World Oceans Final
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
The Big Bang occurred roughly ---- years ago.
13 billion
Classify the planets of the solar system based on their composition.
Rocky planets: Venus, Mars, Earth, and Mercury
Gas planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus
Arrange the oceans in order from greatest average depth (on the top) to least average depth (on the bottom).
Greatest average depth to least average depth: Pacific, Indian, Atlantic, Southern, and Arctic
Arrange the following reservoirs in order from the one that holds the greatest volume of water (on the top) to the one that holds the least (on the bottom).
Oceans (greatest vol), ice caps and glaciers, groundwater, freshwater lakes, atmosphere, and rivers (least vol)
Arrange the eons of geologic time in chronological order from the most recent in time (on the top) to the earliest in time (on the bottom).
Phanerozoic (most recent), Proterozoic, Archean, Hadean (earliest)
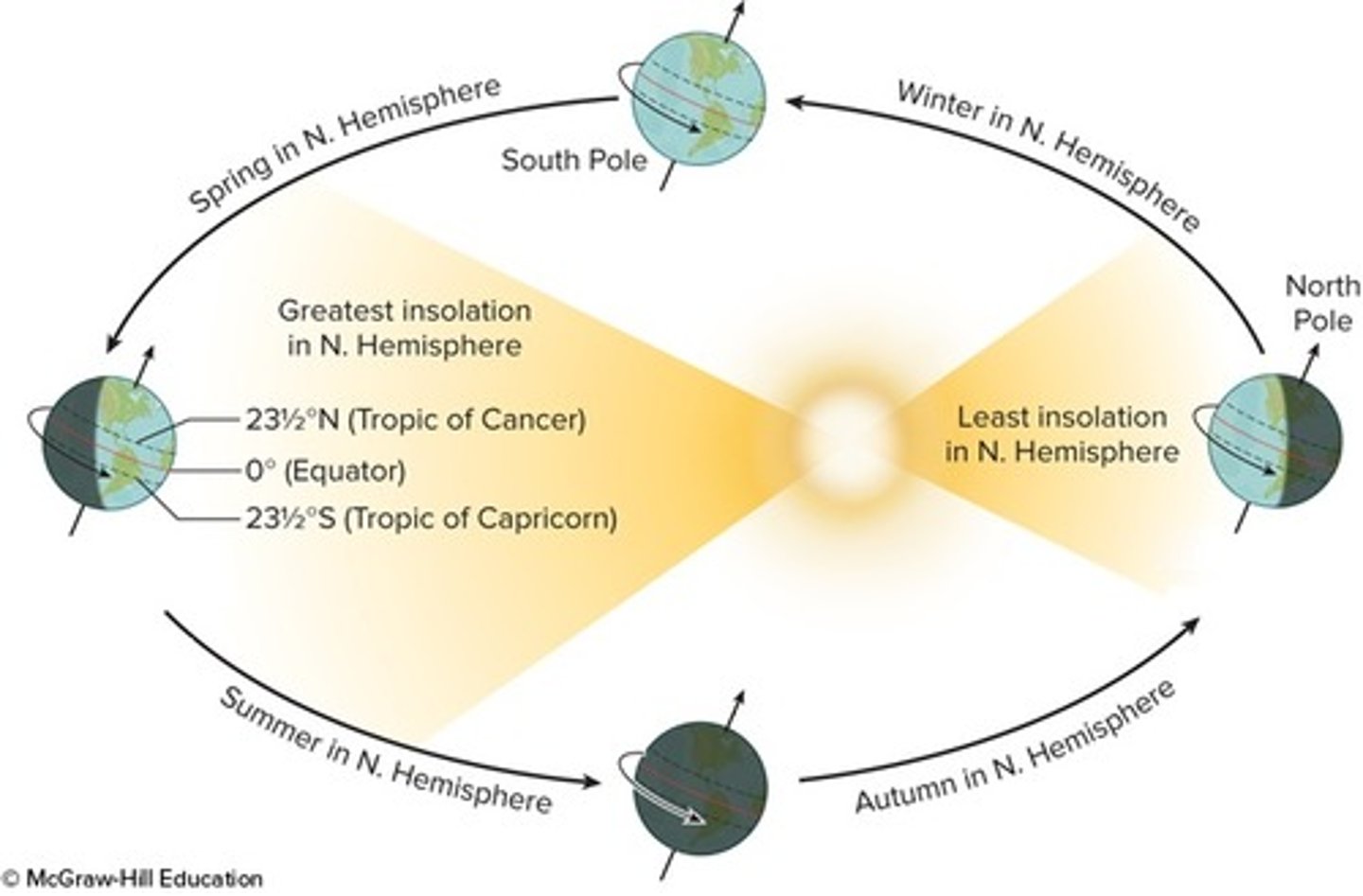
Label each position of the Earth relative to the Sun
from left clockwise: summer solstice, vernal equinox, winter solstice, autumnal equinox
The residence time for water in any of Earth's principal reservoirs can be calculated by dividing ______.
reservoir volume by rate of water supply
Free oxygen was a common constituent of the Earth's early atmosphere.
False
What percent of a parent radioactive element would remain after three half-lives of decay to its daughter isotope?
12.5
The average depth of the ocean is about ______.
3800 m
Arrange Earth's layers in order from the surface (on the top) to Earth's center (on the bottom).
Lithosphere (Earth's surface), Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer core, Inner core (Earth's center)
Identify the location of each of the following:
top to bottom: crust, moho, lithosphere, mantle, asthenosphere
Locate the following types of plate boundaries:
divergent: <-- -->
Convergent: --> <--
Transform: ⇌
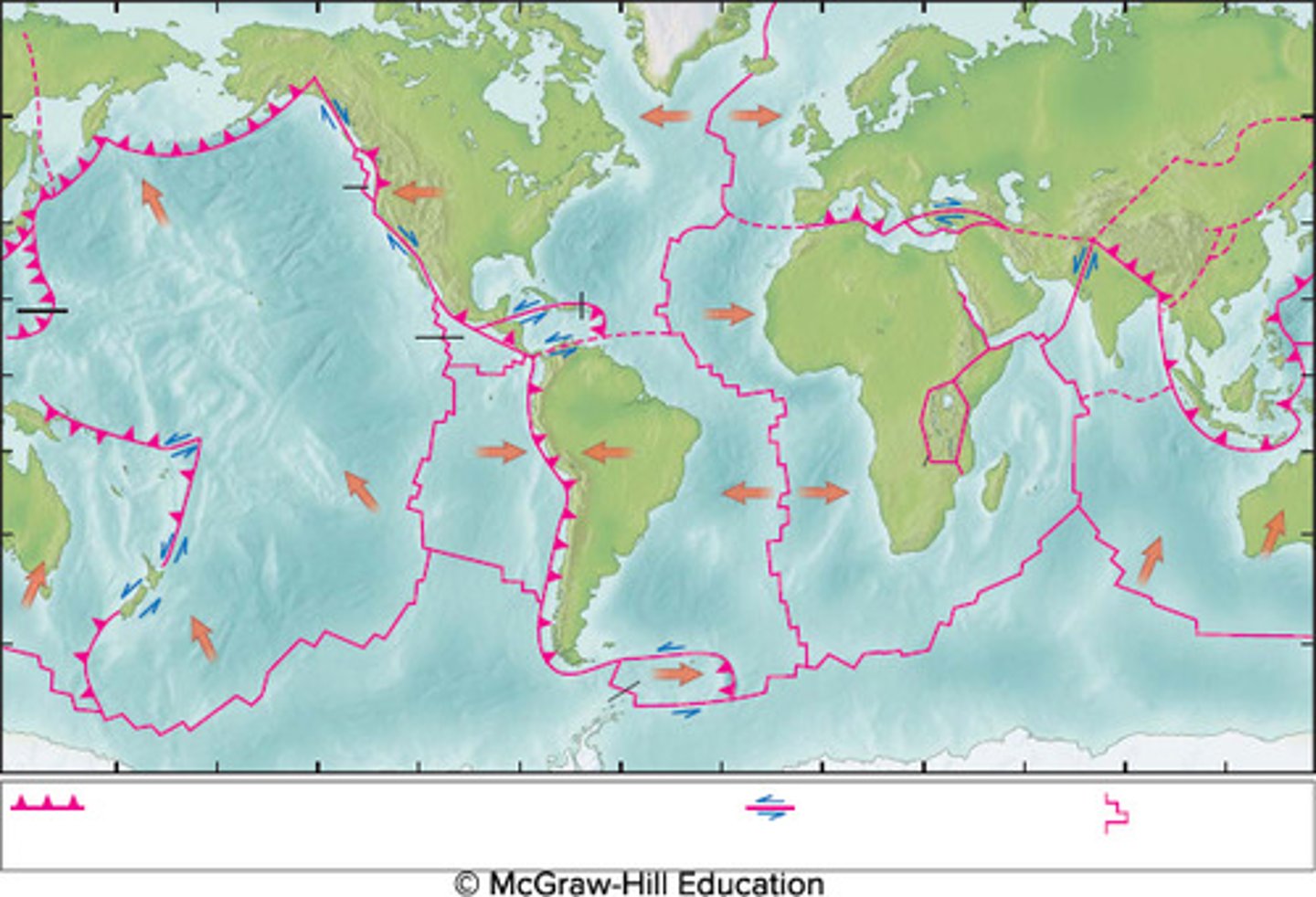
Identify the locations of the following major plate-boundary features on the map.
Top left to right: Mariana Trench, San Andreas Fault, Himalayan Mountain Range
Bottom left to right: East Pacific Rise, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and Rift Valley
Identify all of the different observations Alfred Wegener used to support his theory of continental drift.
Geographic fit of the continents, Studies of fossil plants and animals, Patterns of glaciation, Matching bodies of rock on either side of the Atlantic, Alignment of mountain ranges when the Atlantic is closed
The density of Earth materials _______ as the core is approached.
increases
California is an example of a passive continental margin.
False
Subduction explains the fact that the oldest oceanic crust is close to 200 million years old, compared to the oldest continental rocks that are ______.
4.4 billion years old
Magnetic stripes on the seafloor are created at ______.
spreading centers
The oceans' oldest sediments are found ______.
on top of the basalt layer, far from spreading centersCorrect
Identify the correct sediment classification for each of the following sediments.
Manganese nodule: Hydrogenous
Diatom and radiolarian ooze: biogenous
Red clay: Lithogenous
Tektite: Cosmogenous
Arrange the following sediment sizes in order from largest (on the top) to smallest (on the bottom).
Boulder, cobble, pebble, granule, sand, silt, clay
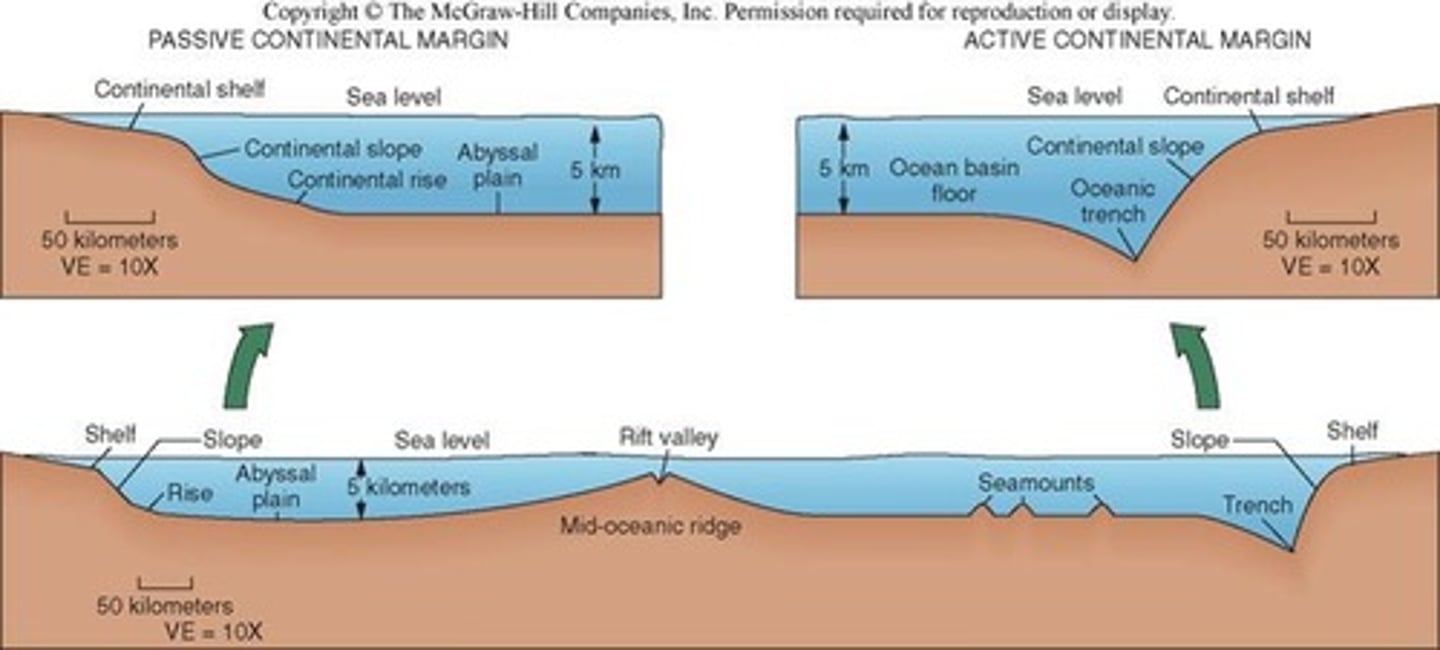
Identify the location of each of the following:
left to right: passive margin, abyssal plain, divergent boundary, seamount, trench, active margin
Match the seafloor features with the province or regime they best represent.
Guyot: Abyssal plain
Trench: Active margin
Submarine canyon: continental slope
Rift Valley: Mid-ocean ridge
Identify the location of each of the following parts of a typical passive continental margin:
left to right: continental shelf, shelf break, continental slope, continental rise
Oil and gas represent only 50% of the mineral value presently taken from the seafloor.
False
Manganese nodule mining is being considered because of their high content of the element ______.
cobalt
Gas hydrates are rich in ______.
methane
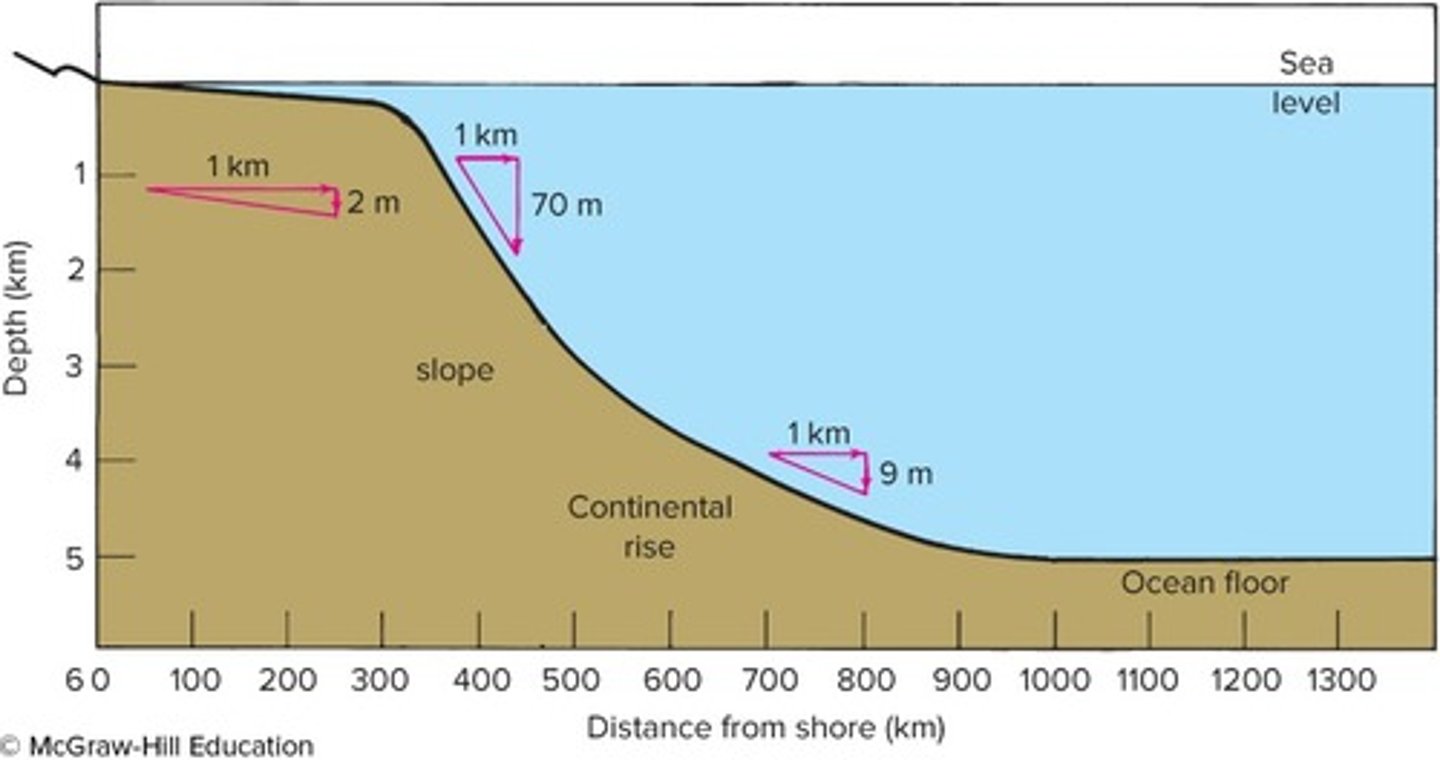
The particle size of terrigenous sediments generally ________ with distance from shore.
decreases
The east coast of South America ______.
is a passive continental margin and has a relatively wide continental shelf
Match the gain or loss of heat energy with the correct water phase transition.
melting: +80 calories
warming: +100 calories
evaporating: +540 calories
freezing: -80 calories
cooling: -100 calories
condensing: -540 calories
Identify the different types of heat transfer illustrated in this image.
pot: conduction
water: convection
radiation: fire
Order the following segments of the visible spectrum of light in the order of greatest depth of penetration into the ocean, from the deepest penetrating (top) to the shallowest penetrating (bottom)
Violet, blue, green, yellow, orange, red
A water molecule can bond with other water molecules by ________ bonds.
hydrogen
Covalent bonds link a water molecule's ______.
positively charged hydrogen atoms and negatively charged oxygen atom
Light and sound are _______ by seawater.
refracted, scattered, absorbed, and attenuated
Water at hydrothermal vents is in the liquid state despite being at 300°C because of _____.
high pressure
________ is a measure of the total kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a substance.
Heat
Heat is measured in ______.
calories
Which processes cause surface seawater to increase in density?
Sea ice formation and surface water evaporation
Arrange the following seawater constituents in order from the longest residence time (on the top) to the shortest residence time (on the bottom).
chloride, sodium, calcium, water, iron
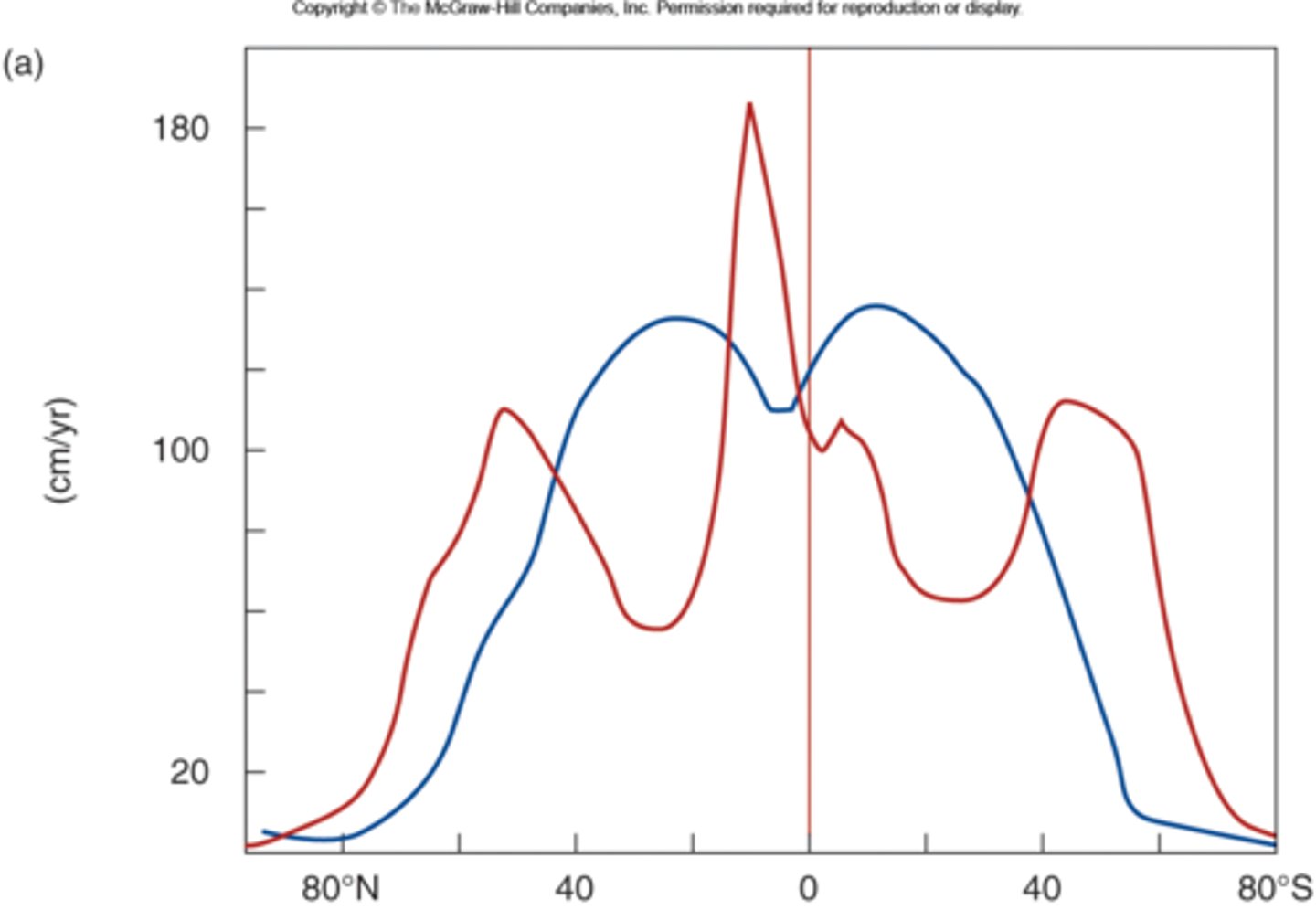
Identify the correct plots of evaporation and precipitation with latitude.
blue: evaporation
red: precipitation
Identify regions with the correct relative sea surface salinity.
intermediate: 34
High: 37 (far from coasts)
Low: 30 (close to coast)
Salinity may be measured by checking the water's _______.
conductivity
The major ionic constituents of sea salt are normally found to _______.
have a constant ratio of each constituent to each other, behave as conservative materials, and have the same ratio to each other even when diluted by rainwater
Nutrients are nonconservative constituents of seawater because they _______.
do not maintain constant ratios to each other and are recycled into plants and animals
Sources of the oceans' salts are believed to include _______.
Earth's crust, Earth's early atmosphere, and volcanic eruptions
Dittmar analyzed approximately seventy seawater samples collected around the world during the Challenger Expedition. He concluded that _______.
the major ions were always present in the same ratios
As we go below the euphotic zone of the open ocean and into greater depths, _______.
carbon dioxide increases with depth
The biological pump _______.
removes particles from the surface ocean to greater depths
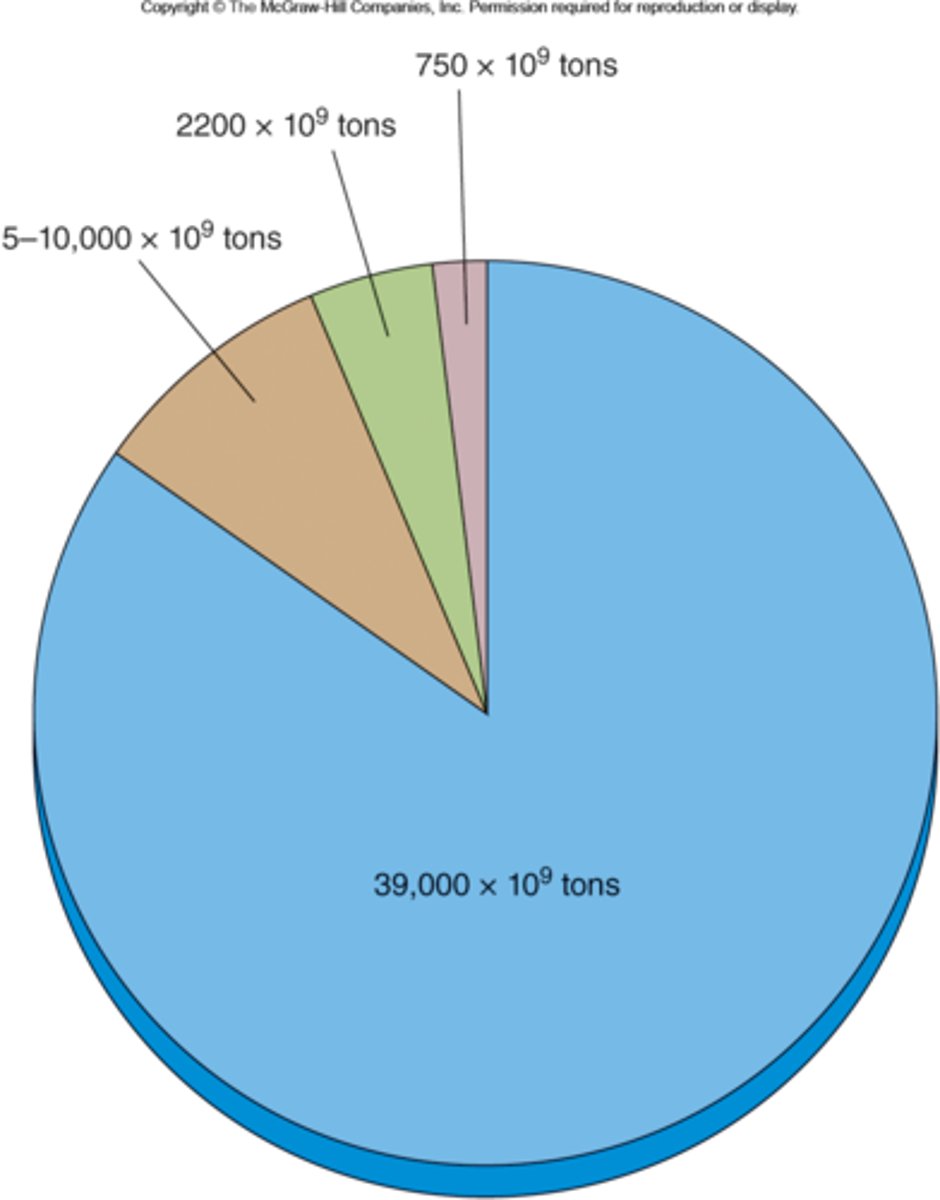
Identify which carbon dioxide reservoir corresponds to the correct amount of carbon dioxide stored.
blue: oceans
brown: geological
green: terrestrial
pink: atmosphere
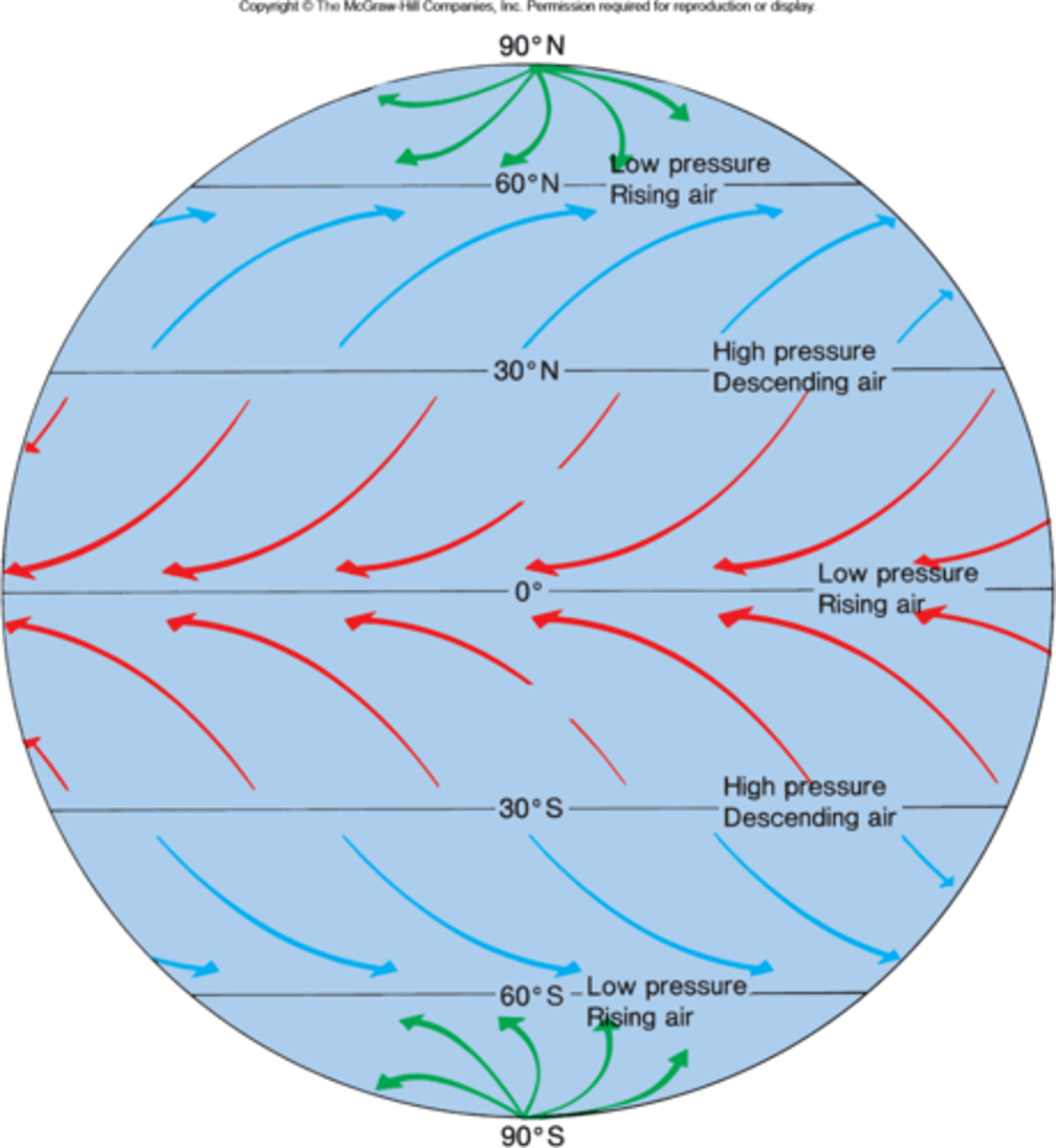
Locate the latitude band where each of the following prevailing winds are found.
top to bottom: Polar Easterlies Northern Hemisphere, Westerlies Northern Hemisphere, Northeast trades, Southeast trades, Westerlies Southern Hemisphere, Polar Easterlies Southern Hemisphere
Match the nature of the Coriolis efffect with the geographic location on Earth.
Southern Hemisphere: deflection to the left
Northern Hemisphere: deflection to the right
Equator: no deflection
Arrange the following gases in order from the highest concentration in the atmosphere (on the top) to the lowest (on the bottom).
Nitrogen (highest concentration), oxygen, argon, neon, helium, hydrogen (lowest concentration)
A wind blowing from the northwest to the southeast is called a ______ wind.
Northwest
If the world's sea ice melted, sea level would rise.
False
Earth's surface winds are caused by air moving from a region of ______ to a region of ________.
high pressure; low pressure
El Niño events are associated with _______.
high pressure in the western Pacific
Ozone destruction appears to be related to increasing levels of _________ in the atmosphere.
chlorine
Atmospheric pressure is greatest in the _______.
troposphere
Identify what water property changes rapidly in the following regions.
Salinity: Halocline
Density: Pycnocline
Temperature: Thermocline
Identify what water property changes rapidly in the following regions.
permanent and season thermocline: mid latitude
permanent thermocline: low latitude
barely any curve: high latitude
Label each salinity profile with the correct latitude.
left side:high latitudes
right side: low latitudes
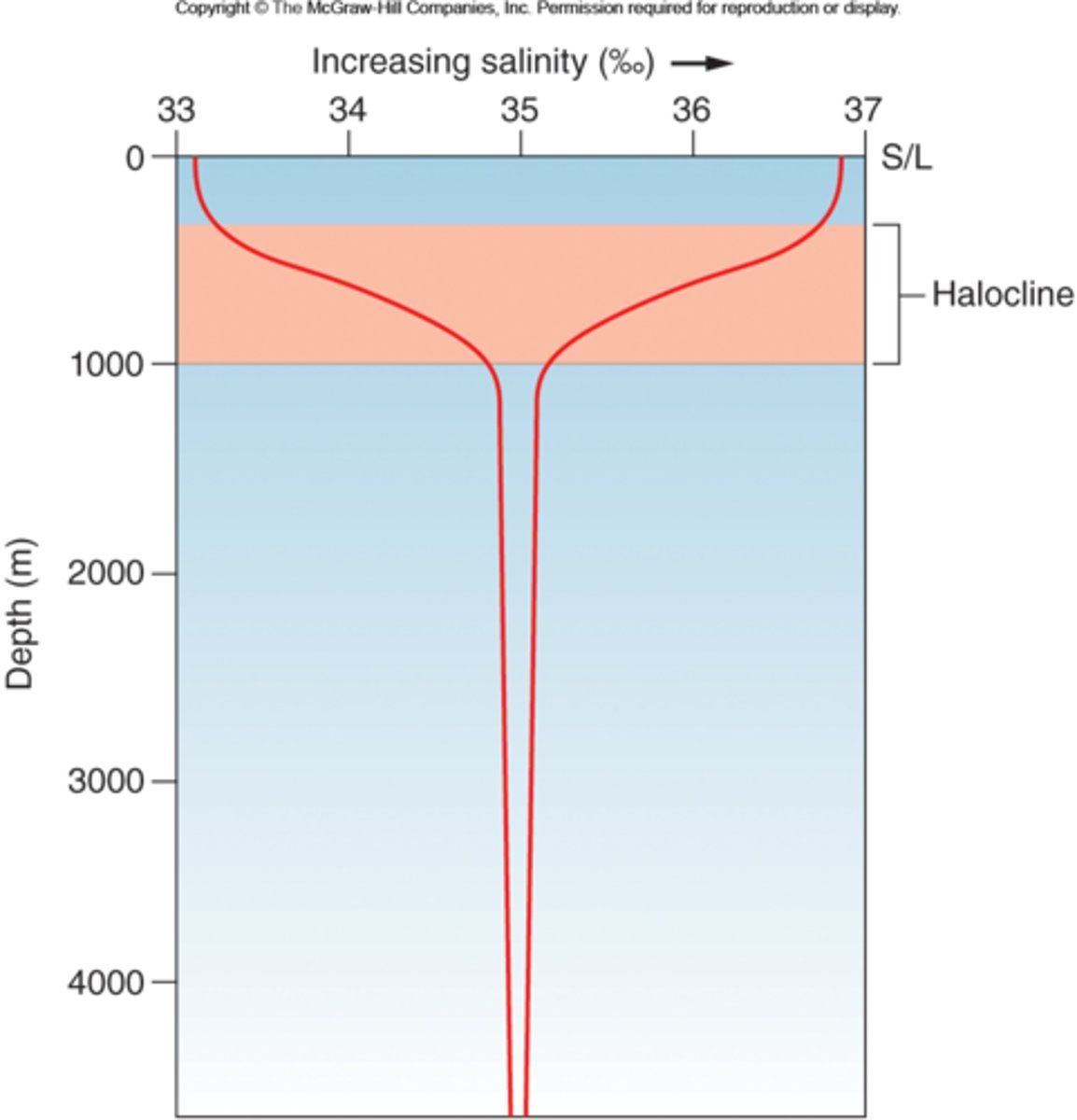
Identify the location of the following water masses:
34.9%: North Atlantic Deep Water
35.5%: Mediterranean Outflow Water
At top: Surface Water
34.6%: Antarctic Immediate Water
34.8%: Antarctic Bottom Water
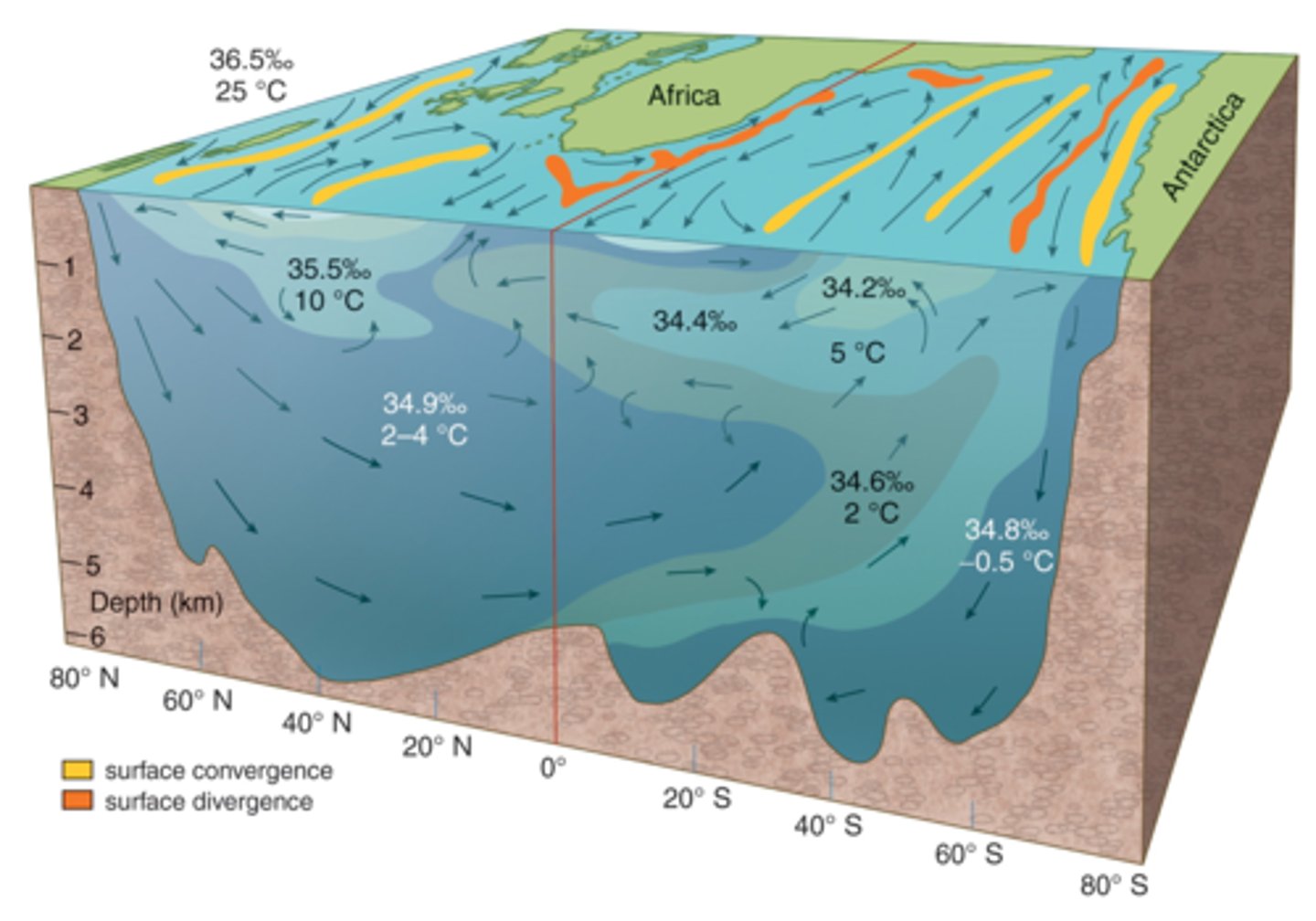
Locate each of the following surface currents:
top left to right: California, Gulf Stream
bottom left to right: Kuroshio, Brazil, Agulhas
If two surface water types with the same density but different salinities and temperatures mix, the resulting water will be _______.
denser than both parent types
An average value for the salinity of seawater could be (pick the best choice) _______.
35 g/kg
A seasonal north wind blowing along the west coast of a landmass in the Northern Hemisphere produces _______.
upwelling in summer
Of the major ocean gyres, cool currents are _______.
eastern boundary currents
Thermohaline circulation is driven by changes in _______.
density
Arrange the following types of waves in order from longest wave period (on the top) to shortest wave period (on the bottom).
Tides (longest period), tsunami, short waves, capillary waves (shortest period)
Identify the location of the following:
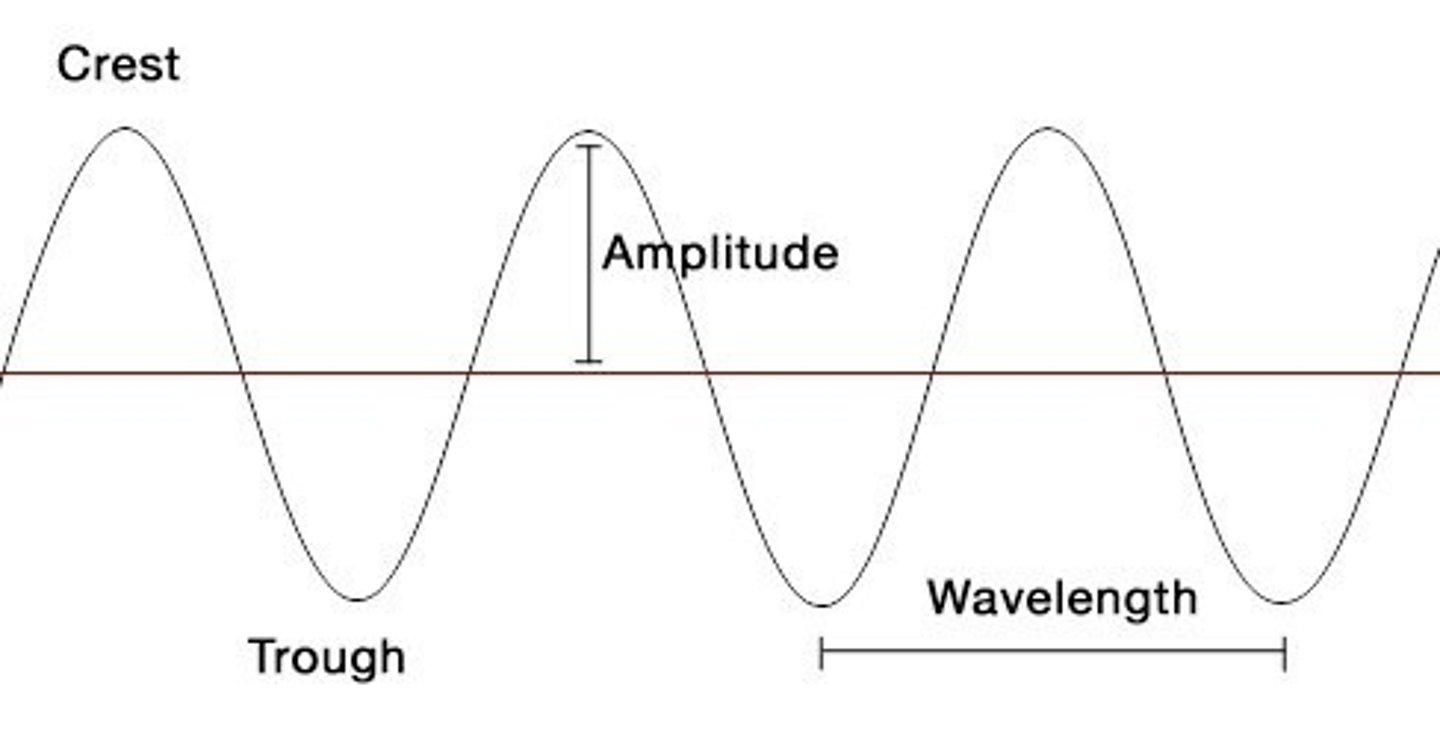
Classify the wave types below: are they deep-water or shallow-water waves? Note that some types may appear in both categories.
Deep-water waves: capillary waves, wind waves
Shallow-water waves: wind waves, tsunami, tides
A ________ is a wave generated by a submarine earthquake.
tsunami
Constructive interference between waves increases the height of the resulting wave.
True
The most common generating force for water waves is wind.
True
The restoring force of a fully developed wind wave is _______.
gravity
The speed of a surface gravity wave is described by the _______.
wavelength divided by wave period
Water particle orbits for a shallow water wave are _______.
elliptic and flatten with depth
A wave breaks when _______.
h/L = 1/7
Label each of the following water levels:
left to right: higher low water, lower high water, lower low water, higher high water
Identify the phases of the Moon with the corresponding type of tide.
Full Moon and New Moon: Spring tide
First quarter and last quarter moon: Neap tide
Label the stages of a tidal cycle.
top: flood tide, ebb tide
bottom: low slack water, high slack water
Match the duration of the time cycles involved in tidal variations.
Lunar month: 29.5 days
Solar year: 365.25 days
Diurnal tidal cycle: 24.83 hours
Semidiurnal tidal cycle: 12.42 hours
Tidal day: 24.83 hours
Solar day: 24 hours
A tidal pattern of two high tides and two low tides each day is known as a diurnal tidal pattern.
False
The Sun plays a greater role in producing the tides than the moon.
False
Using equilibrium tidal theory, the tide may be considered a wave with a wavelength approximately ______.
half the circumference of Earth
Since the earth turns _______ the tide wave tends to move _______ around Earth.
eastward; westward
The tidal range toward the center of an ocean basin with a rotary standing tide is _______ the range at the edges of the basin.
smaller than
The possibility of obtaining large amounts of energy from the tides exists where ______.
there are large tidal ranges and there are narrow channels with swift tidal currents
Identify which beach profile corresponds to which season of the year.
top: summer
bottom: winter
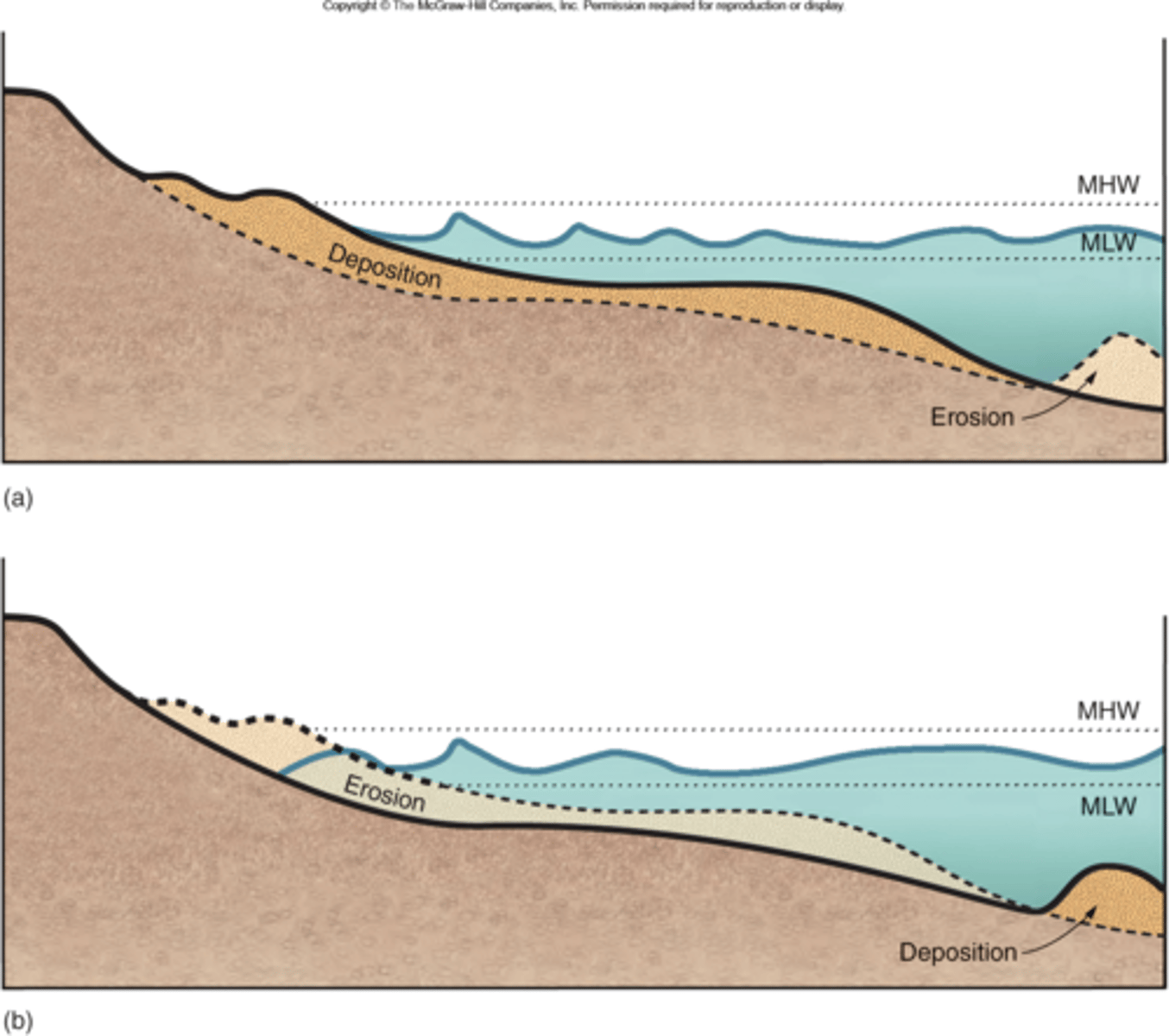
Label the parts of the beach face.
left to right: beach face, runnel, ridge
Label the figure with the surf zone and swash zone and the direction of longshore transport.
swash zone: closest to shore
surf zone: after the swash
direction: parallel to shore
Beaches gain sand under severe, high-energy winter waves and lose sand under the milder, low-energy summer waves.
False
Rip currents move water toward the beach.
False
At present, sea level is decreasing around the world's coasts.
False
A coral reef coast is a product of ______.
living organisms
A beach in dynamic equilibrium
gains and loses sand in equal quantities.
The beach face ______.
is found between high-tide and low-tide levels
An estuary that is found within the mouth of a river where freshwater flows out to sea at the surface while seawater flows upstream along the bottom is ______.
a salt wedge