Health Policy 4 | Access, Cost, Quality, Value, Triple and Qudruple Aim
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are the three core topics of health policy?
The three core topics of health policy are Access, Cost, and Quality.

Define access to healthcare
Access is "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best health outcomes."

What are the two main components of healthcare access?
Ability to pay – Having financial resources or insurance to cover healthcare costs.
Availability – Access to healthcare facilities, professionals, transportation, culturally competent care, and timely services.

What are some key barriers to accessing healthcare?
Lack of insurance or underinsurance
High out-of-pocket costs
Unavailable services due to location, transportation, or workforce shortages
Cultural or language barriers
Patients' lack of understanding of the healthcare system

What are the benefits of having access to healthcare?
Improved health outcomes
Stronger provider-patient relationships
Timely diagnosis and treatment
Increased use of preventive services
Lower mortality rates
Reduced financial hardship
Decreased healthcare disparities

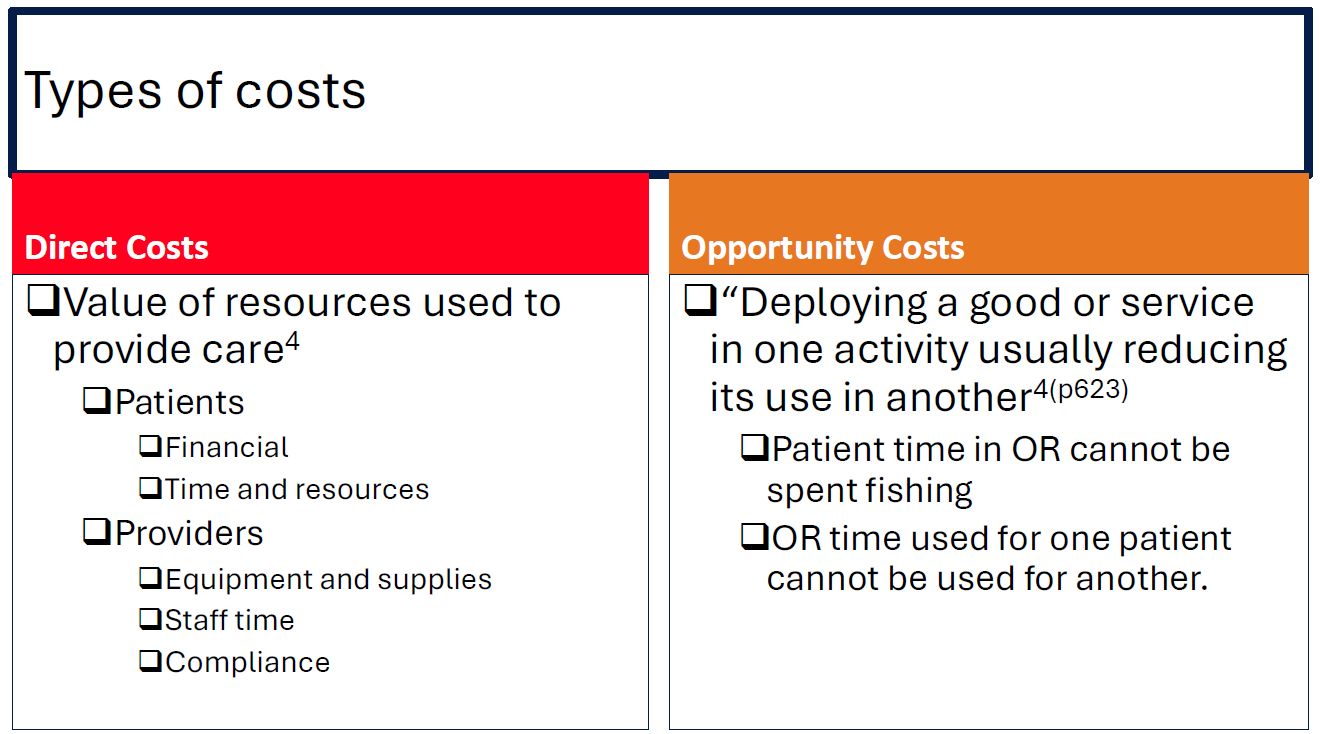
What are the two main types of healthcare costs?
Direct costs – The value of resources used for patient care, including financial costs, time, and equipment.
Opportunity costs – The value of what is lost by choosing one option over another (e.g., time spent in surgery cannot be spent on other activities).
What are some factors that influence healthcare costs?
Fee-for-service model (Price x Quantity)
Unnecessary services ($210 billion)
Waste ($130 billion)
Fraud ($75 billion)
Missed prevention ($55 billion)
Administrative expenses ($190 billion)
High prices of medical services ($105 billion)

How is healthcare quality defined?
Quality is "the degree to which health services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes and are consistent with current medical knowledge."

What factors impact healthcare quality?
Structural factors – Nurse-to-patient ratios
Processes – Evidence-based treatment protocols
Human factors – Training, attitudes, communication, sleep, patient involvement

What is high-value care?
High-value care is "the best care for the patient, with the optimal result for circumstances, delivered at the right price."

What is the value equation in healthcare?
Value = (Outcomes + Safety + Service) / Total Costs

What are the six characteristics of high-value care?
Safe – Avoiding medical errors and harm.
Timely – Reducing delays in care.
Effective – Providing evidence-based treatments.
Efficient – Avoiding waste.
Equitable – Ensuring fair access to care for all.
Patient-centered – Involving patients in decision-making.
STEEEP

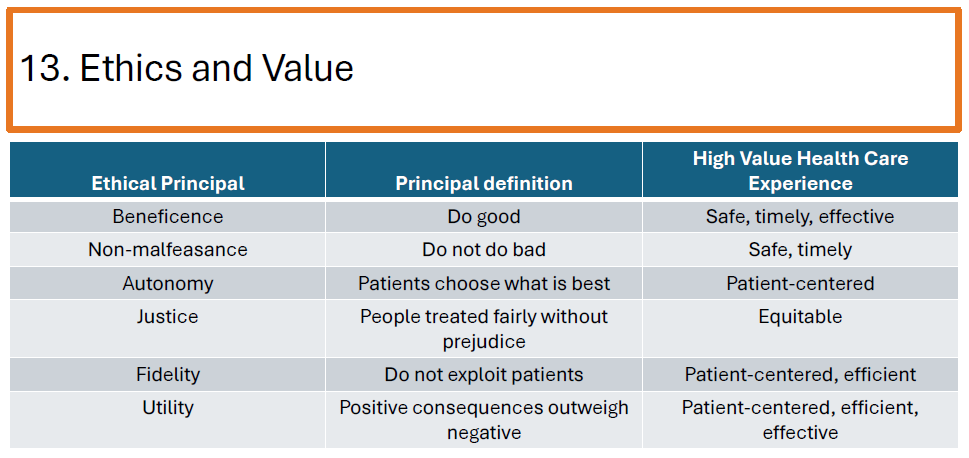
How does value in healthcare relate to ethics?
Beneficence – Providing good care (safe, timely, effective).
Non-malfeasance – Avoiding harm.
Autonomy – Allowing patients to make their own decisions.
Justice – Ensuring fair access to care.
Fidelity – Avoiding patient exploitation.
Utility – Maximizing positive consequences over negatives.
What are some obstacles to achieving high-value care?
Conflicting financial incentives
Lack of cost-awareness among insured patients and providers
Poor care coordination leading to duplicate tests
Difficulty measuring value
Lack of cost transparency for health professionals

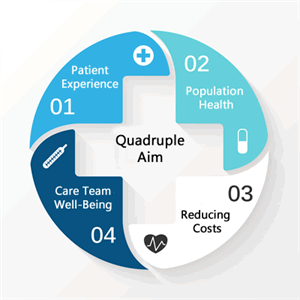
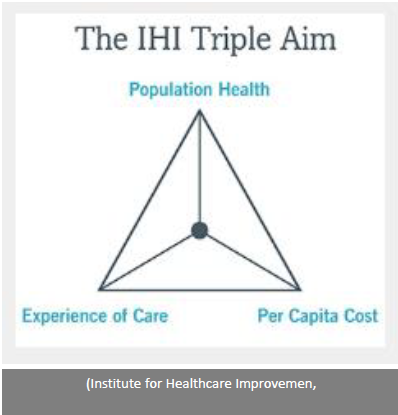
What is the Triple Aim in healthcare?
The Triple Aim is a framework in healthcare that focuses on improving 3 key areas:
Improving the patient experience (quality and satisfaction).
Improving population health.
Reducing per capita healthcare costs.
Why was the Quadruple Aim introduced, and what does it add to the Triple Aim?
The Quadruple Aim adds provider well-being to the Triple Aim to address burnout, job dissatisfaction, and workforce retention among healthcare professionals.