HL PDA III Exam I - GABAergic Hypnotics LOs
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
True or False: an ideal hypnotic would change the normal sleep pattern, not cause side effects the next day, have no drug interactions, and be safe to use chronically
False
Explanation: we do not want to disrupt normal sleep patterns, but everything else is correct
What are the stages of sleep?
NREM-1, NREM-2, NREM-3, REM
What is NREM?
non rapid eye movement (has 3 stages)
What is stage 1 NREM?
between wakefulness and sleep,
some eye movement,
tonic muscle activity,
brief duration
What is stage 2 NREM?
little to no eye movement,
less tonic muscle activity,
brief duration
What is stage 3 NREM?
Delta sleep,
low tonic muscle actiity,
deepest stage of sleep,
restorative
What is delta sleep?
high amplitude slow activity delta waves are seen on an EEG
What is REM?
rapid eye movement sleep
What happens during REM?
brain becomes electrically and metabolically active,
increased cerebral blood flow,
muscle atonia,
dreaming,
increased internal temperature (poikilothermia)
True or False: 4-6 cycles of delta → REM sleep
True
Explanation: each lasts 70-120 minutes, but time in REM increases with each cycle to a max of 30-60 minutes
What is melatonin?
hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycle
True or False: melatonin is biosynthesized from 5-HT, released from pineal gland, and interacts with receptors in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
True
Explanation: this is associated with our circadian clock and when increased melatonin is in the SCN we become sleepy
True or False: darkness promotes biosynthesis of melatonin so there is increased activation of melatonin receptors in the SCN
True
Explanation: on the other hand, light inhibits biosynthesis of melatonin signaling the body through SCN when to wake up
What is a diurnal cycle?
24 hour cycle
What is the diurnal cycle of sleep?
circadian rhythm for melatonin release → sleep regulation
What happens during evening hours in regards to melatonin?
Biosynthesis of melatonin rises in the evening and peaks during sleep,
Tissue levels of melatonin increase within the pineal gland and SCN,
Diurnal variation in melatonin levels can be measured via blood
What are the types of GABAergic hypnotics?
benzos and non-benzos
What drugs are melatonin congeners/agonists?
ramelteon and tasimelteon
What drugs are orexin inhibitors/antagonists?
daridorexant, lemborexant, suvorexant
Which benzos and non-benzos are short acting (t1/2 < 6 hours)?
Midazolam (Versed): IV
Triazolam (Halcion): PO
Eszopiclone (Lunesta): PO
Zaleplon (Sonata): PO
Zolpidem (Ambien): PO
Which benzos and non-benzos are intermediate acting (t1/2 6-24 hours)?
Alprazolam (Xanax): PO
Lorazepam (Ativan): IM, IV, PO
Temazepam (Restoril): PO
Which benzos and non-benzos are long acting (t1/2 > 24 hours)?
Clonazepam (Klonopin): PO
Diazepam (Valium): IM, IV, PO, PR
What is the MOA of BZRA (non-benzos)?
agonists at the benzodiazepine binding site on GABAA (same binding site as benzos)
True or False: non-benzos do NOT produce a GABAergic effect unless GABA is present
True
Explanation: they selectively bind to GABA-A receptors with an alpha-1 subunit
What is the physiological response of non-benzos?
sedative, hypnotic, amnesic, and motor impairing
Explanation: they do NOT produce anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, or alcohol potentiating effects
What is the MOA of melatonin congener/agonists?
agonists at MT1 and MT2 receptors
True or False: melatonin congeners/agonists lengthen sleep latency
False
Explanation: they shorten it!
True or False: melatonin agonists are well tolerated, have no dependency concerns, and low incidence of daytime adverse effects
True
Explanation: they are not controlled medications
What is the MOA of dual-orexin inhibitors?
competitive antagonist at OX1R and OX2R receptors (duality)
What is the physiological effect of dual-orexin inhibitors?
decreases sleep latency and increases sleep maintenance
True or False: OX-A and OX-B are inhibitory neuropeptides involving CNS signaling
False
Explanation: they are excitatory
What are DORAs?
dual-orexin receptor antagonists
True or False: eszopiclone is an R-enantiomer of racemic zopiclone
False
Explanation: it is an S-enantiomer
True or False: eszopiclone is enantiopure
True
True or False: food delays absorption for zolpidem
True
Explanation: take on an empty tummy
True or False: high-fat meals delay absorption for lunesta
True
Describe the excretion of nonbenzos
nearly the entire z-drug is excreted as urinary metabolites
Explanation: there is very little unchanged drug
How are nonbenzos metabolized?
CYP3A4 liver enzymes metabolize 50% or more of the dose and there are no relevant active metabolites
What is the half-life of zolpidem and lunesta?
2 - 2.5 hours
What is the half-life of zaleplon?
1 hour
Explanation: shorter duration of action and little-no daytime effects, but can wear off TOO soon
What are adverse effects of nonbenzos?
Complex sleep behaviors (sleep walking, driving, etc…),
Tolerance and dependence (use lowest dose),
CNS (dizziness, drowsiness, headache)
True or False: melatonin agonists have high oral bioavailability
False
Explanation: they have low oral bioavailability
How are melatonin agonists metabolized?
CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and CYP2C- extensively metabolize these drugs
True or False: dual orexin inhibitors have high oral bioavailability
True
Explanation: take on an empty stomach for rapid onset of action
How are dual orexin inhibitors metabolized?
CYP3A4/5 mostly
What are adverse effects of dual orexin inhibitors?
somnolence, fatigue, headache
True or False: orexin inhibitors are C-IV, but have low risk for dependency
True
True or False: benzos are mostly excreted in the urine and feces as unchanged drug
True
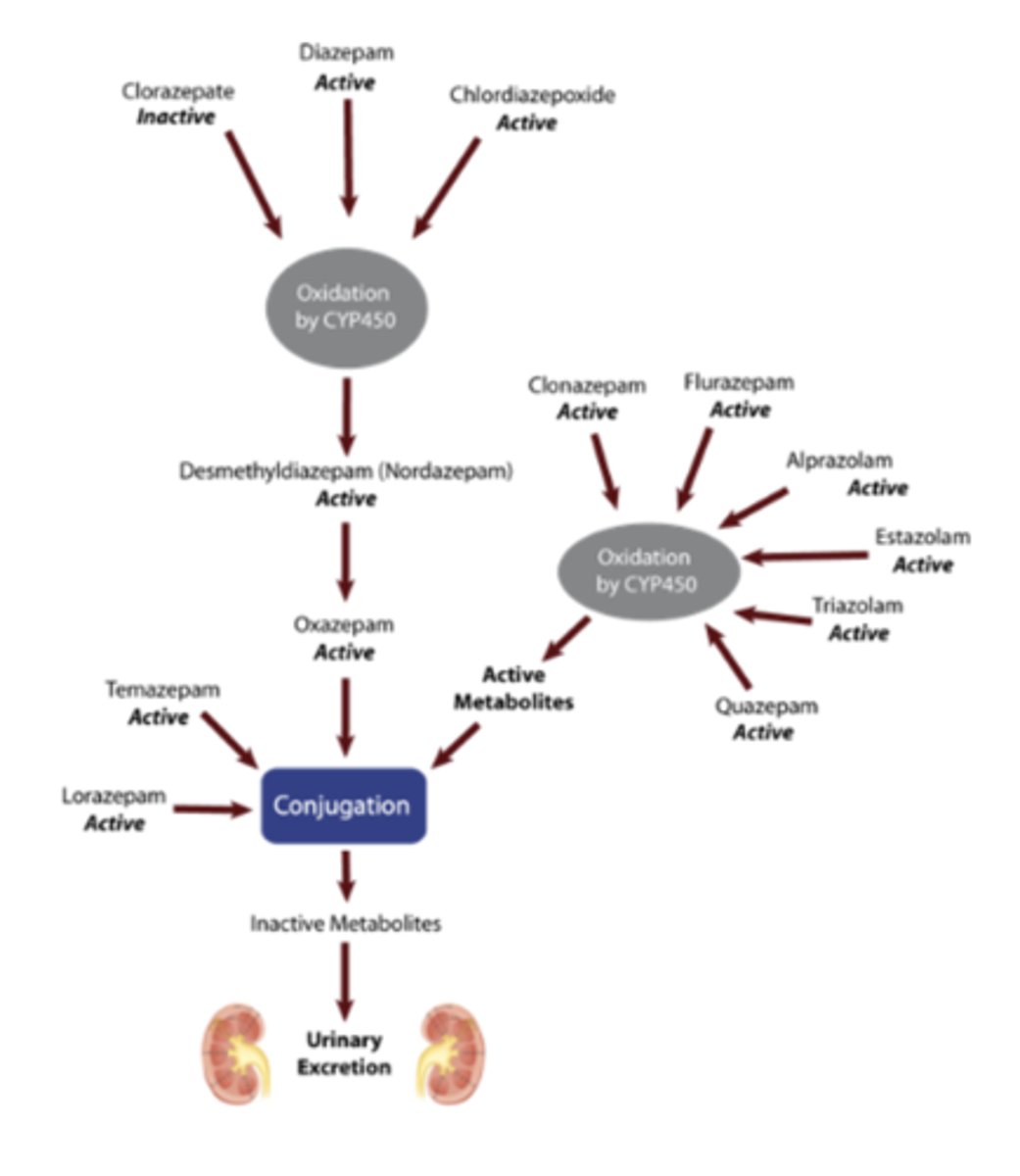
Which benzos avoid oxidative metabolism?
LOTs are directly glucuronidated which is good for patients with liver insufficiency
Explanation: loraze, oxaze, triaze