A1.2: Nucleic Acids (copy)
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What did Hershey and Chase do?
Used a virus that infects E.Coli cells to investigate if genes were made of DNA or Protein.
How did the Hershey and Chase experiment work? (very long, just remember, radioactive staining, centrifuge, pellet vs supernatant phosphorous vs sulfur concentrations)
Viral proteins in E.coli were made in the cytoplasm soon after the T2 virus came into contact with the E.coli
Showing that viral genes entered the bacterium
T2 viruses only consist of DNA inside a protein coat, and since DNA contains phosphorous but not sulfur and protein contains sulfur but not phosphorous, Hershey and Chase used radioactive labelling on the phosphorous and sulfur strains of T2 virus
After the labelled T2s were left with E.Coli with enough time for bacterial infection, the mixture was centrifuged to make a pellet and supernatant then the radioactivity was located using a geiger counter
The bacterium was the pellets, the geiger counter showed that the radioactive sulfur was in higher concentration in the supernatant than pellet, and the phosphorous was low concentration in the supernatant high concentration in the pellet
What are the two ends of a nucleotide strand?
3´and 5´ends (3 prime and 5 prime)
What end of a nucleotide is what?
The 3’ end in DNA has a deoxyribose to which the phosphate of another nucletide could be linked.
The phosphate would bond with the -OH group on the C3 of the deoxyribose.
The 5´end in DNA has a phosphate that is attached to the C5 of deoxyribose.
What does DNA polymerase do during replication?
Add phosphate of a free nucleotide to the deoxyribose at the 3´end of the stand. The direction of replication is therefore 5´to 3´
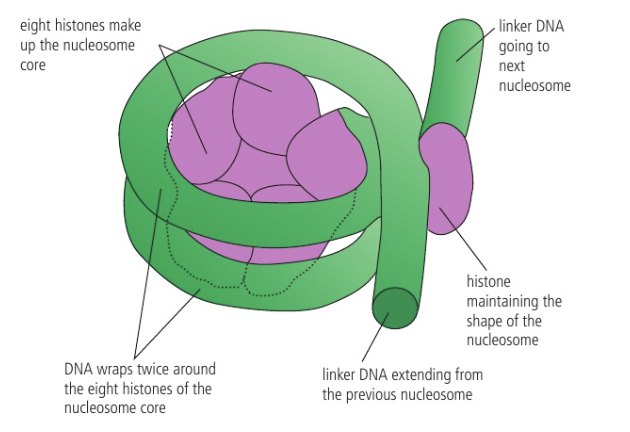
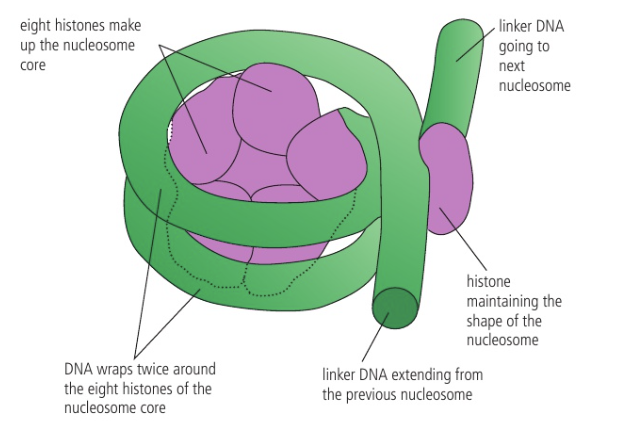
What are nucleosomes?
Globular structures that have a core of eight histone proteins with DNA wrapped around.
Another histone protein called H1 binds the DNA to the core. A short section of linker DNA connects one nucleosome to the next.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
A linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. It determines the protein's shape, function, and stability.
Define gene expression then sum up the timing of the stages of gene expression (in eukaryotes and prokaryotes)
Gene expression is the production of mRNA by transcription of a gene and then the production of polypeptides by translation of the mRNA
In prokaryotes translation occurs right away after transcription because there’s no nuclear membrane
In eukaryotes the mRNA is produced by transcription in the nucleus, it’s modified in the nucleus then passed out to the cytoplasm and translated there.
What is a polysome?
A group of ribosomes moving along the same mRNA as they simultaneously translate it. Google pictures, you should be able to identify this.
List all of the structural features of a ribosome.
Proteins and ribosomal RNA molecules both form part of the structure
There are two sub-units, one large and one small
There is a binding site for mRNA on the small sub-unit
There are three binding sites for tRNA on the large sub-unit
A site for tRNA bringing in amino acid
P site for the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide
E site for the tRNA about to exit the ribosome
What are the types of ribosomes?
Cytoplasm free ribosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum bound ribosomes
histones
a protein that provides structural support for a chromosome. Each chromosome contains a long molecule of DNA, which must fit into the cell nucleus. To do that, the DNA wraps around complexes of histone proteins, giving the chromosome a more compact shape.
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of protein and a single molecule of DNA that serve to carry the genomic information from cell to cell. In plants and animals (including humans), chromosomes reside in the nucleus of cells.
DNA nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine (A, T, G, C)
nitrogenous base pairs
Adenine-Thymine, Guanine-Cytosine (A-T) (G-C)
transcription
Process of converting DNA into RNA by copying the genetic information. Occurs in the nucleus of a cell and is essential for protein synthesis.
Purines
Purines are nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. They consist of Adenine and Guanine. Purines play a crucial role in cellular energy transfer and are essential for the synthesis of nucleic acids. They also serve as building blocks for ATP, the energy currency of cells.
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. They include Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil. Pyrimidines have a single-ring structure and pair with purines in nucleic acids.
triplet codon
A triplet codon refers to a sequence of three nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. There are 64 possible triplet codons, including start and stop codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a signal to start or stop protein synthesis.
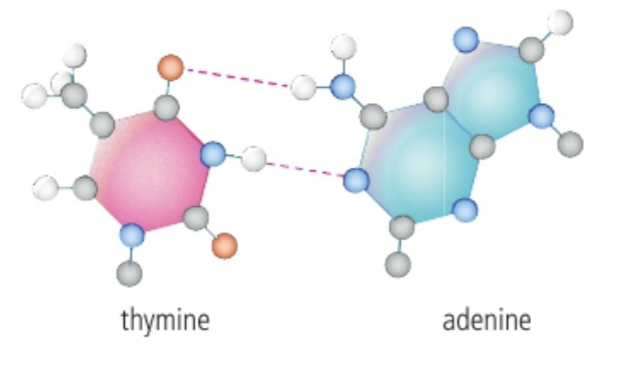
Hydrogen bonding between Thymine and Adenine
two hydrogen bonds
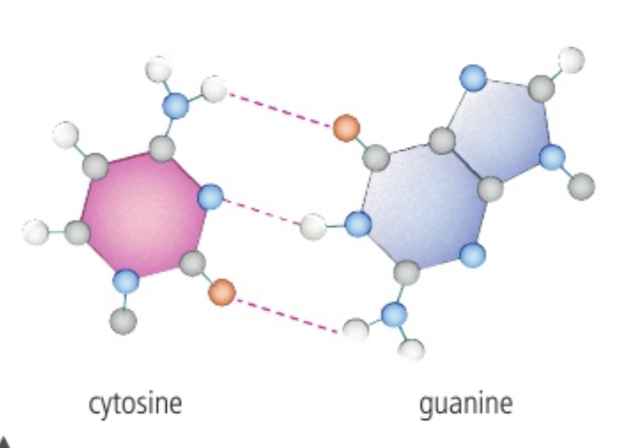
Hydrogen bonding between Guanine and Cytosine
three hydrogen bonds
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Type of RNA that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. It has an anticodon that pairs with the codon on messenger RNA.
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a type of RNA molecule found in the ribosomes of cells. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by helping to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. These rRNA molecules combine with proteins to form ribosomes, which are responsible for translating the genetic information stored in mRNA into functional proteins.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that serves as the primary energy currency of cells. It is composed of adenosine and three phosphate groups. ATP stores and releases energy during cellular processes such as metabolism and muscle contraction. ATP is essential for various biological processes and is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for energy transfer in cells.
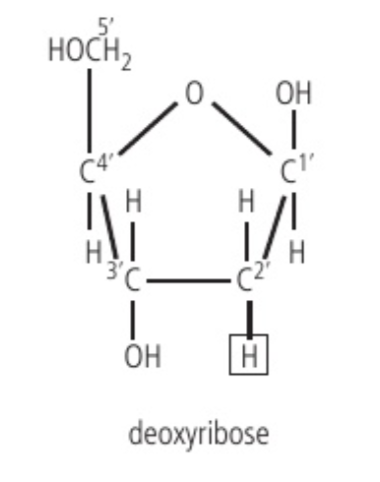
deoxyribose
A sugar molecule found in DNA, forming the backbone of the DNA double helix structure. Molecular formula of C5H10O4.
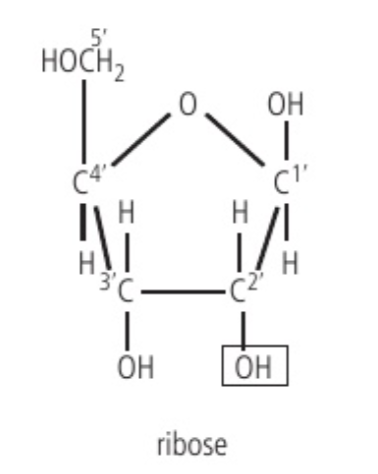
ribose
A five-carbon sugar found in RNA molecules. It is essential for the formation of the backbone of RNA and plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. Molecular formula of C5H10O5.
Chargaff's rule and its outcome
Chargaff's rule: The amount of adenine (A) is equal to thymine (T), and the amount of guanine (G) is equal to cytosine (C) in DNA. This rule provides the basis for complementary base pairing in DNA strands, ensuring accurate replication and protein synthesis.
tetranucleotide theory
Theory proposing that DNA consists of repeating sequences of four nucleotides, forming a stable double helix structure. It has been proven false, due to Chargaff’s rule.
phosphate group
Phosphate Group is a chemical entity consisting of phosphorus bonded to four oxygen atoms. It is crucial for biological processes, including energy transfer (e.g., ATP formation) and DNA/RNA structure. Phosphate groups are found in nucleotides and phospholipids, and can have a negative charge, affecting molecule reactivity. They also play a key role in cellular processes like signal transduction and metabolism.
polymers
large molecules made by bonding (chemically linking) a series of building blocks.
nitrogenous base
a type of organic molecule that contains nitrogen and is a fundamental component of nucleic acids, such as DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Nitrogenous bases are essential for the genetic code and the transmission of genetic information.
pentose sugar
a type of simple sugar (carbohydrate) that contains five carbon atoms in its molecular structure. Pentose sugars are important components of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and also play a role in certain metabolic pathways.
RNA nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine (A, U, C, G)
RNA strand diagram
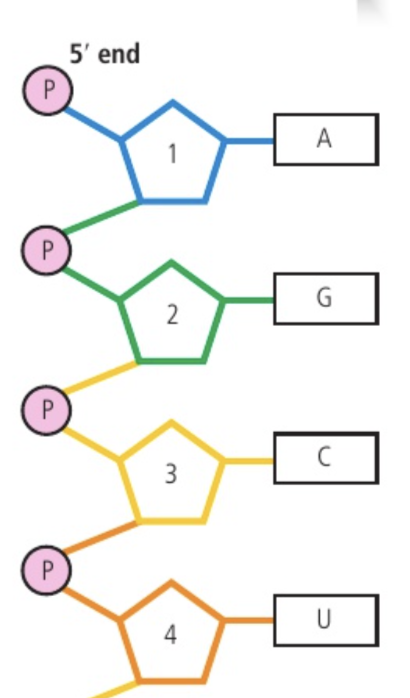
DNA strand diagram
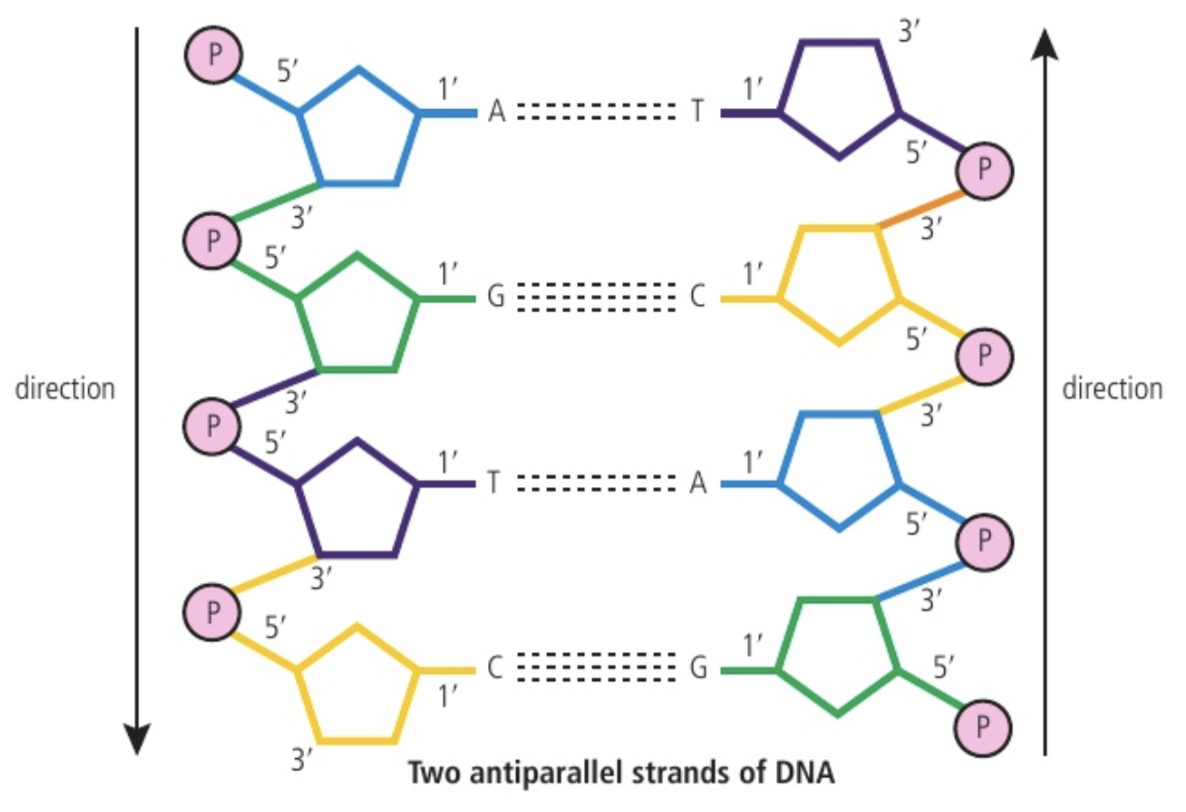
parallel & antiparallel
the orientation of the two strands in a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule. These terms describe how the individual strands of the molecule align with respect to each other.
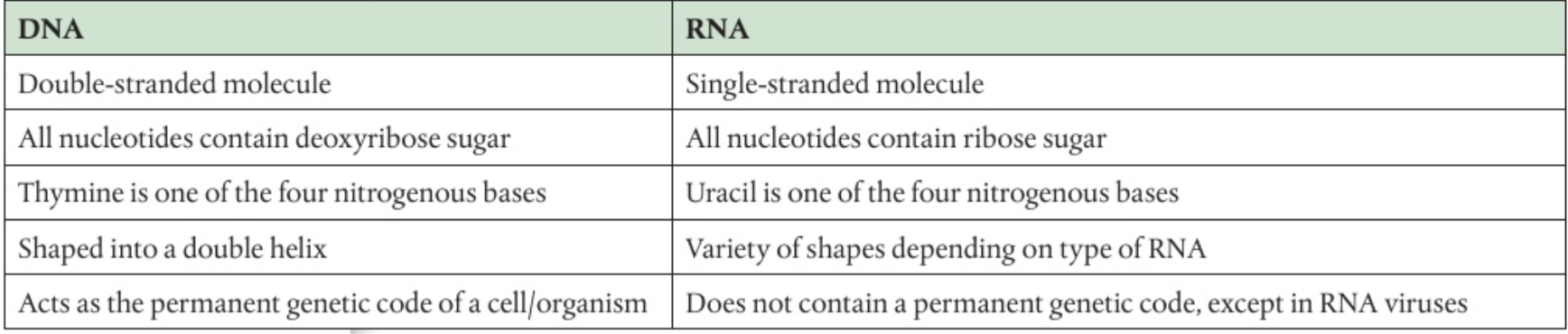
Differences between DNA and RNA
triphosphate
A triphosphate is a molecule consisting of three phosphate groups bonded together. It is an important component of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA
Why are organisms so different from one another?
DNA base sequences are different even though the code to read the sequences is the same.
5’ and 3’ designations
the fifth and third carbon atoms in the ribose and deoxyribose sugars. DNA does not have a single 5’ end or 3’ end. DNA is composed of two strands and each strand has a 5’ and 3’ end.
importance of directionality
DNA and RNA molecules have a 5' end, where nucleotides are added sequentially during replication and transcription processes. This directionality is crucial for the accurate synthesis of genetic information and protein production.
linker DNA
stretches of DNA sequences found between genes or functional elements in a genome. It is found between two adjoining nucleosomes.