Lab 1: The Scientific Method, Measurements, and Using a Spectrophotometer
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Any scientific study begins by making what?
Observations
What may observations lead a scientist to ask?
A particular question to explain those observations.
What is a hypothesis?
A possible explanation to answer a question

What must a hypothesis be to be scientific?
Must be testable and falsifiable

Prediction
Made based on a particular experiment to test a given hypothesis
Data from the experiment either _ or _ a given hypothesis. Often the results will generate what?
Support; refute; Will often generate more questions that can then be tested
The steps of the scientific method can be listed as?
Observations
Questions
Form hypothesis
Test Hypothesis
Observe, record, and study data
Draw conclusion
What is an independent variable?
Condition manipulated by the scientist
(It is a variable not a group)
Dependent Variable
What will be measured or observed as a result of specific conditions in the experiment
(Variable, not a group)
In general what is the goal of the experiment?
To determine the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable

Experimental group
Group of test subjects in which the independent variable is manipulated in order to test its effects on the dependent variable
There are often multiple experimental groups in an experiment

Control group
The group that provides a baseline for comparison of the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
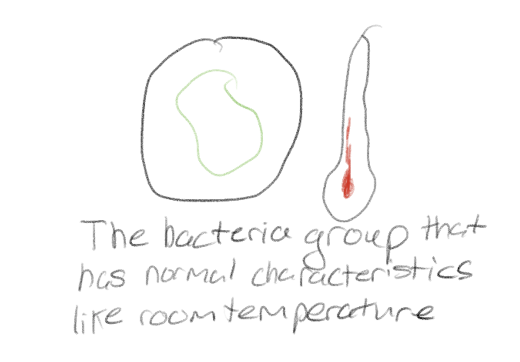
What is a controlled experiment?
All factors except for the independent variable are kept the same (as much as possible) between the different groups in that experiment
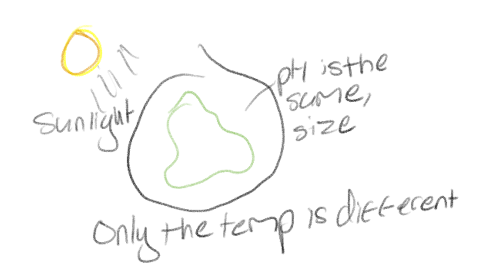
What does to control for a particular factor in an experiment mean?
To make sure that factor is unchanged between all groups or its effects has been removed from the outcome (as much as possible)
Metric system
Standardized system of measurement used by scientists around the world. It is used in everyday life in most countries.
Where do we use the metric units in the U.S.?
Metric systems are standard in some fields, like science and medicine

What makes the metric system easy to use?
Each category of measurement has on basic unit, and all other units in that category are derived as multiples of ten
It is easy to convert 7 millimeters to 0.7 centimeters, justly remembering that they are 10 millimeters in a centimeter.
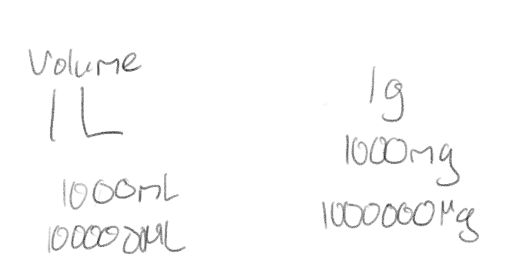
What is the basic metric unit of volume? What units do we usually use in a laboratory?
Liter; milliliters and microliters
What are we going to use to measure volume?
A graduated cylinder
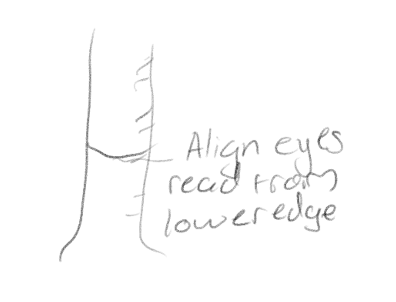
How do we measure volume in a graduated cylinder?
When water is poured into the cylinder, the upper surface of the water column forms a curved line called a meniscus, read the volume of the water by aligning your eyes with the meniscus and reading from the lower edge
What are 3 ways we can measure volume?
Water capacity
Water displacement
Linear dimensions
How can we measure volume using water capacity?
You can measure volume of a hollow container by measuring the amounts of water that it holds.
You can do that by filling a container with water and then transferring the entire volume to a graduated cylinder
How can we measure volume using linear dimensions?
1 mL = 1cm3
You can calculate the volume by measuring and multiplying the length, width, and height.
How can we measure volume using water displacement?
Determining volume can be difficult when working with irregularly shaped object
So if that object sinks in water you can drop it into a graduated cylinder with water (if object is big than you need something bigger than a graduated cylinder) and subtract the initial water volume from the volume of water with the object.
What is the basic metric unit of mass? What units are often used in laboratories for mass?
Gram; usually milligrams and micrograms
What is density?
The density of an object is defined as its mass per unit of volume.
What is the density of water?
One millimeter of pure water weighs 1 gram. Therefore the density of water is 1 g/mL
When does something sink or float in water?
If a substance is less dense than water, it will likely float (less than 1 g/mL)
If a substance is more dense than water, it will likely sink (more than 1g/mL)
What are micropipettes?
Pipettes that are used to deliver small volumes (smaller than a milliliter)
What are the two micropipettes that we are using?
P-20 and the P-200
How do you properly use a micropipette?
Set the pipe the volume only within the range specified
Do not twist the volume adjustment knob beyond the pipette’s maximum or minimum values
Keep pipette in a vertical position
Use your thumb to carefully control the speed of the plunger
How do you draw up liquid into the pipette tip?
You hodge your dominant hand with your thumb on the plunger/ And slowly press down on the plunger until you feel the first stop
Keep it almost vertical and wait 1-2 seconds before removing the pipette from the liquid
How do you expel liquid from the pipette tip?
Hold the pipette with one hand, and hold the tube with the one that you are ejecting the fluid into the other
Depress slowly to the first stop then continue to depress for the the second stop
Always remove a tip before using a new reagent
What is a spectrophotometer?
Is an instrument that passes light ( at a specific wavelength) through a solution and measures the amount of light that solution absorbs or transmits.
What is absorbance?
The amount of light absorbedd by a substance is proportional to the concentration of light-scattering substance dissolved in a solution
It is prevented from passing through the solution
What is a curvette?
It is the glass equipment that contains the sample to be measured
What is optical density?
The absorbance that is detected by the photocell and yields an absorbance value (optical density) of the experimental sample
What is a blank?
It contains everything in the experimental tube except the material to be tested
The other curvettes would be compared to this so that an accurate reading of the sample may be made
Pre-Lab review
…
What steps are involved in the scientific method?
Observations
Question
Form hypothesis
Test hypothesis
Observe, record, and study data
Draw conclusion
What characteristics does a hypothesis have to have in order to be considered scientific?
It must be testable and falsifiable
Describe the types of variables involved in scientific experiments?
Independent variable: The variable that we are manipulating
Dependent variable: The variable that we are measuring
What are the two types of groups used in scientific experiments?
Experimental group: The groups that are effected by the independent variable
Control group: the group that are normal (is not effected by the independent variable)
What makes the metric system easy to use?
There is one name for the unit and they are in multiples of ten with prefixes
Complete these conversions. If your answer requires more than three decimal places, use scientific notation.
0.2 L = _ mL = _ µL
100 µL = _ mL = _ L
0.5 mL = _ µL = _ L
100 mg = _ µg = _g
2 g= _mg = _ µg
200; 200000
0.1; 1.0×10-4
500; 5.0×10-4
100000; 0.1
2000; 2000000
List three different ways to measure the volume of an object?
Water displacement
Water capacity
Linear dimensions
Describe the proper way to read the volume of water in a graduated cylinder.
Read the volume of water by aligning your eyes with the meniscus and read from the lower edge
Using the displacement principle, explain why you do not fill up your bathtub to the brim then get in it.
Because you as an object takes up space the volume of the water and you will add up together and push water out because the total volume is more than the bathtub can handle
Describe how to calculate the density of an object?
It is the weight of the object in grams divided the volume of the object in milliliters
What should you use to measure 75 mL, 500 mL, 500µL, 15µL, 5µL, 150µL
8mL.
A 1L graduated cylinder, a 100 mL graduated cylinder, a 1 mL pipette, a P-200 micropipette, and a P-20 micropipette?
For 75 mL you would use the 100 mL graduated cylinder
For 500 mL you would use a 1L graduated cylinder
500 µL, 1mL pipette
15, 5 µL, P-20
150 µL, P-200
8 mL, 100 mL graduated cylinder
How would the volume of bromophenol blue solution change the Absorbance: optical density (OD)
Since there is more volume of the solution there would be more absorbtion