Intro to EKG: Interpreting EKGs
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
0.2
One large box, at normal paper speed, is equivalent to _._ seconds and is made up of 5 small boxes
300, 1500
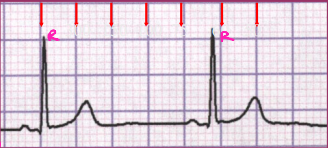
Determining Heart Rate with a Normal Rhythm
-# of large boxes between RR cycles: ____/# of large boxes between R waves
-# of small boxes between RR cycles: ____/# of small boxes between R waves
R, 6, 10
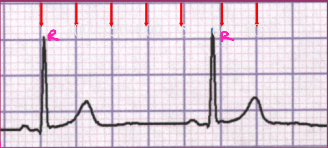
Determining Heart Rate with an Irregular Rhythm
-Count the number of _ waves in a _-second strip (30 large boxes) and multiply by __
60-100
The normal range for heart rate is __-___ bpm
sinus, upright, II, 3
Atrial Sinus
-Produces normal/abnormal _______ rhythms, showing if the SA node is firing regularly
-You can determine if the rhythm is sinus by seeing if the P wave is ________ in lead __ and if there is regularity in the beats with less than _ small boxes difference
rate, axis, morphology
Reading EKGs: Order of Operations
Determine _____
Examine rhythm
Note the _____
Intervals
Hypertrophy
__________
90, -30
If the average vector is between __ and ___, then it is normal
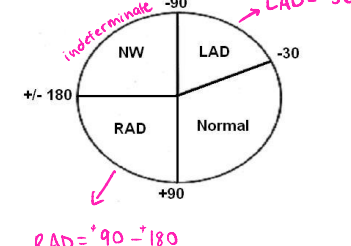
-30, -90
If the average vector is between ___ and ___, then there is left axis deviation
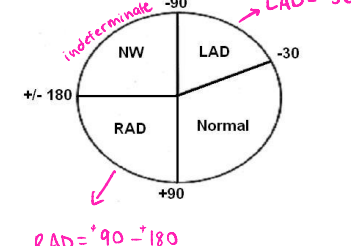
90, 180
If the average vector is between __ and ___, then there is right axis deviation
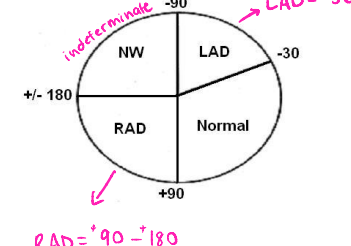
-90, 180
If the average vector is between ___ and ± ____, then it is an indeterminate/northwest axis deviation
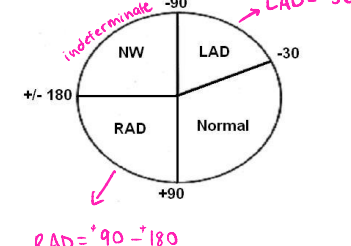
positive, positive
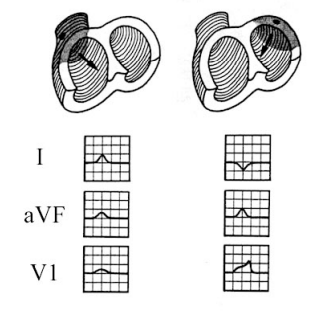
Normal QRS Axis
-The QRS complex is _______ in Lead I and _______ in aVWF
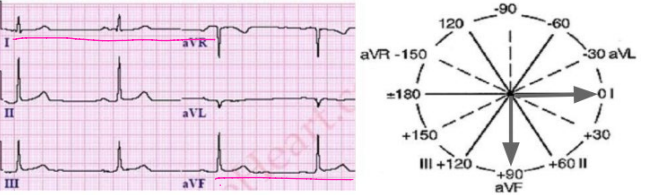
negative, positive
Right Axis Deviation
-The QRS complex is ________ in Lead I and _______ in aVF
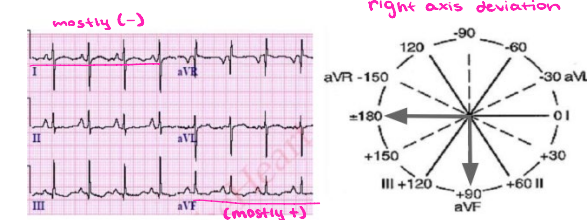
positive, negative
Left Axis Deviation
-The QRS complex is ________ in Lead I and ________ in aVF
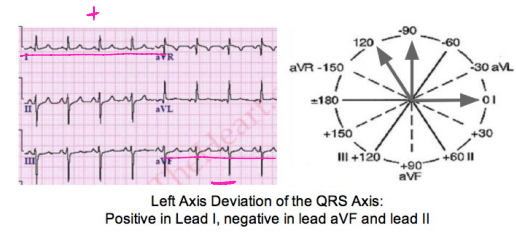
negative, negative
Northwest/Indeterminate Deviation
-The QRS complex is ________ in lead I and _________ in lead aVF
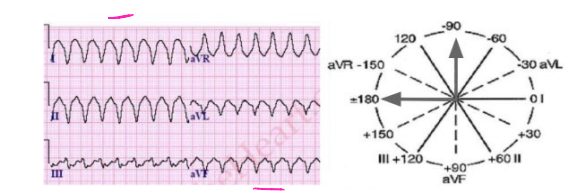
.12, .2, .12, .42
Normal Rates and Reference Ranges
-HR = 60-100 bpm
-P wave = < .__ seconds
-PRI = .12-._ seconds
-QRS complex = < .__ seconds
-QT interval = .__ seconds
-T wave = more concerned with morphology
depolarization, 3
P Wave
-Represents atrial ____________
-Count from beginning of wave to end of wave
-Should be < 0.12 sec (<_ small boxes), can also count half boxes
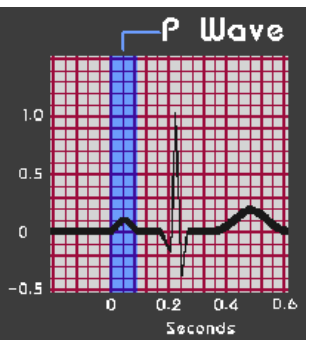
P, QRS, atrial, ventricular
P-R Interval
-Measure from the beginning of the _ wave to beginning of ___ complex
-Represents the time to travel through _______ muscle to _________ muscle
-Normal is .2 seconds
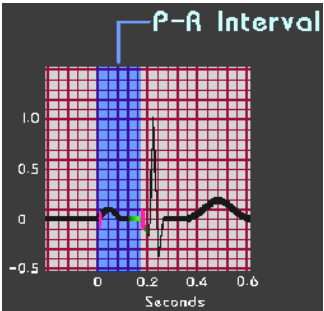
ventricular, .12
QRS Complex
-Represents ___________ depolarization
-Normal value is < .__ seconds
-Measure from start of Q wave to the end of S wave (aka J point)
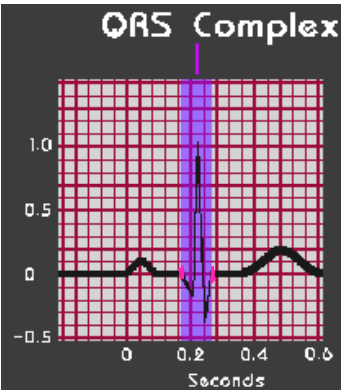
repolarization, flat
ST Segment
-Represents early ___________
-Usually ____, AKA isoelectric
-Important in exercise testing, for it indicates oxygenation
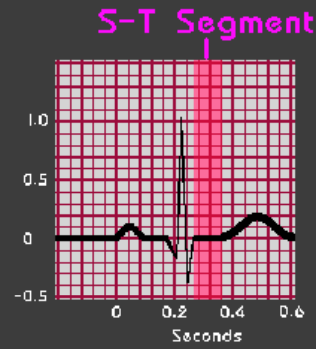
repolarization, resting
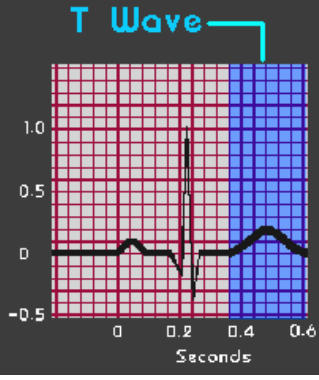
T Wave
-Ventricular ____________, which is the return of stimulated muscle to _______ state
-Before the next cardiac cycle can begin
normal, 60-100
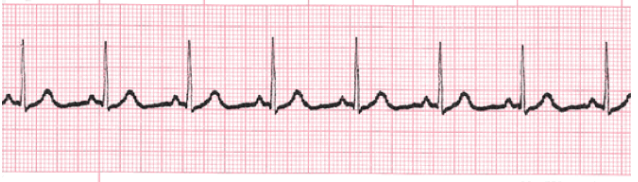
Normal Sinus Rhythm
-Rate, rhythm, intervals, and morphology are _______
-Rate = __-___ BPM
-Rhythm = regular
-Intervals = less than 3 small boxes
normal, less
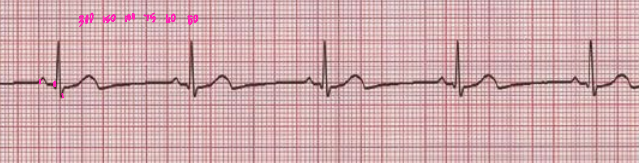
Sinus Bradycardia
-Rhythm, intervals, and morphology are _______
-The heart rate is _____ than 60 bpm
normal, 100, separate
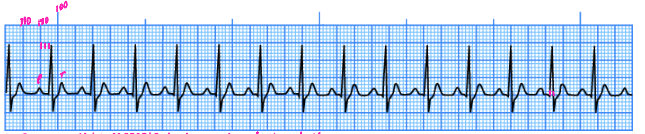
Sinus Tachycardia
-Rhythm, intervals, and morphology are ______
-Rate is greater than ___ bpm
-P and T wave must be __________ to be considered sinus tachy
irregular, intervals, 3
Sinus Arrhythmia/Dysrhythmia
-Rate, intervals, and morphology are normal
-Rhythm is _________
-R-R ________ vary by _ or more intervals, switching between longer and shorter periods of time