GB1- Chapter 9
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
oxidizing
giving hydrogens and electrons
energy vs. chemical
energy enters environment as light and exits as heat. it is often transferred by electron carrier- NADH
essential chemical elements are recycled
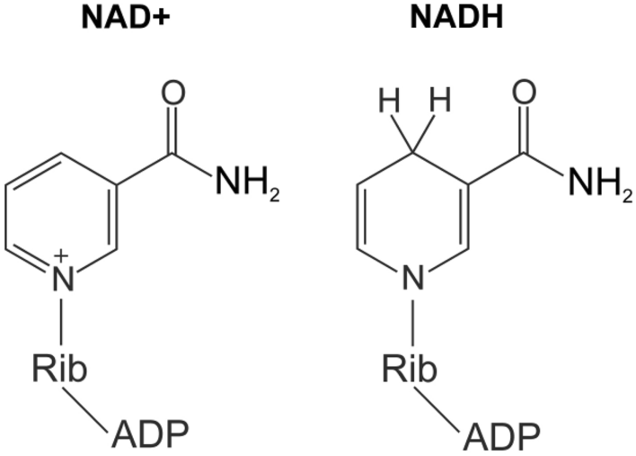
NADH- nicotinamide-adenine dinucelotide
NAD+: coenzyme that acts as a donor and acceptor (electron carrier) of electrons within all eukaryotes
important in cellular respiration
FAD- Flavin adenine dinuleotide
redox reaction
FAD- oxidized form/ lost electrons
FADH2- reduced form/ gained electrons
electron carrier in cellular respiration especially in ETC
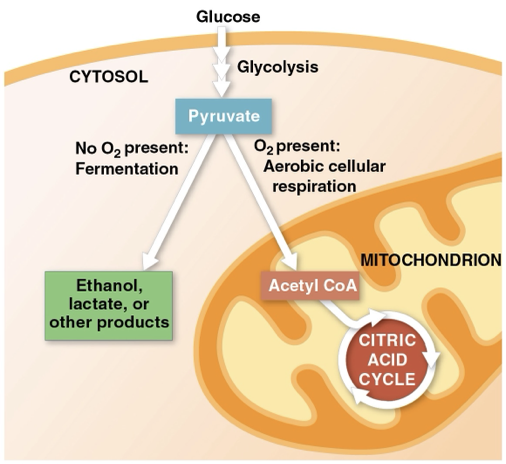
Fermentation
partial degradation of sugars without oxygen
Aerobic respiration- consumes organic molecules + oxygen/ produces ATP
Anaerobic respiration- consumes compounds/ produces ATP
cellular respiration
has both aerobic and anaerboic respiration, but commonly known as aerobic. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, but glucose is mainly traced.
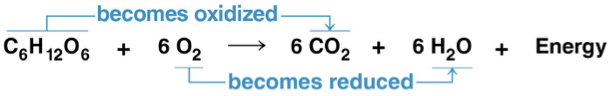
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat)
oxygen is required to make ATP! without oxygen, death by affixation will occur due to no ATP production.
energy is released as hydrogens/ electrons are transferred to O atoms- less free energy- more stable
glucose oxidation moves electrons from higher energy state to lower energy state with O atoms. ATP is synthesized with the released energy.
oxidation happens in a series of steps because too much free energy is harmful to living things - electron travels with a hydrogen atom (proton) hydrogen atoms are first passed to electron carriers instead of going directly to O2.
catabolic pathways
releases energy by breaking down complex molecules.
linked to work by ATP
cells must constantly create a ATP supply from ADP and phosphate.
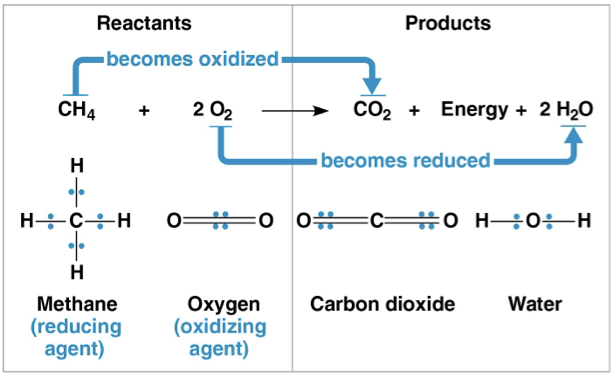
redox reactions
chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants
oxidation- loss of electrons
reduction- gaining electrons
reducing agent- the thing getting oxidized
oxidizing agent- the thing reducing
less electronegative atom- more stable
more electronegative atom- less stable
electron loses potential energy when it becomes more electronegative
coenzyme
an organic molecule that helps enzymes function by binding to their active sites and participating in catalytic reactions.
derived from vitamins
harvesting energy from glucose from cellular respiration
glysolysis- breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules
pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle- completes the breakdown of glucose into CO2
oxidative phosphorylation- ETC and chemiosis
what would happen if NADH transferred electrons directly to oxygen?
energy would be released in one explosive reaction
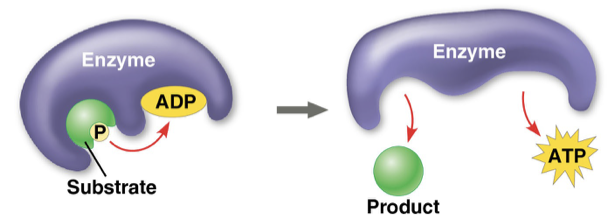
substrate-level phosphorylation
occurs when a enzyme transfers a phosphate group directly from a substrate to ADP
hexokinase
adds a phosphate to the 6th carbon
kinases
catalyzes the transfer of Y phosphate group of ATP onto a substrate
Adolases
break down sugars
isomerase
enzyme that catalyzes isomerization- transfer of molecule conformation
ex) cis and trans forms that affect protein conformation
adolases
break down sugars
complete glucose oxidation
eukaryotes if O2 is present, pyruvate enters mitchodonria to complete glucose oxidation
aerobic prokaryotes- complete glucose oxidation finishes in the cytosol
cytochromes
proteins with heme groups containing an iron atom
reasons why exact ATP number isn’t known
photophosphorylation and redox reactions aren’t coupled. The ratio of NADH and ATP aren’t whole numbers
ATP yield depends on whether the electron is passed to NAD or FAD
proton motive force is used to drive other forces too
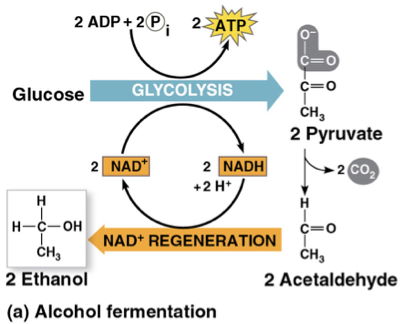
alcohol fermentation
step 1: produces CO2 from reducing pyruvate
step 2: produces NAD and ethanol
latic acid fermentation
pyruvate is directly reduced by NADH, forming lactate and NAD+
lactic acid fermentation by fungi and bacteria produces cheese and yogurt
human muscle cells fermentation
red skeletal muscle- oxidizes glucose completely to CO2
white skeletal muscle- produces lactate even under aerobic conditions
obligrate anaerobes
only carries out fermentation/ anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2
facultative anaerobes
can survive by using either fermentation or cellular respiration.
pyruvate is a optional fork for them
ex) yeast and many bacteria
glycolysis can use
carbohydrates including starch, glycogen, and several disaccharides. fats are also digested for glycerol and fatty acids
deamination
proteins used for fuel must be digested into amino acids and their amino groups must be removed
nitrogenous waste
excreted as ammonia, urea, or other products
beta oxidation
fatty acids are broken down and yield acetyl CoA, NADH, FADH2- products of cellular respiration
oxidixed gram of fat produces twice as much ATP as oxidized gram of carbohydrate