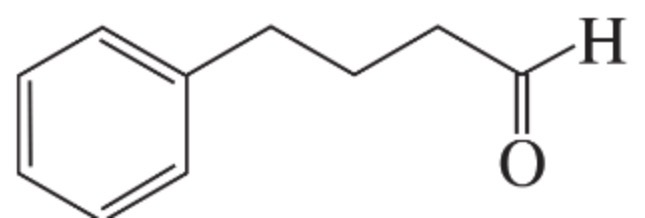
draw 2-phenylpentanoic acid
Bromine (Br) + bromine -> ? + ?
elecrtophilic substitution:
bromobenzene + H+
electrophile used in electrophilic substitution of bromine and benzene?
Br+
how is Br+ generated for bromination of benzene?
Br2 + FeBr3 -> Br+ + FeBr4-
or Br2 + AlBr3 -> Br+ + AlBr4-
two potential halogen carriers used to react bromine with benzene?
AlBr3 + FeBr3
why is this reaction needed between the halogen carrier and bromine?
a stronger electrophile (Br+ is stronger than Br2)
1st mechanism step of reaction of bromine with benzene?
C-Br bond forming as 2 e- from pi system form a bond, pi system breaks
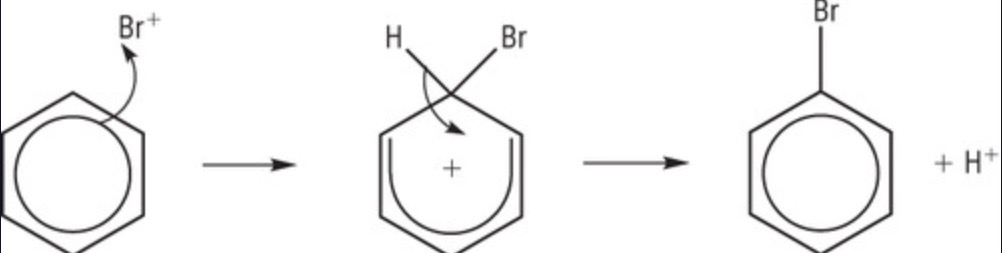
is the intermediate formed more or less stable?
less stable
why is the intermediate formed less stable?
pi system broken
2nd step of bromine + benzene?
C-H bond breaks, e- put back in pi system = reformed
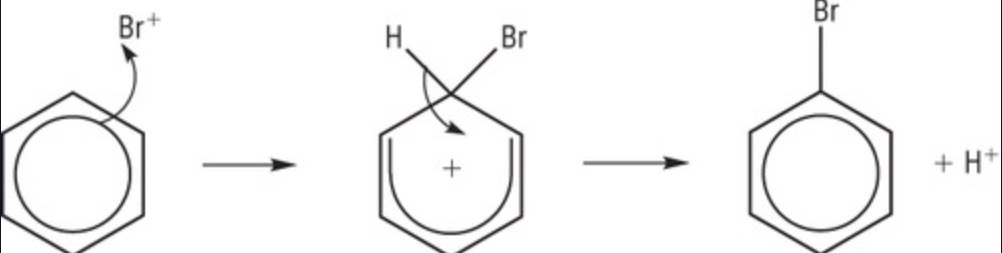
how does AlBr3 act as a catalyst?
used to generate the electrophile at start
AlBr4 used to break C-H bond in step 2 = AlBr3 reformed
why is benzene able to undergo electrophilic substitution but not electrophilip addition?
in addition ring is permanently broken, so product is less stable than benzene started with, only temporary in substitution,
Br+ is a VERY strong electrophile
acyl chloride functional group?
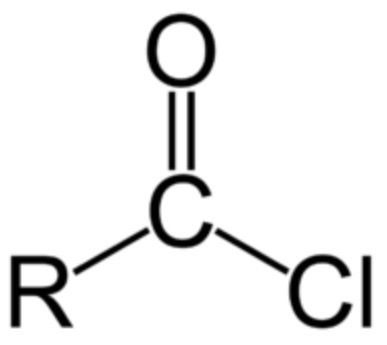
acyl chloride + benzene -> ? + ?
ketone + HCl
e.g. phenylethanone
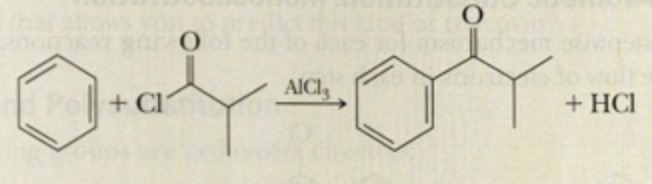
what type of reaction is acyl chloride + benzene (friedel-crafts acylation)?
electrophilic substitution reaction
what occurs during friedel-crafts acylation?
acyl group substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring
carbonyl group bonds directy to benzene ring
hydrogen substituted reacts with Cl
why do we need to use a halogen carrier in friedel-crafts acylation?
acyl chlorides arent strong enough electrophiles to react with benzene by themselves
halogen carrier used?
AlCl3
ethanoyl chloride+ AlCl3 -> ?
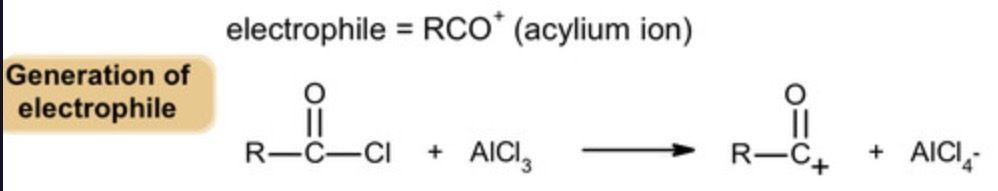
electrophile used in friedel-crafts acylation?
acylium ion
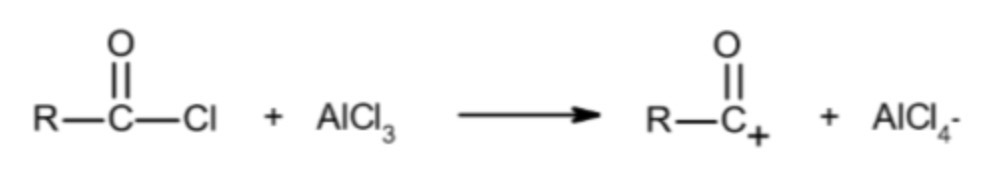
CH3CH2COCl + AlCl3 -> ? + ?
formation of electrophile: chlorine removed from acyl chloride
CH3CH2CO+ + AlCl4-
1st mechanism step of benzene + acyl chloride?
C-C formed, pi system breaks
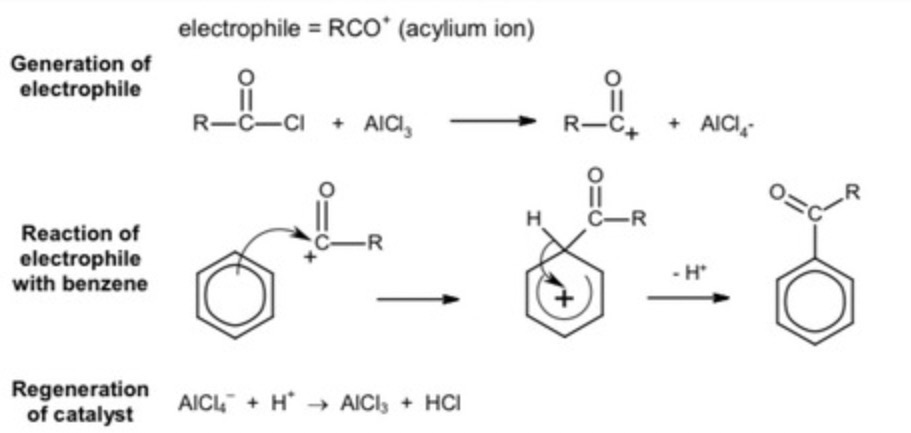
step 2 mechanism of benzene + acyl chloride?
C-H bond breaks, pi system reforms
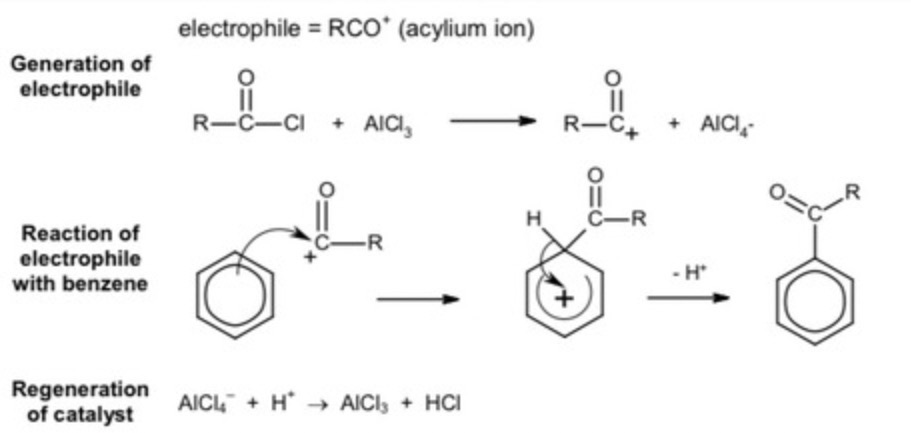
what acts as a catalyst in the acyl chloride + benzene reaction?
aluminium chloride