Renal 1 - Osmotic and Ionic Regulation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Origins of Life
Began in a saltwater environment
As organisms began to move, they encountered different environments
Aquatic Environments
Can vary greatly in their salinity
– Chesapeake Bay (is an estuary with mixing of salt + fresh water)
Brackish Waters
Estuaries
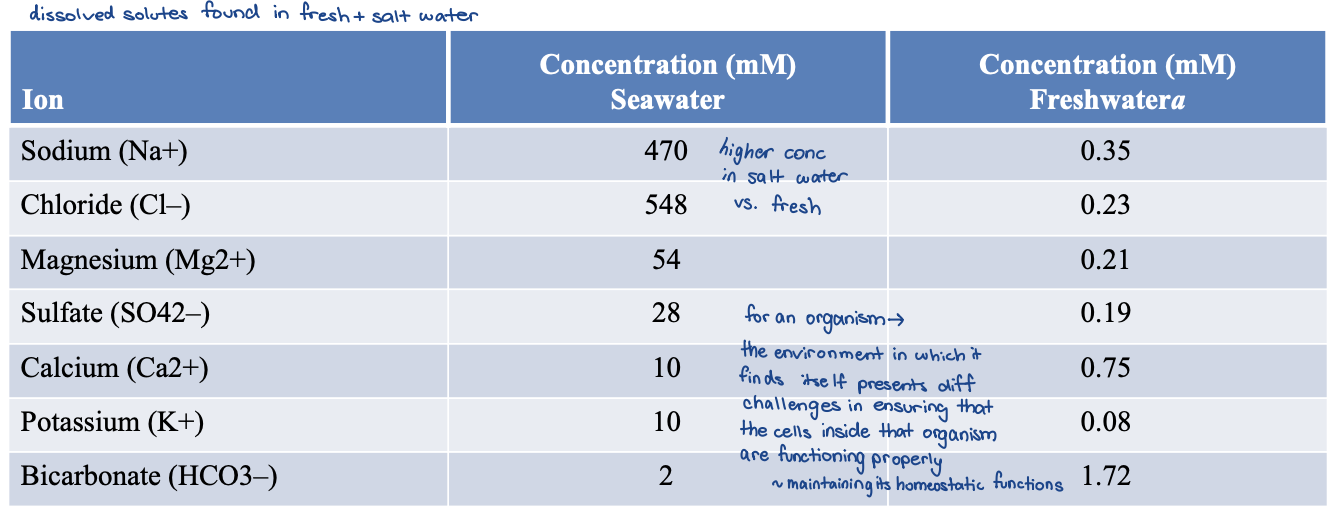
Concentrations of major ions in seawater and freshwater
Changing Environment
Cells and organisms need to function in varied environments
Strategies include:
Maintaining tight control of internal environment (regulators)
Maintain cellular function while matching the environment (conformers)
regulators
Maintaining tight control of internal environment
organisms that maintain that internal enviro regardless of what external enviro is like
ex. maintain amount of solutes (Na, Cl) inside the organism despite what’s going on outside, need to ensure internal conc does’t change
conformers
Maintain cellular function while matching the environment
need to ensure cellular function continues even with internal enviro changing to match external
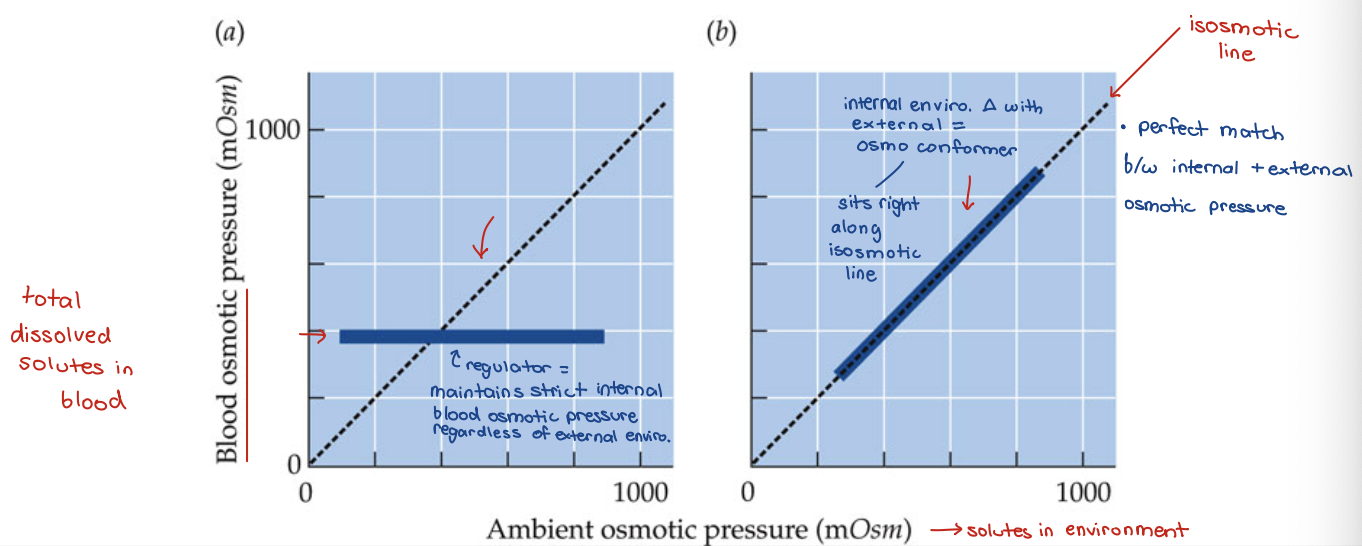
Regulation and Conformity
Under regulatory control -
osmotic regulation → total dissolved solutes (ensure # doesn’t change)
ionic regulation → regulate specific ions
volume regulation → organisms like crabs and lobsters bring in excess salt to inflate body, since water follows salt, when molting (changing exoskeleton) thus allows them to control volume/size of body by shuttling salt and water around
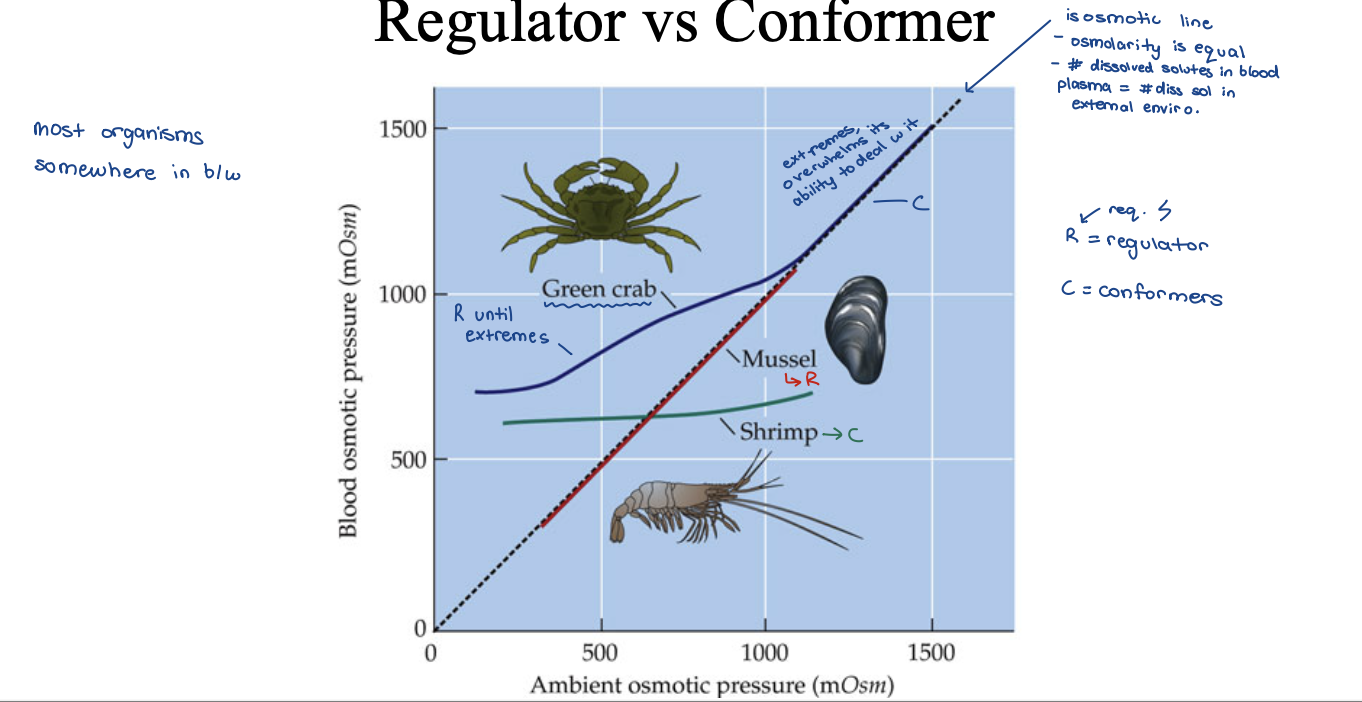
osmotic regulators vs conformers
regulator vs conformer (examples)
mussel = conformer
shrimp = regulator
green crab = regulator until extremes then conforms
Osmosis
diffusion of water
Water will move to areas of higher concentration (tries to equilibriate)
Water will move towards areas with LESS “free water” (water not bound up + surrounding solutes)
Osmolarity
Measurement of TOTAL dissolved solutes
regulators in freshwater
External Environment is Hypo-osmotic (hypo = less)
regulators in salt water
External Environment is Hyperosmotic (hyper = more)
isosmotic
having same/equal osmotic pressure
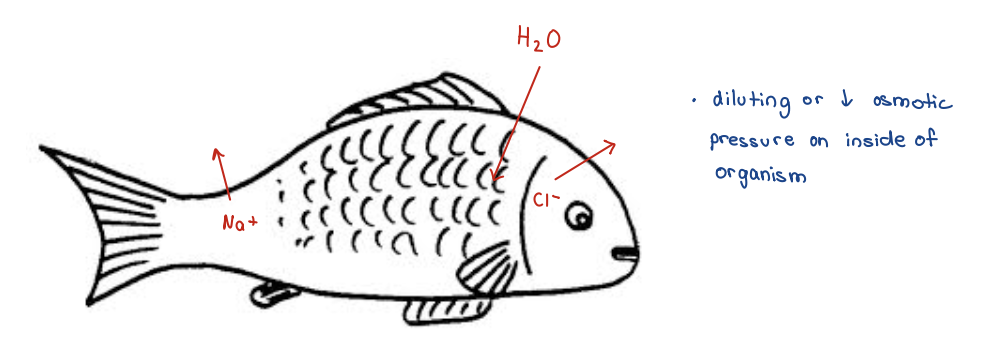
Challenges to Freshwater Regulators
Constantly taking in water through osmosis
Constantly LOSING ions
(water is hyposmotic to organism)
Challenges to Marine (Salt Water) Regulators
Constantly Losing water
Constantly LOADING ions
(hyperosmotic water)
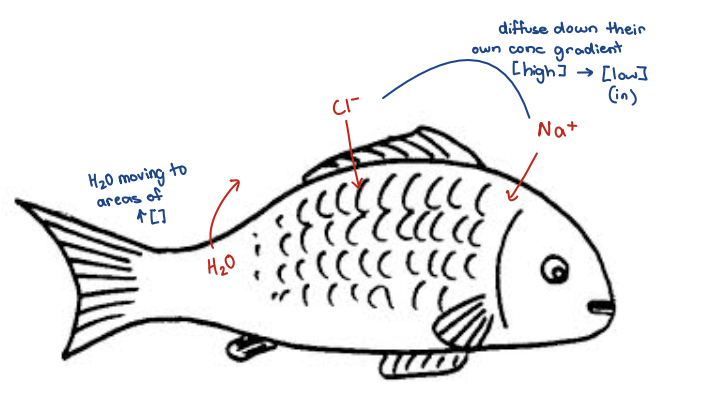
Organs of Salt/Water Balance Gills
this organ allows regulators to deal w challenges of maintaining balance
folds increase SA of gills and is very permeable
Gills
High permeability and large surface area
benefits to gas exchange (ensures lots of contact w water where O2 can be drawn out)
O2 is very low (low in water so need to acquire more O2 somehow)
Counterproductive for water-salt balance
large SA increases osmosis of water
permeability allows for movement of ions
Animals w high O2 demands (ex. salmon, fish that swim a lot) must deal w high water-salt exchange
gill anatomy
Mitochondria Rich Cell (MRC)
pavement cell
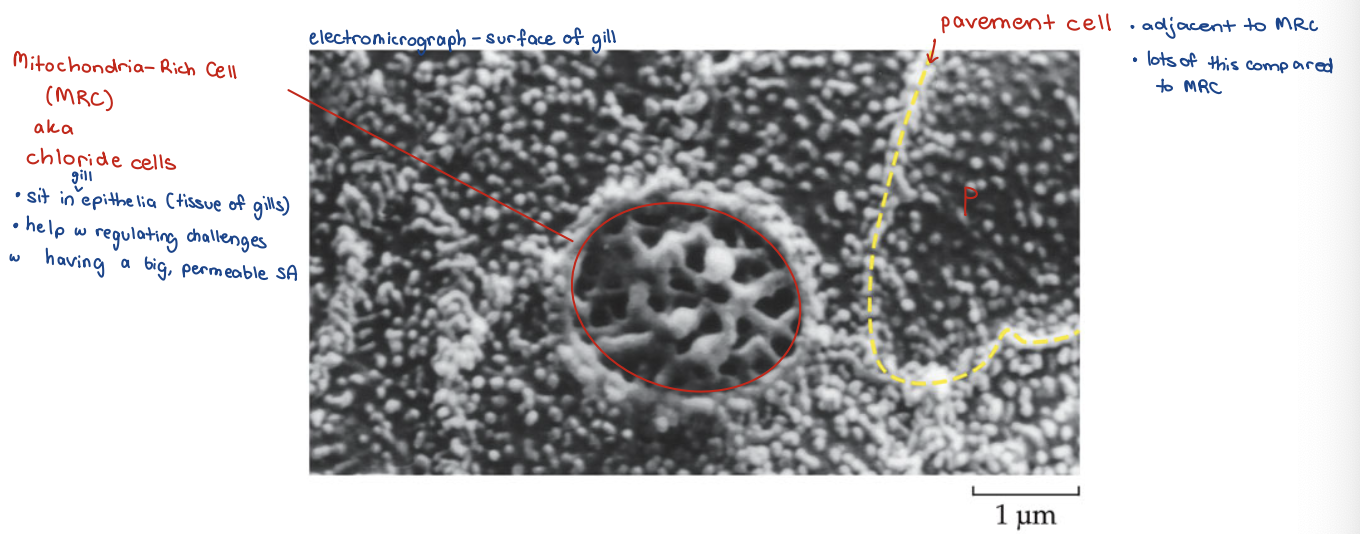
Cell Types Gills
Pavement Cells
– Occupy ~ 90% of gill epithelium
– Principally responsible for O2 uptake
Mitochondria-Rich Cells (MRCs)
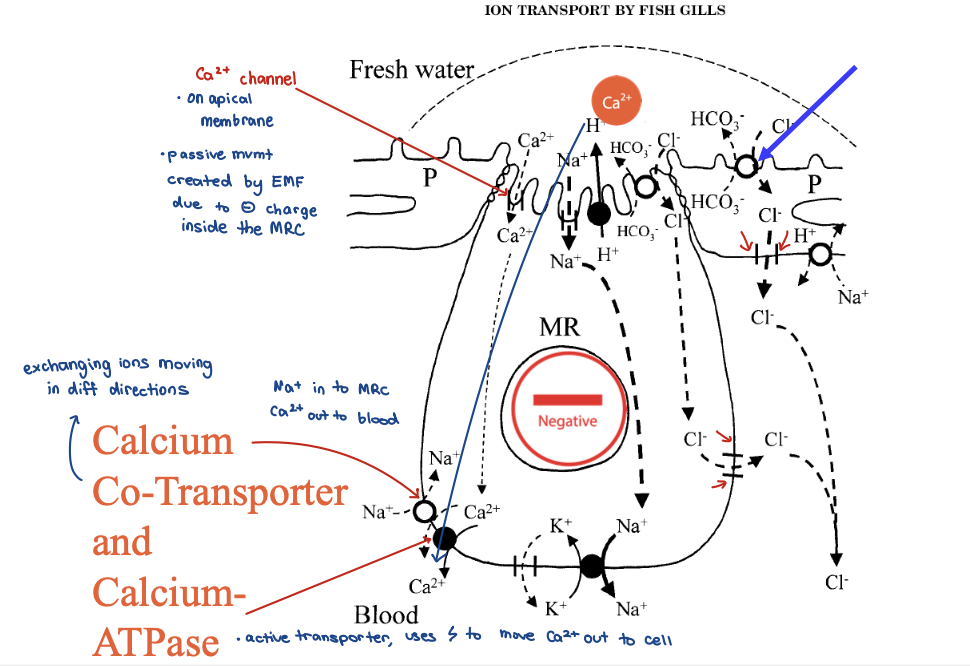
– Uptake of Cl-, Na+, and Ca2+ in freshwater
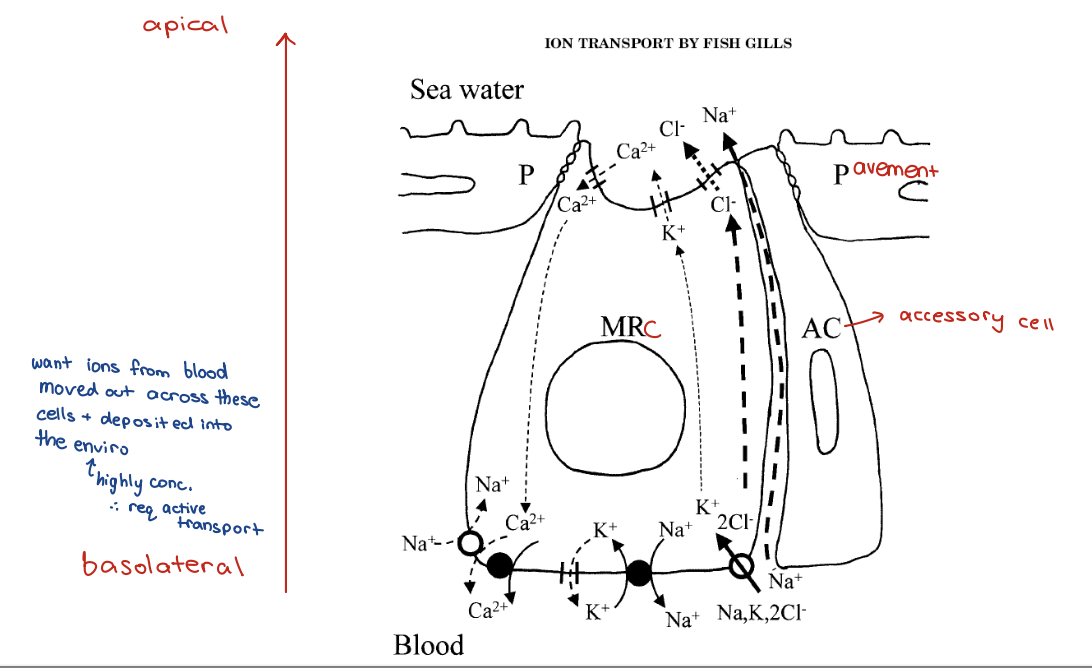
– Excretion of Cl- and Na+ in salt water
– Partially Under Hormonal Control
– Density and TYPE can be changed in varying conditions
MRC cross section of gill
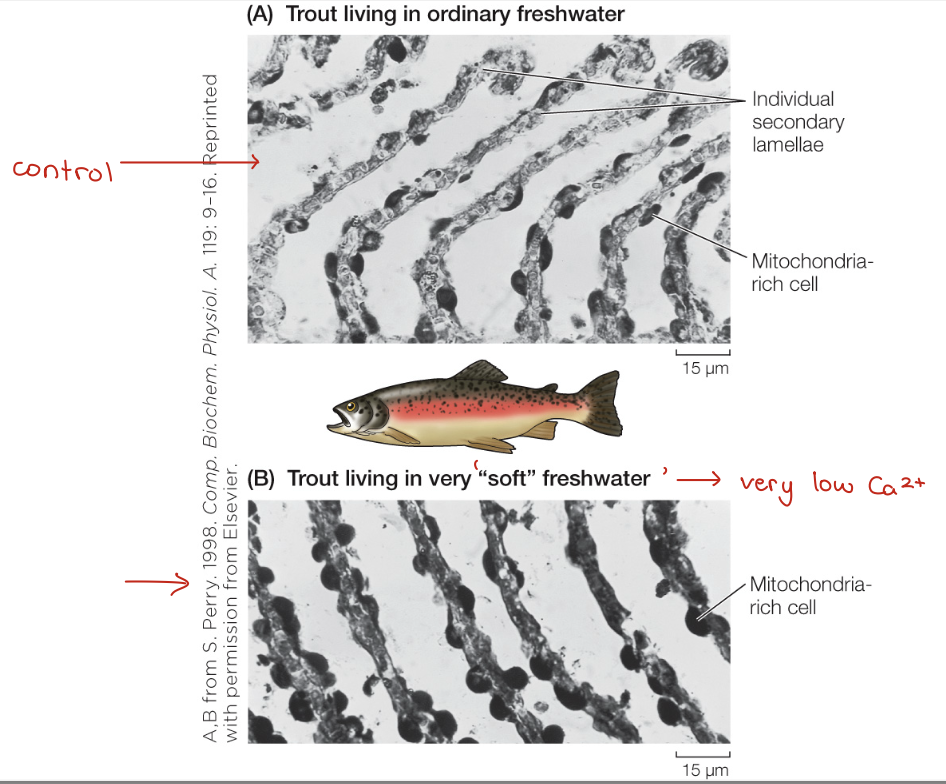
Reminder of the Challenges
in freshwater (osmotic pressure in org > external enviro)
influx of H2O
loss of ions → [ion]in > [ion]out so wants to move down conc gradient
in salt water
loss of H2O
influx of ions
Solution to challenges – Active Transport
In Freshwater
– Mitochondria-Rich Cells bring ions in (mitochondria are the power plants of cells, create ATP which powers transport)
– Water loading countered by production of copious amounts of dilute urine
• In Salt Water
– Mitochondria-Rich Cells move ions out, (push to enviro where there is a high conc.)
– Water loss countered by drinking
freshwater gills - membranes and cells 1
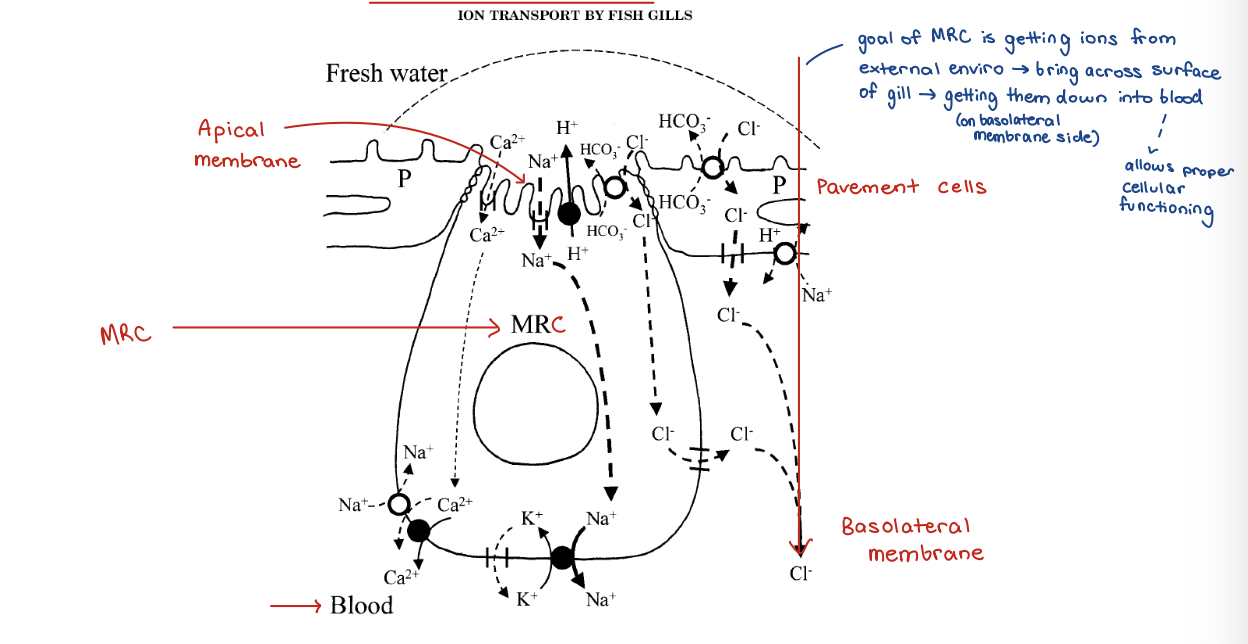
freshwater gills - V-type 2
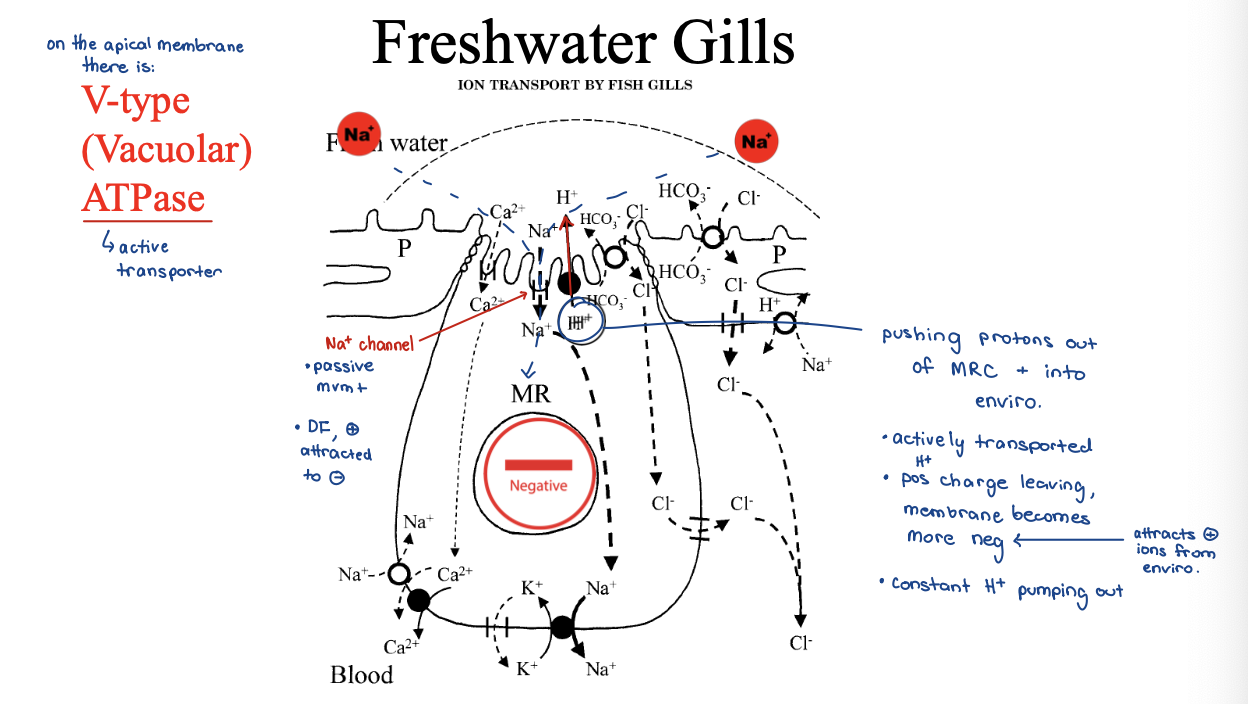
freshwater gills - sodium potassium pump 3
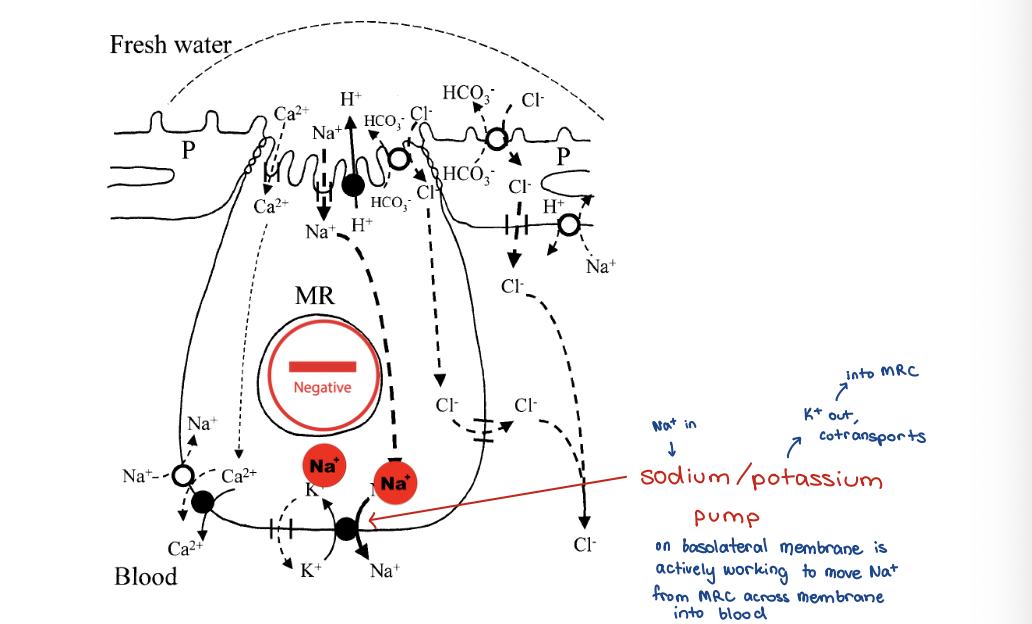
freshwater gills - K+ leak channels 4
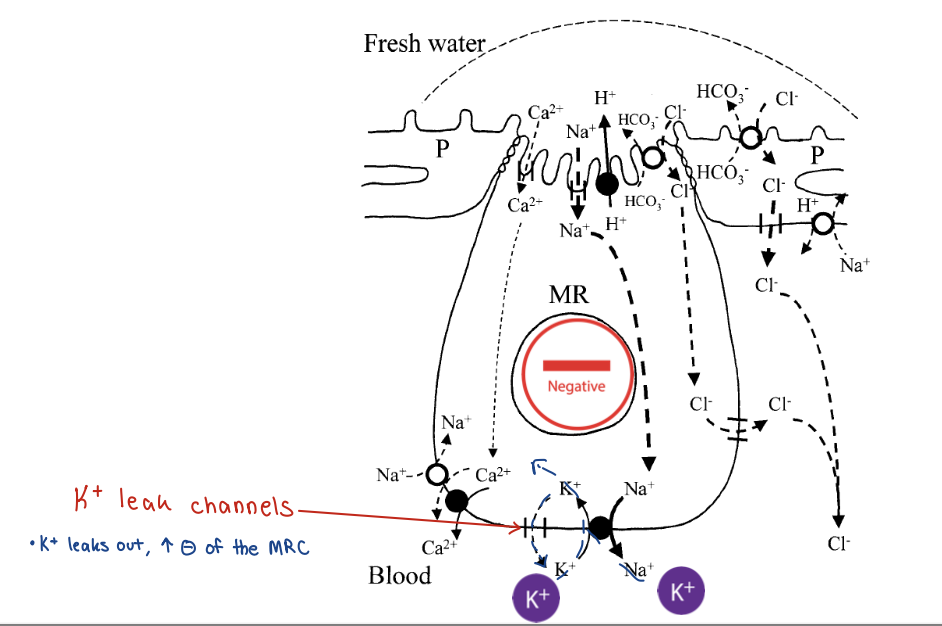
freshwater gills - electroneutral anion exchanger + CFTR 5
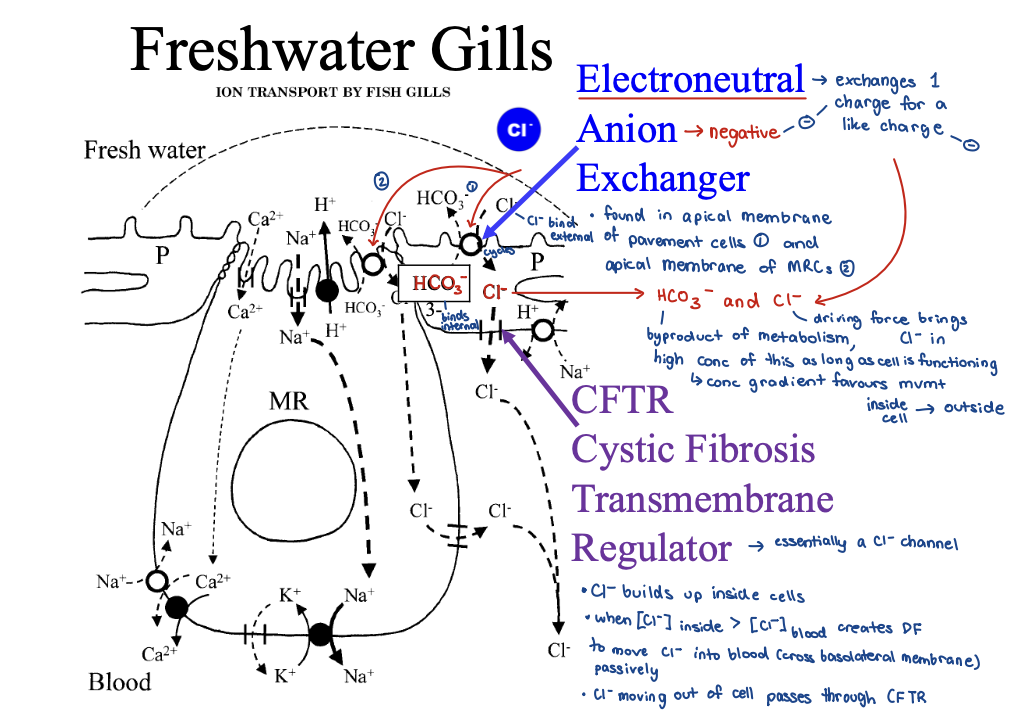
cystic fibrosis
genetic mutation in CFTR
reduces Cl- clearance
maintains higher than normal electronegative potential in the cell
bc less negative leaving the cell so stronger electromotive force drawing cations into cells
reduces extracellular removal of cations (Na+)
increased solute buildup, water follows solutes → waterlogged → makes it more prone to infection
increase mucosal buildup → causes respiratory and digestive difficulties
freshwater gills - calcium co-transporter and calcium-ATPase 6
marine animals - summary
– Lose Water through osmosis
– Re-hydrate by drinking seawater
– Load up on ions that need to be removed
drinking seawater 1
Water in the gut will be HYPEROSMOTIC to blood plasma
Will draw water out of the blood plasma by osmosis
Na and Cl will diffuse INTO blood plasma due to concentration difference
Net result would be VERY concentrated blood plasma
This is why we (mammals) can’t drink seawater to rehydrate
drinking seawater 2
Later parts of the intestine, Na and Cl are ACTIVELY transported out of the gut
Creates a gradient that favours water retention
50 – 85% of water is absorbed into the blood
97% of Na and Cl MUST be absorbed!!
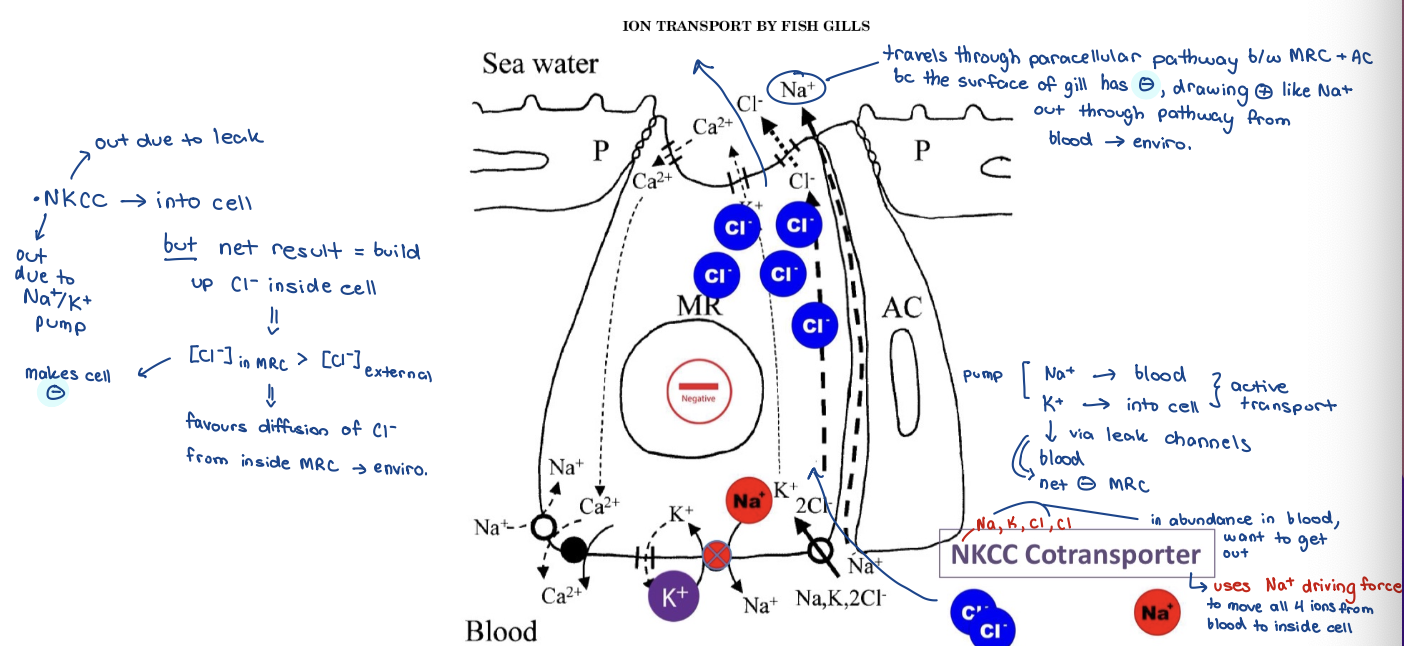
Ion Regulation
Excess ions MUST be removed
Occurs in the gills
Also contain MRCs and pavement cells
– As well as accessory cells
marine gills - membranes and cells 1
marine gills - NKCC cotransporter 2
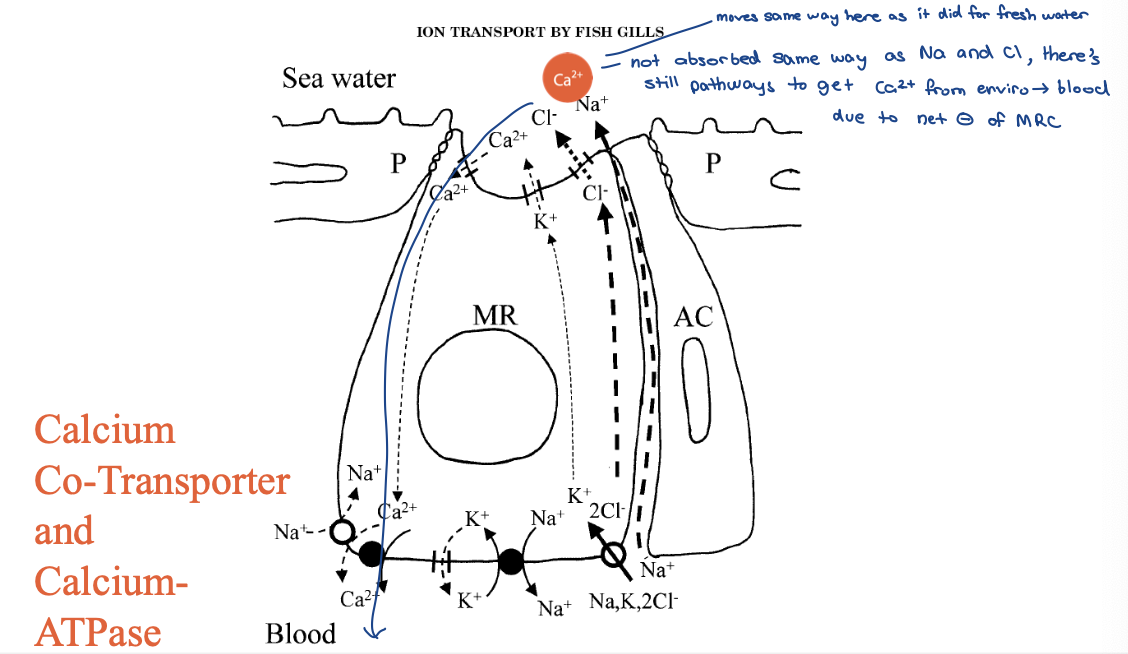
marine gills - calcium co-transporter and calcium-ATPase 3
terrestrial organisms
No longer surrounded by water
challenge, need to make sure that water is maintained inside organism
Marine Birds/Reptiles 1
blood is hypo-osmotic to saltwater
water loss
salt loading
Marine Birds/Reptiles 2
Less Permeable integument (skin surface)
– Decreases water loss
Water loss through respiration
Hyperosmotic H2O ingested
– Either directly, or through food source
Must remove excess solutes (ex. Na, Cl)
Marine Birds - Strategies
Gulls (Charadriiformes)
Penguins (Sphenisciformes)
Albatross (Procellariiformes)
Pelicans (Pelecaniformes)
have ducts connecting salt glands to nostrils, excess NaCl excreted out through nostril
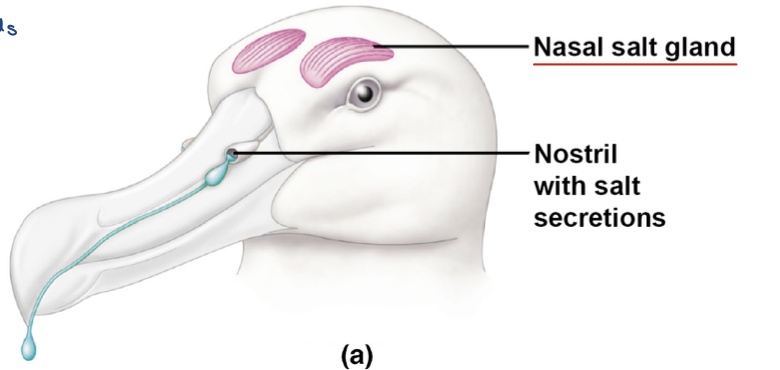
marine birds - how to get NaCl out of blood
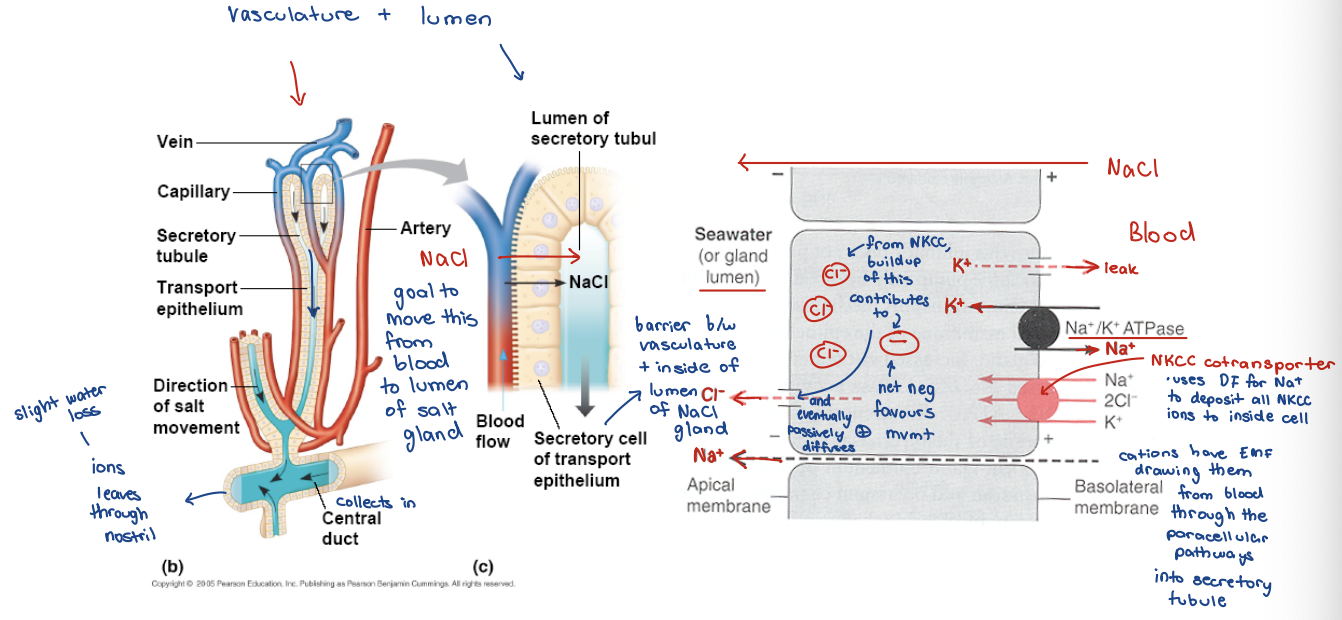
salt glands
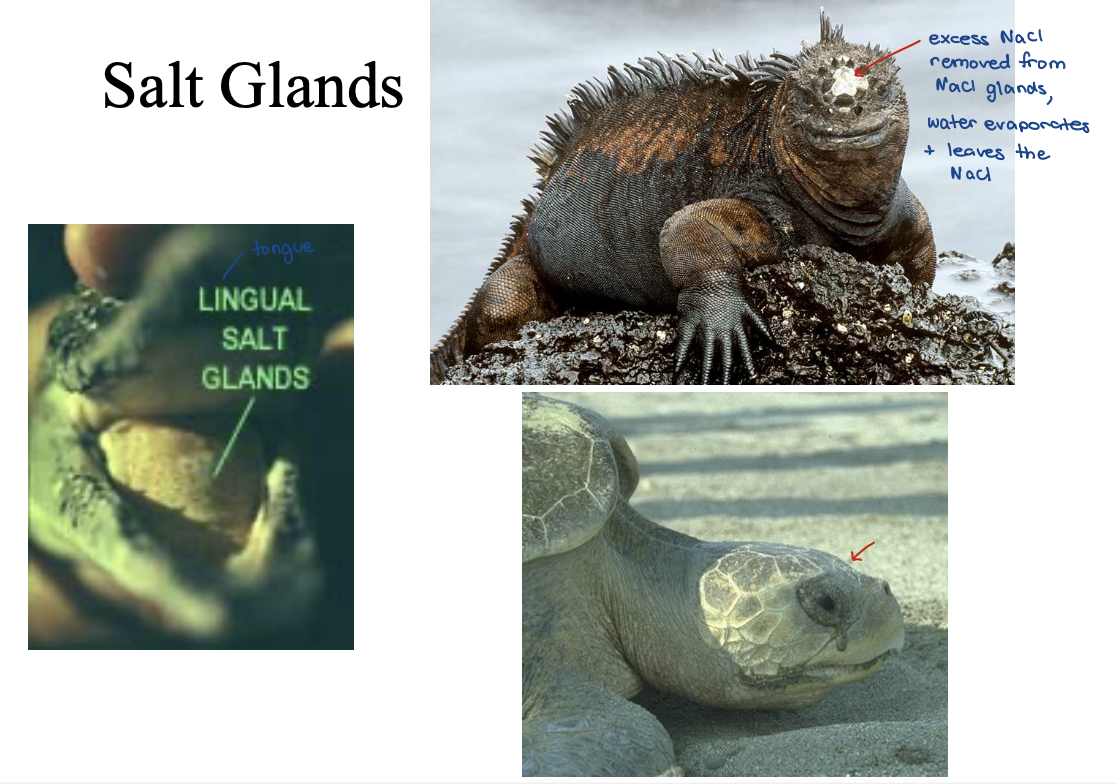

special cases
Elasmobranchii
– Sharks, Rays, Skates
Marine Osmoconformers → matches internal enviro to external
– Produce high concentrations of organic solutes
– Urea (stable form of nitrogen, byproduct of metabolism converted to this)
– TMAO (-counteracts toxic effects of urea)
Special Cases - Salmon
– Born in freshwater
– Migrate to seawater to grow
– Return to freshwater to reproduce
salmon - behavioural
spend time in brackish waters → mixture of fresh and salt water
increase or reduce the amount of water that is consumed (reduce: salt → fresh)
salmon - physiological
Kidney function changes
• High volume of dilute urine in freshwater saltwater
Gills that take up ions in freshwater, remove them in sea water