unit 3 transition metal complexes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what is a transition element
element with partially filled d or f valence shells. groups 3-11.
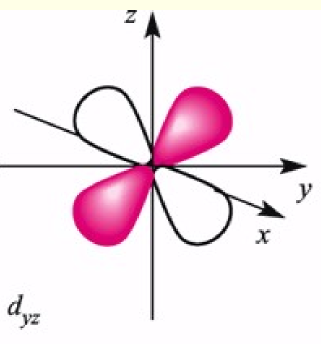
dyz orbital
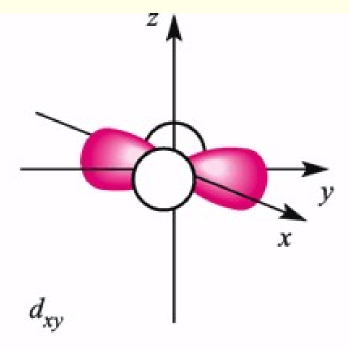
dxy orbital
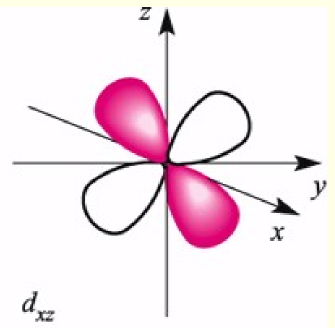
dxz orbital
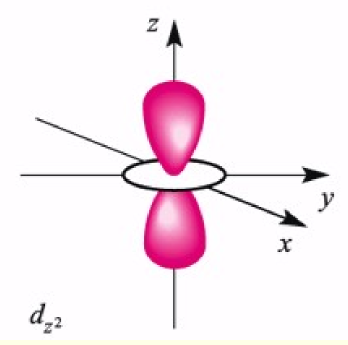
dz2 orbital
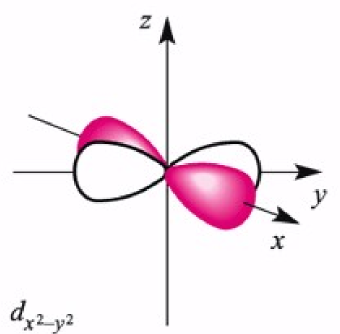
dx2-y2 orbital
d-electron filling for transition metalls
(n+1)s orbital is filled before nd (eg 4s before 3d)
exceptions to d-electron filling for first row
Cr and Cu are anomalous due to extra stability gained from half/fully filled subshells meaning an electron is bumped from 4s to 3d
d-orbital filling for a metal in a compound
filling order reverts to 3d before 4s
d-orbitals on ionisation
any s electrons are removed before the d electrons
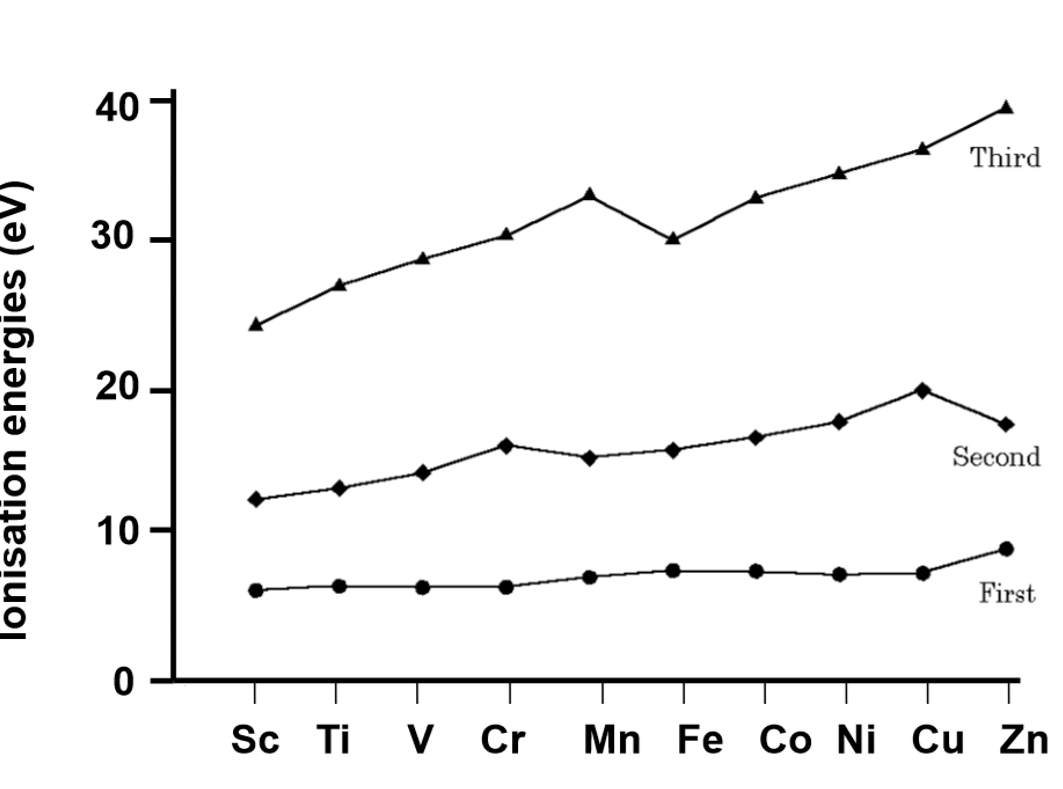
trend in IE for d-block
general trend is for IE to increase across a period due to increasing Zeff. some IEs are anomalously low:
for IE1, Cr and Cu
for IE2, Mn and Zn are low
for IE3, Fe is low
what is a transition metal complex
has a central metal atom or ion surrounded by a set of molecules or ions termed ligands that bind to the metal through electron donation to form dative covalent bonds
coordination complex
none of the ligands bind through a carbon atom
organometallic complex
at least one ligand binds through a carbon atom
coordination number and symbol
CN
number of bonds between the metal and surrounding ligands
how are complexes written/drawn
complex and any counterions are distinguished by placing only the complex inside square brackets. charge for the complex is giving outside the square brackets.
coordinating atom is distinguished when drawn or ambiguous
optionally, the oxidation state for the metal is given next to the metal
simplest idea of metal-ligand bonding
the ligand donates an electron pair to the metal. lone pairs are a good source.
the metal-ligand bond is often dative covalent. the metal accepts electrons so it is a good lewis acid, the ligand donates electrons so it is a lewis base.
good bases are generally also good ligands as they have an available electron pair. transition metals can readily form such complexes as they have energetically available empty d-orbitals.
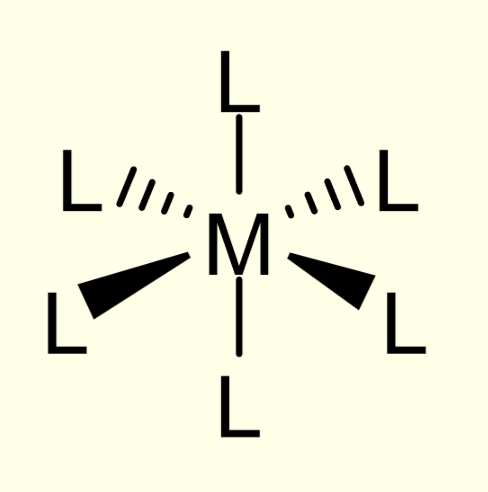
octahedral complexes:
diagram
CN
adjacent and opposite angles
CN = 6
adjacent angles = 90
opposite angles = 180
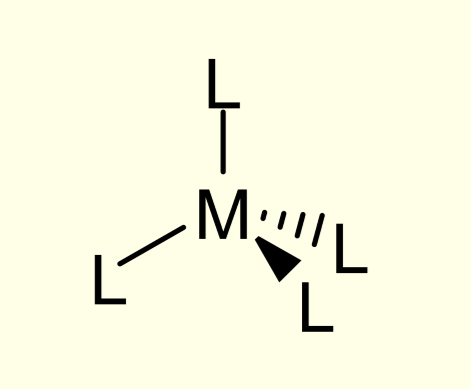
tetrahedral complexes:
diagram
CN
adjacent angles
CN = 4
adjacent angles = 109.5
square planar complexes:
diagram
CN
adjacent and opposite angles
CN = 4
adjacent angles = 90
opposite angles = 180
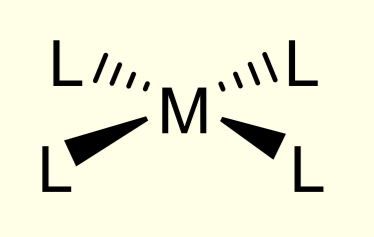
dentate prefixes
mono, bi, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta and octa
water ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
H2O
aquo
ammonia ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
NH3
ammine
fluoride ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
F-
fluorido
chloride ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
Cl-
chlorido
bromide ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligandBr-
Br-
bromido
hydroxide ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
OH-
hydroxido
methoxide ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
OMe-
methoxo
cyanide ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
CN-
cyanido
carbon monoxide ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
CO
carbonyl
thiocyanide ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
SCN- or NCS-
thiocyanato or isothiocyanato
trimethylphosphine ligands: formula and name of coordinated ligand
PMe3
trimethylphosphine
chelate rings
formed by polydentate ligands where two or more donor atoms coordinate to a single metal
constitutional/linkage isomers
same formula, different atom-to-atom connectivity. ligands that can coordinate to a metal through different atoms
eg NO2: M-NO2 or M-ONO
geometrical isomers
ligands are arranged differently in space
geometrical isomers in tetrahedral complexes
none
geometrical isomers in square planar complexes
occurs if two ligands are the same. if there are more than 2 types of atom, it is only the 2 same atoms that are important
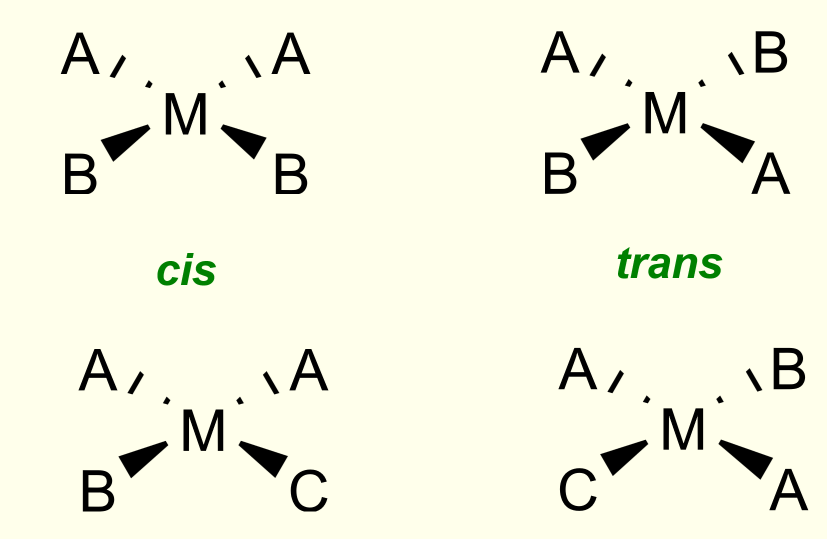
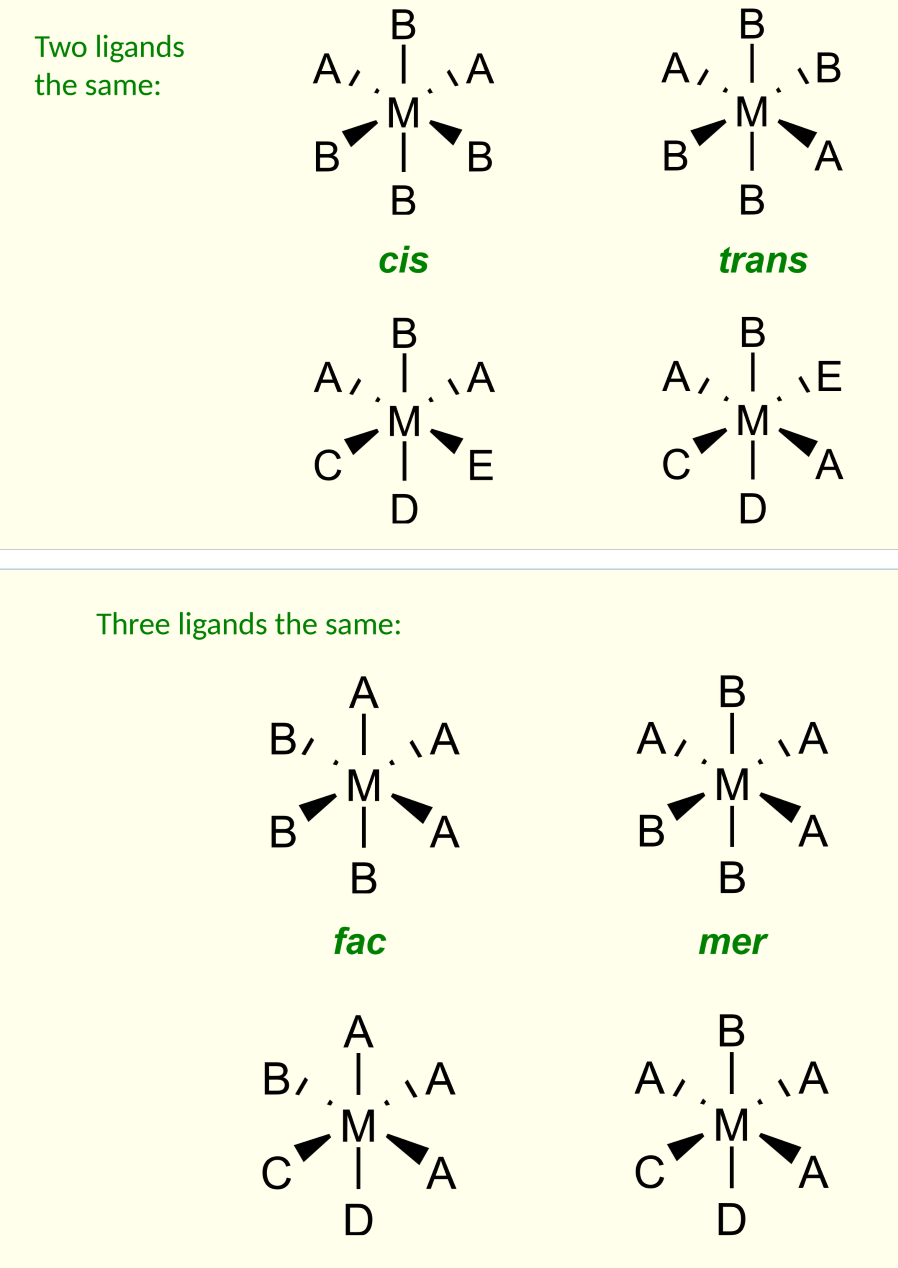
geometrical isomers in octahedral complexes
occur when two or three ligands are the same.
for three the same:
three identical forming a face = fac
three in a plane = mer
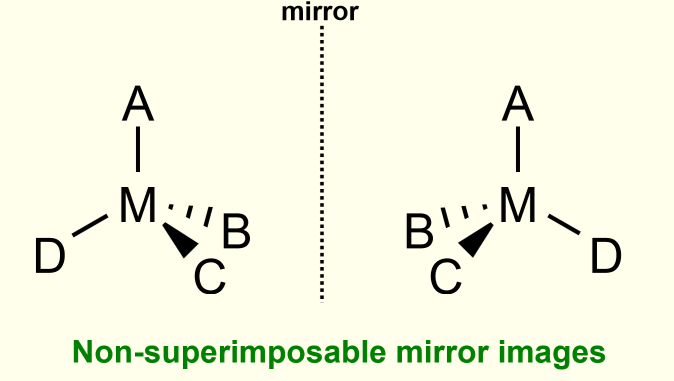
optical isomerism
occurs where two isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
the objects are termed chiral and the isomer pair are enantiomers.
optical isomerism in tetrahedral complexes
occurs only if all four ligands are different
optical isomerism in square planar complexes
no optical isomers, mirror images can be superimposed
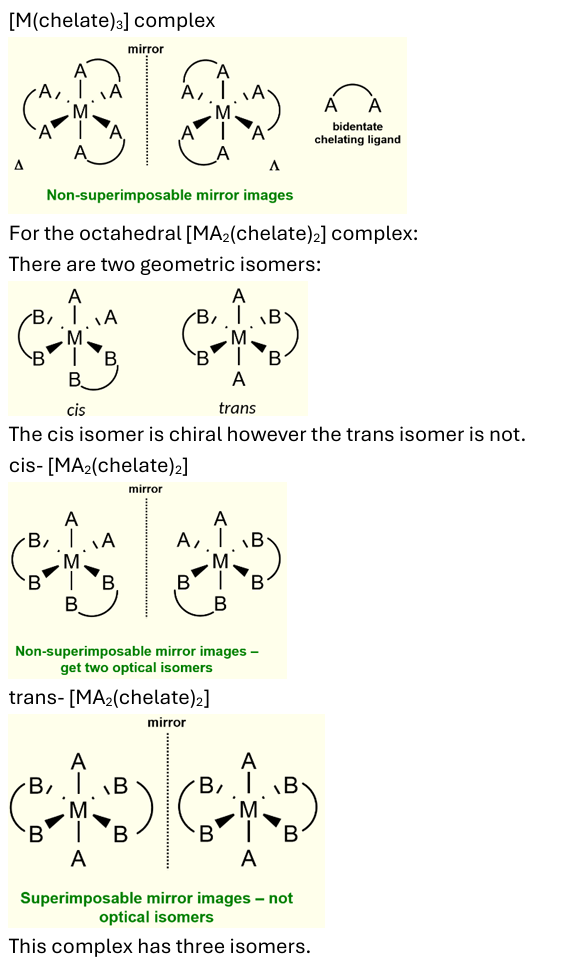
optical isomerism in octahedral complexes
does not occur with monodentate ligands. can occur when there are two or three bidentate chelating ligands.
order of naming transition metal complexes
in complex, ligands first, alphabetically, then metal
in compound, cation first, anion last
oxidation state for metal is indicated by roman numerals in brackets. this is important as the number of counterions is not stated.
if the complex is anionic, the metal ends in ate.
prefixes to state number of ligand (and name to use if ligand’s name already uses one of these)
di (bis)
tri (tris)
tetra (tetrakis)
penta (pentakis)
hex (hexakis)