3- Halogenoalkanes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
General formula for halogenoalkanes
CnH2n+1X (X is the halogen)
Nomenclature of halogenoalkanes
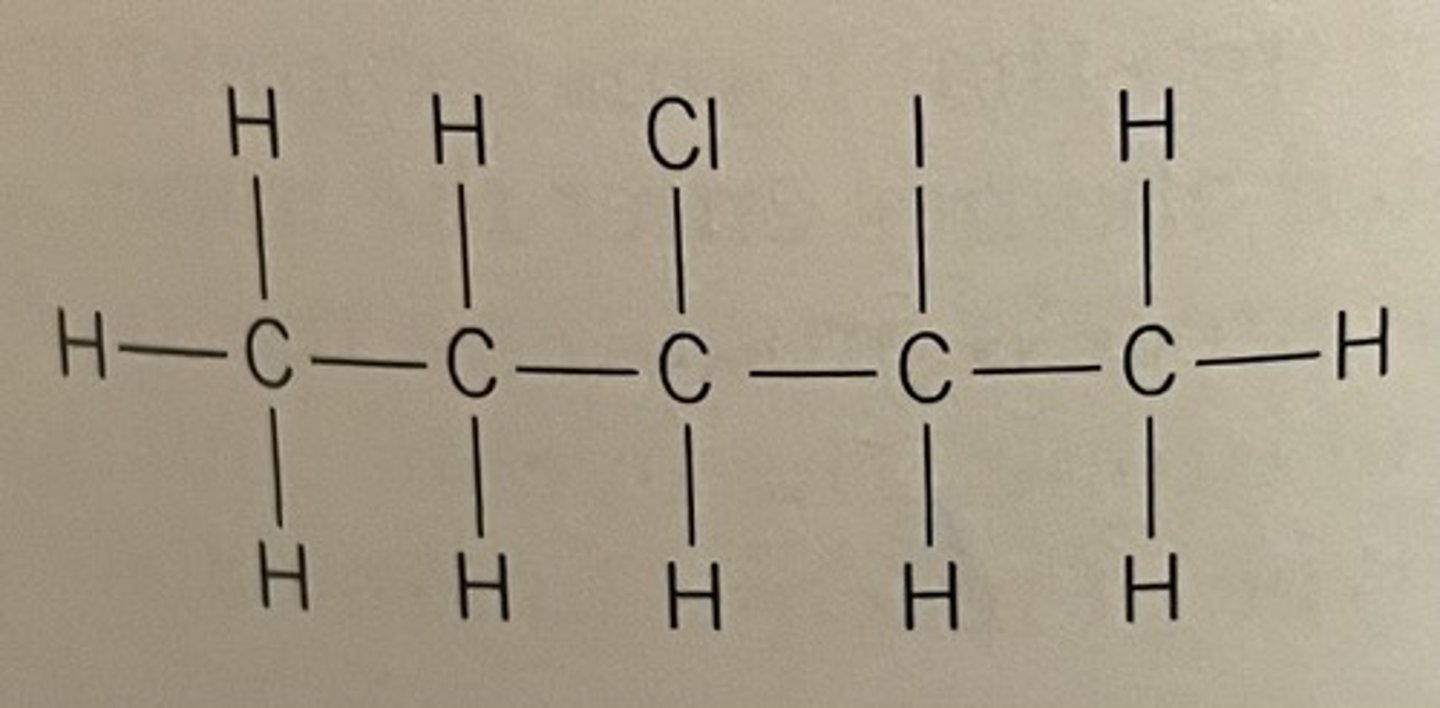
If a molecule has more than one different halogen in it, we number the molecule in alphabetical order
For example: this is 3-chloro-2-iodopentane not 2-iodo-3-chloropentane
Bond polarity of halogenoalkanes
Have C-X bond, this bond is polar (CS+ - XS-) because halogens are more electronegative than carbon
Solubility of halogenoalkanes
Polar C-X bonds not polar enough to make the halogenoalkanes soluble in water, but they do mix with hydrocarbons (oil) in dry-cleaning fluids
Boiling point of halogenoalkanes
-Increases with the increased chain length
-Boiling point increases going down the halogen group
Both effects due to increased van der waal forces, the larger the molecule, the greater number of electrons and therefor the larger the van der waal forces
Branched halogenoalkanes reduces the boiling point as the molecule is not so tightly packed together
Why do halogenoalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes with similar chain lengths?
They have higher relative molecular masses and they are more polar
Reactivity: bond enthalpy and bond polarity
Bond enthalpy:
F is the smallest atom in G7, the shared electrons in the C-F are strongly attracted to the fluorine nucleus (this makes a strong bond, least prone to reactivity).
Down the group, the shared electrons in the C-X bond get further away from the halogen nucleus, bond becomes weaker, reactivity increases
Bond polarity:
Opposingly suggests that the C-F bond would be the most reactive as it is the most polar, CS+ has most positive charge and is therefore more easily attacked by a nucleophile
Experiments confirm bond enthalpy>bond polarity
What is meant by a free radical?
Unpaired electron
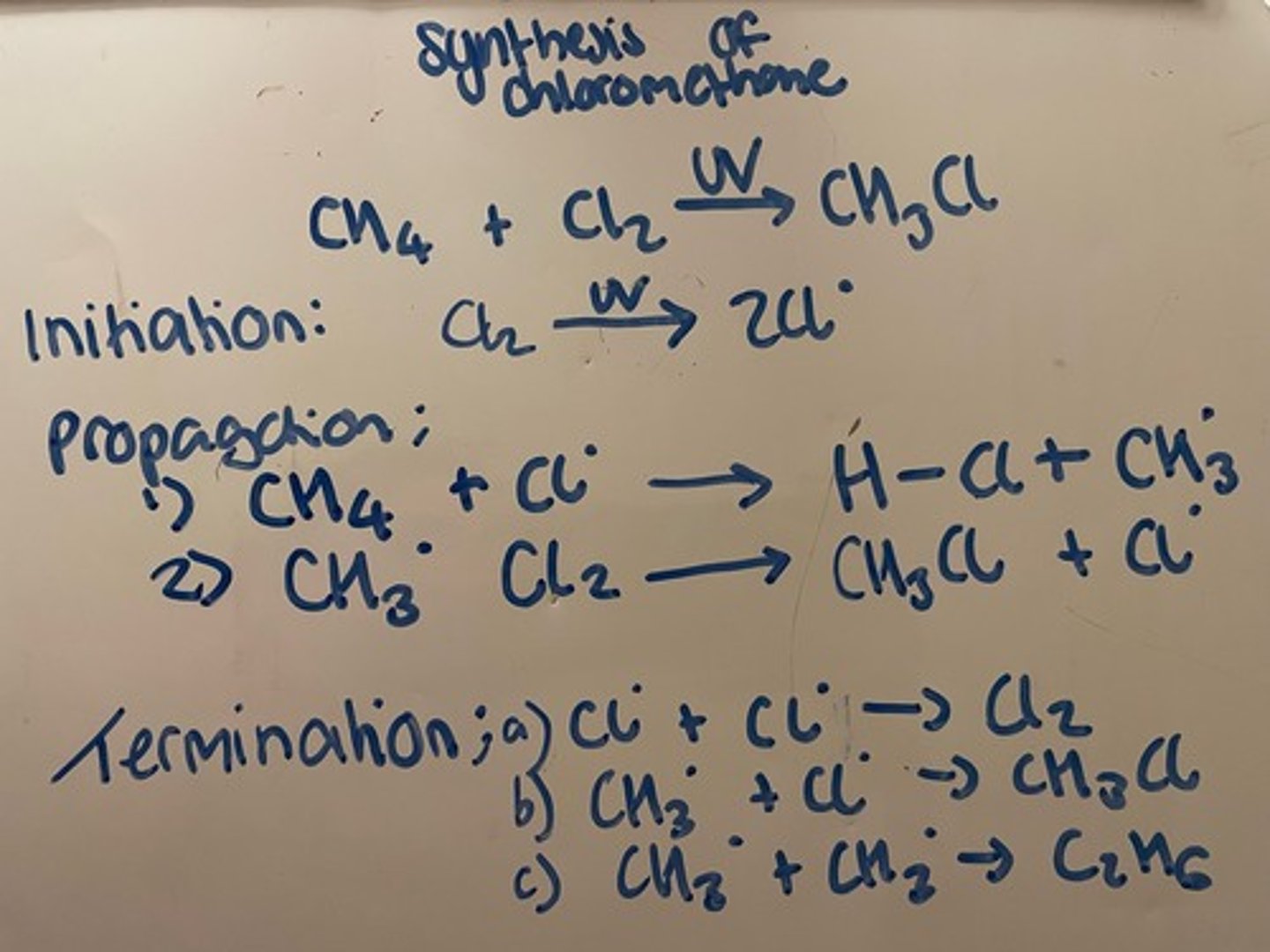
Explain the synthesis of chloromethane to involve initiation, propagation and termination
Initiation: UV light provides sufficient energy to break Cl-Cl bond, bond splits equally so that each atom keeps an electron, forming 2 chlorine free radicals (highly reactive)
Propagation: split into 2 steps
1. A chlorine free radical bonds with a H in CH4 to form H-Cl and CH3, radical is not used up so moves to CH3
2. CH3 radical breaks Cl2 bond so that one Cl radical bonds with CH3 and one Cl radical is left over (must use Cl2 as this is the only halogen available to make a halogenoalkane)
Termination: free radicals are stopped if two radicals join together. This can be done in several combinations
Cl2 and CH3Cl can react again if UV light is still present
How can you check your steps of synthesising a chloroalkane are correct?
A product of second step must be a reactant in the first
Radical product of step one must a reactant in step 2
After the synthesis of chloromethane what will occur when
a) The chlorine is in excess
b) The methane is in excess
a) Hydrogen atoms on methane will eventually be replaced by chlorine atoms, you will get dichloromethane then tri then tetra and so forth
b) Chlorine will be used up quickly, product will mostly be chloromethane

What are CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) and how are they dangerous
Halogenoalkane molecules where all of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by Cl and F atoms
The CFCs are then broken down by the UV light causing the formation of chlorine radicals
These radicals react with ozone and break down the ozone layer

What is Ozone
O3, in the upper atmosphere acts as a chemical sunscreen
Absorbs UV light from sun, stopping it from reaching us
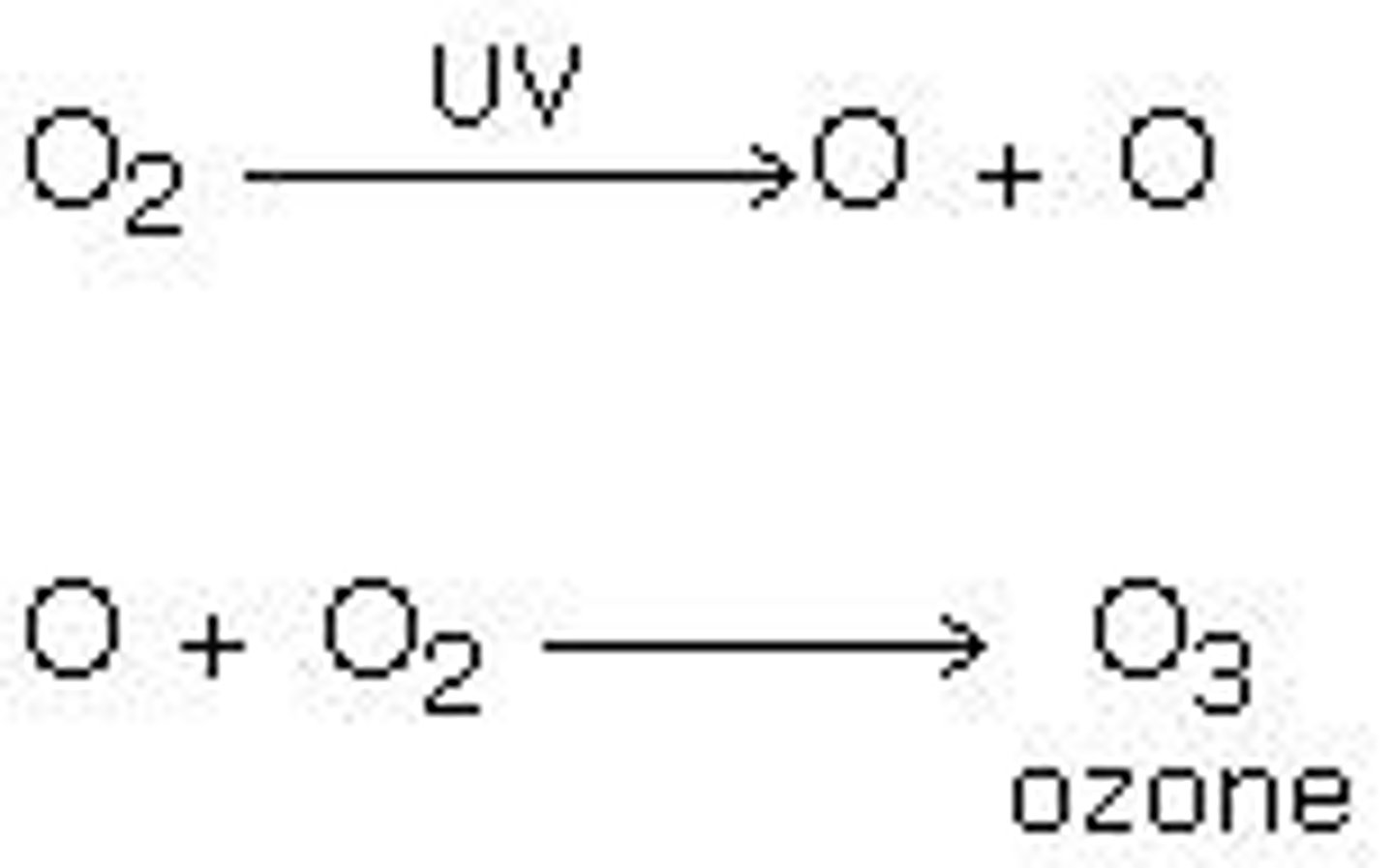
Formation of Ozone
Free radical attacks there oxygen molecules forming Ozone
Break down of ozone layer by radicals from CFCs
Initiation : C-Cl bond in CFC broken by sunlight to form C and Cl radical
Propagation:
1) Cl radical bonds with an O in O3
2) ClO radical form reacts with more ozone in the atmosphere
There is an overall equation for both propagation steps
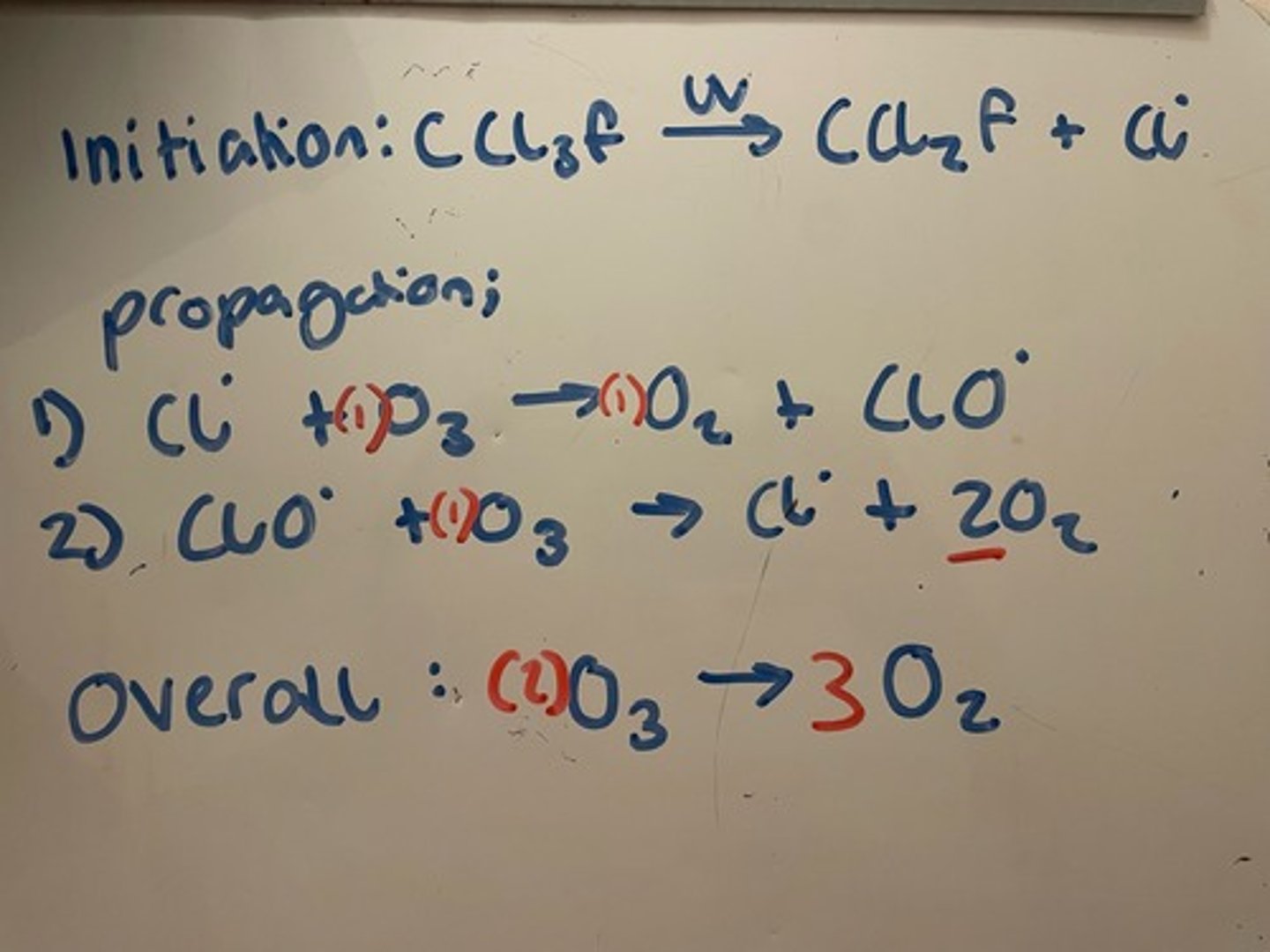
Evaluate the effect of CFCs
Used to be used in fire extinguishers, propellants in aerosols and as a coolant gas in fridges
Consequence: CFCs reacts with Ozone via a free radical substitution, which breaks down the ozone layer exposing us to more damaging UV rays
Banned as damaging consequences outweighed the uses
HCFCs AND HFCs less dangerous, temporary alternative
Identify the condition that causes a bond in CCl4 to break in the upper atmosphere. Deduce an equation for the formation of the reactive species. (2)
-UV light
-CCl4 ---> Cl3. +.Cl
A small amount of the freon CF3Cl with a mass of 1.78 × 10-4 kg escaped from a refrigerator, into a room of volume 100 m3. Assuming that the freon is evenly distributed throughout the air in the room, calculate the number of freon molecules in a volume of 500 cm3.
Give your answer to the appropriate number of significant figures. The Avogadro constant = 6.02 × 10^23 mol−1.
Mr of CF3Cl=104.5
Moles freon = convert to grams first 0.178/104.5 = 0.0017
Number of molecules 0.0017 x 6.022x10^23 = 1.02x10^21
Moles in 500cm = 1.02x10^21 x 0.0005= 5.1x10^17/100m = 5.1x10^15
The mechanism for the reaction of fluorine with either an alkane or a fluoroalkane is similar to that for the reaction of chlorine with methane.
a) Name the type of mechanism for the reaction of chlorine with methane.
b ) Write equations for the following steps in the mechanism for the reaction of fluorine with with fluoromethane (CH3F) to form difluoromethane (CH2F2)
-Initiation step
-First propagation step
-Second propagation step
-A termination step leading to the formation of 1,2-difluoroethane.
a) Free radical substitution
b) Initiation: F2--->2F•
First propagation: F• + CH3F ---> •CH2F + HF
Second propagation: F2 +•CH2F ---> CH2F2 +F•
Termination: •CH2F + •CH2F ---> CH2FCH2F
Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution, the formation of an alcohol, E, is more likely but in ethanolic solution the formation of alkenes is more likely.
a) For each type of product, name the type of reaction occurring and state the role of the potassium hydroxide.
b) Name alcohol E and draw its structural formula. By reference to the structure of the halogenoalkane, explain why the initial step in the mechanism of the reaction producing the alcohol occurs
a) Alcohol: substitution
Alcohol role: nucleophile
Alkene: elimination
Alkene role: base
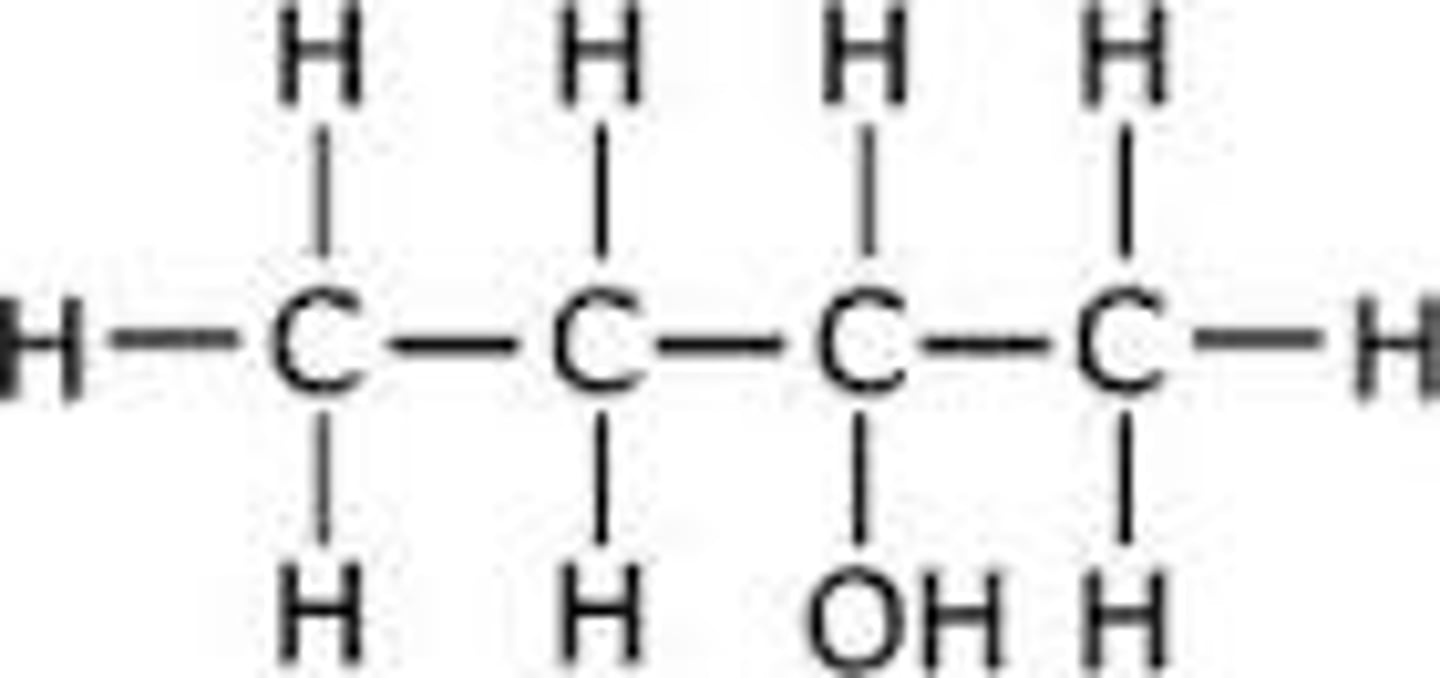
b) Butan-2-ol (1)
CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 (1)
C-Br bond is polar (1) C-Br bond breaks (1) Attacks the C forming a carbonium ion (1)
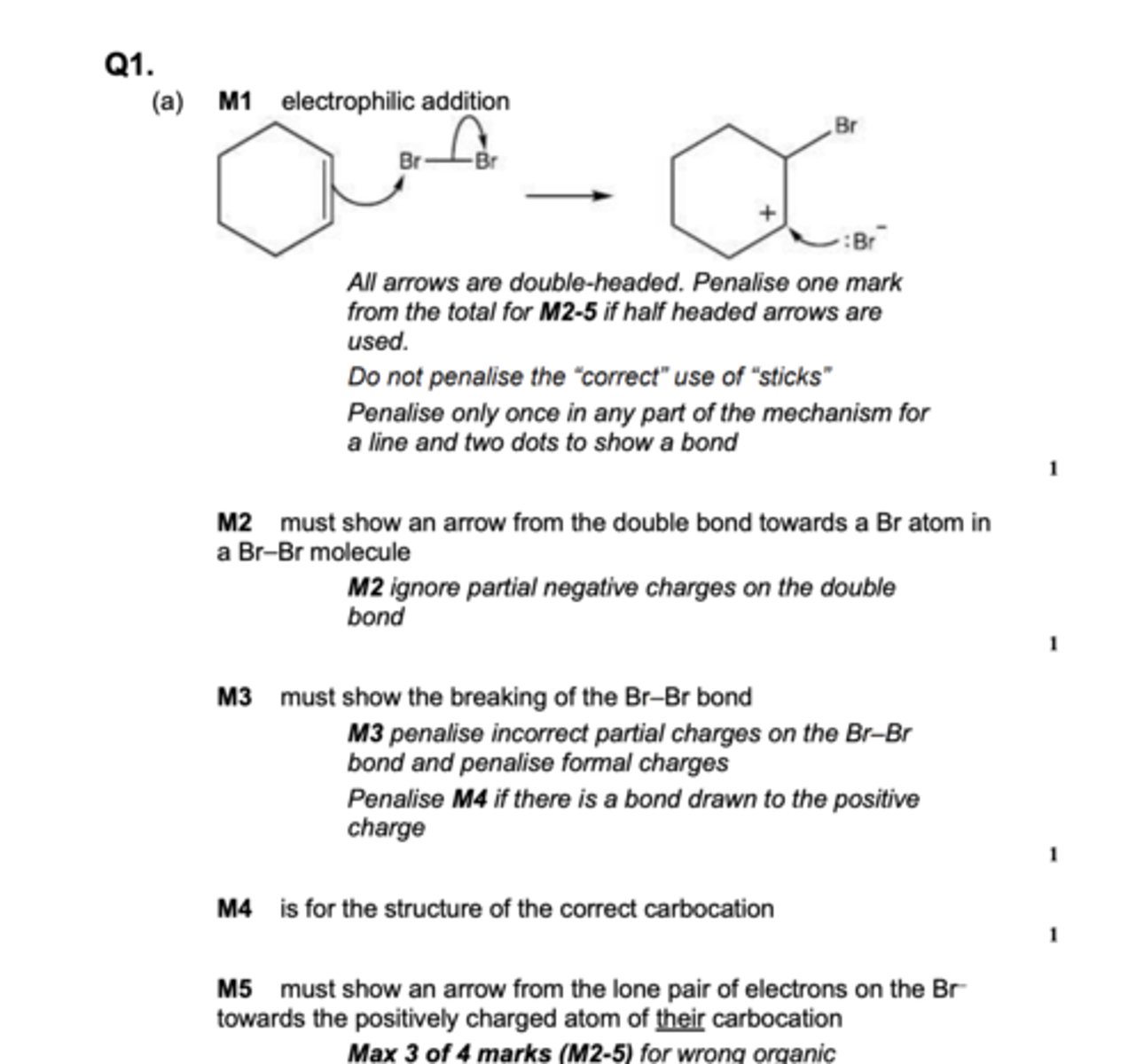
Alkenes react with bromine, BR2
Name and outline the mechanism for the reaction of cyclohexene with Br2
Electrophilic addition
CFC-11 is a greenhouse gas that can contribute to global warming. State and explain how CFC-11 is able to contribute to global warming (2)
Absorbs infrared radiation (1)
Molecule has polar bonds (1)
What is the minimum volume in dm3 of air needed for the complete combustion of 1dm3 of methane? Assume that air contains 20% of oxygen by volume.
CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O
So 1 volume of methane requires 1 volume of oxygen
20% in volume = so in 100dm3 of air there is 20dm3 of oxygen
How much air gives us 2dm3 of oxygen?
0.2 x X = 2
X is 10dm3
CFC-11 is a greenhouse gas that can contribute to global warming. State and explain how CFC-11 is able to contribute to global warming (2 marks)
Absorbs infrared radiation (1) molecule has polar bonds (1)