Hair & Fibers
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What characteristics make hair a useful forensics tool?
Cuticle and medulla
Is hair considered class or individual? Why?
Class because hairs from different people can look the same. Unless there is a follicular tag to contain DNA
How would you decided approximately how long ago a hair sample was dyed?
Hair grows at a rate of 0.4mm/day. Measure how much the hair has “grown out”
If you were asked whether a particular hair sample were human or animal, what would you look for?
Look at the medulla. Humans have thin, intermittent medullas if they have one at all. Animal medullas are larger and can be a variety of different styles

What type of animal medulla is this?
Uniserial
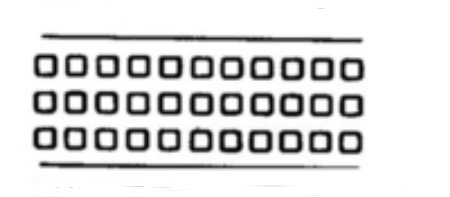
What type of animal medulla is this?
Multiserial
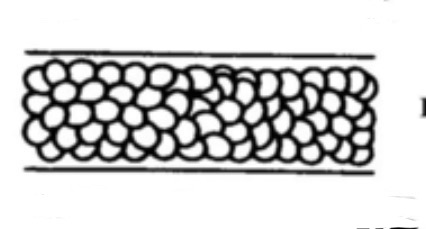
What type of animal medulla is this
Vacuolated
What type of animal medulla is this?
Lattice

What type of animal medulla is this?
Amorphous
If you were asked to compare and unknown sample to a known sample of human hair to match or identify origin, what would you look for?
Look at the medulla, structure of the hair (split ends), evidence of hair coloring. Hair is usually not seen as viable evidence.
What are the characteristics of a fiber, a filament, and fabric?
Color, diameter, striation/pitting, cross sectional shape, smell when burnt, dye content, chemical composition
Are inorganic fibers natural or synthetic?
Synthetic
List four synthetic fibers
Rayon, nylon, polyester, acetate
Can a fiber be individualized to a particular textile fabric? Why or how
Only if the process/dye is unique
Can a piece of fabric be individualized to a particular garment? Why or how?
Yes, the fibers and weave patterns need to match
Many fibers look very similar under the microscope, but there are major differences between synthetic and natural fibers. What would you look for in determining whether a particular fiber was synthetic or natural?
A more “organic” looking fiber irregularities is natural. Synthetic is very organized
What is the more common natural fiber used in textiles?
Cotton
What is the more common synthetic fiber
Polyester
What is trace evidence? What is the common basis for analyzing trace evidence, that is, what are the goals?
Physical evidence found in very small amounts that may prove a suspect was or was not at a crime scene
During a trial, what are the primary concerns in analyzing and using extremely small bits of trace evidence?
The evidence could easily be lost or planted or accidentally left at the crime scene
What is the purpose of hair?
Regulate body temperature, decrease friction, protect against sunlight, act as a sense organ
Hair grows out of the hair _____
Follicle
Bulb embedded in the hair follicle
Root
Initial growth phase of the root, root bulb is flame shaped, follicular tag is translucent tissue with DNA
Anagen
second root growth phase, roots have an elongated appearance
Catagen
Third root growth phase, hair is naturally pushed out of follicle, root has a club shaped appearance
Telogen
Scale structure covering exterior of hair
Cuticle

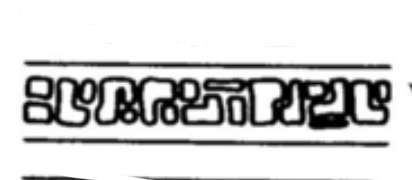
What type of cuticle pattern is this?
Imbricate
What type of cuticle pattern is this?
Coronal
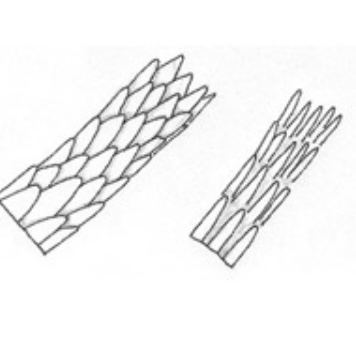
What type of cuticle pattern is this?
Spinous
The main body of the hair shaft
Cortex
What is the cortex made of?
Spindle shaped cortical cells and pigment granules
The cellular column through the center of the hair
Medulla
The diameter of medulla compared to the diameter of the shaft
Medullary index
The medullary index in humans is _____
Less and 1/3
The medullary index in animals is ________
Greater than 1/3
True or False: the medullary is usually fragmented or absent in humans
True
The medullary shape is ______ in humans
Cylindrical
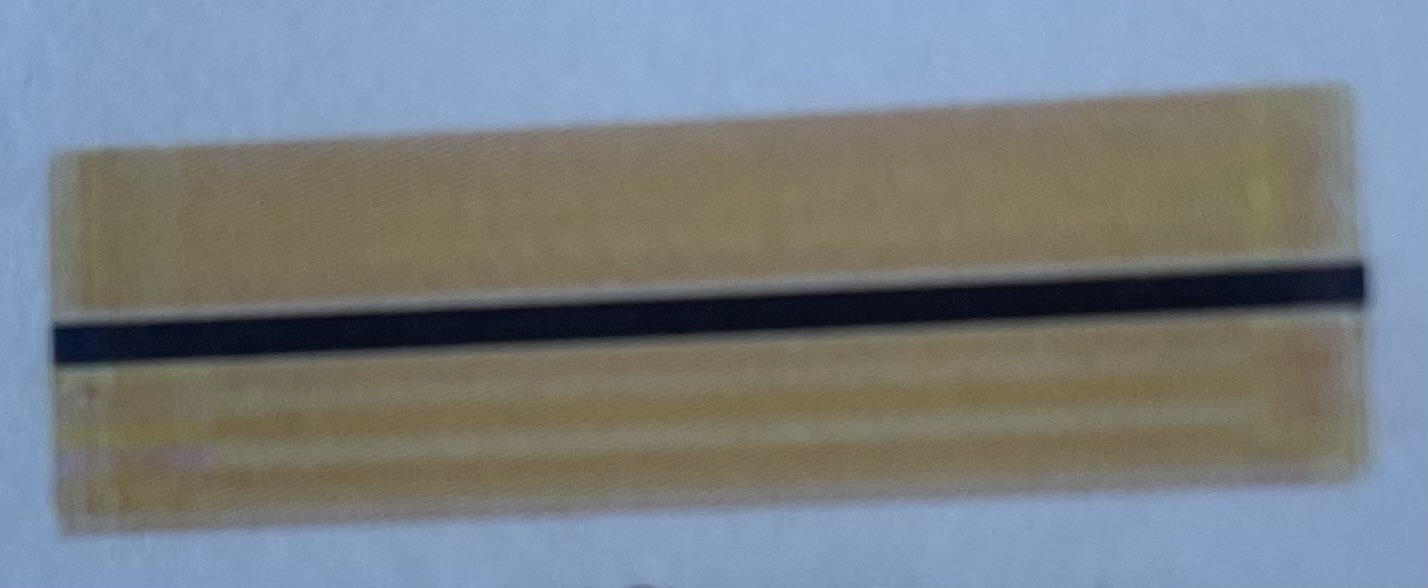

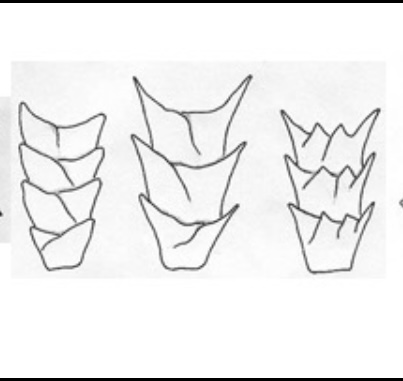
What type of medullary shape is this?
Continuous
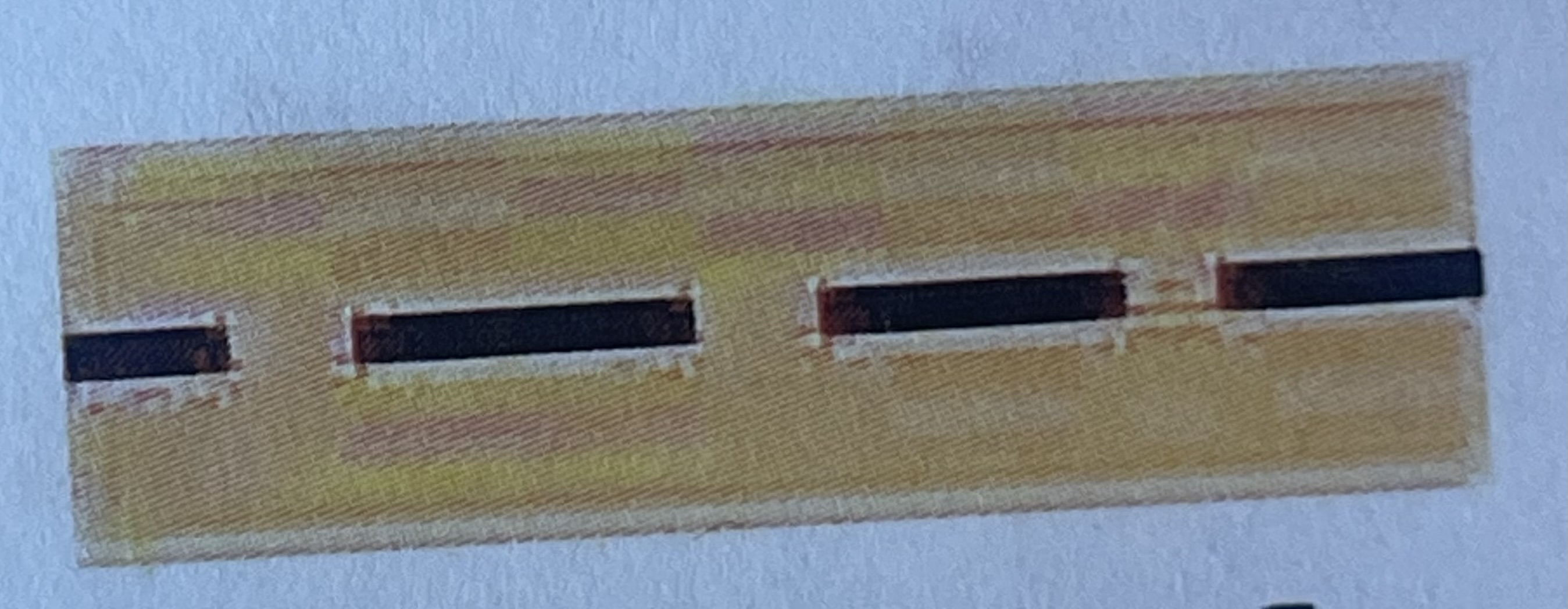
What type of medullary shape is this?
Interrupted

What type of medullary shape is this?
Fragmented
What are the primary things investigators look for in hair identification?
Color, length, diameter of hair, medullary shape, shape, color intensity of pigment granules
What are the secondary things investigators look for in hair identification?
Growth, bleached, dyed, natural, fungal infections
What two things differentiate animal hair from human hair?
Ovoid bodies and medulla
Form the outer coat of the animal, shed water, and protect the inner hair and skin
Guard hair
Tail and mane hairs whose morphology may differ substantially from the main body hairs of the animal
Sensory fur
For inner coat and provide insulation
Under fur or wool hairs